
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
What is Excel Interior?
Excel provides essentially no support in worksheet functions for Working with cell colors. However, colors are often used in spreadsheets to indicate some sorts of value or category. Thus comes the need for functions that can work with colors on the worksheet. So it appears in the version in Excel 2007 as a new function. It contains all kinds of colors. Below I will show you how to insert interior in Excel with MS Excel and how to do this with Spire.XLS.
How to insert interior in Excel with MS Excel?
To insert interior in Excel with Microsoft Excel, you can follow the sections below:
- Open the worksheet in Excel
- Highlight the zones that you want to insert interior
- Rightclick and choose Setting Cell Format
- Choose Fill->Fill Effect in the dialog box of Setting Cell Format
- In the box, you can change the Color and the Shade Format to your desired effect
How to Insert Interior with Spire.XLS?
It's convenient to realize C#/.NET Excel Integration via Spire.XLS. In interior method, to realize interior you may set the color gradient by assigning sheet.Range[string.Format("E{0}:K{0}", i)].Style.Interior.FillPattern property with ExcelPatternType.Gradient. You can set the BackKnownColor and ForeKnownColor of the sheet. What's more, you can set the gradient style, in the demo, we set the gradient style vertical. In order to reflect the effect, we merge the worksheet range from E to K. In this demo, we use Enum method to enumerate many kinds of colors and define a random object to fill the cell with a gradient color randomly.
First, let's preview the effect screenshot:
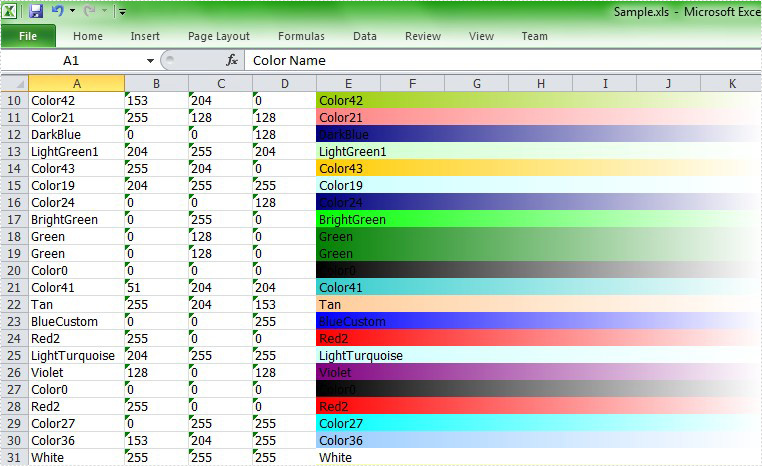
Here comes to the full code in C# and VB.NET.
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Drawing;
using System;
namespace Interior
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a workbook
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Initialize the worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Specify the version
workbook.Version = ExcelVersion.Version2007;
//Define the number of the colors
int maxColor = Enum.GetValues(typeof(ExcelColors)).Length;
//Create a random object
Random random = new Random((int)System.DateTime.Now.Ticks);
for (int i = 2; i < 40; i++)
{
//Random backKnownColor
ExcelColors backKnownColor = (ExcelColors)(random.Next(1, maxColor / 2));
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Color Name";
sheet.Range["B1"].Text = "Red";
sheet.Range["C1"].Text = "Green";
sheet.Range["D1"].Text = "Blue";
//Merge the sheet"E1-K1"
sheet.Range["E1:K1"].Merge();
sheet.Range["E1:K1"].Text = "Gradient";
sheet.Range["A1:K1"].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
sheet.Range["A1:K1"].Style.Font.Size = 11;
//Set the text of color in sheetA-sheetD
string colorName = backKnownColor.ToString();
sheet.Range[string.Format("A{0}", i)].Text = colorName;
sheet.Range[string.Format("B{0}", i)].Text = workbook.GetPaletteColor(backKnownColor).R.ToString();
sheet.Range[string.Format("C{0}", i)].Text = workbook.GetPaletteColor(backKnownColor).G.ToString();
sheet.Range[string.Format("D{0}", i)].Text = workbook.GetPaletteColor(backKnownColor).B.ToString();
//Merge the sheets
sheet.Range[string.Format("E{0}:K{0}", i)].Merge();
//Set the text of sheetE-sheetK
sheet.Range[string.Format("E{0}:K{0}", i)].Text = colorName;
//Set the interior of the color
sheet.Range[string.Format("E{0}:K{0}", i)].Style.Interior.FillPattern = ExcelPatternType.Gradient;
sheet.Range[string.Format("E{0}:K{0}", i)].Style.Interior.Gradient.BackKnownColor = backKnownColor;
sheet.Range[string.Format("E{0}:K{0}", i)].Style.Interior.Gradient.ForeKnownColor = ExcelColors.White;
sheet.Range[string.Format("E{0}:K{0}", i)].Style.Interior.Gradient.GradientStyle = GradientStyleType.Vertical;
sheet.Range[string.Format("E{0}:K{0}", i)].Style.Interior.Gradient.GradientVariant = GradientVariantsType.ShadingVariants1;
}
//AutoFit Column
sheet.AutoFitColumn(1);
//Save the file
workbook.SaveToFile("Sample.xls",ExcelVersion.Version97to2003);
//Launch the file
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("Sample.xls");
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Xls
Imports System.Drawing
Imports System
Module Module1
Sub Main()
'Create a workbook
Dim workbook As New Workbook()
'Initialize the worksheet
Dim sheet As Worksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Specify the version
workbook.Version = ExcelVersion.Version2007
'Define the number of the colors
Dim maxColor As Integer = [Enum].GetValues(GetType(ExcelColors)).Length
'Create a random object
Dim random As New Random()
For i As Integer = 2 To 39
'Random backKnownColor
Dim backKnownColor As ExcelColors = DirectCast(random.[Next](1, maxColor \ 2), ExcelColors)
sheet.Range("A1").Text = "Color Name"
sheet.Range("B1").Text = "Red"
sheet.Range("C1").Text = "Green"
sheet.Range("D1").Text = "Blue"
'Merge the sheet"E1-K1"
sheet.Range("E1:K1").Merge()
sheet.Range("E1:K1").Text = "Gradient"
sheet.Range("A1:K1").Style.Font.IsBold = True
sheet.Range("A1:K1").Style.Font.Size = 11
'Set the text of color in sheetA-sheetD
Dim colorName As String = backKnownColor.ToString()
sheet.Range(String.Format("A{0}", i)).Text = colorName
sheet.Range(String.Format("B{0}", i)).Text = workbook.GetPaletteColor(backKnownColor).R.ToString()
sheet.Range(String.Format("C{0}", i)).Text = workbook.GetPaletteColor(backKnownColor).G.ToString()
sheet.Range(String.Format("D{0}", i)).Text = workbook.GetPaletteColor(backKnownColor).B.ToString()
'Merge the sheets
sheet.Range(String.Format("E{0}:K{0}", i)).Merge()
'Set the text of sheetE-sheetK
sheet.Range(String.Format("E{0}:K{0}", i)).Text = colorName
'Set the interior of the color
sheet.Range(String.Format("E{0}:K{0}", i)).Style.Interior.FillPattern = ExcelPatternType.Gradient
sheet.Range(String.Format("E{0}:K{0}", i)).Style.Interior.Gradient.BackKnownColor = backKnownColor
sheet.Range(String.Format("E{0}:K{0}", i)).Style.Interior.Gradient.ForeKnownColor = ExcelColors.White
sheet.Range(String.Format("E{0}:K{0}", i)).Style.Interior.Gradient.GradientStyle = GradientStyleType.Vertical
sheet.Range(String.Format("E{0}:K{0}", i)).Style.Interior.Gradient.GradientVariant = GradientVariantsType.ShadingVariants1
Next
'AutoFit Column
sheet.AutoFitColumn(1)
'Save doc file.
workbook.SaveToFile("Sample.xls",ExcelVersion.Version97to2003)
'Launching the MS Word file.
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("Sample.xls")
End Sub
End Module
After running the demo, you will find color interior in your 2007 worksheet.
In today's digital age, managing and manipulating Excel files programmatically has become an essential skill for developers. Whether you're building a reporting tool, automating data processing, or enhancing your applications with dynamic data handling, having a robust library at your disposal can make all the difference. Enter Spire.XLS for .NET - a versatile and powerful library that allows you to create, read, write, and edit Excel files seamlessly using C#.
In this article, you will learn how to edit Excel documents effortlessly using C# and Spire.XLS for .NET.
- Read and Write Excel Files in C#
- Apply Styles and Formats to Excel Cells in C#
- Find and Replace Text in Excel in C#
- Add Formulas and Charts to Excel in C#
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Read and Write Excel Files in C#
One of the most common tasks when working with Excel files in C# is reading and writing data. Spire.XLS for .NET provides the CellRange.Value property, enabling developers to easily retrieve or assign values to individual cells.
The step to read and write an Excel file using C# are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file from a given file path.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Get a specific cell using the Worksheet.Range[] property
- Get or set the cell value using the CellRange.Value property.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
namespace ReadAndWriteExcel
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Sample.xlsx");
// Get a specific worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Get a specific cell
CellRange cell = worksheet.Range["A1"];
// Read the cell value
String text = cell.Value;
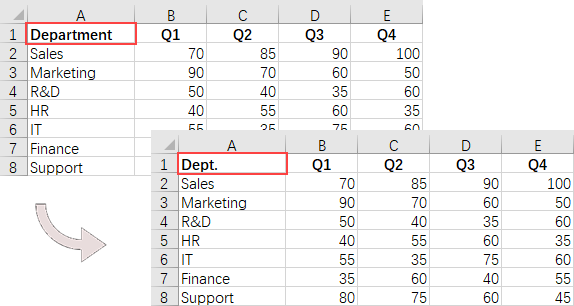
// Determine if the cell value is "Department"
if (text == "Department")
{
// Update the cell value
cell.Value = "Dept.";
}
// Save the workbook to a different
workbook.SaveToFile("ModifyExcel.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
// Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
Apply Styles and Formats to Excel Cells in C#
Styling and formatting Excel documents is an important aspect of creating professional-looking reports. Spire.XLS for .NET offers a variety of APIs within the CellRange class for managing cell styles, fonts, colors, and alignments, as well as adjusting row heights and column widths.
The steps to apply styles and formats to Excel cells are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file from a given file path.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Get all located range using the Worksheet.AllocatedRange property.
- Get a specific row using the CellRange.Rows[] property, and set the cell color, text color, text alignment, and row height using the properties under the CellRange object.
- Get a specific column using the CellRange.Columns[] property, and set the column width using the ColumnWidth property under the CellRange object.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Drawing;
namespace FormatCells
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Sample.xlsx");
// Get a specific worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Get all located range from the worksheet
CellRange allocatedRange = worksheet.AllocatedRange;
// Iterate through the rows
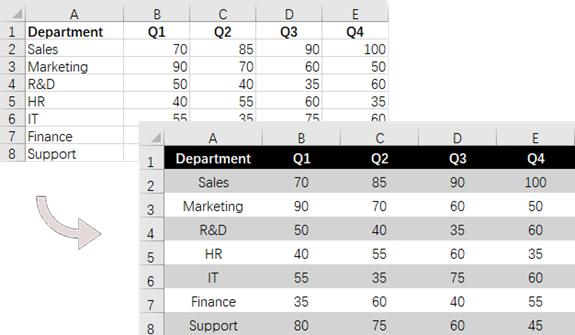
for (int rowNum = 0; rowNum < allocatedRange.RowCount; rowNum++)
{
if(rowNum == 0)
{
// Apply cell color to the header row
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].Style.Color = Color.Black;
// Change the font color of the header row
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].Style.Font.Color = Color.White;
}
// Apply alternate colors to other rows
else if (rowNum % 2 == 1)
{
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].Style.Color = Color.LightGray;
}
else if (rowNum % 2 == 0)
{
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].Style.Color = Color.White;
}
// Align text to center
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center;
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center;
// Set the row height
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].RowHeight = 20;
}
// Iterate through the columns
for (int columnNum = 0; columnNum < allocatedRange.ColumnCount; columnNum++)
{
// Set the column width
if (columnNum > 0)
{
allocatedRange.Columns[columnNum].ColumnWidth = 10;
}
}
// Save the workbook to a different
workbook.SaveToFile("FormatExcel.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
// Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
Find and Replace Text in Excel in C#
The find and replace feature in Excel enhances data accuracy and consistency while significantly improving efficiency. With Spire.XLS for .NET, you can easily locate a cell containing a specific string using the Worksheet.FindString() method and then update the cell value with the CellRange.Value property.
The steps to find and replace text in Excel using C# are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file from a given file path.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Find the cell that contains a specified string using the Worksheet.FindString() method.
- Update the cell value using the CellRange.Value property.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
namespace FindAndReplaceText
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Sample.xlsx");
// Get a specific worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
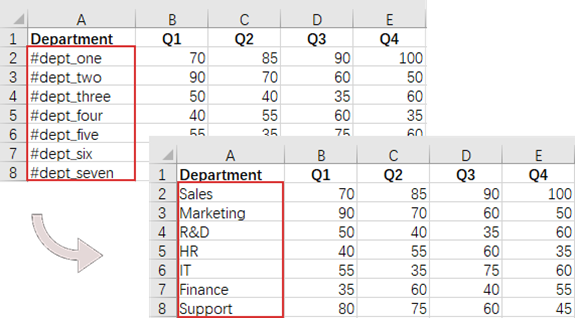
// Define an array of department names for replacement
String[] departments = new String[] { "Sales", "Marketing", "R&D", "HR", "IT", "Finance", "Support" };
// Define an array of placeholders that will be replaced in the Excel sheet
String[] placeholders = new String[] { "#dept_one", "#dept_two", "#dept_three", "#dept_four", "#dept_five", "#dept_six", "#dept_seven" };
// Iterate through the placeholder strings
for (int i = 0; i < placeholders.Length; i++)
{
// Find the cell containing the current placeholder string
CellRange cell = worksheet.FindString(placeholders[i], false, false);
// Replace the text in the found cell with the corresponding department name
cell.Text = departments[i];
}
// Save the workbook to a different
workbook.SaveToFile("ReplaceText.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
// Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
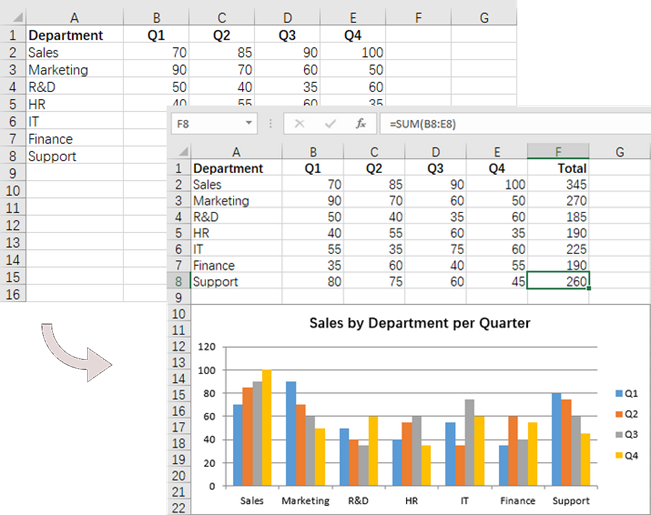
Add Formulas and Charts to Excel in C#
In addition to basic file operations, Spire.XLS for .NET provides a variety of advanced techniques for working with Excel files. These techniques can be used to automate complex tasks, perform calculations, and generate dynamic reports.
The following are the steps to add formulas and create a chart in Excel using C#:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file from a given file path.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Get a specific cell using the Worksheet.Range[] property.
- Add a formula to the cell using the CellRange.Formula property.
- Add a column chart to the worksheet using the Worksheet.Charts.Add() method.
- Set the chart data range, position, title and other attributes using the methods and properties under the Chart object.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
namespace AddFormulaAndChart
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Sample.xlsx");
// Get a specific worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Get all located range
CellRange allocatedRange = worksheet.AllocatedRange;
// Iterate through the rows
for (int rowNum = 0; rowNum < allocatedRange.RowCount; rowNum++)
{
if (rowNum == 0)
{
// Write text in the cell F1
worksheet.Range[rowNum + 1, 6].Text = "Total";
// Apply style to the cell
worksheet.Range[rowNum + 1, 6].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
worksheet.Range[rowNum + 1, 6].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Right;
}
else
{
// Add formulas to the cells from F2 to F8
worksheet.Range[rowNum + 1, 6].Formula = $"=SUM(B{rowNum + 1}:E{rowNum + 1})";
}
}
// Add a clustered column chart
Chart chart = worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered);
// Set data range for the chart
chart.DataRange = worksheet.Range["A1:E8"];
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false;
// Set position of the chart
chart.LeftColumn = 1;
chart.TopRow = 10;
chart.RightColumn = 8;
chart.BottomRow = 23;
// Set and format chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Sales by Department per Quarter";
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 13;
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = true;
// Save the workbook to a different
workbook.SaveToFile("AddFormulaAndChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
// Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
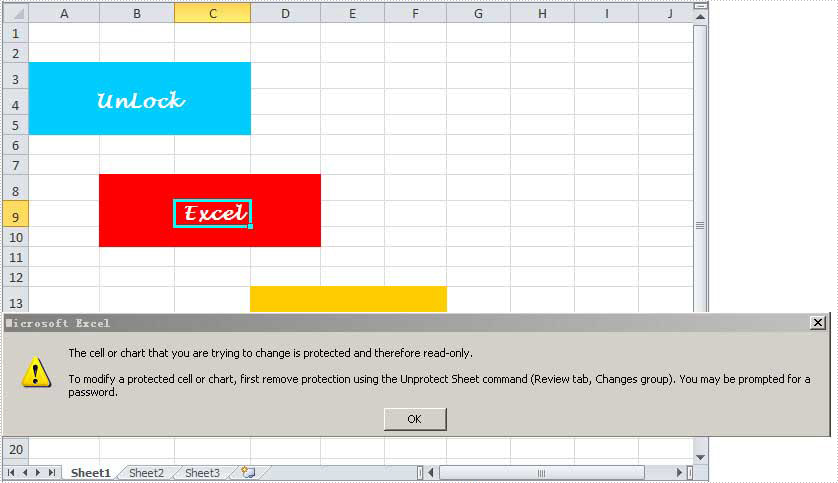
This section aims at providing developers a solution to unlock sheet in Excel workbook with C#, VB.NET via this Excel library Spire.XLS for .NET.
Spire.XLS for .NET enables you to unlock any sheet in Excel file only by one line of key code: Spire.Xls.Worksheet.Unprotect(string password); Besides, as an MS Excel component, Spire.XLS for .NET also enables you to create, read and handle Excel files with fast speed. Below is an Excel file with protected worksheets which will be unlocked in my task.
Since you will use Spire.XLS for .NET, you have to download Spire.XLS for .NET and install it on system. When you create your project, please do not forget to add Spire.XLS.dll as reference from Bin folder. The default path is "..\Spire.XLS\Bin\NET4.0\Spire.XLS.dll". Please note that Spire.XLS for .NET supports .NET Framework 2.0 and above. Here is the whole code for unlocking Excel sheet:
namespace UnlockExcelSheet
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//initialize an instance of Workbook
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel file with protected worksheet
workbook.LoadFromFile(@"..\Unlock Excel Worksheet.xlsx");
//get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Unprotect worksheet
sheet.Unprotect("iceblue");
//Save the file
workbook.SaveToFile("Sample.xlsx",ExcelVersion.Version2010);
//Launch the file
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("Sample.xlsx");
}
}
}
Namespace UnlockExcelSheet
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
'initialize an instance of Workbook
Dim workbook As New Workbook()
'Load an Excel file with protected worksheet
workbook.LoadFromFile("..\Unlock Excel Worksheet.xlsx")
'get the first worksheet
Dim sheet As Worksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Unprotect worksheet
sheet.Unprotect("iceblue")
'Save the file
workbook.SaveToFile("Sample.xlsx",ExcelVersion.Version2010)
'Launch the file
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("Sample.xlsx")
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
After executing above code, you can see that the protected worksheet in the original Excel file has been unlocked, we can edit it also. Please see following image.
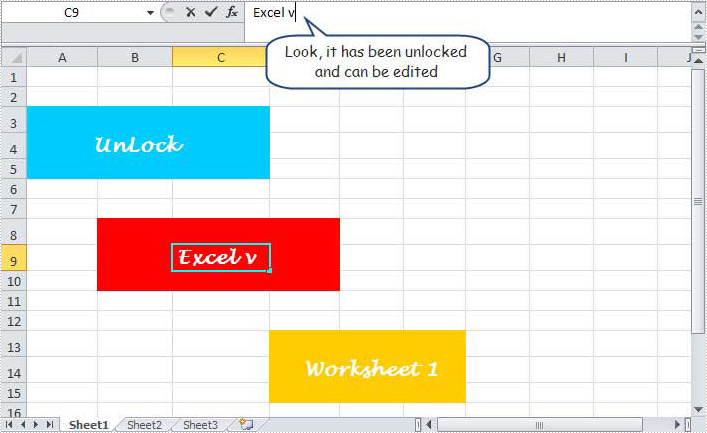
In this section, I have introduced the solution to unlock any sheet in Excel file via Spire.XLS for .NET. I hope it can help you. If you have any questions, feedbacks and advice, you can put them on E-iceblue Forum. We will promise a prompt reply.
