.NET (1317)
Children categories
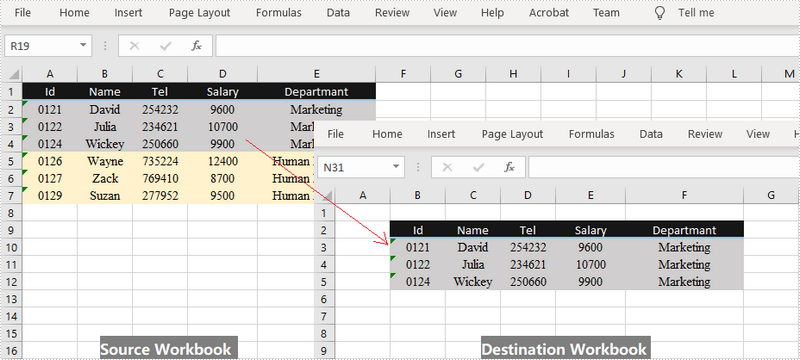
When you're dealing Excel documents, it is a common task that you may need to copy data from a main workbook and paste into a separate workbook. You can copy either a selected cell range or an entire worksheet between different workbooks. This article demonstrates how to copy a selected cell range from one workbook to another by using Spire.XLS for .NET.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for.NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLLs files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
- Package Manager
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Copy a Cell Range Between Different Workbooks
Spire.XLS offers the Worksheet.Copy() method to copy data from a source range to a destination range. The destination range can be a cell range inside the same workbook or from a different workbook. The following are the steps to copy a cell range from a workbook to another.
- Create a Workbook object to load the source Excel document.
- Get the source worksheet and the source cell range using Workbook.Worksheets property and Worksheet.Range property respectively.
- Create another Workbook object to load the destination Excel document.
- Get the destination worksheet and cell range.
- Copy the data from the source range to the destination range using Worksheet.Copy(CellRange source, CellRange destRange).
- Copy the column widths from the source range to the destination range, so that the data can display properly in the destination workbook.
- Save the destination workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
namespace CopyCellRange
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook sourceBook = new Workbook();
//Load the source workbook
sourceBook.LoadFromFile(@"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\source.xlsx");
//Get the source worksheet
Worksheet sourceSheet = sourceBook.Worksheets[0];
//Get the source cell range
CellRange sourceRange = sourceSheet.Range["A1:E4"];
//Create another Workbook objecy
Workbook destBook = new Workbook();
//Load the destination workbook
destBook.LoadFromFile(@"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\destination.xlsx");
//Get the destination worksheet
Worksheet destSheet = destBook.Worksheets[0];
//Get the destination cell range
CellRange destRange = destSheet.Range["B2:F5"];
//Copy data from the source range to the destination range
sourceSheet.Copy(sourceRange, destRange);
//Loop through the columns in the source range
for (int i = 0; i < sourceRange.Columns.Length; i++)
{
//Copy the column widths also from the source range to destination range
destRange.Columns[i].ColumnWidth = sourceRange.Columns[i].ColumnWidth;
}
//Save the destination workbook to an Excel file
destBook.SaveToFile("CopyRange.xlsx");
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Xls
Namespace CopyCellRange
Class Program
Shared Sub Main(ByVal args() As String)
'Create a Workbook object
Dim sourceBook As Workbook = New Workbook()
'Load the source workbook
sourceBook.LoadFromFile("C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\source.xlsx")
'Get the source worksheet
Dim sourceSheet As Worksheet = sourceBook.Worksheets(0)
'Get the source cell range
Dim sourceRange As CellRange = sourceSheet.Range("A1:E4")
'Create another Workbook objecy
Dim destBook As Workbook = New Workbook()
'Load the destination workbook
destBook.LoadFromFile("C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\destination.xlsx")
'Get the destination worksheet
Dim destSheet As Worksheet = destBook.Worksheets(0)
'Get the destination cell range
Dim destRange As CellRange = destSheet.Range("B2:F5")
'Copy data from the source range to the destination range
sourceSheet.Copy(sourceRange, destRange)
'Loop through the columns in the source range
Dim i As Integer
For i = 0 To sourceRange.Columns.Length- 1 Step i + 1
'Copy the column widths also from the source range to destination range
destRange.Columns(i).ColumnWidth = sourceRange.Columns(i).ColumnWidth
Next
'Save the destination workbook to an Excel file
destBook.SaveToFile("CopyRange.xlsx")
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
 Extracting tables from PDF files is a common requirement in data processing, reporting, and automation tasks. PDFs are widely used for sharing structured data, but extracting tables programmatically can be challenging due to their complex layout. Fortunately, with the right tools, this process becomes straightforward. In this guide, we’ll explore how to extract tables from PDF in C# using the Spire.PDF for .NET library, and export the results to TXT and CSV formats for easy reuse.
Extracting tables from PDF files is a common requirement in data processing, reporting, and automation tasks. PDFs are widely used for sharing structured data, but extracting tables programmatically can be challenging due to their complex layout. Fortunately, with the right tools, this process becomes straightforward. In this guide, we’ll explore how to extract tables from PDF in C# using the Spire.PDF for .NET library, and export the results to TXT and CSV formats for easy reuse.
Table of Contents:
- Prerequisites for Reading PDF Tables in C#
- Understanding PDF Table Structure
- How to Extract Tables from PDF in C#
- Extract PDF Tables to a Text File in C#
- Export PDF Tables to CSV in C#
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Prerequisites for Reading PDF Tables in C#
Spire.PDF for .NET is a powerful library for processing PDF files in C# and VB.NET. It supports a wide range of PDF operations, including table extraction, text extraction, image extraction, and more.
The easiest way to add the Spire.PDF library is via NuGet Package Manager.
1. Open Visual Studio and create a new C# project. (Here we create a Console App)
2. In Visual Studio, right-click your project > Manage NuGet Packages.
3. Search for “Spire.PDF” and install the latest version.
Understanding PDF Table Structure
Before coding, let’s clarify how PDFs store tables. Unlike Excel (which explicitly defines rows/columns), PDFs use:
- Text Blocks: Individual text elements positioned with coordinates.
- Borders/Lines: Visual cues (horizontal/vertical lines) that humans interpret as table edges.
- Spacing: Consistent gaps between text blocks to indicate cells.
The Spire.PDF library infers table structure by analyzing these visual cues, matching text blocks to rows/columns based on proximity and alignment.
How to Extract Tables from PDF in C#
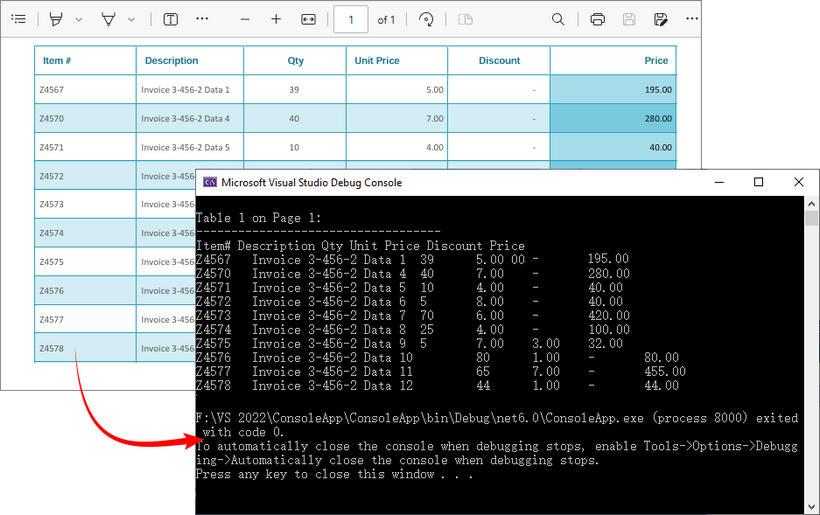
If you need a quick way to preview table data (e.g., debugging or verifying extraction), printing it to the console is a great starting point.
Key methods to extract data from a PDF table:
- PdfDocument: Represents a PDF file.
- LoadFromFile: Loads the PDF file for processing.
- PdfTableExtractor: Analyzes the PDF to detect tables using visual cues (borders, spacing).
- ExtractTable(pageIndex): Returns an array of PdfTable objects for the specified page.
- GetRowCount()/GetColumnCount(): Retrieve the dimensions of each table.
- GetText(rowIndex, columnIndex): Extracts text from the cell at the specified row and column.
using Spire.Pdf;
using Spire.Pdf.Utilities;
namespace ExtractPdfTable
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a PdfDocument object
PdfDocument pdf = new PdfDocument();
// Load a PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("invoice.pdf");
// Initialize an instance of PdfTableExtractor class
PdfTableExtractor extractor = new PdfTableExtractor(pdf);
// Loop through the pages
for (int pageIndex = 0; pageIndex < pdf.Pages.Count; pageIndex++)
{
// Extract tables from a specific page
PdfTable[] tableList = extractor.ExtractTable(pageIndex);
// Determine if the table list is null
if (tableList != null && tableList.Length > 0)
{
int tableNumber = 1;
// Loop through the table in the list
foreach (PdfTable table in tableList)
{
Console.WriteLine($"\nTable {tableNumber} on Page {pageIndex + 1}:");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------------------------");
// Get row number and column number of a certain table
int row = table.GetRowCount();
int column = table.GetColumnCount();
// Loop through rows and columns
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < column; j++)
{
// Get text from the specific cell
string text = table.GetText(i, j);
// Print cell text to console with a separator
Console.Write($"{text}\t");
}
// New line after each row
Console.WriteLine();
}
tableNumber++;
}
}
}
// Close the document
pdf.Close();
}
}
}
When to Use This Method
- Quick debugging or validation of extracted data.
- Small datasets where you don’t need persistent storage.
Output: Retrieve PDF table data and output to the console
Extract PDF Tables to a Text File in C#
For lightweight, human-readable storage, saving tables to a text file is ideal. This method uses StringBuilder to efficiently compile table data, preserving row breaks for readability.
Key features of extracting PDF tables and exporting to TXT:
- Efficiency: StringBuilder minimizes memory overhead compared to string concatenation.
- Persistent Storage: Saves data to a text file for later review or sharing.
- Row Preservation: Uses \r\n to maintain row structure, making the text file easy to scan.
using Spire.Pdf;
using Spire.Pdf.Utilities;
using System.Text;
namespace ExtractTableToTxt
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a PdfDocument object
PdfDocument pdf = new PdfDocument();
// Load a PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("invoice.pdf");
// Create a StringBuilder object
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
// Initialize an instance of PdfTableExtractor class
PdfTableExtractor extractor = new PdfTableExtractor(pdf);
// Declare a PdfTable array
PdfTable[] tableList = null;
// Loop through the pages
for (int pageIndex = 0; pageIndex < pdf.Pages.Count; pageIndex++)
{
// Extract tables from a specific page
tableList = extractor.ExtractTable(pageIndex);
// Determine if the table list is null
if (tableList != null && tableList.Length > 0)
{
// Loop through the table in the list
foreach (PdfTable table in tableList)
{
// Get row number and column number of a certain table
int row = table.GetRowCount();
int column = table.GetColumnCount();
// Loop through the rows and columns
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < column; j++)
{
// Get text from the specific cell
string text = table.GetText(i, j);
// Add text to the string builder
builder.Append(text + " ");
}
builder.Append("\r\n");
}
}
}
}
// Write to a .txt file
File.WriteAllText("ExtractPDFTable.txt", builder.ToString());
}
}
}
When to Use This Method
- Archiving table data in a lightweight, universally accessible format.
- Sharing with teams that need to scan data without spreadsheet tools.
- Using as input for basic scripts (e.g., PowerShell) to extract specific values.
Output: Extract PDF table data and save to a text file.

Pro Tip: For VB.NET demos, convert the above code using our C# ⇆ VB.NET Converter.
Export PDF Tables to CSV in C#
CSV (Comma-Separated Values) is the industry standard for tabular data, compatible with Excel, Google Sheets, and databases. This method formats the extracted tables into a valid CSV file by quoting cells and handling special characters.
Key features of extracting tables from PDF to CSV:
- StreamWriter: Writes data incrementally to the CSV file, reducing memory usage for large PDFs.
- Quoted Cells: Cells are wrapped in double quotes (" ") to avoid misinterpreting commas within text as column separators.
- UTF-8 Encoding: Supports special characters in cell text.
- Spreadsheet Ready: Directly opens in Excel, Google Sheets, or spreadsheet tools for analysis.
using Spire.Pdf;
using Spire.Pdf.Utilities;
using System.Text;
namespace ExtractTableToCsv
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a PdfDocument object
PdfDocument pdf = new PdfDocument();
// Load a PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("invoice.pdf");
// Create a StreamWriter object for efficient CSV writing
using (StreamWriter csvWriter = new StreamWriter("PDFtable.csv", false, Encoding.UTF8))
{
// Create a PdfTableExtractor object
PdfTableExtractor extractor = new PdfTableExtractor(pdf);
// Loop through the pages
for (int pageIndex = 0; pageIndex < pdf.Pages.Count; pageIndex++)
{
// Extract tables from a specific page
PdfTable[] tableList = extractor.ExtractTable(pageIndex);
// Determine if the table list is null
if (tableList != null && tableList.Length > 0)
{
// Loop through the table in the list
foreach (PdfTable table in tableList)
{
// Get row number and column number of a certain table
int row = table.GetRowCount();
int column = table.GetColumnCount();
// Loop through the rows
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
// Creates a list to store data
List<string> rowData = new List<string>();
// Loop through the columns
for (int j = 0; j < column; j++)
{
// Retrieve text from table cells
string cellText = table.GetText(i, j).Replace("\"", "\"\"");
// Add the cell text to the list and wrap in double quotes
rowData.Add($"\"{cellText}\"");
}
// Join cells with commas and write to CSV
csvWriter.WriteLine(string.Join(",", rowData));
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
When to Use This Method
- Data analysis (import into Excel for calculations).
- Migrating PDF tables to databases (e.g., SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MySQL).
- Collaborating with teams that rely on spreadsheets.
Output: Parse PDF table data and export to a CSV file.
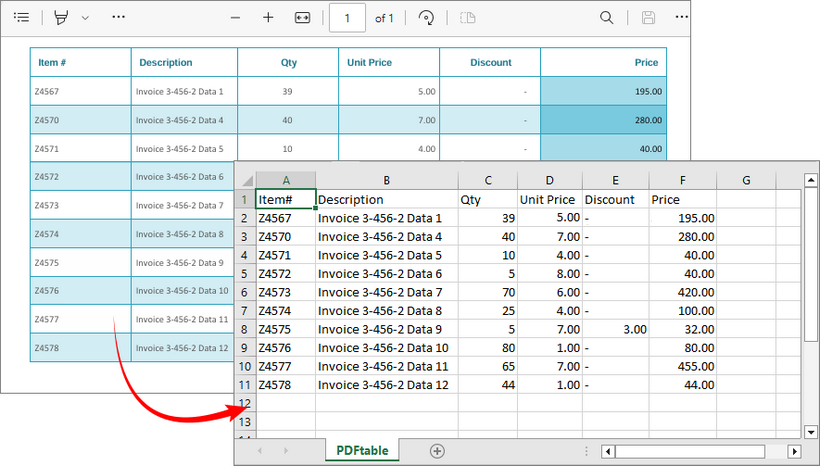
Recommendation: Integrate with Spire.XLS for .NET to extract tables from PDF to Excel directly.
Conclusion
This guide has outlined three efficient methods for extracting tables from PDFs in C#. By leveraging the Spire.PDF for .NET library, you can automate the PDF table extraction process and export results to console, TXT, or CSV for further analysis. Whether you’re building a data pipeline, report generator, or business tool, these approaches streamline workflows, save time, and minimize human error.
Refer to the online documentation and obtain a free trial license here to explore more advanced PDF operations.
FAQs
Q1: Why use Spire.PDF for .NET to extract tables?
A: Spire.PDF provides a dedicated PdfTableExtractor class that detects tables based on visual cues (borders, spacing, and text alignment), simplifying the process of parsing structured data from PDFs.
Q2: Can Spire.PDF extract tables from scanned (image-based) PDFs?
A: No. The .NET PDF library works only with text-based PDFs (where text is selectable). For scanned PDFs, use Spire.OCR to extract text before parsing tables.
Q3: Can I extract tables from multiple PDFs at once?
A: Yes. To batch-process multiple PDFs, use Directory.GetFiles() to list all PDF files in a folder, then loop through each file and run the extraction logic. For example:
string[] pdfFiles = Directory.GetFiles(@"C:\Invoices\", "*.pdf");
foreach (string file in pdfFiles)
{
// Run extraction code for each file
}
Q4: How can I improve performance when extracting tables from large PDFs?
A: For large PDFs (100+ pages), optimize performance by:
- Processing pages in batches instead of loading the entire PDF at once.
- Disposing of unused PdfTable or PdfDocument objects with the using statements to free memory.
- Skipping pages with no tables early (
using if (tableList == null || tableList.Length == 0)).
Sometimes you may want to print Word documents in accordance with your own preferences, for instance, print your files on custom paper sizes to make them more personalized. In this article, you will learn how to achieve this function using Spire.Doc for .NET.
Install Spire.Doc for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Doc for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLLs files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
- Package Manager
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
Print Word on a Custom Paper Size
The table below shows a list of core classes, methods and properties utilized in this scenario.
| Name | Description |
| Document Class | Represents a document model for Word. |
| PaperSize Class | Specifies the size of a piece of paper. |
| PrintDocument Class | Defines a reusable object that sends output to a printer, when printing from a Windows Forms application. |
| PrintDocument.DefaultPageSettings Property | Gets or sets page settings that are used as defaults for all pages to be printed. |
| Document.PrintDocument Property | Gets the PrintDocument object. |
| DefaultPageSettings.PaperSize Property | Sets the custom paper size. |
| Document.LoadFromFile() Method | Loads the sample document. |
| PrintDocument.Print() Method | Prints the document. |
The following are the steps to print Word on a custom paper size.
- Instantiate a Document object
- Load the sample document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the PrintDocument object using Document.PrintDocument property.
- Set the custom paper size using DefaultPageSettings.PaperSize Property.
- Print the document using PrintDocument.Print() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Doc;
using System.Drawing.Printing;
namespace PrintWord
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Instantiate a Document object.
Document doc = new Document();
//Load the document
doc.LoadFromFile(@"Sample.docx");
//Get the PrintDocument object
PrintDocument printDoc = doc.PrintDocument;
//Customize the paper size
printDoc.DefaultPageSettings.PaperSize = new PaperSize("custom", 900, 800);
//Print the document
printDoc.Print();
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Doc
Imports System.Drawing.Printing
Namespace PrintWord
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
'Instantiate a Document object.
Dim doc As New Document()
'Load the document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
'Get the PrintDocument object
Dim printDoc As PrintDocument = doc.PrintDocument
'Customize the paper size
printDoc.DefaultPageSettings.PaperSize = New PaperSize("custom", 900, 800)
'Print the document
printDoc.Print()
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
LaTeX is a powerful tool to typeset mathematical equations. It supports plenty of mathematical symbols and notations to create mathematical equations, for instance, fractions, integrals and more.
Spire.Presentation API provides developers with the ability to create and add mathematical equations to PowerPoint shape using LaTeX code. The following steps demonstrate how to achieve this function using Spire.Presentation:
- Create a Presentation instance.
- Get the reference of a slide by using its index.
- Use ShapeList.AppendShape method to add a shape to the first slide.
- Use ParagraphCollection.AddParagraphFromLatexMathCode(string) method to create a mathematical equation from LaTeX code and add it to the shape.
- Save the result document using Presentation.SaveToFile(string, FileFormat) method.
The following code shows how to add mathematical equations to PowerPoint in C#.
using Spire.Presentation;
using System.Drawing;
namespace MathEquations
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//The LaTeX codes
string latexCode1 = @"x^{2} + \sqrt{x^{2}+1}=2";
string latexCode2 = @"F(x) &= \int^a_b \frac{1}{3}x^3";
string latexCode3 = @"\alpha + \beta \geq \gamma";
string latexCode4 = @"\overrightarrow{abc}";
string latexCode5 = @"\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & \cdots & 0\\ 1 & 0 & \cdots & 0\\ \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots\\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix}";
string latexCode6 = @"\log_a{b}";
//Create a Presentation instance
Presentation ppt = new Presentation();
//Get the first slide by using its index
ISlide slide = ppt.Slides[0];
//Add a shape to the slide
IAutoShape shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, new RectangleF(30, 100, 200, 30));
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Clear();
//Add a math equation to the shape using the LaTeX code
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.AddParagraphFromLatexMathCode(latexCode1);
//Add a shape to the slide
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, new RectangleF(240, 100, 200, 40));
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Clear();
//Add a math equation to the shape using the LaTeX code
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.AddParagraphFromLatexMathCode(latexCode2);
//Add a shape to the slide
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, new RectangleF(30, 180, 200, 40));
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Clear();
//Add a math equation to the shape using the LaTeX code
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.AddParagraphFromLatexMathCode(latexCode3);
//Add a shape to the slide
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, new RectangleF(240, 180, 200, 40));
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Clear();
//Add a math equation to the shape using the LaTeX code
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.AddParagraphFromLatexMathCode(latexCode4);
//Add a shape to the slide
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, new RectangleF(30, 280, 200, 70));
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Clear();
//Add a math equation to the shape using the LaTeX code
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.AddParagraphFromLatexMathCode(latexCode5);
//Add a shape to the slide
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, new RectangleF(240, 280, 200, 40));
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Clear();
//Add a math equation to the shape using the LaTeX code
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.AddParagraphFromLatexMathCode(latexCode6);
for (int i = 0; i < slide.Shapes.Count; i++)
{
slide.Shapes[i].Fill.FillType = Spire.Presentation.Drawing.FillFormatType.None;
slide.Shapes[i].Line.FillType = Spire.Presentation.Drawing.FillFormatType.None;
}
//Save the result document
ppt.SaveToFile("MathEquations.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013);
}
}
}
The following code shows how to add mathematical equations to PowerPoint in VB.NET.
Imports Spire.Presentation
Imports System.Drawing
Namespace MathEquations
Friend Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(ByVal args As String())
'The LaTeX codes
Dim latexCode1 As String = "x^{2} + \sqrt{x^{2}+1}=2"
Dim latexCode2 As String = "F(x) &= \int^a_b \frac{1}{3}x^3"
Dim latexCode3 As String = "\alpha + \beta \geq \gamma"
Dim latexCode4 As String = "\overrightarrow{abc}"
Dim latexCode5 As String = "\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & \cdots & 0\\ 1 & 0 & \cdots & 0\\ \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots\\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix}"
Dim latexCode6 As String = "\log_a{b}"
'Create a Presentation instance
Dim ppt As Presentation = New Presentation()
'Get the first slide by using its index
Dim slide As ISlide = ppt.Slides(0)
'Add a shape to the slide
Dim shape As IAutoShape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, New RectangleF(30, 100, 200, 30))
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Clear()
'Add a math equation to the shape using the LaTeX code
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.AddParagraphFromLatexMathCode(latexCode1)
'Add a shape to the slide
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, New RectangleF(240, 100, 200, 40))
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Clear()
'Add a math equation to the shape using the LaTeX code
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.AddParagraphFromLatexMathCode(latexCode2)
'Add a shape to the slide
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, New RectangleF(30, 180, 200, 40))
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Clear()
'Add a math equation to the shape using the LaTeX code
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.AddParagraphFromLatexMathCode(latexCode3)
'Add a shape to the slide
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, New RectangleF(240, 180, 200, 40))
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Clear()
'Add a math equation to the shape using the LaTeX code
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.AddParagraphFromLatexMathCode(latexCode4)
'Add a shape to the slide
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, New RectangleF(30, 280, 200, 70))
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Clear()
'Add a math equation to the shape using the LaTeX code
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.AddParagraphFromLatexMathCode(latexCode5)
'Add a shape to the slide
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, New RectangleF(240, 280, 200, 40))
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Clear()
'Add a math equation to the shape using the LaTeX code
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.AddParagraphFromLatexMathCode(latexCode6)
For i As Integer = 0 To slide.Shapes.Count - 1
slide.Shapes(i).Fill.FillType = Spire.Presentation.Drawing.FillFormatType.None
slide.Shapes(i).Line.FillType = Spire.Presentation.Drawing.FillFormatType.None
Next
'Save the result document
ppt.SaveToFile("MathEquations.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
The following is the output document after adding mathematical equations:
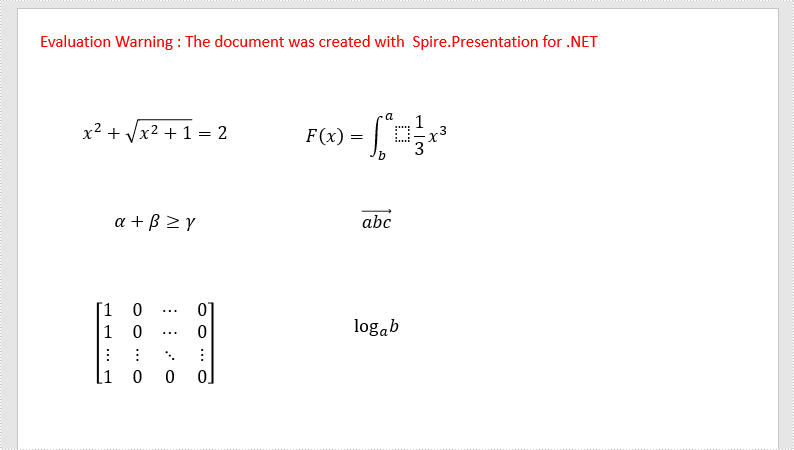
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Replace Text with Regular Expression (Regex) in PowerPoint in C#, VB.NET
2021-08-23 07:49:36 Written by KoohjiSpire.Presentation for .NET provides you with the ability to replace text with regular expression using the ReplaceTextWithRegex method of IShape class. The ReplaceTextWithRegex method accepts the following parameters:
Regex: the regular expression to search text.
string: the text to replace with.
The following example demonstrates how to replace text with regular expression in a PowerPoint document using Spire.Presentation for .NET.
using Spire.Presentation;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
namespace ReplaceTextWithRegex
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Presentation instance
Presentation ppt = new Presentation();
//Load a sample document
ppt.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx");
//Get the first slide
ISlide slide = ppt.Slides[0];
//Replace "ABC" and the subsequent to the end of the line as "ABC DEF"
Regex regex = new Regex("ABC.*");
string newvalue = "ABC DEF";
foreach (IShape shape in slide.Shapes)
{
shape.ReplaceTextWithRegex(regex, newvalue);
}
//Save the result document
ppt.SaveToFile("ReplaceTextWithRegex.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013);
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Presentation
Imports System.Text.RegularExpressions
Namespace ReplaceTextWithRegex
Friend Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(ByVal args As String())
'Create a Presentation instance
Dim ppt As Presentation = New Presentation()
'Load the sample document
ppt.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
'Get the first slide
Dim slide As ISlide = ppt.Slides(0)
'Replace "ABC" and the subsequent to the end of the line as "ABC DEF"
Dim regex As Regex = New Regex("ABC.*")
Dim newvalue As String = "ABC DEF"
For Each shape As IShape In slide.Shapes
shape.ReplaceTextWithRegex(regex, newvalue)
Next
'Save the result document
ppt.SaveToFile("ReplaceTextWithRegex.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
The input PowerPoint document:

The output PowerPoint document:

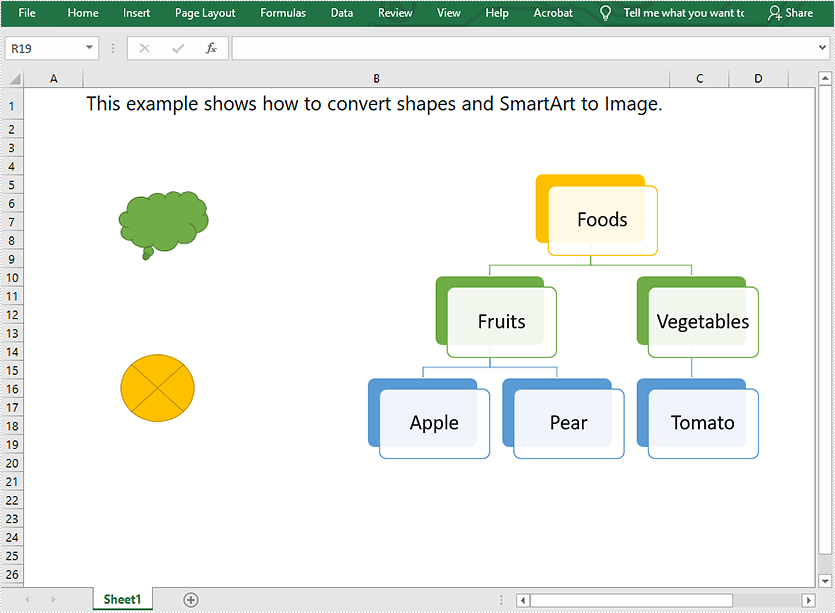
This article demonstrates how to convert shapes and SmartArt graphics in Excel to Image in C# using Spire.XLS for .NET.
The input Excel file:
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Drawing.Imaging;
namespace Convert_Shapes_and_SmartArt_to_Image
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load the Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Create a SaveShapeTypeOption object
SaveShapeTypeOption shapelist = new SaveShapeTypeOption();
//Save shapes and SmartArt graphics in the worksheet to images
List images = sheet.SaveShapesToImage(shapelist);
//Save images to file
int index = 0;
foreach (Image img in images)
{
img.Save("Image/" + "toImage" + index + ".Png", ImageFormat.Png);
index++;
}
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Xls
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports System.Drawing.Imaging
Namespace Convert_Shapes_and_SmartArt_to_Image
Friend Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(ByVal args As String())
'Create a Workbook object
Dim workbook As Workbook = New Workbook()
'Load the Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
'Get the first worksheet
Dim sheet As Worksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Create a SaveShapeTypeOption object
Dim shapelist As SaveShapeTypeOption = New SaveShapeTypeOption()
'Save shapes and SmartArt graphics in the worksheet to images
Dim images As List(Of Bitmap) = sheet.SaveShapesToImage(shapelist)
'Save images to file
Dim index As Integer = 0
For Each img As Image In images
img.Save("Image/" & "toImage" & index & ".Png", ImageFormat.Png)
index += 1
Next
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
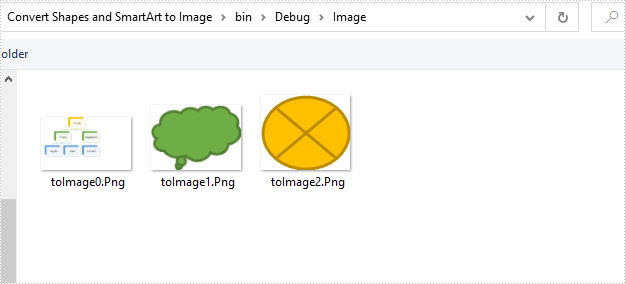
Converted images:
This article will demonstrate how to repeat the table’s header row in C#/VB.NET by using Spire.PDF for .NET.
using Spire.Pdf;
using Spire.Pdf.Graphics;
using Spire.Pdf.Grid;
using System.Drawing;
namespace PDFGrid
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a pdf document
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
//Add a page to pdf
PdfPageBase page = doc.Pages.Add();
//Create a PdfGrid object
PdfGrid grid = new PdfGrid();
//Set the cell padding of the grid
grid.Style.CellPadding = new PdfPaddings(1, 1, 1, 1);
//Set the Columns of the grid
grid.Columns.Add(3);
//Set the header rows and define the data
PdfGridRow[] pdfGridRows = grid.Headers.Add(2);
for (int i = 0; i < pdfGridRows.Length; i++)
{
pdfGridRows[i].Style.Font = new PdfTrueTypeFont(new Font("Arial", 11f, FontStyle.Regular), true);
pdfGridRows[i].Cells[0].Value = "Vendor Name";
pdfGridRows[i].Cells[1].Value = "Address";
pdfGridRows[i].Cells[2].Value = "City";
}
//Repeat the table header rows if the grid exceed one page
grid.RepeatHeader = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 60; i++)
{
PdfGridRow row = grid.Rows.Add();
//Add the data to the table
for (int j = 0; j < grid.Columns.Count; j++)
{
row.Cells[j].Value = "(Row " + i + ", column " + j + ")";
}
}
//draw grid on the pdf page
PdfLayoutResult pdfLayoutResult = grid.Draw(page, new PointF(0, 20));
float y = pdfLayoutResult.Bounds.Y + pdfLayoutResult.Bounds.Height;
PdfPageBase currentPage = pdfLayoutResult.Page;
//Save the doucment to file
doc.SaveToFile("PDFGrid.pdf");
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Pdf
Imports Spire.Pdf.Graphics
Imports Spire.Pdf.Grid
Imports System.Drawing
Namespace PDFGrid
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(ByVal args() As String)
'Create a pdf document
Dim doc As PdfDocument = New PdfDocument
'Add a page to pdf
Dim page As PdfPageBase = doc.Pages.Add
'Create a PdfGrid object
Dim grid As PdfGrid = New PdfGrid
'Set the cell padding of the grid
grid.Style.CellPadding = New PdfPaddings(1, 1, 1, 1)
'Set the Columns of the grid
grid.Columns.Add(3)
'Set the header rows and define the data
Dim pdfGridRows() As PdfGridRow = grid.Headers.Add(2)
Dim i As Integer = 0
Do While (i < pdfGridRows.Length)
pdfGridRows(i).Style.Font = New PdfTrueTypeFont(New Font("Arial", 11!, FontStyle.Regular), true)
pdfGridRows(i).Cells(0).Value = "Vendor Name"
pdfGridRows(i).Cells(1).Value = "Address"
pdfGridRows(i).Cells(2).Value = "City"
i = (i + 1)
Loop
'Repeat the table header rows if the grid exceed one page
grid.RepeatHeader = true
Dim i As Integer = 0
Do While (i < 60)
Dim row As PdfGridRow = grid.Rows.Add
'Add the data to the table
Dim j As Integer = 0
Do While (j < grid.Columns.Count)
row.Cells(j).Value = ("(Row " _
+ (i + (", column " _
+ (j + ")"))))
j = (j + 1)
Loop
i = (i + 1)
Loop
'draw grid on the pdf page
Dim pdfLayoutResult As PdfLayoutResult = grid.Draw(page, New PointF(0, 20))
Dim y As Single = (pdfLayoutResult.Bounds.Y + pdfLayoutResult.Bounds.Height)
Dim currentPage As PdfPageBase = pdfLayoutResult.Page
'Save the doucment to file
doc.SaveToFile("PDFGrid.pdf")
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
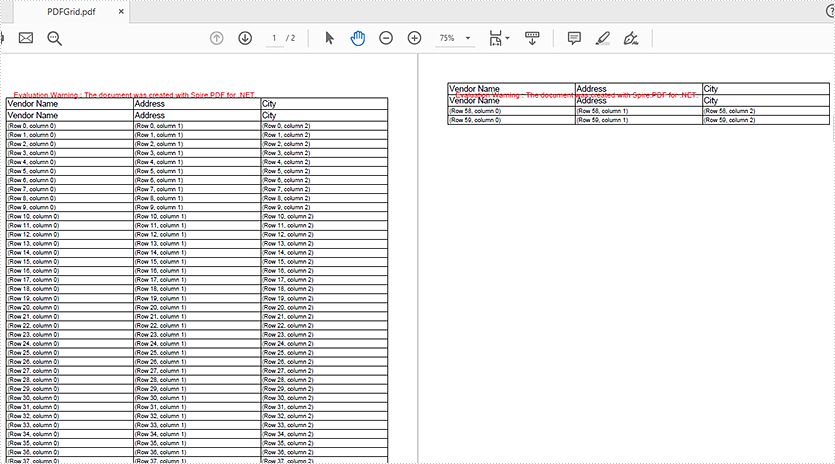
Effective screenshot of repeating the table's header row:
In the earlier tutorial, we have given a brief introduction on how to insert Textbox in Word and this article will demonstrate how to position the text vertically in a text box using Spire.Doc for .NET.
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
using System;
namespace WordTextbox
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Instantiate document object
Document document = new Document();
//Add a section
Section section = document.AddSection();
//Set the margin
section.PageSetup.Margins.Left = 90;
section.PageSetup.Margins.Right = 90;
Paragraph paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
//Add texbox 1
TextBox textBox1 = paragraph.AppendTextBox(section.PageSetup.Margins.Left - 20, section.PageSetup.PageSize.Height + 20);
//Fix the position of textbox
textBox1.Format.HorizontalOrigin = HorizontalOrigin.Page;
textBox1.Format.HorizontalPosition = 0;
textBox1.Format.VerticalPosition = -10f;
textBox1.Format.VerticalOrigin = VerticalOrigin.Page;
//Set the text vertically
textBox1.Format.TextAnchor = ShapeVerticalAlignment.Center;
textBox1.Format.LayoutFlowAlt = TextDirection.LeftToRight;
//Add text and set the font
Paragraph textboxPara1 = textBox1.Body.AddParagraph();
TextRange txtrg = textboxPara1.AppendText("Name_______Number_________Class__________");
txtrg.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial";
txtrg.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 10;
txtrg.CharacterFormat.TextColor = System.Drawing.Color.Black;
textboxPara1.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center;
//Save the document
document.SaveToFile("Result.docx");
}
}
}
Namespace WordTextbox
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(ByVal args() As String)
Dim document As Document = New Document
Dim section As Section = document.AddSection
section.PageSetup.Margins.Left = 90
section.PageSetup.Margins.Right = 90
Dim paragraph As Paragraph = section.AddParagraph
Dim textBox1 As TextBox = paragraph.AppendTextBox((section.PageSetup.Margins.Left - 20), (section.PageSetup.PageSize.Height + 20))
textBox1.Format.HorizontalOrigin = HorizontalOrigin.Page
textBox1.Format.HorizontalPosition = 0
textBox1.Format.VerticalPosition = -10!
textBox1.Format.VerticalOrigin = VerticalOrigin.Page
textBox1.Format.TextAnchor = ShapeVerticalAlignment.Center
textBox1.Format.LayoutFlowAlt = TextDirection.LeftToRight
Dim textboxPara1 As Paragraph = textBox1.Body.AddParagraph
Dim txtrg As TextRange = textboxPara1.AppendText("Name_______Number_________Class__________")
txtrg.CharacterFormat.FontName= "Arial"
txtrg.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 10
txtrg.CharacterFormat.TextColor = System.Drawing.Color.Black
textboxPara1.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
document.SaveToFile("Result.docx")
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
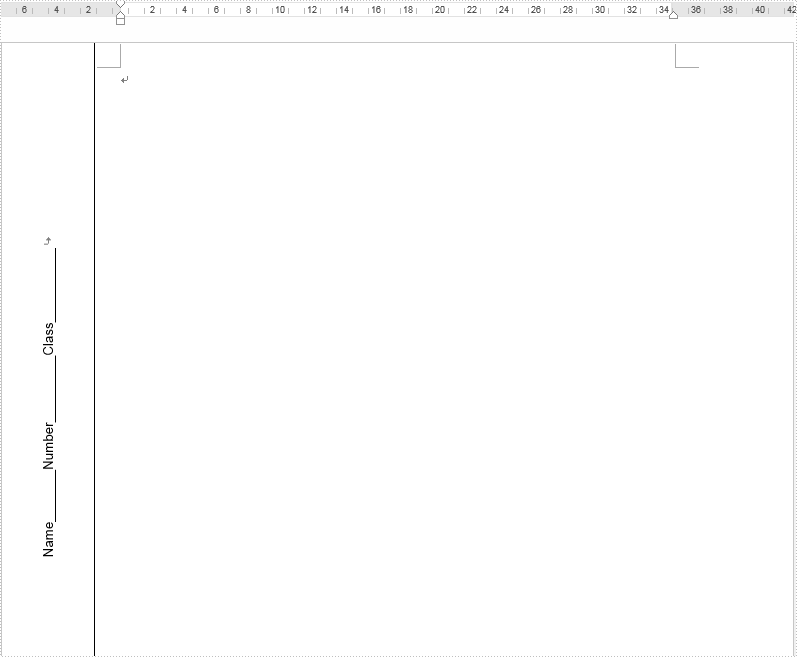
Output
This article demonstrates the steps to use Spire.OCR for .NET in .NET Core applications.
Step 1: Create a .NET Core project in Visual Studio.
Step 2: Add reference to Spire.OCR for .NET DLLs in your project.
You can add reference to Spire.OCR for .NET DLLs through one of the following two ways:
1. Install Spire.OCR for .NET through NuGet using NuGet Package Manager (recommended):
- In Solution Explorer, right-click the project or "Dependencies" and select "Manage NuGet Packages".
- Click "Browse" tab and search Spire.OCR.
- Install Spire.OCR.
2. Manually add reference to Spire.OCR for .NET DLLs.
- Download Spire.OCR for .NET package from the following link, unzip it, you will get the DLLs from the "netstandard2.0" folder.
- Right-click the project or "Dependencies" – select "Add Reference" – click "Browse" – select all DLLs under "netstandard2.0" folder – click "Add".
- Install the other two packages: SkiaSharp and System.Text.Encoding.CodePages in your project via the NuGet Package Manager.
Right-click the project or "Dependencies" – select "Manage NuGet Packages" – click "Browse" – type the package name – select the package from the search results – click "Install".
Step 3: Copy dependency DLLs to running directory of your project.
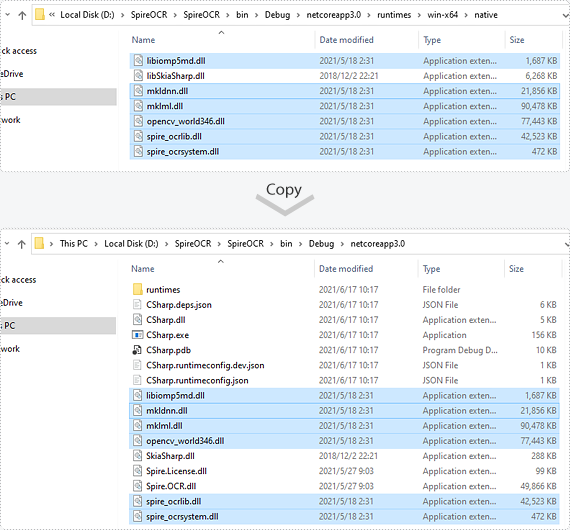
If you install Spire.OCR from NuGet and your project's target framework is .NET Core 3.0 or above, please build the project, then copy the 6 DLLs from bin\Debug\netcoreapp3.0\runtimes\win-x64\native folder to the running directory such as bin\Debug\netcoreapp3.0 or C:\Windows\System32 .
If your project's target framework is below .NET Core 3.0 or you download Spire.OCR from our website, please copy the 6 DLLs from Spire.OCR\Spire.OCR_Dependency\x64 folder to the running directory such as bin\Debug\netcoreapp2.1 or C:\Windows\System32.
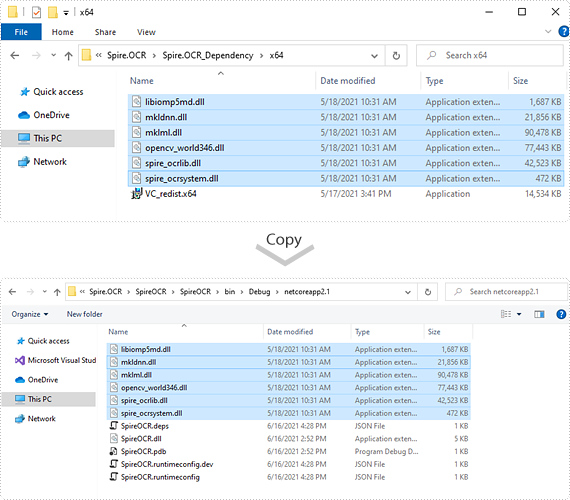
Step 4: Now you have successfully included Spire.OCR in your project. You can refer the following code example to scan images using Spire.OCR.
- C#
using Spire.OCR;
using System.IO;
namespace SpireOCR
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
OcrScanner scanner = new OcrScanner();
scanner.Scan("image.png");
File.WriteAllText("output.txt", scanner.Text.ToString());
}
}
}
It is possible to perform Word to PDF conversion in Azure apps such as Azure Web apps and Azure Functions apps using Spire.Doc for .NET. In this article, you can see the code example to achieve this function with Spire.Doc for .NET.
The input Word document:
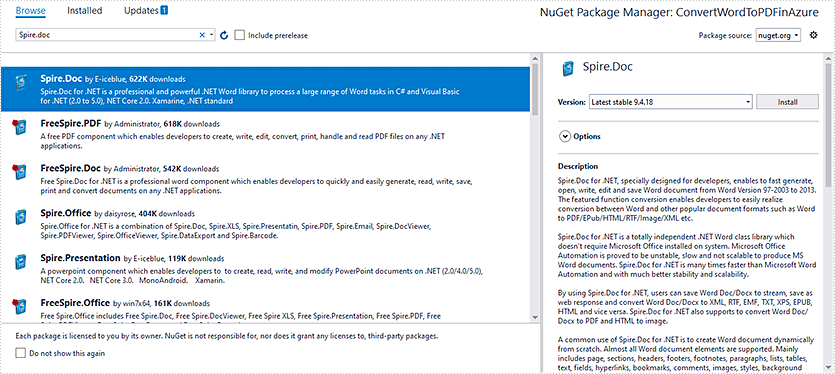
Step 1: Install Spire.Doc NuGet Package as a reference to your project from NuGet.org.
Step 2: Add the following code to convert Word to PDF.
//Create a Document instance Document document = new Document(false);
//Load the Word document
document.LoadFromFile(@"sample.docx");
//Create a ToPdfParameterList instance
ToPdfParameterList ps = new ToPdfParameterList
{
UsePSCoversion = true
};
//Save Word document to PDF using PS conversion
document.SaveToFile("ToPdf.pdf", ps);
Private Sub SurroundingSub()
Dim document As Document = New Document(false)
document.LoadFromFile("sample.docx")
Dim ps As ToPdfParameterList = New ToPdfParameterList With {
.UsePSCoversion = True
}
document.SaveToFile("ToPdf.pdf", ps)
End Sub
The Output PDF document: