.NET (1317)
Children categories
By default, the font color of a word document is black. To achieve a more distinctive visual effect, we can change it to red, green or any other colors we like.
This article describes how to change word font color with Spire.Doc for WPF in C#, VB.NET.
At first, please download Spire.Doc and install it correctly, then add Spire.Doc. Wpf.dll and Spire.License.dll from the installation folder as reference.
Below is the screenshot of the original word document:

Detail steps:
Use namespace:
using System.Drawing; using System.Windows; using Spire.Doc; using Spire.Doc.Documents;
Step 1: Initialize a new instance of Document class and load the sample document from file.
Document document = new Document();
document.LoadFromFile("Story.docx");
Step 2: Get its first section and first paragraph (the Title), then set text color for paragraph 1.
Section section = document.Sections[0]; Paragraph p1 = section.Paragraphs[0]; ParagraphStyle s1 = new ParagraphStyle(document); s1.Name = "TitleTextColor"; s1.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.RosyBrown; document.Styles.Add(s1); p1.ApplyStyle(s1.Name);
Step 3: Get the second paragraph and set text color for paragraph 2.
Paragraph p2 = section.Paragraphs[1]; ParagraphStyle s2 = new ParagraphStyle(document); s2.Name = "BodyTextColor"; s2.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.DarkBlue; document.Styles.Add(s2); p2.ApplyStyle(s2.Name);
Step 4: Save and launch the file.
document.SaveToFile("FontColor.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("FontColor.docx");
Output:

Full codes:
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows;
namespace WpfApplication1
{
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
//Load Document
Document document = new Document();
document.LoadFromFile("Story.docx");
//Set Text Color for Paragraph 1(the Title)
Section section = document.Sections[0];
Paragraph p1 = section.Paragraphs[0];
ParagraphStyle s1 = new ParagraphStyle(document);
s1.Name = "TitleTextColor";
s1.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.RosyBrown;
document.Styles.Add(s1);
p1.ApplyStyle(s1.Name);
//Set Text Color for Paragraph 2
Paragraph p2 = section.Paragraphs[1];
ParagraphStyle s2 = new ParagraphStyle(document);
s2.Name = "BodyTextColor";
s2.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.DarkBlue;
document.Styles.Add(s2);
p2.ApplyStyle(s2.Name);
//Save and Launch
document.SaveToFile("FontColor.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("FontColor.docx");
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Doc
Imports Spire.Doc.Documents
Imports System.Drawing
Imports System.Windows
Namespace WpfApplication1
Public Partial Class MainWindow
Inherits Window
Public Sub New()
InitializeComponent()
End Sub
Private Sub button1_Click(sender As Object, e As RoutedEventArgs)
'Load Document
Dim document As New Document()
document.LoadFromFile("Story.docx")
'Set Text Color for Paragraph 1(the Title)
Dim section As Section = document.Sections(0)
Dim p1 As Paragraph = section.Paragraphs(0)
Dim s1 As New ParagraphStyle(document)
s1.Name = "TitleTextColor"
s1.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.RosyBrown
document.Styles.Add(s1)
p1.ApplyStyle(s1.Name)
'Set Text Color for Paragraph 2
Dim p2 As Paragraph = section.Paragraphs(1)
Dim s2 As New ParagraphStyle(document)
s2.Name = "BodyTextColor"
s2.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.DarkBlue
document.Styles.Add(s2)
p2.ApplyStyle(s2.Name)
'Save and Launch
document.SaveToFile("FontColor.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("FontColor.docx")
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
By using Spire.XLS, developers can easily set the IconSetType of conditional formatting. This article will demonstrate how to set the traffic lights icons in C# with the help of Spire.XLS.
Note: Before Start, please download the latest version of Spire.XLS and add Spire.xls.dll in the bin folder as the reference of Visual Studio.
Here comes to the code snippets:
Step 1: Create a new excel document instance and get the first worksheet.
Workbook wb = new Workbook(); Worksheet sheet = book.Worksheets[0];
Step 2: Add some data to the Excel sheet cell range and set the format for them.
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Traffic Lights"; sheet.Range["A2"].NumberValue = 0.95; sheet.Range["A2"].NumberFormat = "0%"; sheet.Range["A3"].NumberValue = 0.5; sheet.Range["A3"].NumberFormat = "0%"; sheet.Range["A4"].NumberValue = 0.1; sheet.Range["A4"].NumberFormat = "0%"; sheet.Range["A5"].NumberValue = 0.9; sheet.Range["A5"].NumberFormat = "0%"; sheet.Range["A6"].NumberValue = 0.7; sheet.Range["A6"].NumberFormat = "0%"; sheet.Range["A7"].NumberValue = 0.6; sheet.Range["A7"].NumberFormat = "0%";
Step 3: Set the height of row and width of column for Excel cell range.
sheet.AllocatedRange.RowHeight = 20; sheet.AllocatedRange.ColumnWidth = 25;
Step 4: Add a conditional formatting of cell range and set its type to CellValue.
ConditionalFormatWrapper format1 = sheet.Range.ConditionalFormats.AddCondition(); format1.FormatType = ConditionalFormatType.CellValue; format1.FirstFormula = "300"; format1.Operator = ComparisonOperatorType.Less; format1.FontColor = Color.Black; format1.BackColor = Color.LightSkyBlue;
Step 5: Add a conditional formatting of cell range and set its type to IconSet.
ConditionalFormatWrapper format = sheet.AllocatedRange.ConditionalFormats.AddCondition(); format.FormatType = ConditionalFormatType.IconSet; format.IconSet.IconSetType = IconSetType.ThreeTrafficLights1;
Step 6: Save the document to file.
wb.SaveToFile("Light.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
Effective screenshots of the traffic lights icons set by Spire.XLS.
![]()
XMP is a file labeling technology that lets you embed metadata into files themselves during the content creation process. With an XMP enabled application, your workgroup can capture meaningful information about a project (such as titles and descriptions, searchable keywords, and up-to-date author and copyright information) in a format that is easily understood by your team as well as by software applications, hardware devices, and even file formats.
In the Spire.PDF Version 3.6.135 and above, we add a new feature to read, set and load an existing XMP data from XML documents. This article presents how to set XMP Metadata while creating a PDF document.
Code Snippet:
Step 1: Initialize a new instance of PdfDocument class.
string input = "..\\..\\..\\..\\..\\..\\Data\\SetXMPMetadata.pdf"; // Open a PDF document. PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument(); doc.LoadFromFile(input); // Set XMP metadata for the document. doc.DocumentInformation.Author = "E-iceblue"; doc.DocumentInformation.Creator = "Spire.PDF"; doc.DocumentInformation.Keywords = "XMP"; doc.DocumentInformation.Producer = "E-icenlue Co,.Ltd"; doc.DocumentInformation.Subject = "XMP Metadata"; doc.DocumentInformation.Title = "Set XMP Metadata in PDF"; // Specify the output file name for the modified PDF. string output = "SetXMPMetadata.pdf"; // Save the PDF document with the updated XMP metadata. doc.SaveToFile(output);
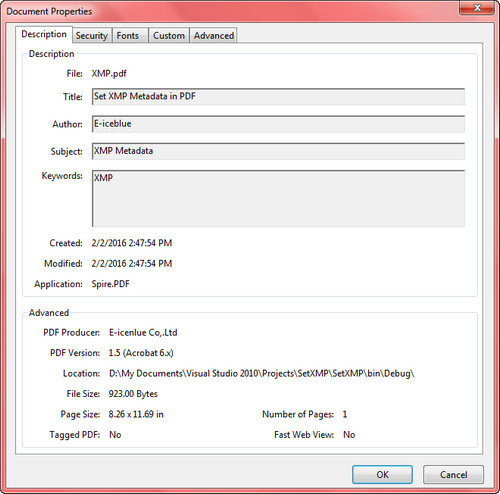
Output:
To view metadata in a PDF document, open it with Acrobat or Acrobat Reader and select ‘Document Properties’ in the File menu.
Full Code:
using Spire.Pdf;
using Spire.Pdf.Xmp;
using System;
namespace SetXMPMetadata
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string input = "..\\..\\..\\..\\..\\..\\Data\\SetXMPMetadata.pdf";
// Open a PDF document.
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
doc.LoadFromFile(input);
// Set XMP metadata for the document.
doc.DocumentInformation.Author = "E-iceblue";
doc.DocumentInformation.Creator = "Spire.PDF";
doc.DocumentInformation.Keywords = "XMP";
doc.DocumentInformation.Producer = "E-icenlue Co,.Ltd";
doc.DocumentInformation.Subject = "XMP Metadata";
doc.DocumentInformation.Title = "Set XMP Metadata in PDF";
// Specify the output file name for the modified PDF.
string output = "SetXMPMetadata.pdf";
// Save the PDF document with the updated XMP metadata.
doc.SaveToFile(output);
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Pdf
Imports Spire.Pdf.Xmp
Namespace SetXMPMetadata
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
Load the input PDF file
Dim input As String = "..\..\..\..\..\..\Data\SetXMPMetadata.pdf"
' Create a new PdfDocument object
Dim doc As New PdfDocument()
' Load the PDF document from the input file
doc.LoadFromFile(input)
' Set the author information in the document properties
doc.DocumentInformation.Author = "E-iceblue"
' Set the creator information in the document properties
doc.DocumentInformation.Creator = "Spire.PDF"
' Set the keywords information in the document properties
doc.DocumentInformation.Keywords = "XMP"
' Set the producer information in the document properties
doc.DocumentInformation.Producer = "E-icenlue Co,.Ltd"
' Set the subject information in the document properties
doc.DocumentInformation.Subject = "XMP Metadata"
' Set the title information in the document properties
doc.DocumentInformation.Title = "Set XMP Metadata in PDF"
' Specify the output file name
Dim output As String = "SetXMPMetadata.pdf"
' Save the modified document to the output file
doc.SaveToFile(output)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
With the help of Spire.PDF, we can add several kinds of layers such as line, image, string, ellipse, rectangle and pie to any page of a new or an existing pdf document. At the same time, it also supports us to delete specific layer from a pdf document.
In this section, we're going to demonstrate how to delete layer in PDF using Spire.PDF for .NET. To add layer to PDF, please check this article: How to add layers to PDF file in C#.
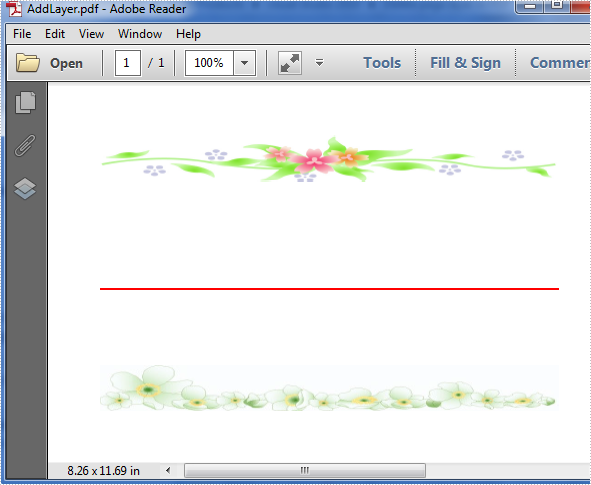
Below is the screenshot of the original PDF document which contains three layers: a red line layer and two image layers.
Before start, download Spire.PDF and install it correctly, next add the corresponding dll file from the installation folder as reference of your project.
Detail steps:
Step 1: Initialize a new instance of PdfDocument class and load the sample document from file.
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
doc.LoadFromFile("AddLayer.pdf");
Step 2: Get its first page and delete the specific layer by name from page one.
PdfPageBase page = doc.Pages[0];
page.PageLayers.DeleteOldLayer("red line");
Step 3: Save and launch the file.
doc.SaveToFile("delete.pdf");
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("delete.pdf");
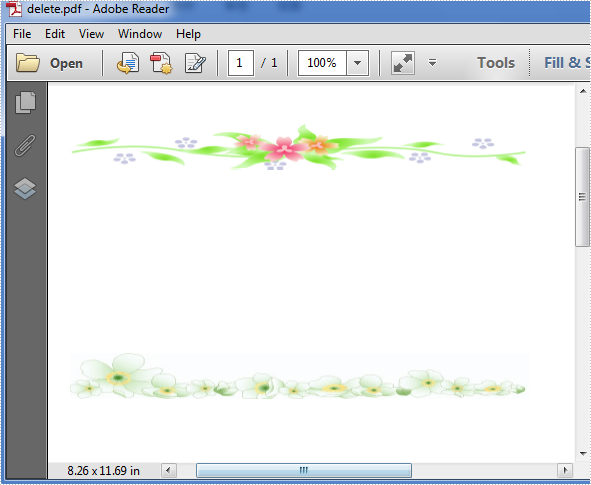
Effective screenshot after deleting:
Full codes:
using Spire.Pdf;
namespace Delete_page_layer_in_PDF
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Load the document from disk
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
doc.LoadFromFile(@"..\..\..\..\..\..\Data\DeleteLayer.pdf");
// Remove the "red line" layer from the document
doc.Layers.RemoveLayer("red line");
// Save the modified document to a new file
doc.SaveToFile("Output.pdf");
// View the Pdf file
PDFDocumentViewer("Output.pdf");
}
}
}
Sometimes, hide row and column can make the data processing job easier and more efficient when working with a large excel file. However, hidden rows and columns are always hidden and invisible, for this reason, you need to unhide them before showing the whole excel file.
Spire.XLS for WPF provides developers four methods: HideRow(), HideColumn(), ShowRow() and ShowColumn() to hide or unhide excel row and column in WPF.
Please check the screenshot of the original excel worksheet:
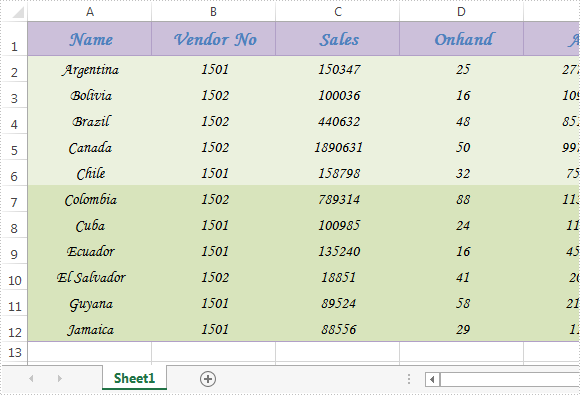
Before using the code, make sure that Spire.XLS is installed on system correctly, next create a WPF application project and add the dll file from the installation folder as reference, after that use following namespace:
using System.Windows; using Spire.Xls;
Code snippets:
Step 1: Initialize a new instance of Workbook class and load the original excel file.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("Excel.xlsx");
Step 2: Get the first worksheet of the file.
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
Step 3: Hide or unhide row and column.
Hide the 8th row and the 3rd column:
sheet.HideRow(8); sheet.HideColumn(3);
Unhide:
sheet.ShowRow(8); sheet.ShowColumn(3);
Step 4: Save and launch the file.
Effective screenshot after hiding:
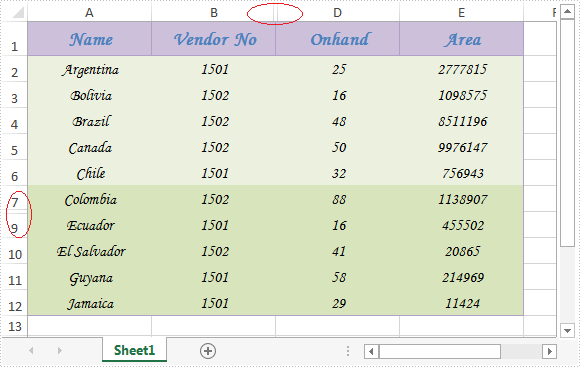
Full codes:
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Windows;
namespace WpfApplication1
{
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
//initialize a new instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//load the sample excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Excel.xlsx");
//get its first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//hide the 8th row and the 3rd column of the first worksheet
sheet.HideRow(8);
sheet.HideColumn(3);
/*//unhide
sheet.ShowRow(8);
sheet.ShowColumn(3);*/
//save and launch the file
workbook.SaveToFile("Sample.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start(workbook.FileName);
}
}
}
Creating, Writing and Saving Excel file are basic tasks in our daily life. This guide will demonstrate how to create an Excel file, insert some data and save the file with specified file format using Spire.XLS for WPF.
Apart from creating Excel from scratch, Spire.XLS also supports to load an existing Excel file, modify the data and do a large range of manipulations in Excel.
Code Snippets:
Step 1: Initialize a new instance of Workbook class. By default, three blank worksheets will be added into the workbook accordingly.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
Step 2: Get the first worksheet from workbook and rename the sheet as "Test”.
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]; sheet.Name = "Test";
Step 3: Insert some text value and number value into the specified cells.
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Text"; sheet.Range["A2"].Text = "Number"; sheet.Range["B1"].Text = "Hello World"; sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 3.1415926; sheet.Range["A7"].Text = "This Excel file is created by Spire.XLS for WPF";
Step 4: Save the file in the format of Excel 2013.
workbook.SaveToFile("sample.xlsx",ExcelVersion.Version2013);
Output:
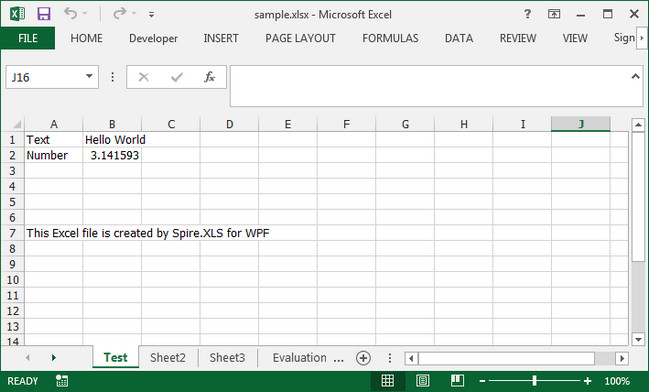
Full Code:
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Windows;
namespace WpfApplication1
{
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
sheet.Name = "Test";
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Text";
sheet.Range["A2"].Text = "Number";
sheet.Range["B1"].Text = "Hello World";
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 3.1415926;
sheet.Range["A7"].Text = "This Excel file is created by Spire.XLS for WPF";
workbook.SaveToFile("sample.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("sample.xlsx");
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Xls
Imports System.Windows
Namespace WpfApplication1
Public Partial Class MainWindow
Inherits Window
Public Sub New()
InitializeComponent()
End Sub
Private Sub button1_Click(sender As Object, e As RoutedEventArgs)
Dim workbook As New Workbook()
Dim sheet As Worksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
sheet.Name = "Test"
sheet.Range("A1").Text = "Text"
sheet.Range("A2").Text = "Number"
sheet.Range("B1").Text = "Hello World"
sheet.Range("B2").NumberValue = 3.1415926
sheet.Range("A7").Text = "This Excel file is created by Spire.XLS for WPF"
workbook.SaveToFile("sample.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("sample.xlsx")
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
With the help of Spire.XLS for WPF, developers can easily save the whole Excel Worksheet to Image for their WPF applications. Sometimes we don’t want to share the whole Excel file with data to others and only want to show some charts on the Excel. Spire.XLS for WPF offers a method of workbook.SaveChartAsImage(); to enable us to save the Excel chart to image easily. In the following section, we will demonstrate how to save the Excel chart as image in .png for example for WPF applications.
Firstly, please view the whole Excel worksheet with data and two charts, a pie chart and a bar chart:
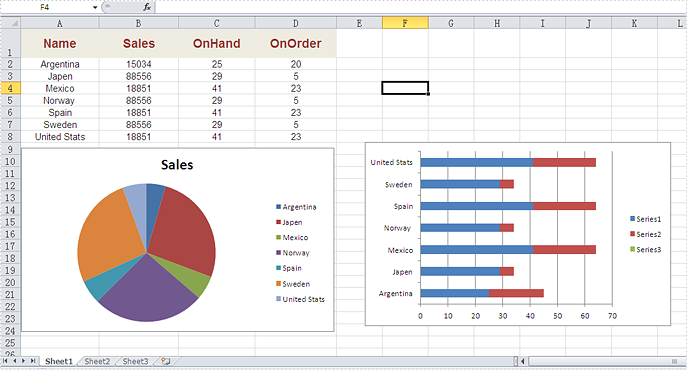
Note: Before Start, please download the latest version of Spire.XLS and add Spire.Xls.Wpf.dll in the bin folder as the reference of Visual Studio.
Here comes to the code snippets of how to save excel chart as image:
Step 1: Create a new Excel workbook and load from file.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
Step 2: Get the first worksheet from workbook.
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
Step 3: Save all the charts in the first worksheet as images.
System.Drawing.Image[] imgs = workbook.SaveChartAsImage(sheet);
for (int i = 0; i < imgs.Length; i++)
{
imgs[i].Save(string.Format("img-{0}.png", i), ImageFormat.Png);
}
Effective screenshots:
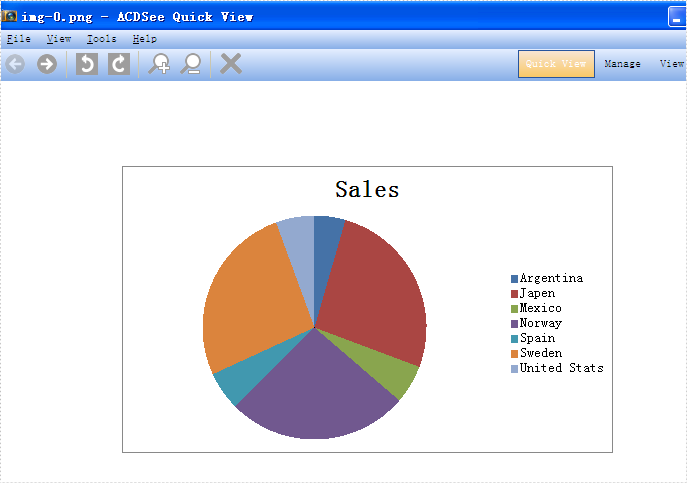
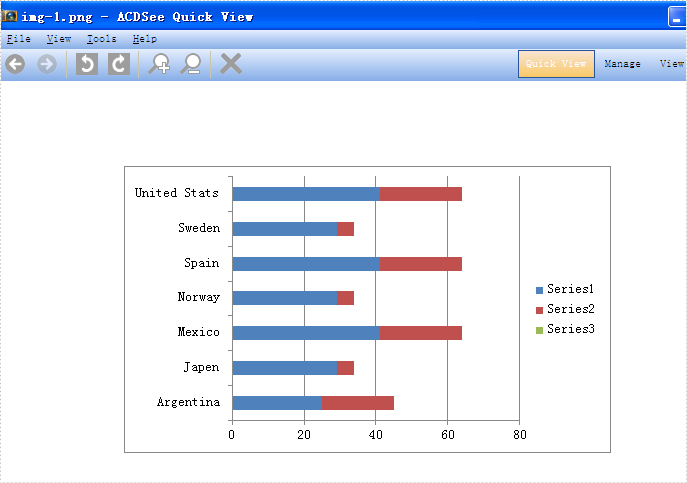
Full codes:
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Drawing.Imaging;
using System.Windows;
namespace WpfApplication1
{
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
System.Drawing.Image[] imgs = workbook.SaveChartAsImage(sheet);
for (int i = 0; i < imgs.Length; i++)
{
imgs[i].Save(string.Format("img-{0}.png", i), ImageFormat.Png);
}
}
}
}
Using Spire.Doc for WPF, programmers can easily create, open, modify and save Word documents in WPF applications. In this article, we’ll introduce how to insert a paragraph to desired position in an existing Word document.
To begin with, you need to download Spire.Doc for WPF and add the Spire.Doc.Wpf.dll and Spire.License.dll as the references to your WPF project. Then add a button in MainWindow and double click the button to write code.
Here are code snippets in the button click event:
Step 1: Initialize a new instance of Document class and load the sample Word document.
Document document = new Document();
document.LoadFromFile("sample.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
Step 2: Initialize a new instance of Paragraph class and append some text to it.
Paragraph paraInserted = new Paragraph(document);
TextRange textRange1 = paraInserted.AppendText("Hello, this is a new paragraph.");
Step 3: Set the text formatting of the paragraph.
textRange1.CharacterFormat.TextColor = System.Drawing.Color.Purple; textRange1.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 11; textRange1.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Calibri Light";
Step 4: Insert the paragraph at the first section at index 1, which indicates the position of the second paragraph in the section.
document.Sections[0].Paragraphs.Insert(1, paraInserted);
Step 5: Save the file.
document.SaveToFile("result.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
Output:

Full Code:
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
using System.Windows;
namespace WpfApplication1
{
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
Document document = new Document();
document.LoadFromFile("sample.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
Paragraph paraInserted = new Paragraph(document);
TextRange textRange1 = paraInserted.AppendText("Hello, this is a new paragraph.");
textRange1.CharacterFormat.TextColor = System.Drawing.Color.Purple;
textRange1.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 11;
textRange1.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Calibri Light";
document.Sections[0].Paragraphs.Insert(1, paraInserted);
document.SaveToFile("result.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Doc
Imports Spire.Doc.Documents
Imports Spire.Doc.Fields
Imports System.Windows
Namespace WpfApplication1
Public Partial Class MainWindow
Inherits Window
Public Sub New()
InitializeComponent()
End Sub
Private Sub button1_Click(sender As Object, e As RoutedEventArgs)
Dim document As New Document()
document.LoadFromFile("sample.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
Dim paraInserted As New Paragraph(document)
Dim textRange1 As TextRange = paraInserted.AppendText("Hello, this is a new paragraph.")
textRange1.CharacterFormat.TextColor = System.Drawing.Color.Purple
textRange1.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 11
textRange1.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Calibri Light"
document.Sections(0).Paragraphs.Insert(1, paraInserted)
document.SaveToFile("result.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
This article is going to introduce how to create, write and save word document in WPF via Spire.Doc for WPF.
Spire.Doc for WPF enables users to do a large range of manipulations (such as create, write, open, edit, convert and save, etc.) on word with high performance and efficiency. In addition, as a powerful and independent library, it doesn’t require Microsoft Office or any other 3rd party tools to be installed on system.
Note: please download and install Spire.Doc correctly and add the dll file from the installation folder as reference.
First, let’s begin to create a word document in WPF.
Use namespace:
using System.Windows; using Spire.Doc; using Spire.Doc.Documents;
Step 1: Create a new word document instance, next add a section and a paragraph to it.
//Create New Word Document doc = new Document(); //Add Section Section section = doc.AddSection(); //Add Paragraph Paragraph Para = section.AddParagraph();
Second, we’re going to write something into the document.
Step 2: Append some text to it.
//Append Text
Para.AppendText("Hello! "
+ "I was created by Spire.Doc for WPF, it's a professional .NET Word component "
+ "which enables developers to perform a large range of tasks on Word document (such as create, open, write, edit, save and convert "
+ "Word document) without installing Microsoft Office and any other third-party tools on system.");
Third, save the generated document.
Step 3: Save and launch the document.
//Save and launch
doc.SaveToFile("MyWord.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("MyWord.docx");
Output:

Full codes:
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using System.Windows;
namespace WpfApplication1
{
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
//Create New Word
Document doc = new Document();
//Add Section
Section section = doc.AddSection();
//Add Paragraph
Paragraph Para = section.AddParagraph();
//Append Text
Para.AppendText("Hello! "
+ "I was created by Spire.Doc for WPF, it's a professional .NET Word component "
+ "which enables developers to perform a large range of tasks on Word document (such as create, open, write, edit, save and convert "
+ "Word document) without installing Microsoft Office and any other third-party tools on system.");
//Save and launch
doc.SaveToFile("MyWord.docx", Spire.Doc.FileFormat.Docx);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("MyWord.docx");
}
}
}
Embed uninstalled fonts by font document when convert word to PDF
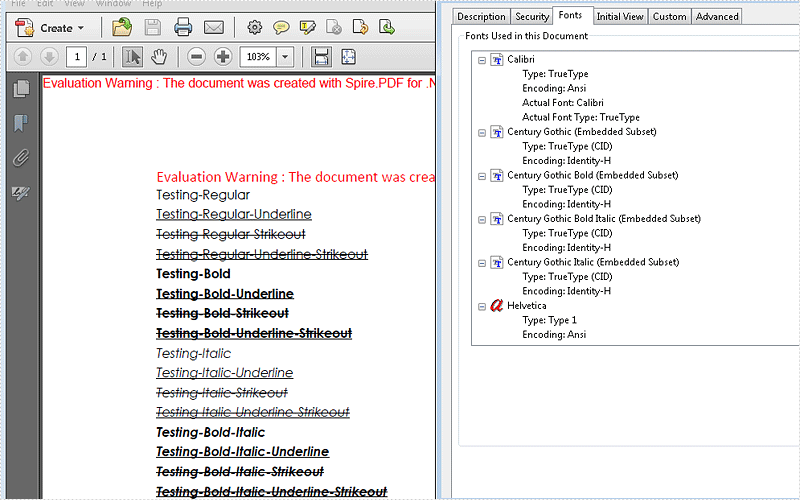
2016-01-21 08:27:32 Written by KoohjiWe have already shown you how to use uninstalled font by font document when converting word to PDF. Now starts from Spire.Doc 5.6.3, Spire.Doc newly supports to set the font styles for the uninstalled fonts when convert word documents to PDF. Here comes to the code snippets of how to set the font styles for embed the uninstalled fonts by font documents:
Note: Before Start, please download the latest version of Spire.XLS and add Spire.xls.dll in the bin folder as the reference of Visual Studio.
Step 1: Create a new workbook and load from file.
Document document = new Document();
document.LoadFromFile("Testing.docx");
Step 2: Create an instance for class ToPdfParameterList named parms.
ToPdfParameterList parms = new ToPdfParameterList();
Step 3: Define the path of the uninstalled fonts.
{
new PrivateFontPath("Century Gothic",FontStyle.Regular,"fonts\\GOTHIC.TTF"),
new PrivateFontPath("Century Gothic",FontStyle.Bold,"fonts\\GOTHICB.TTF"),
new PrivateFontPath("Century Gothic",FontStyle.Italic,"fonts\\GOTHICI.TTF") ,
new PrivateFontPath("Century Gothic",FontStyle.Bold|FontStyle.Italic,"fonts\\GOTHICBI.TTF")
};
Step 4: Save the document to file and launch to preview it.
document.SaveToFile("Testing.pdf", parms);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("Testing.pdf");
Effective screenshot of the embedded uninstalled fonts by setting the font style after converts to PDF: