Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
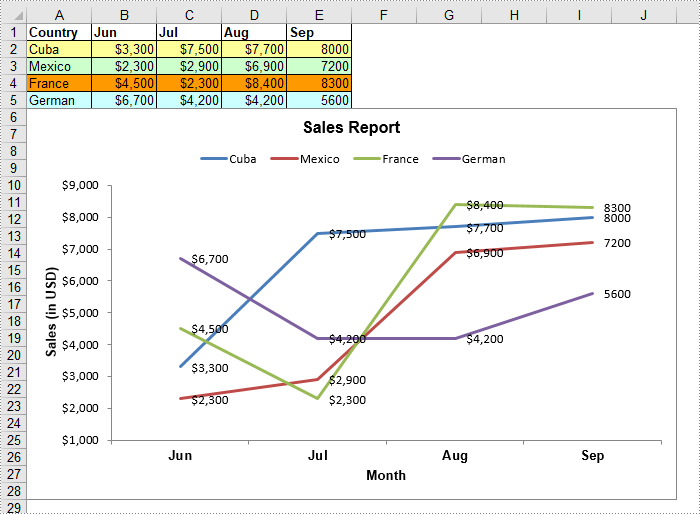
A line chart, also known as a line graph, is a type of chart that displays information as a series of data points connected by straight line segments. It is generally used to show the changes of information over a period of time, such as years, months or days. In this article, you will learn how to create a line chart in Excel in C# and VB.NET using Spire.XLS for .NET.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Create a Line Chart in Excel using C# and VB.NET
The following are the main steps to create a line chart:
- Create an instance of Workbook class.
- Get the first worksheet by its index (zero-based) though Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Add some data to the worksheet.
- Add a line chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Line) method.
- Set data range for the chart through Chart.DataRange property.
- Set position, title, category axis title and value axis title for the chart.
- Loop through the data series of the chart, show data labels for the data points of each data series by setting the ChartSerie.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue property as true.
- Set the position of chart legend through Chart.Legend.Position property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
using Spire.Xls.Charts;
using System.Drawing;
namespace CreateLineChart
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Set sheet name
sheet.Name = "Line Chart";
//Hide gridlines
sheet.GridLinesVisible = false;
//Add some data to the the worksheet
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Country";
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "Cuba";
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "Mexico";
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "France";
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "German";
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Jun";
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 3300;
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 2300;
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 4500;
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 6700;
sheet.Range["C1"].Value = "Jul";
sheet.Range["C2"].NumberValue = 7500;
sheet.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 2900;
sheet.Range["C4"].NumberValue = 2300;
sheet.Range["C5"].NumberValue = 4200;
sheet.Range["D1"].Value = "Aug";
sheet.Range["D2"].NumberValue = 7700;
sheet.Range["D3"].NumberValue = 6900;
sheet.Range["D4"].NumberValue = 8400;
sheet.Range["D5"].NumberValue = 4200;
sheet.Range["E1"].Value = "Sep";
sheet.Range["E2"].NumberValue = 8000;
sheet.Range["E3"].NumberValue = 7200;
sheet.Range["E4"].NumberValue = 8300;
sheet.Range["E5"].NumberValue = 5600;
//Set font and fill color for specified cells
sheet.Range["A1:E1"].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
sheet.Range["A2:E2"].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightYellow;
sheet.Range["A3:E3"].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightGreen1;
sheet.Range["A4:E4"].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightOrange;
sheet.Range["A5:E5"].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightTurquoise;
//Set cell borders
sheet.Range["A1:E5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeTop].Color = Color.FromArgb(0, 0, 128);
sheet.Range["A1:E5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeTop].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
sheet.Range["A1:E5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].Color = Color.FromArgb(0, 0, 128);
sheet.Range["A1:E5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
sheet.Range["A1:E5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeLeft].Color = Color.FromArgb(0, 0, 128);
sheet.Range["A1:E5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeLeft].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
sheet.Range["A1:E5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeRight].Color = Color.FromArgb(0, 0, 128);
sheet.Range["A1:E5"].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeRight].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin;
//Set number format
sheet.Range["B2:D5"].Style.NumberFormat = "\"$\"#,##0";
//Add a line chart to the worksheet
Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Line);
//Set data range for the chart
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:E5"];
//Set position of the chart
chart.LeftColumn = 1;
chart.TopRow = 6;
chart.RightColumn = 11;
chart.BottomRow = 29;
//Set and format chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Sales Report";
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = true;
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 12;
//Set and format category axis title
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Title = "Month";
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Font.IsBold = true;
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = true;
//Set and format value axis title
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.Title = "Sales (in USD)";
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = false;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.TextRotationAngle = -90;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinValue = 1000;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = true;
//Loop through the data series of the chart
foreach (ChartSerie cs in chart.Series)
{
cs.Format.Options.IsVaryColor = true;
//Show data labels for data points
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = true;
}
//Set position of chart legend
chart.Legend.Position = LegendPositionType.Top;
//Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("LineChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Why Export Datatable to RTF?
RTF is a Microsoft specification and certified file format used with DOC and DOCX. It is a core part of the Microsoft Office system. RTF usually used for cut and paste, including paste special and used when opening documents into Word. RTF does not cause document corruption.
RTF allows Workshare tremendous flexibility in successfully translating between any number of document types because of its ubiquity. Workshare products can not only maintain document fidelity, but provide portability advantages when moving around different Microsoft Word systems, or translating to other document types.
How to Export DataTable to RTF through DataGridView?
Download Spire.DataExport (or Spire.Office) with .NET Framework together. Only 2 Simple steps you can finish the whole datatable to RTF exporting process.
Step 1: Load Data Information
Before exporting data from DataTable, we should load data information from data source. And select which information we need export. Through DataGridVew, we even can preview and modify data information. So, in this step, our job is to prepare data which is about to be exported out.
private void btnLoad_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
oleDbConnection.ConnectionString = this.textBox1.Text;
OleDbCommand oleDbCommand = new OleDbCommand();
oleDbCommand.CommandText = this.textBox2.Text;
oleDbCommand.Connection = oleDbConnection;
using (OleDbDataAdapter da = new OleDbDataAdapter(oleDbCommand))
{
DataTable dt = new DataTable();
da.Fill(dt);
dataGridView1.DataSource = dt;
}
}
Effect Screenshot
Step 2: Set Export into RTF
Spire.DataExport allows user to export data into most popular file formats including MS Excel, RTF, HTML, PDF, XML, CSV, DBF, DIF, etc. Here we need set it as RTF format. Spire.DataExport will create a new RTF file and through DataGridView export data into RTF file. You also can rename the file as you like.
private void btnRun_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Spire.DataExport.RTF.RTFExport RTFExport = new Spire.DataExport.RTF.RTFExport();
RTFExport.DataSource = Spire.DataExport.Common.ExportSource.DataTable;
RTFExport.DataTable = this.dataGridView1.DataSource as DataTable;
RTFExport.ActionAfterExport = Spire.DataExport.Common.ActionType.OpenView;
RTFExport.FileName = "RTF0722.rtf";
RTFExport.SaveToFile();
}
Effect Screenshot
When we export data out from Database we may have requirements of exporting data from Datatable to CSV because CSV is a simple file format that is widely supported. CSV (The comma-separated values) file format is a set of file formats used to store tabular data in which numbers and text are stored in plain textual form that can be read in a text editor. Lines in the text file represent rows of a table, and commas in a line separate what are fields in the table row.
Here we mainly discuss how to Export Datatable to CSV with Spire.DataExport for .NET.
Download Spire.DataExport (or Spire.Office) with .NET Framework together. Only 2 Simple steps you can finish the whole datatable to CSV exporting process.
Step 1: Load Data Information
Before exporting data from DataTable, we should load data information from data source. And select which information we need export. Through DataGridVew, we even can preview and modify data information. So, in this step, our job is to prepare data which is about to be exported out.
private void btnLoad_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (OleDbConnection oleDbConnection = new OleDbConnection())
{
oleDbConnection.ConnectionString = this.textBox1.Text;
OleDbCommand oleDbCommand = new OleDbCommand();
oleDbCommand.CommandText = this.textBox2.Text;
oleDbCommand.Connection = oleDbConnection;
using (OleDbDataAdapter da = new OleDbDataAdapter(oleDbCommand))
{
DataTable dt = new DataTable();
da.Fill(dt);
dataGridView1.DataSource = dt;
}
}
}
Effect Screenshot
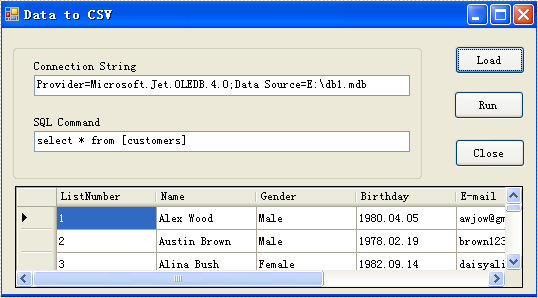
Step 2: Set Export into CSV
Spire.DataExport allows user to export data into most popular file formats including MS Excel, MS Word, HTML, PDF, XML, CSV, DBF, DIF, etc. Here we need set it as CSV format. Spire.DataExport will create a new CSV file and through DataGridView export data into CSV file. You also can rename the file as you like.
private void btnRUN_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
TXTExport CSVExport = new TXTExport();
CSVExport.DataSource = Spire.DataExport.Common.ExportSource.DataTable;
CSVExport.DataTable = this.dataGridView1.DataSource as DataTable;
CSVExport.ActionAfterExport = Spire.DataExport.Common.ActionType.OpenView;
CSVExport.FileName = "CSV0721.csv";
CSVExport.SaveToFile();
}
Effect Screenshot