.NET (1316)
Children categories
C#: Check Whether a PDF is Password Protected and Determine the Correct Password
2025-04-03 03:47:00 Written by KoohjiPassword protection is a widely used security feature in PDFs to restrict access and prevent unauthorized modifications. Before working with a PDF, it is essential to determine whether it is password-protected. If protection is enabled, verifying the correct password allows you to unlock the document, ensuring smooth access for viewing, editing, or extracting its contents.
In this article, we will guide you through the process of checking whether a PDF is password-protected and how to verify the correct password using C# and the Spire.PDF for .NET library.
Install Spire.PDF for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.PDF for.NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLLs files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.PDF
Check Whether a PDF is Password Protected in C#
Spire.PDF for .NET provides the PdfDocument.IsPasswordProtected(string fileName) method to determine whether a PDF file is password-protected. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Specify the input and output file paths.
- Use the PdfDocument.IsPasswordProtected(string fileName) method to check whether the PDF is password protected.
- Save the verification result to a text file.
- C#
using Spire.Pdf;
using System.IO;
namespace CheckIfPdfIsProtected
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Specify the input and output file paths
string pdfPath = "sample.pdf";
string resultFilePath = "verification_results.txt";
// Check whether the PDF file is password-protected
bool isProtected = PdfDocument.IsPasswordProtected(pdfPath);
// Create a StreamWriter to write the result to a text file
using (StreamWriter writer = new StreamWriter(resultFilePath))
{
// Write the verification result to the text file
string resultMessage = isProtected ? "The PDF is password-protected." : "The PDF is not password-protected.";
writer.WriteLine(resultMessage);
}
}
}
}

Determine the Correct Password of a PDF in C#
Spire.PDF for .NET does not have a direct method to verify if a password is correct, but this can be done by attempting to open the file with the given password. If the password is incorrect, an exception will be thrown. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Specify the input and output file paths.
- Check whether the PDF file is password-protected using the PdfDocument.IsPasswordProtected(string fileName) method.
- Create an array of potential passwords to test.
- Iterate through the array, and load the PDF with each password using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile(string filename, string password) method.
- If no exception is thrown, the password is correct. Otherwise, the password is incorrect.
- Save the verification result to a text file.
- C#
using Spire.Pdf;
using System;
using System.IO;
namespace DetermineTheCorrectPasswordOfPdf
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Specify the input and output file paths
string pdfPath = "sample.pdf";
string resultFilePath = "verification_results.txt";
// Check whether the PDF file is password-protected
bool isProtected = PdfDocument.IsPasswordProtected(pdfPath);
// Create an array of potential passwords to test
string[] passwords = new string[5] { "password1", "password2", "password3", "admin123", "test" };
// Create a StreamWriter to write results to a text file
using (StreamWriter writer = new StreamWriter(resultFilePath))
{
// If the PDF is protected, start testing passwords
if (isProtected)
{
// Iterate through each password in the array
for (int passwordcount = 0; passwordcount < passwords.Length; passwordcount++)
{
try
{
// Create a new PdfDocument object and try loading the document with the current password
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
doc.LoadFromFile(pdfPath, passwords[passwordcount]);
// If successful, write that the password is correct to the text file
writer.WriteLine("Password " + passwords[passwordcount] + " is correct");
}
catch
{
// If an exception occurs, write that the password is not correct to the text file
writer.WriteLine("Password " + passwords[passwordcount] + " is not correct");
}
}
}
else
{
// If the PDF is not password protected, note this in the text file
writer.WriteLine("The PDF is not password protected.");
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Verification results have been saved to: " + resultFilePath);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}

Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.PDF for .NET without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
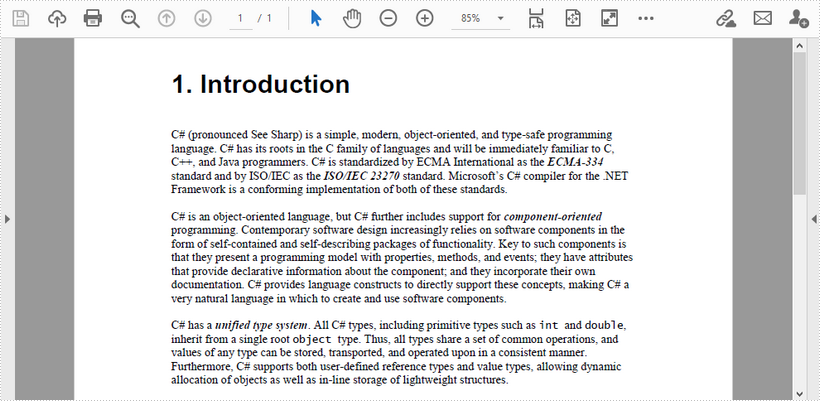
This article demonstrates how to add line numbers before chunks of text in a PDF page by using Spire.PDF for .NET.
Below is a screenshot of the input document.
using Spire.Pdf;
using Spire.Pdf.General.Find;
using Spire.Pdf.Graphics;
using System.Drawing;
namespace AddLineNumber
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a PdfDocument object
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
//Load PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile(@"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\input.pdf");
//Get the first page
PdfPageBase page = doc.Pages[0];
//Find specified text in the first line
PdfTextFinder finder = new PdfTextFinder(page);
finder.Options.Parameter = Spire.Pdf.Texts.TextFindParameter.WholeWord;
PdfTextFragment topLine = finder.Find("C# (pronounced See Sharp)")[0];
//Get line height
float lineHeight = topLine.Bounds[0].Height;
//Get a Y coordinate for the starting position of line numbers
float y = topLine.Bounds[0].Location.Y - 2;
//Find specified text in the second line
PdfTextFinder secondfinder = new PdfTextFinder(page);
secondfinder.Options.Parameter = Spire.Pdf.Texts.TextFindParameter.WholeWord;
PdfTextFragment secondLine = secondfinder.Find("language. C#")[0];
//Calculate line spacing
float lineSpacing = secondLine.Bounds[0].Top - topLine.Bounds[0].Bottom;
//Find specified text in the last line
PdfTextFinder bottomfinder = new PdfTextFinder(page);
bottomfinder.Options.Parameter = Spire.Pdf.Texts.TextFindParameter.WholeWord;
PdfTextFragment bottomLine = bottomfinder.Find("allocation of objects")[0];
//Get the bottom Y coordinate of the last line, which is the height of the line number area
float height = bottomLine.Bounds[0].Bottom;
//Create a font with the same size as the text in the PDF
PdfFont font = new PdfFont(PdfFontFamily.TimesRoman, 11f);
int i = 1;
while (y < height)
{
//Draw line numbers at the beginning of each line
page.Canvas.DrawString(i.ToString(), font, PdfBrushes.Black, new PointF(15, y));
y += lineHeight + lineSpacing;
i++;
}
//Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("result.pdf");
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Pdf
Imports Spire.Pdf.General.Find
Imports Spire.Pdf.Graphics
Imports System.Drawing
Namespace AddLineNumber
Class Program
Shared Sub Main(ByVal args() As String)
'Create a PdfDocument object
Dim doc As New PdfDocument()
'Load PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\input.pdf")
'Get the first page
Dim page As PdfPageBase = doc.Pages(0)
'Find specified text in the first line
Dim finder As New PdfTextFinder(page)
finder.Options.Parameter = Spire.Pdf.Texts.TextFindParameter.WholeWord
Dim topLine As PdfTextFragment = finder.Find("C# (pronounced See Sharp)")(0)
'Get line height
Dim lineHeight As Single = topLine.Bounds(0).Height
'Get a Y coordinate for the starting position of line numbers
Dim y As Single = topLine.Bounds(0).Location.Y - 2
'Find specified text in the second line
Dim secondfinder As New PdfTextFinder(page)
secondfinder.Options.Parameter = Spire.Pdf.Texts.TextFindParameter.WholeWord
Dim secondLine As PdfTextFragment = secondfinder.Find("language. C#")(0)
'Calculate line spacing
Dim lineSpacing As Single = secondLine.Bounds(0).Top - topLine.Bounds(0).Bottom
'Find specified text in the last line
Dim bottomfinder As New PdfTextFinder(page)
bottomfinder.Options.Parameter = Spire.Pdf.Texts.TextFindParameter.WholeWord
Dim bottomLine As PdfTextFragment = bottomfinder.Find("allocation of objects")(0)
'Get the bottom Y coordinate of the last line, which is the height of the line number area
Dim height As Single = bottomLine.Bounds(0).Bottom
'Create a font with the same size as the text in the PDF
Dim font As PdfFont = New PdfFont(PdfFontFamily.TimesRoman, 11.0F)
Dim i As Integer = 1
While y < height
'Draw line numbers at the beginning of each line
page.Canvas.DrawString(i.ToString(), font, PdfBrushes.Black, New PointF(15, y))
y += lineHeight + lineSpacing
i += 1
End While
'Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("result.pdf")
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
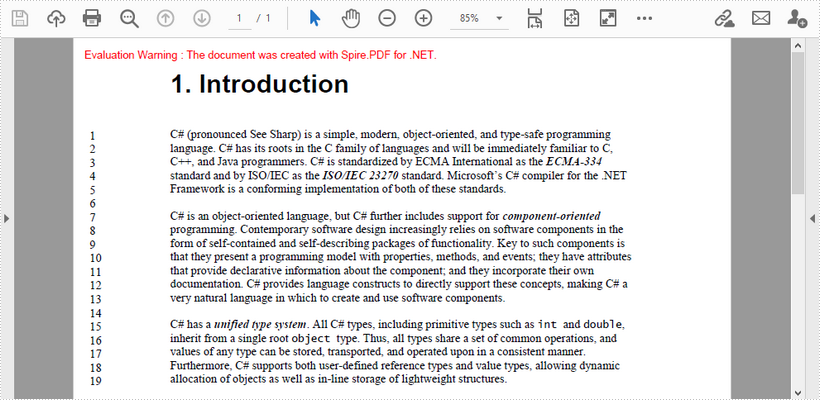
Output
Get the differences by comparing two Word documents in C#/VB.NET
2021-01-04 07:37:21 Written by AdministratorWe have introduced how to compare two Word documents in C# and VB.NET. From Spire.Doc V8.12.14, it supports to get the differences between two Word documents in a structure list. This article will show you how to use Spire.Doc to get the differences by comparing two Word documents.
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
using Spire.Doc.Formatting.Revisions;
using System;
namespace GetWordDifferences
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Load the first Word document
Document doc1 = new Document();
doc1.LoadFromFile("Sample1.docx");
//Load the second Word document
Document doc2 = new Document();
doc2.LoadFromFile("Sample2.docx");
//Compare the two Word documents
doc1.Compare(doc2, "Author");
foreach (Section sec in doc1.Sections)
{
foreach (DocumentObject docItem in sec.Body.ChildObjects)
{
if (docItem is Paragraph)
{
Paragraph para = docItem as Paragraph;
if (para.IsInsertRevision)
{
EditRevision insRevison = para.InsertRevision;
EditRevisionType insType = insRevison.Type;
string insAuthor = insRevison.Author;
DateTime insDateTime = insRevison.DateTime;
}
else if (para.IsDeleteRevision)
{
EditRevision delRevison = para.DeleteRevision;
EditRevisionType delType = delRevison.Type;
string delAuthor = delRevison.Author;
DateTime delDateTime = delRevison.DateTime;
}
foreach (ParagraphBase paraItem in para.ChildObjects)
{
if (paraItem.IsInsertRevision)
{
EditRevision insRevison = paraItem.InsertRevision;
EditRevisionType insType = insRevison.Type;
string insAuthor = insRevison.Author;
DateTime insDateTime = insRevison.DateTime;
}
else if (paraItem.IsDeleteRevision)
{
EditRevision delRevison = paraItem.DeleteRevision;
EditRevisionType delType = delRevison.Type;
string delAuthor = delRevison.Author;
DateTime delDateTime = delRevison.DateTime;
}
}
}
}
}
//Get the difference about revisions
DifferRevisions differRevisions = new DifferRevisions(doc1);
var insetRevisionsList = differRevisions.InsertRevisions;
var deletRevisionsList = differRevisions.DeleteRevisions;
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Doc
Imports Spire.Doc.Documents
Imports Spire.Doc.Fields
Imports Spire.Doc.Formatting.Revisions
Imports System
Namespace GetWordDifferences
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(ByVal args() As String)
'Load the first Word document
Dim doc1 As Document = New Document
doc1.LoadFromFile("Sample1.docx")
'Load the second Word document
Dim doc2 As Document = New Document
doc2.LoadFromFile("Sample2.docx")
'Compare the two Word documents
doc1.Compare(doc2, "Author")
For Each sec As Section In doc1.Sections
For Each docItem As DocumentObject In sec.Body.ChildObjects
If (TypeOf docItem Is Paragraph) Then
Dim para As Paragraph = CType(docItem,Paragraph)
If para.IsInsertRevision Then
Dim insRevison As EditRevision = para.InsertRevision
Dim insType As EditRevisionType = insRevison.Type
Dim insAuthor As String = insRevison.Author
Dim insDateTime As DateTime = insRevison.DateTime
ElseIf para.IsDeleteRevision Then
Dim delRevison As EditRevision = para.DeleteRevision
Dim delType As EditRevisionType = delRevison.Type
Dim delAuthor As String = delRevison.Author
Dim delDateTime As DateTime = delRevison.DateTime
End If
For Each paraItem As ParagraphBase In para.ChildObjects
If paraItem.IsInsertRevision Then
Dim insRevison As EditRevision = paraItem.InsertRevision
Dim insType As EditRevisionType = insRevison.Type
Dim insAuthor As String = insRevison.Author
Dim insDateTime As DateTime = insRevison.DateTime
ElseIf paraItem.IsDeleteRevision Then
Dim delRevison As EditRevision = paraItem.DeleteRevision
Dim delType As EditRevisionType = delRevison.Type
Dim delAuthor As String = delRevison.Author
Dim delDateTime As DateTime = delRevison.DateTime
End If
Next
End If
Next
Next
'Get the difference about revisions
Dim differRevisions As DifferRevisions = New DifferRevisions(doc1)
Dim insetRevisionsList = differRevisions.InsertRevisions
Dim deletRevisionsList = differRevisions.DeleteRevisions
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
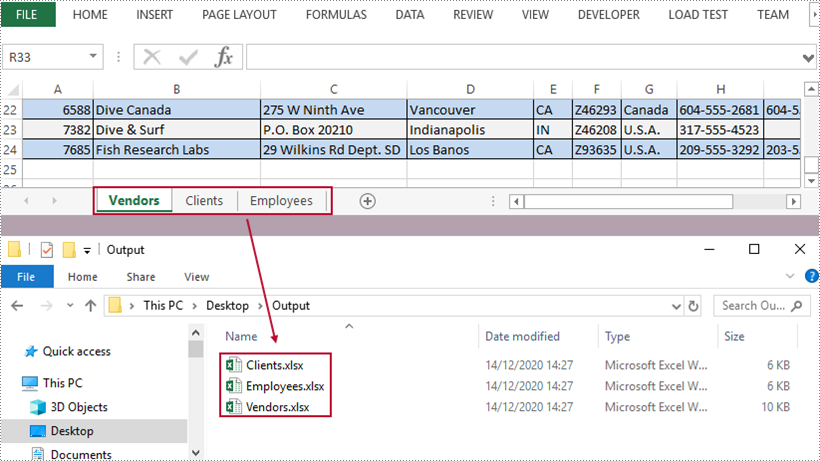
A workbook containing multiple worksheets helps to centrally manage relevant information, but sometimes we have to split the worksheets into separate Excel files so that individual worksheets can be distributed without disclosing other information. In this article, you will learn how to split Excel worksheets into separate workbooks in C# and VB.NET using Spire.XLS for .NET.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Split Excel Sheets into Separate Files
The following are the main steps to split Excel sheets into separate workbooks using Spire.XLS for .NET.
- Create a Workbook object
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Declare a new Workbook variable, which is used to create new Excel workbooks.
- Loop through the worksheets in the source document.
- Initialize the Workbook object, and add the copy of a specific worksheet of source document into it.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
using System;
namespace SplitWorksheets
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel document
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\data.xlsx");
//Declare a new Workbook variable
Workbook newWb;
//Declare a String variable
String sheetName;
//Specify the folder path which is used to store the generated Excel files
String folderPath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Output\\";
//Loop through the worksheets in the source file
for (int i = 0; i < wb.Worksheets.Count; i++)
{
//Initialize the Workbook object
newWb = new Workbook();
//Remove the default sheets
newWb.Worksheets.Clear();
//Add the specific worksheet of the source document to the new workbook
newWb.Worksheets.AddCopy(wb.Worksheets[i]);
//Get the worksheet name
sheetName = wb.Worksheets[i].Name;
//Save the new workbook to the specified folder
newWb.SaveToFile(folderPath + sheetName + ".xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
}
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
This article will show you how to add lines to Excel worksheets through two points. We could set the point’s location via relative location and Absolute location in pixels.
using Spire.Xls;
using Spire.Xls.Core.Spreadsheet.Shapes;
using System.Drawing;
namespace Word
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Initiate a Workbook object and get the first worksheet
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Add a line with relative location
XlsLineShape line = worksheet.TypedLines.AddLine() as XlsLineShape;
//set the column index of the starting point
line.LeftColumn = 2;
line.LeftColumnOffset = 2;
line.TopRow = 5;
line.TopRowOffset = 10;
//set the column index of the end point
line.RightColumn = 10;
line.RightColumnOffset = 10;
line.BottomRow =5;
line.BottomRowOffset = 10;
//Set the color
line.Color = Color.Red;
//Add a line with Absolute location in pixels
XlsLineShape line1 = worksheet.TypedLines.AddLine() as XlsLineShape;
//Set the start point and end point
line1.StartPoint = new Point(20, 30);
line1.EndPoint = new Point(200, 30);
//Set the color
line1.Color = Color.Blue;
workbook.SaveToFile("Addlines.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Xls
Imports Spire.Xls.Core.Spreadsheet.Shapes
Imports System.Drawing
Namespace Word
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(ByVal args() As String)
'Initiate a Workbook object and get the first worksheet
Dim workbook As Workbook = New Workbook
Dim worksheet As Worksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Add a line with relative location
Dim line As XlsLineShape = CType(worksheet.TypedLines.AddLine,XlsLineShape)
'set the column index of the starting point
line.LeftColumn = 2
line.LeftColumnOffset = 2
line.TopRow = 5
line.TopRowOffset = 10
'set the column index of the end point
line.RightColumn = 10
line.RightColumnOffset = 10
line.BottomRow = 5
line.BottomRowOffset = 10
'Set the color
line.Color = Color.Red
'Add a line with Absolute location in pixels
Dim line1 As XlsLineShape = CType(worksheet.TypedLines.AddLine,XlsLineShape)
'Set the start point and end point
line1.StartPoint = New Point(20, 30)
line1.EndPoint = New Point(200, 30)
'Set the color
line1.Color = Color.Blue
workbook.SaveToFile("Addlines.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Effective screenshot:
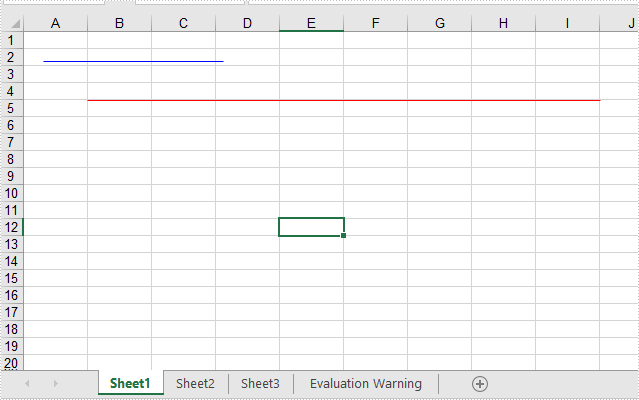
When sending an Excel document to others for review, it is recommended to turn on the Track Changes to ensure that all changes made to the worksheet or workbook are recorded. For the altered cells in Excel, each one will be highlighted with a blue triangle in the upper left corner of the cell. You can then view the changes and decide whether to accept or reject them. This article will demonstrate how to programmatically accept or reject all tracked changes in an Excel workbook using Spire.XLS for .NET.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
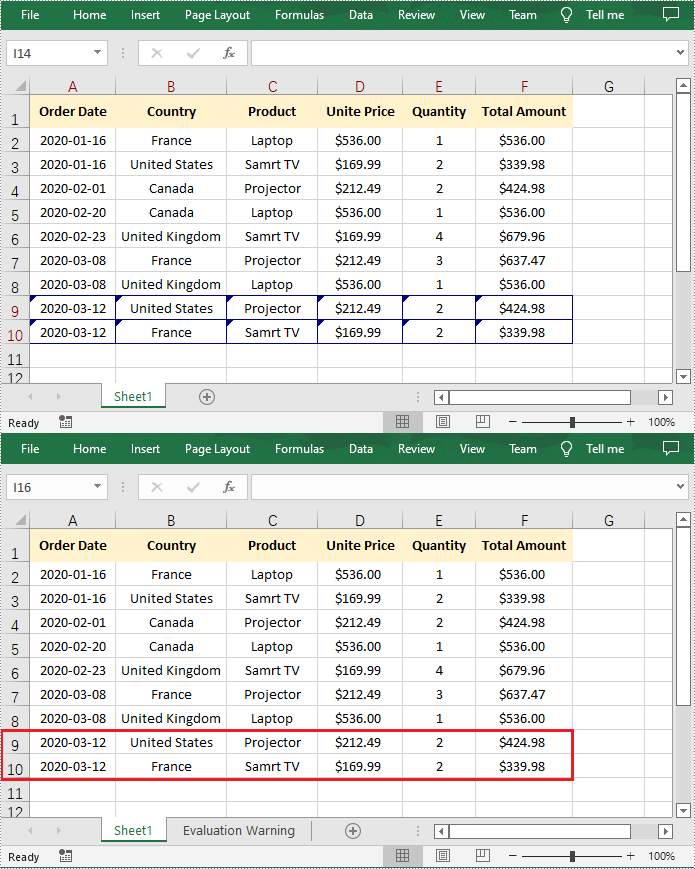
Accept All Tracked Changes in a Workbook
To accept tracked changes in a workbook, you'll first need to determine whether the workbook has tracked changes using Workbook.HasTrackedChanges property. If yes, you can then accept all changes at once using Workbook.AcceptAllTrackedChanges() method. The following are the steps to accept all tracked changes in an Excel workbook.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Determine if the workbook has tracked changes using Workbook.HasTrackedChanges property.
- Accept all tracked changes in the workbook using Workbook.AcceptAllTrackedChanges() method.
- Save the result document using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
namespace AcceptTrackedChanges
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load a sample Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
//Determine if the workbook has tracked changes
if (workbook.HasTrackedChanges)
{
//Accept all tracked changes in the workbook
workbook.AcceptAllTrackedChanges();
}
//Save the result document
workbook.SaveToFile("AcceptChanges.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2013);
}
}
}
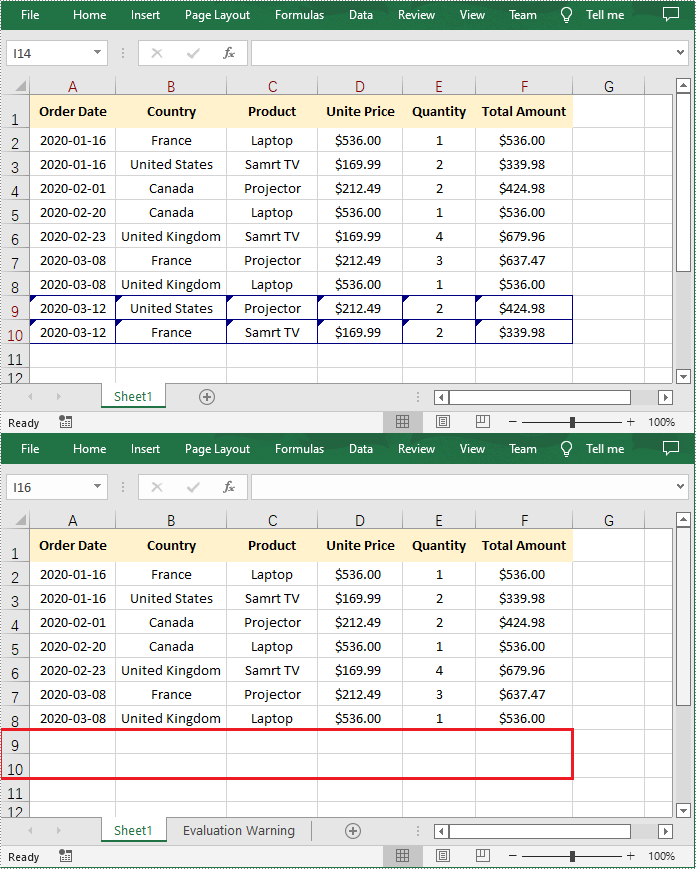
Reject All Tracked Changes in a Workbook
If the tracked changes have been proven to exist in a workbook, Spire.XLS for .NET also provides the Workbook.RejectAllTrackedChanges() method to reject all tracked changes at once. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Determine if the workbook has tracked changes using Workbook.HasTrackedChanges property.
- Reject all tracked changes in the workbook using Workbook.RejectAllTrackedChanges() method.
- Save the result document using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
namespace AcceptTrackedChanges
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load a sample Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
//Determine if the workbook has tracked changes
if (workbook.HasTrackedChanges)
{
//Reject all tracked changes in the workbook
workbook.RejectAllTrackedChanges();
}
//Save the result document
workbook.SaveToFile("RejectChanges.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2013);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
A digital signature is a type of electronic signature that can be used to verify the authenticity and integrity of digital documents. It can help recipients identify where the digital documents originate from and whether they have been changed by a third party after they were signed. In this article, we will demonstrate how to add or delete digital signatures in Excel in C# and VB.NET using Spire.XLS for .NET.
- Add a Digital Signature to Excel in C# and VB.NET
- Delete All Digital Signatures from Excel in C# and VB.NET
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
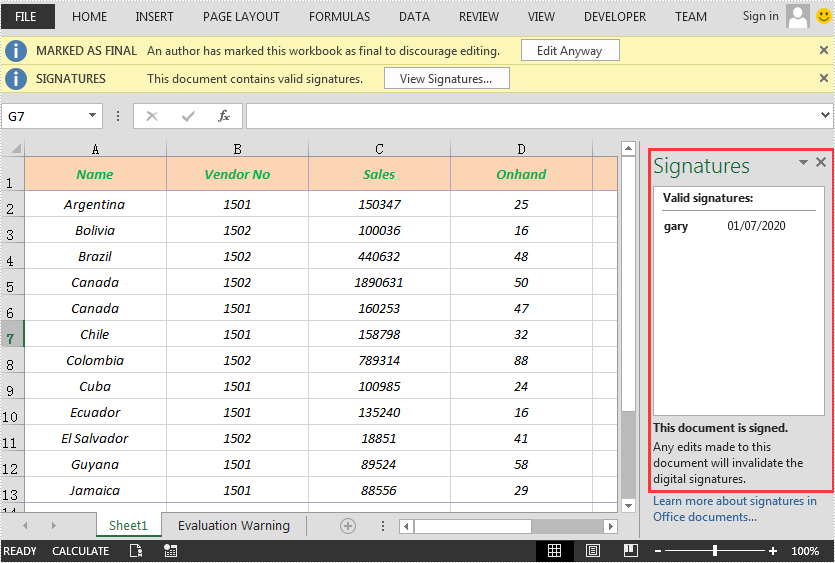
Add a Digital Signature to Excel in C# and VB.NET
You can add a digital signature to protect the integrity of an Excel file. Once the digital signature is added, the file becomes read-only to discourage further editing. If someone makes changes to the file, the digital signature will become invalid immediately.
Spire.XLS for .NET provides the AddDigitalSignature method of Workbook class to add digital signatures to an Excel file. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Initialize an instance of the X509Certificate2 class with the specified certificate (.pfx) file path and the password of the .pfx file.
- Initialize an instance of the DateTime class.
- Add a digital signature to the file using Workbook.AddDigitalSignature(X509Certificate2, string, DateTime) method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
using Spire.Xls.Core.MergeSpreadsheet.Interfaces;
using System;
using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;
namespace AddSignatureInExcel
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
//Add digital signature to the file
X509Certificate2 cert = new X509Certificate2("gary.pfx", "e-iceblue");
DateTime certtime = new DateTime(2020, 7, 1, 7, 10, 36);
IDigitalSignatures signature = workbook.AddDigitalSignature(cert, "e-iceblue", certtime);
//Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("AddDigitalSignature.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2013);
}
}
}
Delete All Digital Signatures from Excel in C# and VB.NET
Spire.XLS for .NET provides the RemoveAllDigitalSignatures method of Workbook class for developers to remove digital signatures from an Excel file. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove all digital signatures from the file using Workbook.RemoveAllDigitalSignatures() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
namespace DeleteSignatureInExcel
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("AddDigitalSignature.xlsx");
//Remove all the digital signatures in the file
workbook.RemoveAllDigitalSignatures();
//Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("RemoveDigitalSignature.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2013);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
This article will show you how to use Spire.XLS for .NET to create a bubble chart in Excel in C# and VB.NET.
using Spire.Xls;
namespace BubbleChart
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a new workbook
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Add a worksheet and set name
workbook.CreateEmptySheets(1);
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
sheet.Name = "Chart data";
//Initialize chart and set its type
Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Bubble);
//Set the position of the chart in the worksheet
chart.LeftColumn = 1;
chart.RightColumn = 10;
chart.TopRow = 1;
chart.BottomRow = 20;
//Set title for the chart and values
Spire.Xls.Charts.ChartSerie cs1 = chart.Series.Add("Bubble Chart");
cs1.EnteredDirectlyValues = new object[] { 2.2, 5.6 };
cs1.EnteredDirectlyCategoryLabels = new object[] { 1.1, 4.4 };
cs1.EnteredDirectlyBubbles = new object[] { 3, 6 };
//Save the document to file
workbook.SaveToFile("Output.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Xls
Namespace BubbleChart
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(ByVal args() As String)
'Create a new workbook
Dim workbook As Workbook = New Workbook
'Add a worksheet and set name
workbook.CreateEmptySheets(1)
Dim sheet As Worksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
sheet.Name = "Chart data"
'Initialize chart and set its type
Dim chart As Chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Bubble)
'Set the position of the chart in the worksheet
chart.LeftColumn = 1
chart.RightColumn = 10
chart.TopRow = 1
chart.BottomRow = 20
'Set title for the chart and values
Dim cs1 As Spire.Xls.Charts.ChartSerie = chart.Series.Add("Bubble Chart")
cs1.EnteredDirectlyValues = New Object() {2.2, 5.6}
cs1.EnteredDirectlyCategoryLabels = New Object() {1.1, 4.4}
cs1.EnteredDirectlyBubbles = New Object() {3, 6}
'Save the document to file
workbook.SaveToFile("Output.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
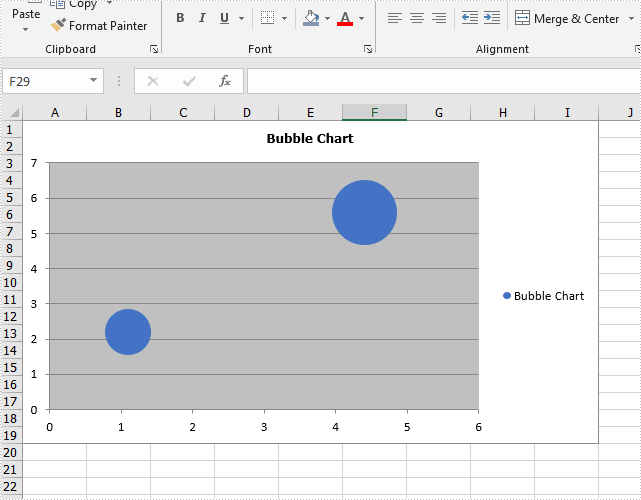
Effective screenshot of Excel Bubble chart:
This article demonstrates how to add hyperlinks to SmartArt Nodes in a PowerPoint document in C# and VB.NET using Spire.Presentation for .NET.
using Spire.Presentation;
using Spire.Presentation.Diagrams;
namespace SmartArt
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Presentation instance
Presentation ppt = new Presentation();
//Load the PowerPoint document
ppt.LoadFromFile("SmartArt.pptx");
//Get the first slide
ISlide slide = ppt.Slides[0];
//Get the SmartArt
ISmartArt smartArt = slide.Shapes[0] as ISmartArt;
//Add hyperlink to the first node of the SmartArt to link to a web page
smartArt.Nodes[0].Click = new ClickHyperlink("https://www.e-iceblue.com");
//Add hyperlink to the first node of the SmartArt to link to a specific slide
smartArt.Nodes[1].Click = new ClickHyperlink(ppt.Slides[1]);
//Save the result document
ppt.SaveToFile("Result.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013);
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Presentation
Imports Spire.Presentation.Diagrams
Namespace SmartArt
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(ByVal args As String())
Dim ppt As Presentation = New Presentation()
ppt.LoadFromFile("SmartArt.pptx")
Dim slide As ISlide = ppt.Slides(0)
Dim smartArt As ISmartArt = TryCast(slide.Shapes(0), ISmartArt)
smartArt.Nodes(0).Click = New ClickHyperlink("https://www.e-iceblue.com")
smartArt.Nodes(1).Click = New ClickHyperlink(ppt.Slides(1))
ppt.SaveToFile("Result.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Output:

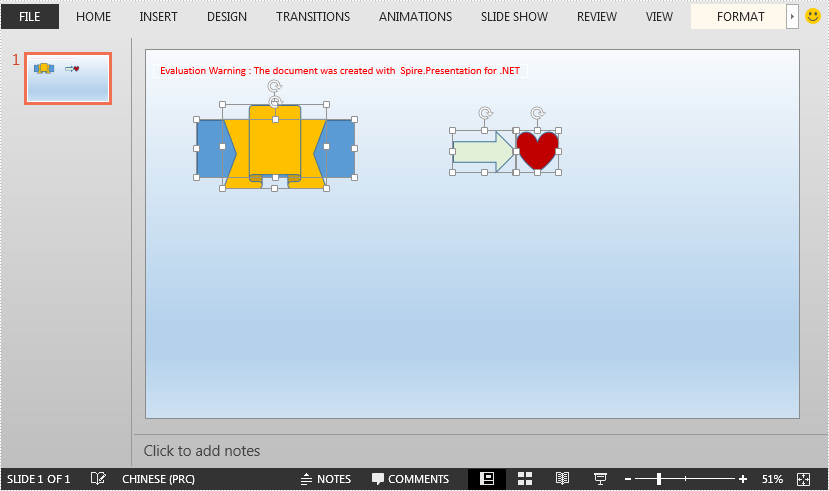
This article demonstrates how to ungroup grouped shapes in a PowerPoint document using Spire.Presentation for .NET.
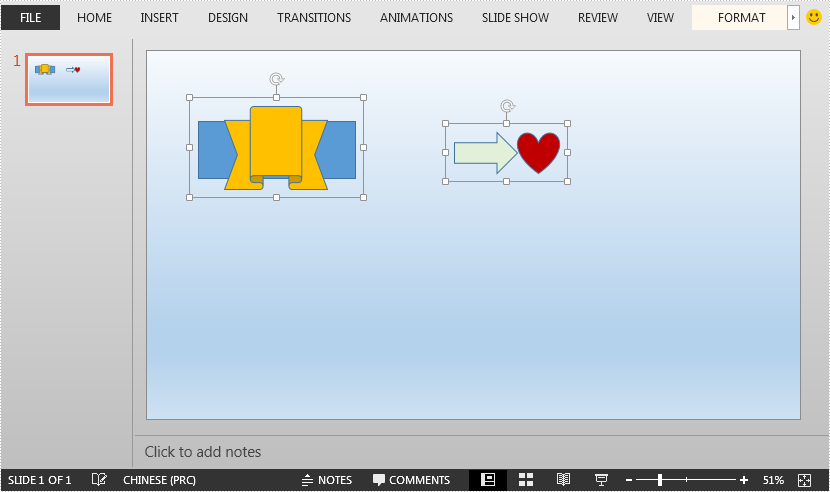
The input PowerPoint document:
using Spire.Presentation;
namespace UngroupShapes
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Presentation instance
Presentation ppt = new Presentation();
//Load the PowerPoint document
ppt.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx");
//Get the first slide
ISlide slide = ppt.Slides[0];
//Loop through the shapes in the slide
for(int i = 0; i< slide.Shapes.Count;i++)
{
IShape shape = slide.Shapes[i];
//Detect if the shape is a grouped shape
if (shape is GroupShape)
{
GroupShape groupShape = shape as GroupShape;
//Ungroup the grouped shape
slide.Ungroup(groupShape);
}
}
//Save the resultant document
ppt.SaveToFile("UngroupShapes.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013);
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Presentation
Namespace UngroupShapes
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(ByVal args As String())
Dim ppt As Presentation = New Presentation()
ppt.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
Dim slide As ISlide = ppt.Slides(0)
For i As Integer = 0 To slide.Shapes.Count - 1
Dim shape As IShape = slide.Shapes(i)
If TypeOf shape Is GroupShape Then
Dim groupShape As GroupShape = TryCast(shape, GroupShape)
slide.Ungroup(groupShape)
End If
Next
ppt.SaveToFile("UngroupShapes.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
The output PowerPoint document after ungrouping shapes: