
.NET (1317)
Children categories
Set vertical alignment for table can show contents in different positions. There are three options including Top, Bottom, Middle. Default is Middle. This article talk about how to set vertical alignment for tables via Spire.Doc, the following is the detailed steps:
Step 1: Create a new Word document and add a new section.
Document document = new Document(); Section section = document.AddSection();
Step 2: Add a table with 3 columns and 3 rows. You can set showBoder property as true when you creating the table. Merge the first column as one cell.
Table table = section.AddTable(true); table.ResetCells(3, 3); table.ApplyVerticalMerge(0, 0, 2);
Step 3: Set the vertical alignment for each cell, default is top. Here we set the first row as Top, second row as Middle, third row as Bottom.
table.Rows[0].Cells[0].CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle; table.Rows[0].Cells[1].CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Top; table.Rows[0].Cells[2].CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Top; table.Rows[1].Cells[1].CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle; table.Rows[1].Cells[2].CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle; table.Rows[2].Cells[1].CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Bottom; table.Rows[2].Cells[2].CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Bottom;
Step 4: Append data to table.
Paragraph paraPic = table.Rows[0].Cells[0].AddParagraph();
DocPicture pic = paraPic.AppendPicture(Image.FromFile("1.png"));
String[][] data = {
new string[] {"","Spire.Office","Spire.DataExport"},
new string[] {"","Spire.Doc","Spire.DocViewer"},
new string[] {"","Spire.XLS","Spire.PDF"}
};
for (int r = 0; r < 3; r++)
{
TableRow dataRow = table.Rows[r];
dataRow.Height = 50;
for (int c = 0; c < 3; c++)
{
if (c == 1)
{
Paragraph par = dataRow.Cells[c].AddParagraph();
par.AppendText(data[r][c]);
dataRow.Cells[c].Width = (section.PageSetup.ClientWidth) / 2;
}
if (c == 2)
{
Paragraph par = dataRow.Cells[c].AddParagraph();
par.AppendText(data[r][c]);
dataRow.Cells[c].Width = (section.PageSetup.ClientWidth) / 2;
}
}
}
Step 5: Save and review.
document.SaveToFile(@"result.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013); System.Diagnostics.Process.Start(@"result.docx");
Result screenshot:
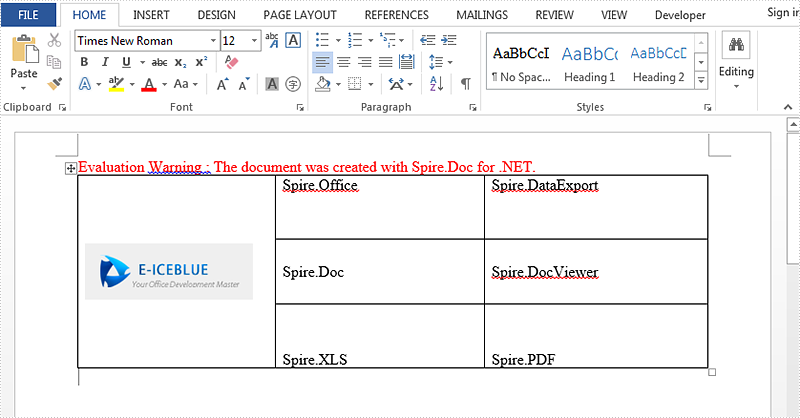
Full code:
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
using System;
using System.Drawing;
namespace SetVerticalAlignment
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Document document = new Document();
Section section = document.AddSection();
Table table = section.AddTable(true);
table.ResetCells(3, 3);
table.ApplyVerticalMerge(0, 0, 2);
table.Rows[0].Cells[0].CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle;
table.Rows[0].Cells[1].CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Top;
table.Rows[0].Cells[2].CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Top;
table.Rows[1].Cells[1].CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle;
table.Rows[1].Cells[2].CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle;
table.Rows[2].Cells[1].CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Bottom;
table.Rows[2].Cells[2].CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Bottom;
Paragraph paraPic = table.Rows[0].Cells[0].AddParagraph();
DocPicture pic = paraPic.AppendPicture(Image.FromFile("1.png"));
String[][] data = {
new string[] {"","Spire.Office","Spire.DataExport"},
new string[] {"","Spire.Doc","Spire.DocViewer"},
new string[] {"","Spire.XLS","Spire.PDF"}
};
for (int r = 0; r < 3; r++)
{
TableRow dataRow = table.Rows[r];
dataRow.Height = 50;
for (int c = 0; c < 3; c++)
{
if (c == 1)
{
Paragraph par = dataRow.Cells[c].AddParagraph();
par.AppendText(data[r][c]);
dataRow.Cells[c].Width = (section.PageSetup.ClientWidth) / 2;
}
if (c == 2)
{
Paragraph par = dataRow.Cells[c].AddParagraph();
par.AppendText(data[r][c]);
dataRow.Cells[c].Width = (section.PageSetup.ClientWidth) / 2;
}
}
}
document.SaveToFile(@"result.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start(@"result.docx");
}
}
}
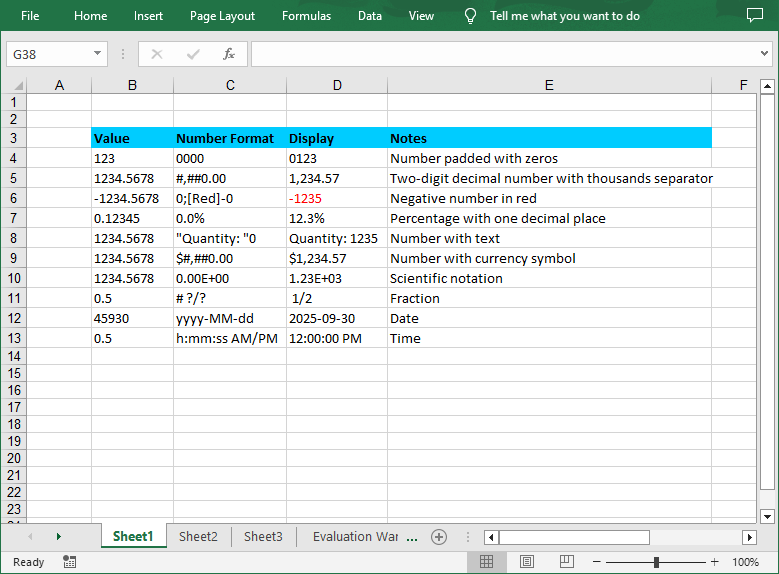
In Excel worksheets, the raw data is often displayed as plain numbers that lack intuitiveness. By setting number format, these numbers can be transformed into a more understandable form. For example, setting sales data in a currency format, i.e., adding a currency symbol and a thousands separator, can make the represented amounts clear at a glance. Formatting market share data into a percentage format can clearly shows the proportions of each part, facilitating quick comparisons and analysis. In this article, you will learn how to set number formats in Excel cells in C# using Spire.XLS for .NET.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Symbols in Excel Number Format
In Excel number format codes, several symbols are used to define how numbers are displayed. Below is a detailed explanation of the common symbols:
| Symbols | Description |
| 0 | A required digit placeholder, padded with zeros if necessary. |
| # | An optional digit placeholder. It does not display insignificant zeros. |
| ? | An optional digit placeholder. It adds spaces to align decimal points and trailing zeros for fractions. |
| . | Represents the decimal point. |
| , | Serves as a thousands separator. |
| ; | Separates different sections of a number format code for positive, negative, zero, and text values. |
| % | Multiplies the number by 100 and adds a percentage sign. |
| E - + | Scientific notation. |
| Currency ($, €, ¥, etc.) | Displays the respective currency symbol. |
| [Color] | Specifies a color for the number display. |
| Date/Time (yyyy, mmmm, mm, dd, hh, ss, AM/PM) | Represent year, full month name, month, day, hour, minute, second, and 12-hour clock markers respectively. |
Set Number Format in Excel Cells in C#
Spire.XLS for .NET provides the CellRange.NumberValue property to set the number value of a cell and the CellRange.NumberFormat property to set the number format with format code. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Get a specified worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Get a specified cell through Worksheet.Range[] property.
- Add text to specified cells through CellRange.Text property.
- Add numeric values to specified cells through CellRange.NumberValue property, and then set the number formats through CellRange.NumberFormat property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
namespace SetNumberFormat
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Add text to sepcified cells and set cell styles
sheet.Range["B3"].Text = "Value";
sheet.Range["C3"].Text = "Number Format";
sheet.Range["D3"].Text = "Display";
sheet.Range["E3"].Text = "Notes";
sheet.Range["B3:E3"].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
sheet.Range["B3:E3"].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.SkyBlue;
// Number padded with zeros
sheet.Range["B4"].Text = "123";
sheet.Range["C4"].Text = "0000";
sheet.Range["D4"].NumberValue = 123;
sheet.Range["D4"].NumberFormat = "0000";
sheet.Range["E4"].Text = "Number padded with zeros";
// Two-digit decimal number with thousands separator
sheet.Range["B5"].Text = "1234.5678";
sheet.Range["C5"].Text = "#,##0.00";
sheet.Range["D5"].NumberValue = 1234.5678;
sheet.Range["D5"].NumberFormat = "#,##0.00";
sheet.Range["E5"].Text = "Two-digit decimal number with thousands separator";
// Negative number in red
sheet.Range["B6"].Text = "-1234.5678";
sheet.Range["C6"].Text = "0;[Red]-0";
sheet.Range["D6"].NumberValue = -1234.5678;
sheet.Range["D6"].NumberFormat = "0;[Red]-0";
sheet.Range["E6"].Text = "Negative number in red";
// Percentage with one decimal place
sheet.Range["B7"].Text = "0.12345";
sheet.Range["C7"].Text = "0.0%";
sheet.Range["D7"].NumberValue = 0.12345;
sheet.Range["D7"].NumberFormat = "0.0%";
sheet.Range["E7"].Text = "Percentage with one decimal place";
// Number with text
sheet.Range["B8"].Text = "1234.5678";
sheet.Range["C8"].Text = "\"Quantity: \"0";
sheet.Range["D8"].NumberValue = 1234.5678;
sheet.Range["D8"].NumberFormat = "\"Quantity: \"0";
sheet.Range["E8"].Text = "Number with text";
// Number with currency symbol
sheet.Range["B9"].Text = "1234.5678";
sheet.Range["C9"].Text = "$#,##0.00";
sheet.Range["D9"].NumberValue = 1234.5678;
sheet.Range["D9"].NumberFormat = "$#,##0.00";
sheet.Range["E9"].Text = "Number with currency symbol";
// Scientific notation format
sheet.Range["B10"].Text = "1234.5678";
sheet.Range["C10"].Text = "0.00E+00";
sheet.Range["D10"].NumberValue = 1234.5678;
sheet.Range["D10"].NumberFormat = "0.00E+00";
sheet.Range["E10"].Text = "Scientific notation";
// Fraction
sheet.Range["B11"].Text = "0.5";
sheet.Range["C11"].Text = "# ?/?";
sheet.Range["D11"].NumberValue = 0.5;
sheet.Range["D11"].NumberFormat = "# ?/?";
sheet.Range["E11"].Text = "Fraction";
// Date
sheet.Range["B12"].Text = "45930";
sheet.Range["C12"].Text = "yyyy-MM-dd";
sheet.Range["D12"].NumberValue = 45930;
sheet.Range["D12"].NumberFormat = "yyyy-MM-dd";
sheet.Range["E12"].Text = "Date";
// Time
sheet.Range["B13"].Text = "0.5";
sheet.Range["C13"].Text = "h:mm:ss AM/PM";
sheet.Range["D13"].NumberValue = 0.5;
sheet.Range["D13"].NumberFormat = "h:mm:ss AM/PM";
sheet.Range["E13"].Text = "Time";
// Set cell styles for the used range
sheet.AllocatedRange.Style.Font.FontName = "Calibri";
sheet.AllocatedRange.Style.Font.Size = 11;
sheet.AllocatedRange.Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left;
// Autofit column width
sheet.AutoFitColumn(2);
sheet.AutoFitColumn(3);
sheet.AutoFitColumn(4);
sheet.AutoFitColumn(5);
// Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("ExcelNumberFormat.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Line numbers is used to display the number of lines counted automatically by Word next to each line of text. It's very useful when we need to refer to specific lines in a document such as contract or legal papers. Line numbers function in word allows us to set the start value, the number interval, the distance from text and the numbering mode of line numbers. Using Spire.Doc, we could achieve all of features mentioned above. This article is going to introduce how to add line numbers in C# using Spire.Doc.
Note: Before start, please download the latest version of Spire.Doc and add Spire.Doc .dll in the bin folder as the reference of visual studio.
Step 1: Load the sample document which only has text.
Document document = new Document();
document.LoadFromFile("T.docx");
Step 2: Set the start value of the line numbers.
document.Sections[0].PageSetup.LineNumberingStartValue = 1;
Step 3: Set the interval between displayed numbers.
document.Sections[0].PageSetup.LineNumberingStep = 6;
Step 4: Set the distance between line numbers and text.
document.Sections[0].PageSetup.LineNumberingDistanceFromText = 40f;
Step 5: Set the numbering mode of line numbers. Here we have four choices: None, Continuous, RestartPage and RestartSection.
document.Sections[0].PageSetup.LineNumberingRestartMode = LineNumberingRestartMode.Continuous;
Step 6: Save the document and launch to see effects.
document.SaveToFile("result.docx",FileFormat.Docx2013);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.docx");
Effects:
Single Page:

Continuous Page:

Full Codes:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using Spire.Doc;
namespace How_to_add_line_numbering
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Document document = new Document();
document.LoadFromFile("T.docx");
document.Sections[0].PageSetup.LineNumberingStartValue = 1;
document.Sections[0].PageSetup.LineNumberingStep = 6;
document.Sections[0].PageSetup.LineNumberingDistanceFromText = 40f;
document.Sections[0].PageSetup.LineNumberingRestartMode = LineNumberingRestartMode.Continuous;
document.SaveToFile("result.docx",FileFormat.Docx2013);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.docx");
}
}
}
We have introduced how to add shapes to the slides by Spire.Presentaion. Spire.Presentation supports to work with lots of shapes, such as triangle, rectangle, ellipse, star, line and so on. This time we will show you how to add line arrow to the slides in C#.
Here comes to the code snippet.
Step 1: Create a PPT document.
Presentation presentation = new Presentation();
Step 2: Add a line to the slides and set its color to red.
IAutoShape shape = presentation.Slides[0].Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Line, new RectangleF(50, 100, 100, 100)); shape.ShapeStyle.LineColor.Color = Color.Red;
Step 3: Set the line arrow by using LineEndType.
shape.Line.LineEndType = LineEndType.StealthArrow;
Step 4: Save and launch to view the PPTX document.
presentation.SaveToFile("shape.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("shape.pptx");
Effective screenshots:
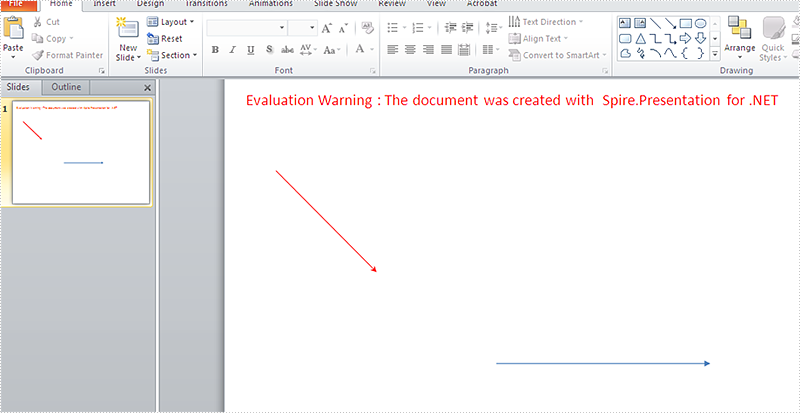
Full codes:
using Spire.Presentation;
using System.Drawing;
namespace AddLineArrow
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Presentation presentation = new Presentation();
IAutoShape shape = presentation.Slides[0].Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Line, new RectangleF(50, 100, 100, 100));
shape.ShapeStyle.LineColor.Color = Color.Red;
shape.Line.LineEndType = LineEndType.StealthArrow;
shape = presentation.Slides[0].Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Line, new RectangleF(300, 250, 150, 150));
shape.Rotation = -45;
shape.Line.LineEndType = LineEndType.TriangleArrowHead;
presentation.SaveToFile("shape.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("shape.pptx");
}
}
}
New method get alias, tag and id of content controls in a Word document in C#
2015-06-05 03:59:58 Written by KoohjiContent controls provide a way for you to design documents. When you add a content control to a document, the control is identified by a border, a title, and temporary text that can provide instructions to the user, and can prevent users from editing or deleting protected sections of a document.
Bind parts of a document or template to data. You can bind content controls to database fields, managed objects in the .NET Framework, XML elements that are stored in the document, and other data sources.
This article illustrates how to get all controls and their properties including alias, id and tag via Spire.Doc with new method and replace the Barcode with another image.
Refer this article to check old method: Get alias, tag and id of content controls in a Word document in C#
The following is test file new.docx.
Here are the steps:
Step 1: Create a new Word document and load the test file.
Document doc = new Document(@"new.docx");
Step 2: Create a list StructureDocument to store tags. Here, each content control will be identified by tag.
public class StructureTags
{
List m_structureDocumnt;
public List StructureDocument
{
get
{
if (m_structureDocumnt == null)
m_structureDocumnt = new List();
return m_structureDocumnt;
}
}
}
Step 3: Use foreach sentence to get all tags in the Word document.
foreach (Section section in doc.Sections)
{
foreach (Body body in section.ChildObjects)
{
ModifyBody(body);
}
}
Step 4: Show the properties of all controls.
List tagInlines = structureTags.StructureDocument;
Console.WriteLine("Part1");
for (int i = 0; i < tagInlines.Count; i++)
{
string alias = tagInlines[i].SDTProperties.Alias; // Can be null or empty
decimal id = tagInlines[i].SDTProperties.Id;
string tag = tagInlines[i].SDTProperties.Tag;
string STDType = tagInlines[i].SDTProperties.SDTType.ToString();
Console.WriteLine("{0,20},{1,15},{2, 10} - {3}", alias, id, STDType, tag);
Console.ReadKey();
}
Step 5: Replace image inside of Picture Content Control.
doc.SaveToFile("replace1.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("replace1.docx");
Result Screenshot:
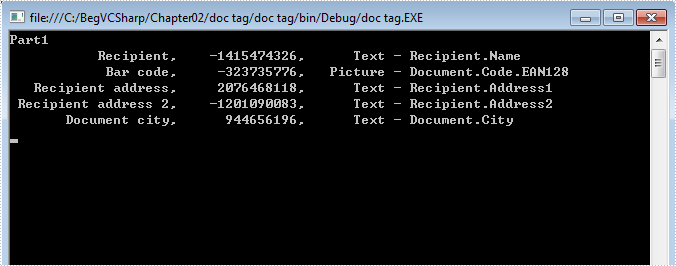
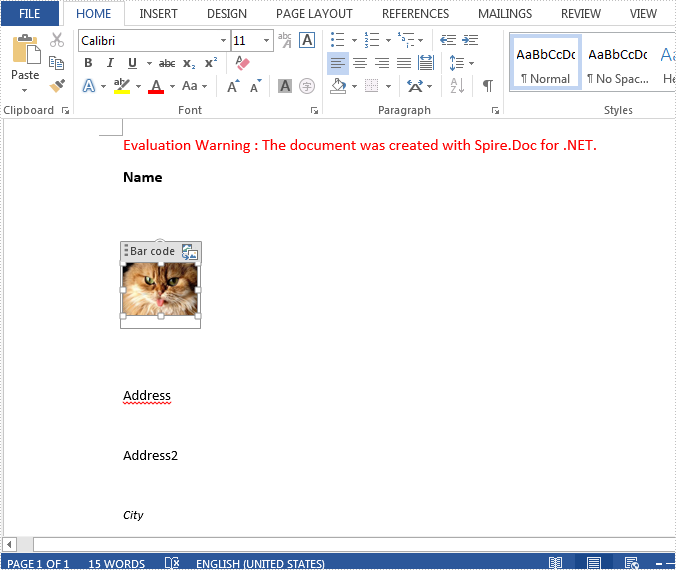
Full code:
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
using System;
using System.Drawing;
namespace GetAlias
{
class Program
{
static StructureTags structureTags = new StructureTags();
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Document doc = new Document(@"new.docx");
foreach (Section section in doc.Sections)
{
foreach (Body body in section.ChildObjects)
{
ModifyBody(body);
}
}
List tagInlines = structureTags.StructureDocument;
Console.WriteLine("Part1");
for (int i = 0; i < tagInlines.Count; i++)
{
string alias = tagInlines[i].SDTProperties.Alias;
decimal id = tagInlines[i].SDTProperties.Id;
string tag = tagInlines[i].SDTProperties.Tag;
string STDType = tagInlines[i].SDTProperties.SDTType.ToString();
Console.WriteLine("{0,20},{1,15},{2, 10} - {3}", alias, id, STDType, tag);
Console.ReadKey();
if (tagInlines[i].SDTProperties.SDTType == SdtType.Picture)
{
DocPicture picture = tagInlines[i].ChildObjects.FirstItem as DocPicture;
if (picture == null)
{
picture = new DocPicture(doc);
picture.LoadImage(Image.FromFile(@"cat.jpg"));
tagInlines[i].ChildObjects.Add(picture);
}
else
{
picture.LoadImage(Image.FromFile(@"cat.jpg"));
}
}
}
doc.SaveToFile("replace1.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("replace1.docx");
}
static void ModifyBody(Body body)
{
if (body == null)
return;
foreach (DocumentObject docObj in body.ChildObjects)
{
if (docObj is StructureDocumentTag)
{
structureTags.StructureDocument.Add(docObj as StructureDocumentTag);
}
else if (docObj is Table)
{
ModifyTable(docObj as Table);
}
else if (docObj is Paragraph)
{
ModifyParagraph(docObj as Paragraph);
}
}
}
static void ModifyTable(Table table)
{
if (table == null)
return;
foreach (TableRow row in table.Rows)
{
foreach (TableCell cell in row.Cells)
{
if (cell is StructureDocumentTagCell)
{
structureTags.StructureDocument.Add(cell as StructureDocumentTagCell);
}
else
{
ModifyBody(cell);
}
}
}
}
static void ModifyParagraph(Paragraph para)
{
if (para == null)
return;
foreach (DocumentObject docObj in para.ChildObjects)
{
if (docObj is StructureDocumentTagInline)
{
structureTags.StructureDocument.Add(docObj as StructureDocumentTagInline);
}
}
}
public class StructureTags
{
List m_structureDocumnt;
public List StructureDocument
{
get
{
if (m_structureDocumnt == null)
m_structureDocumnt = new List();
return m_structureDocumnt;
}
}
}
}
}
Headers and footers are widely used to show addition information such as chapter name, page numbers to keep the document organized. By default, MS Word sets the same headers and footers on each page, but sometimes we need to create different headers or footers for odd and even pages. This article is going to introduce the method to set different odd and even header/footer using Spire.Doc in C#.
Note: Before Start, please download the latest version of Spire.Doc and add Spire.Doc .dll in the bin folder as the reference of Visual Studio.
Step 1: Create a new document and load from file.
Document document = new Document();
document.LoadFromFile("T1.docx");
Step 2: Add a section and set the property true.
Section section = document.Sections[0]; section.PageSetup.DifferentOddAndEvenPagesHeaderFooter = true;
Step 3: Create odd and even footer, odd and even header, and set their format.
//add EvenFooter
Paragraph P1 = section.HeadersFooters.EvenFooter.AddParagraph();
TextRange EF = P1.AppendText("Even Footer Demo from E-iceblue Using Spire.Doc");
EF.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Calibri";
EF.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 20;
EF.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.Green;
EF.CharacterFormat.Bold = true;
P1.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center;
//add OddFooter
Paragraph P2 = section.HeadersFooters.OddFooter.AddParagraph();
TextRange OF = P2.AppendText("Odd Footer Demo");
P2.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center;
OF.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Calibri";
OF.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 20;
OF.CharacterFormat.Bold = true;
OF.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.Blue;
//add OddHeader
Paragraph P3 = section.HeadersFooters.OddHeader.AddParagraph();
TextRange OH = P3.AppendText("Odd Header Demo");
P3.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center;
OH.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Calibri";
OH.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 20;
OH.CharacterFormat.Bold = true;
OH.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.Blue;
//add EvenHeader
Paragraph P4 = section.HeadersFooters.EvenHeader.AddParagraph();
TextRange EH = P4.AppendText("Even Header Demo from E-iceblue Using Spire.Doc");
P4.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center;
EH.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Calibri";
EH.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 20;
EH.CharacterFormat.Bold = true;
EH.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.Green;
Step 4: Save the document and launch to see effects.
document.SaveToFile("R.docx", FileFormat.Docx2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("R.docx");
Effects:
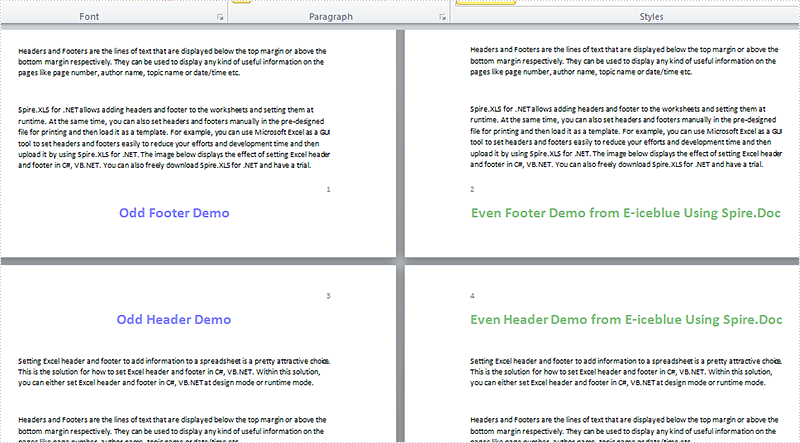
Full code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
using System.Drawing;
namespace Mirror_Margin
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Document document = new Document();
document.LoadFromFile("T1.docx");
Section section = document.Sections[0];
section.PageSetup.DifferentOddAndEvenPagesHeaderFooter = true;
Paragraph P1 = section.HeadersFooters.EvenFooter.AddParagraph();
TextRange EF = P1.AppendText("Even Footer Demo from E-iceblue Using Spire.Doc");
EF.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Calibri";
EF.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 20;
EF.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.Green;
EF.CharacterFormat.Bold = true;
P1.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center;
Paragraph P2 = section.HeadersFooters.OddFooter.AddParagraph();
TextRange OF = P2.AppendText("Odd Footer Demo");
P2.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center;
OF.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Calibri";
OF.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 20;
OF.CharacterFormat.Bold = true;
OF.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.Blue;
Paragraph P3 = section.HeadersFooters.OddHeader.AddParagraph();
TextRange OH = P3.AppendText("Odd Header Demo");
P3.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center;
OH.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Calibri";
OH.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 20;
OH.CharacterFormat.Bold = true;
OH.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.Blue;
Paragraph P4 = section.HeadersFooters.EvenHeader.AddParagraph();
TextRange EH = P4.AppendText("Even Header Demo from E-iceblue Using Spire.Doc");
P4.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center;
EH.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Calibri";
EH.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 20;
EH.CharacterFormat.Bold = true;
EH.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.Green;
document.SaveToFile("R.docx", FileFormat.Docx2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("R.docx");
}
}
}
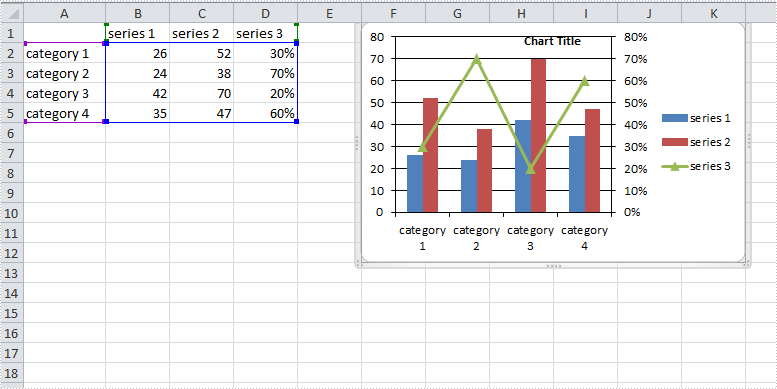
A combination chart that combines two or more chart types in a single chart is often used to emphasize different types of information in that chart. As is shown in the below Excel sheet, we have different type of data in series 3. To clearly display data of different types, it can be helpful to plot varying data sets either with different chart types or on different axes.
In this article, we will introduce how to combine different chart types in one chart and how to add a secondary axis to a chart using Spire.XLS in C#, VB.NET.
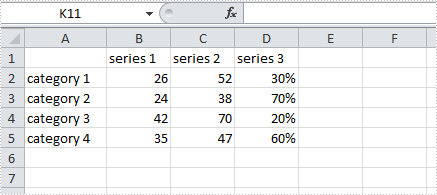
Code Snippet:
Step 1: Create a new instance of Workbook class and the load the sample Excel file.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("data.xlsx");
Step 2: Get the first worksheet from workbook.
Worksheet sheet=workbook.Worksheets[0];
Step 3: Add a chart to worksheet based on the data from A1 to D5.
Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(); chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:D5"]; chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false;
Step 4: Set position of chart.
chart.LeftColumn = 6; chart.TopRow = 1; chart.RightColumn = 12; chart.BottomRow = 13;
Step 5: Apply Column chart type to series 1 and series 2, apply Line chart type to series 3.
var cs1 = (ChartSerie)chart.Series[0]; cs1.SerieType = ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered; var cs2 = (ChartSerie)chart.Series[1]; cs2.SerieType = ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered; var cs3 = (ChartSerie)chart.Series[2]; cs3.SerieType = ExcelChartType.LineMarkers;
Step 6: Add a secondary axis to the chart, plot data of series 3 on the secondary axis.
chart.SecondaryCategoryAxis.IsMaxCross = true; cs3.UsePrimaryAxis = false;
Step 7: Save and launch the file
workbook.SaveToFile("result.xlsx",ExcelVersion.Version2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.xlsx");
Result:
Full Code:
using Spire.Xls;
using Spire.Xls.Charts;
namespace CreateCombinationExcel
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("data.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//add a chart based on the data from A1 to D5
Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add();
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:D5"];
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false;
//set position of chart
chart.LeftColumn = 6;
chart.TopRow = 1;
chart.RightColumn = 12;
chart.BottomRow = 13;
//apply different chart type to different series
var cs1 = (ChartSerie)chart.Series[0];
cs1.SerieType = ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered;
var cs2 = (ChartSerie)chart.Series[1];
cs2.SerieType = ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered;
var cs3 = (ChartSerie)chart.Series[2];
cs3.SerieType = ExcelChartType.LineMarkers;
//add a secondary axis to chart
chart.SecondaryCategoryAxis.IsMaxCross = true;
cs3.UsePrimaryAxis = false;
//save and launch the file
workbook.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.xlsx");
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Xls
Imports Spire.Xls.Charts
Namespace CreateCombinationExcel
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
Dim workbook As New Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("data.xlsx")
Dim sheet As Worksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'add a chart based on the data from A1 to D5
Dim chart As Chart = sheet.Charts.Add()
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range("A1:D5")
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
'set position of chart
chart.LeftColumn = 6
chart.TopRow = 1
chart.RightColumn = 12
chart.BottomRow = 13
'apply different chart type to different series
Dim cs1 = DirectCast(chart.Series(0), ChartSerie)
cs1.SerieType = ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered
Dim cs2 = DirectCast(chart.Series(1), ChartSerie)
cs2.SerieType = ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered
Dim cs3 = DirectCast(chart.Series(2), ChartSerie)
cs3.SerieType = ExcelChartType.LineMarkers
'add a secondary axis to chart
chart.SecondaryCategoryAxis.IsMaxCross = True
cs3.UsePrimaryAxis = False
'save and launch the file
workbook.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010)
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.xlsx")
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
How to save Chart and table on Presentation Slide as image in C#
2015-06-02 07:40:40 Written by KoohjiSpire.Presentation enables developers to export the whole presentation slides with table, chart and shape to image. And it also supports to export the single element in the presentation slides, such as chart, table and shape into image. This article will show you how to save chart and table on Presentation Slide as image in C# and please check the steps as below:
Step 1: Create a presentation document and load from file.
Presentation ppt = new Presentation();
ppt.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx");
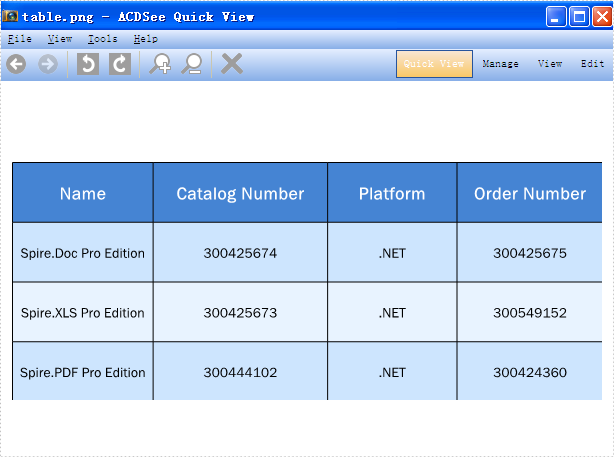
Step 2: Traverse every shape in the slide. Call ShapeList.SaveAsImage(int shapeIndex) to save table and chart as image.
//Save table as image in .Png format
Image image = ppt.Slides[0].Shapes.SaveAsImage(4);
image.Save("table.png", System.Drawing.Imaging.ImageFormat.Png);
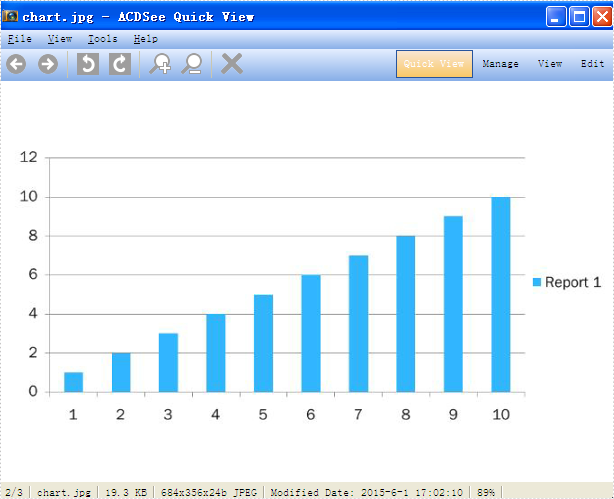
//Save chart as image in .Jpeg format
image = ppt.Slides[1].Shapes.SaveAsImage(3);
image.Save("chart.jpg", System.Drawing.Imaging.ImageFormat.Jpeg);
You can use Shapes.SaveAsEMF method to save the chart and table to image in EMF format.
Effective screenshot:
Save Presentation table as image:
Save Presentation chart as image:
Full codes:
using Spire.Presentation;
using System.Drawing;
namespace SaveTableChartasImage
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Presentation ppt = new Presentation();
ppt.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx");
Image image = ppt.Slides[0].Shapes.SaveAsImage(4);
image.Save("table.png", System.Drawing.Imaging.ImageFormat.Png);
image = ppt.Slides[1].Shapes.SaveAsImage(3);
image.Save("chart.jpg", System.Drawing.Imaging.ImageFormat.Jpeg);
//ppt.Slides[1].Shapes.SaveAsEMF(3, "chart.emf");
}
}
}
C#/VB.NET: Change Security Permissions of PDF Documents
2022-09-29 07:38:00 Written by AdministratorWhen you protect your PDF documents with passwords you can optionally specify a set of permissions. The permissions determine how users can interact with the file. For example, you can apply permissions to your document to prohibit the user from printing or using cut and paste operations. This article demonstrates how to change security permissions of PDF documents using Spire.PDF for .NET in C# and VB.NET.
Install Spire.PDF for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.PDF for.NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.PDF
Change Security Permissions of a PDF Document
The following are the steps to apply security permissions to a PDF document using Spire.PDF for .NET.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a sample PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFileFile() method.
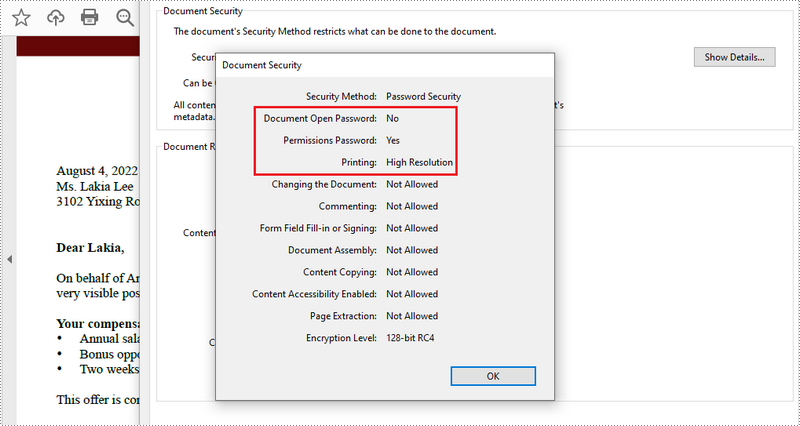
- Specify open password and permission password. The open password can be set to empty so that the generated document will not require a password to open.
- Encrypt the document with the open password and permission password, and set the security permissions using PdfDocument.Security.Encypt() method. This method takes PdfPermissionsFlags enumeration as a parameter, which defines user access permissions for an encrypted document.
- Save the document to another PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Pdf;
using Spire.Pdf.Security;
namespace ChangeSecurityPermission
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a PdfDocument object
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
//Load a sample PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile(@"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\sample.pdf");
//Specify open password
string openPsd = string.Empty;
//Specify permission password
string permissionPsd = "e-iceblue";
//Encrypt the document with open password and permission password, and set the permissions and encryption key size
PdfSecurityPolicy securityPolicy = new PdfPasswordSecurityPolicy(openPsd, permissionPsd);
// Set the encryption algorithm to AES 128-bit
securityPolicy.EncryptionAlgorithm = PdfEncryptionAlgorithm.AES_128;
// Allow printing of the document
securityPolicy.DocumentPrivilege.AllowPrint = true;
// Allow filling form fields in the document
securityPolicy.DocumentPrivilege.AllowFillFormFields = true;
doc.Encrypt(securityPolicy);
//Save the document to another PDF file
doc.SaveToFile("SecurityPermissions.pdf");
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
How to split text into two columns and add line between them
2015-05-28 08:51:50 Written by AdministratorColumns are widely used to set page layout, for which could split text into two or more columns so that the text could flow from one column to the next on the same page. Using Spire.Doc, we could achieve this feature and add a line between columns at the same time. This article is going to introduce how to split text into two columns and add line between them.
Note: please download the latest version of Spire.Doc and add Spire.Doc .dll as reference of Visual Studio.
Step 1: Create a new document and load from file
Document document = new Document();
document.LoadFromFile("S.docx");
Step 2: Add a column to section one, set the width of columns and the spacing between columns. Here we set width as 100f and spacing as 20f.
document.Sections[0].AddColumn(100f, 20f);
Step 3: Add a line between the two columns
document.Sections[0].PageSetup.ColumnsLineBetween = true;
Step 4: Save the document and launch to see effects
document.SaveToFile("result.docx",FileFormat.Docx2013);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.docx");
Before adding the columns:
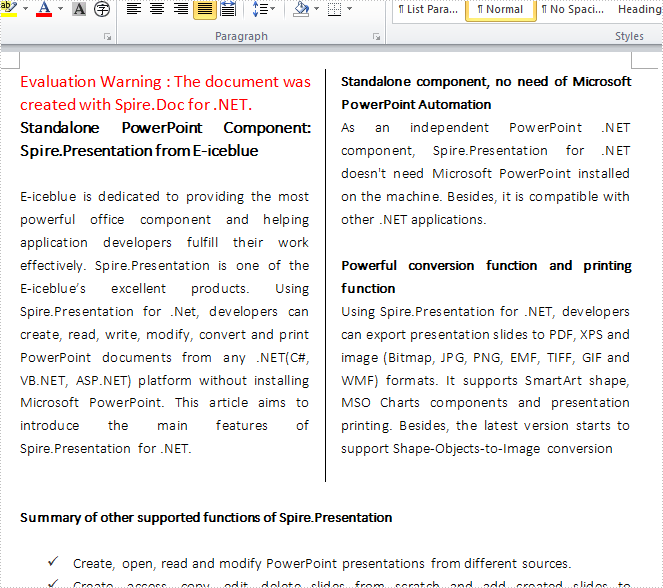
Effects:
Full Code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using Spire.Doc;
namespace Column
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Document document = new Document();
document.LoadFromFile("S.docx");
document.Sections[0].AddColumn(100f, 20f);
document.Sections[0].PageSetup.ColumnsLineBetween = true;
document.SaveToFile("result.docx",FileFormat.Docx2013);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.docx");
}
}
}
