
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Merging and unmerging cells in Excel is a useful feature that enhances the organization and presentation of data in worksheets. By combining multiple cells into a single cell or separating a merged cell back into its original state, you can better format your data for readability and aesthetic appeal. In this article, we will demonstrate how to merge and unmerge cells in Excel in React using Spire.XLS for JavaScript.
Install Spire.XLS for JavaScript
To get started with merging and unmerging cells in Excel in a React application, you can either download Spire.XLS for JavaScript from our website or install it via npm with the following command:
npm i spire.xls
After that, copy the "Spire.Xls.Base.js" and "Spire.Xls.Base.wasm" files to the public folder of your project.
For more details, refer to the documentation: How to Integrate Spire.XLS for JavaScript in a React Project
Merge Specific Cells in Excel
Merging cells allows users to create a header that spans multiple columns or rows, making the data more visually structured and easier to read. With Spire.XLS for JavaScript, developers are able to merge specific adjacent cells into a single cell by using the CellRange.Merge() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object using the wasmModule.Workbook.Create() method.
- Load the Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets.get(index) method.
- Get the range of cells that need to be merged using the Worksheet.Range.get() method.
- Merge the cells into one using the CellRange.Merge() method.
- Save the resulting workbook using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- JavaScript
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
function App() {
// State to hold the loaded WASM module
const [wasmModule, setWasmModule] = useState(null);
// useEffect hook to load the WASM module when the component mounts
useEffect(() => {
const loadWasm = async () => {
try {
// Access the Module and spirexls from the global window object
const { Module, spirexls } = window;
// Set the wasmModule state when the runtime is initialized
Module.onRuntimeInitialized = () => {
setWasmModule(spirexls);
};
} catch (err) {
// Log any errors that occur during loading
console.error('Failed to load WASM module:', err);
}
};
// Create a script element to load the WASM JavaScript file
const script = document.createElement('script');
script.src = `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/Spire.Xls.Base.js`;
script.onload = loadWasm;
// Append the script to the document body
document.body.appendChild(script);
// Cleanup function to remove the script when the component unmounts
return () => {
document.body.removeChild(script);
};
}, []);
// Function to merge cells in an Excel worksheet
const MergeCells = async () => {
if (wasmModule) {
// Load the sample Excel file into the virtual file system (VFS)
let excelFileName = 'MergeCells_Input.xlsx';
await wasmModule.FetchFileToVFS(excelFileName, '', `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}`);
// Create a new workbook
const workbook = wasmModule.Workbook.Create();
// Load the Excel file from the virtual file system
workbook.LoadFromFile(excelFileName);
// Get the first worksheet
let sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get(0);
// Merge the particular cells in the worksheet
sheet.Range.get("A1:D1").Merge();
// Define the output file name
const outputFileName = "MergeCells_output.xlsx";
// Save the workbook to the specified path
workbook.SaveToFile({ fileName: outputFileName, version: wasmModule.ExcelVersion.Version2010 });
// Read the saved file and convert it to a Blob object
const modifiedFileArray = wasmModule.FS.readFile(outputFileName);
const modifiedFile = new Blob([modifiedFileArray], { type: 'application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet' });
// Create a URL for the Blob and initiate the download
const url = URL.createObjectURL(modifiedFile);
const a = document.createElement('a');
a.href = url;
a.download = outputFileName;
document.body.appendChild(a);
a.click();
document.body.removeChild(a);
URL.revokeObjectURL(url);
// Clean up resources used by the workbook
workbook.Dispose();
}
};
return (
<div style={{ textAlign: 'center', height: '300px' }}>
<h1>Merge Cells in an Excel Worksheet into One Using JavaScript in React</h1>
<button onClick={MergeCells} disabled={!wasmModule}>
Merge
</button>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Run the code to launch the React app at localhost:3000. Once it's running, click on the "Merge" button to merge specific cells in an Excel worksheet into one:
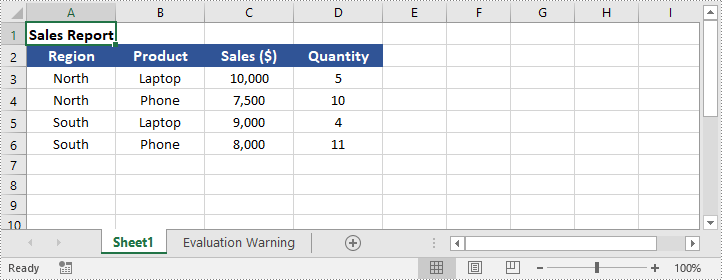
The output Excel worksheet appears as follows:

Unmerge Specific Cells in Excel
Unmerging cells allows users to restore previously merged cells to their original individual state, enabling better data manipulation and formatting flexibility. With Spire.XLS for JavaScript, developers can unmerge specific merged cells using the CellRange.UnMerge() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object using the wasmModule.Workbook.Create() method.
- Load the Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets.get(index) method.
- Get the cell that needs to be unmerged using the Worksheet.Range.get() method.
- Unmerge the cell using the CellRange.UnMerge() method.
- Save the resulting workbook using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- JavaScript
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
function App() {
// State to hold the loaded WASM module
const [wasmModule, setWasmModule] = useState(null);
// useEffect hook to load the WASM module when the component mounts
useEffect(() => {
const loadWasm = async () => {
try {
// Access the Module and spirexls from the global window object
const { Module, spirexls } = window;
// Set the wasmModule state when the runtime is initialized
Module.onRuntimeInitialized = () => {
setWasmModule(spirexls);
};
} catch (err) {
// Log any errors that occur during loading
console.error('Failed to load WASM module:', err);
}
};
// Create a script element to load the WASM JavaScript file
const script = document.createElement('script');
script.src = `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/Spire.Xls.Base.js`;
script.onload = loadWasm;
// Append the script to the document body
document.body.appendChild(script);
// Cleanup function to remove the script when the component unmounts
return () => {
document.body.removeChild(script);
};
}, []);
// Function to unmerge cells in an Excel worksheet
const UnmergeCells = async () => {
if (wasmModule) {
// Load the sample Excel file into the virtual file system (VFS)
let excelFileName = 'MergeCells_Output.xlsx';
await wasmModule.FetchFileToVFS(excelFileName, '', `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}`);
// Create a new workbook
const workbook = wasmModule.Workbook.Create();
// Load the Excel file from the virtual file system
workbook.LoadFromFile(excelFileName);
// Get the first worksheet
let sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get(0);
// Unmerge the particular cell in the worksheet
sheet.Range.get("A1").UnMerge();
// Define the output file name
const outputFileName = "UnmergeCells.xlsx";
// Save the workbook to the specified path
workbook.SaveToFile({ fileName: outputFileName, version: wasmModule.ExcelVersion.Version2010 });
// Read the saved file and convert it to a Blob object
const modifiedFileArray = wasmModule.FS.readFile(outputFileName);
const modifiedFile = new Blob([modifiedFileArray], { type: 'application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet' });
// Create a URL for the Blob and initiate the download
const url = URL.createObjectURL(modifiedFile);
const a = document.createElement('a');
a.href = url;
a.download = outputFileName;
document.body.appendChild(a);
a.click();
document.body.removeChild(a);
URL.revokeObjectURL(url);
// Clean up resources used by the workbook
workbook.Dispose();
}
};
return (
<div style={{ textAlign: 'center', height: '300px' }}>
<h1>Unmerge Cells in an Excel Worksheet Using JavaScript in React</h1>
<button onClick={UnmergeCells} disabled={!wasmModule}>
Unmerge
</button>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Unmerge All Merged Cells in Excel
When dealing with spreadsheets containing multiple merged cells, unmerging them all at once can help restore the original cell structure. With Spire.XLS for JavaScript, developers can easily find all merged cells in a worksheet using the Worksheet.MergedCells property and unmerge them with the CellRange.UnMerge() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object using the wasmModule.Workbook.Create() method.
- Load the Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets.get(index) method.
- Get all merged cell ranges in the worksheet using the Worksheet.MergedCells property.
- Loop through the merged cell ranges and unmerge them using the CellRange.UnMerge() method.
- Save the resulting workbook using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- JavaScript
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
function App() {
// State to hold the loaded WASM module
const [wasmModule, setWasmModule] = useState(null);
// useEffect hook to load the WASM module when the component mounts
useEffect(() => {
const loadWasm = async () => {
try {
// Access the Module and spirexls from the global window object
const { Module, spirexls } = window;
// Set the wasmModule state when the runtime is initialized
Module.onRuntimeInitialized = () => {
setWasmModule(spirexls);
};
} catch (err) {
// Log any errors that occur during loading
console.error('Failed to load WASM module:', err);
}
};
// Create a script element to load the WASM JavaScript file
const script = document.createElement('script');
script.src = `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/Spire.Xls.Base.js`;
script.onload = loadWasm;
// Append the script to the document body
document.body.appendChild(script);
// Cleanup function to remove the script when the component unmounts
return () => {
document.body.removeChild(script);
};
}, []);
// Function to unmerge cells in an Excel worksheet
const UnmergeCells = async () => {
if (wasmModule) {
// Load the sample Excel file into the virtual file system (VFS)
let excelFileName = 'MergeCells_Output.xlsx';
await wasmModule.FetchFileToVFS(excelFileName, '', `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}`);
// Create a new workbook
const workbook = wasmModule.Workbook.Create();
// Load the Excel file from the virtual file system
workbook.LoadFromFile(excelFileName);
// Get the first worksheet
let sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get(0);
// Get all merged cell ranges in the worksheet and put them into a CellRange array
let range = sheet.MergedCells;
// Loop through the array and unmerge all merged cell ranges
for (let cell of range) {
cell.UnMerge();
}
// Define the output file name
const outputFileName = "UnmergeAllMergedCells.xlsx";
// Save the workbook to the specified path
workbook.SaveToFile({ fileName: outputFileName, version: wasmModule.ExcelVersion.Version2010 });
// Read the saved file and convert it to a Blob object
const modifiedFileArray = wasmModule.FS.readFile(outputFileName);
const modifiedFile = new Blob([modifiedFileArray], { type: 'application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet' });
// Create a URL for the Blob and initiate the download
const url = URL.createObjectURL(modifiedFile);
const a = document.createElement('a');
a.href = url;
a.download = outputFileName;
document.body.appendChild(a);
a.click();
document.body.removeChild(a);
URL.revokeObjectURL(url);
// Clean up resources used by the workbook
workbook.Dispose();
}
};
return (
<div style={{ textAlign: 'center', height: '300px' }}>
<h1>Unmerge Cells in an Excel Worksheet Using JavaScript in React</h1>
<button onClick={UnmergeCells} disabled={!wasmModule}>
Unmerge
</button>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.XLS for JavaScript without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Convert Word to Markdown and Markdown to Word with JavaScript in React
2025-02-12 08:00:00 Written by KoohjiSeamless conversion between Word documents and Markdown files is increasingly essential in web development for boosting productivity and interoperability. Word documents dominate in complex formatting, while Markdown offers a simple, universal approach to content creation. Enabling conversion between the two within a React application allows users to work in their preferred format while ensuring compatibility across different platforms, streamlining workflows without relying on external tools. In this article, we will explore how to use Spire.Doc for JavaScript to convert Word to Markdown and Markdown to Word with JavaScript in React applications.
Install Spire.Doc for JavaScript
To get started with conversion between Word and Markdown in a React application, you can either download Spire.Doc for JavaScript from our website or install it via npm with the following command:
npm i spire.doc
After that, copy the "Spire.Doc.Base.js" and "Spire.Doc.Base.wasm" files into the public folder of your project. Additionally, include the required font files to ensure accurate and consistent text rendering.
For more details, refer to the documentation: How to Integrate Spire.Doc for JavaScript in a React Project
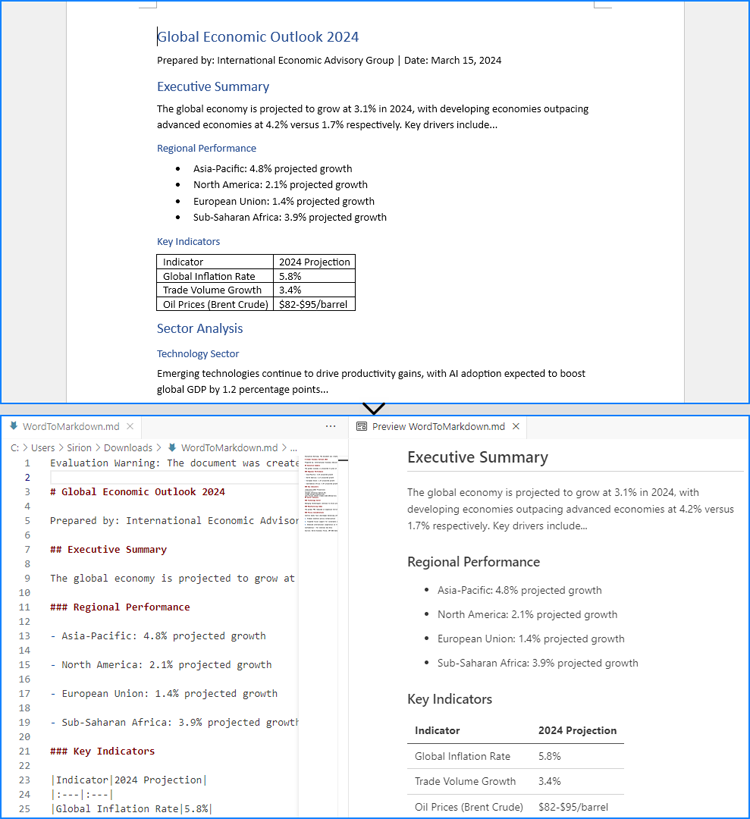
Convert Word to Markdown with JavaScript
The Spire.Doc for JavaScript provides a WebAssembly module that enables loading Word documents from the VFS and converting them to Markdown. Developers can achieve this conversion by fetching the documents to the VFS, loading them using the Document.LoadFromFile() method, and saving them as Markdown with the Document.SaveToFile() method. The process involves the following steps:
- Load the Spire.Doc.Base.js file to initialize the WebAssembly module.
- Fetch the Word document into the virtual file system using the wasmModule.FetchFileToVFS() method.
- Create a Document instance in the WebAssembly module using the wasmModule.Document.Create() method.
- Load the Word document into the Document instance with the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Convert the document to Markdown format and save it to the VFS using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Read and download the file, or use it as needed.
- JavaScript
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
function App() {
// State to store the loaded WASM module
const [wasmModule, setWasmModule] = useState(null);
// useEffect hook to load the WASM module when the component mounts
useEffect(() => {
const loadWasm = async () => {
try {
// Access the Module and spiredoc from the global window object
const { Module, spiredoc } = window;
// Set the wasmModule state when the runtime is initialized
Module.onRuntimeInitialized = () => {
setWasmModule(spiredoc);
};
} catch (err) {
// Log any errors that occur during module loading
console.error('Failed to load the WASM module:', err);
}
};
// Create a script element to load the WASM JavaScript file
const script = document.createElement('script');
script.src = `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/Spire.Doc.Base.js`;
script.onload = loadWasm;
// Append the script to the document body
document.body.appendChild(script);
// Cleanup function to remove the script when the component unmounts
return () => {
document.body.removeChild(script);
};
}, []);
// Function to convert Word to Markdown
const ConvertHTMLStringToPDF = async () => {
if (wasmModule) {
// Specify the output file name
const inputFileName = 'Sample.docx';
const outputFileName = 'WordToMarkdown.md';
// Fetch the font file and add it to the VFS
await wasmModule.FetchFileToVFS(inputFileName, '', `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/`);
// Create an instance of the Document class
const doc = wasmModule.Document.Create();
// Load the Word document
doc.LoadFromFile(inputFileName);
// Save the document to a Markdown file
doc.SaveToFile({fileName: outputFileName, fileFormat: wasmModule.FileFormat.Markdown});
// Release resources
doc.Dispose();
// Read the markdown file
const mdContent = await wasmModule.FS.readFile(outputFileName)
// Generate a Blob from the markdown file and trigger a download
const blob = new Blob([mdContent], {type: 'text/plain'});
const url = URL.createObjectURL(blob);
const a = document.createElement("a");
a.href = url;
a.download = outputFileName;
document.body.appendChild(a);
a.click();
document.body.removeChild(a);
URL.revokeObjectURL(url);
}
};
return (
<div style={{ textAlign: 'center', height: '300px' }}>
<h1>Convert Word to Markdown Using JavaScript in React</h1>
<button onClick={ConvertHTMLStringToPDF} disabled={!wasmModule}>
Convert and Download
</button>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Convert Markdown to Word with JavaScript
The Document.LoadFromFile() method can also be used to load a Markdown file by specifying the file format parameter as wasmModule.FileFormat.Markdown. Then, the Markdown file can be exported as a Word document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
For Markdown strings, developers can write them as Markdown files into the virtual file system using the wasmModule.FS.writeFile() method, and then convert them to Word documents.
The detailed steps for converting Markdown content to Word documents are as follows:
- Load the Spire.Doc.Base.js file to initialize the WebAssembly module.
- Load required font files into the virtual file system using the wasmModule.FetchFileToVFS() method.
- Import Markdown content:
- For files: Use the wasmModule.FetchFileToVFS() method to load the Markdown file into the VFS.
- For strings: Write Markdown content to the VFS via the wasmModule.FS.writeFile() method.
- Instantiate a Document object via the wasmModule.Document.Create() method within the WebAssembly module.
- Load the Markdown file into the Document instance using the Document.LoadFromFile({ filename: string, fileFormat: wasmModule.FileFormat.Markdown }) method.
- Convert the Markdown file to a Word document and save it to the VFS using the Document.SaveToFile( { filename: string, fileFormat:wasmModule.FileFormat.Docx2019 }) method.
- Retrieve and download the generated Word file from the VFS, or process it further as required.
- JavaScript
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
function App() {
// State to store the loaded WASM module
const [wasmModule, setWasmModule] = useState(null);
// useEffect hook to load the WASM module when the component mounts
useEffect(() => {
const loadWasm = async () => {
try {
// Access the Module and spiredoc from the global window object
const { Module, spiredoc } = window;
// Set the wasmModule state when the runtime is initialized
Module.onRuntimeInitialized = () => {
setWasmModule(spiredoc);
};
} catch (err) {
// Log any errors that occur during module loading
console.error('Failed to load the WASM module:', err);
}
};
// Create a script element to load the WASM JavaScript file
const script = document.createElement('script');
script.src = `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/Spire.Doc.Base.js`;
script.onload = loadWasm;
// Append the script to the document body
document.body.appendChild(script);
// Cleanup function to remove the script when the component unmounts
return () => {
document.body.removeChild(script);
};
}, []);
// Function to convert Markdown to Word
const ConvertHTMLStringToPDF = async () => {
if (wasmModule) {
// Specify the output file name
const outputFileName = 'MarkdownStringToWord.docx';
// Fetch the required font files into the VFS
await wasmModule.FetchFileToVFS('Arial.ttf', '/Library/Fonts/', `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/`);
// Create a new Document instance
const doc = wasmModule.Document.Create();
// Fetch the Markdown file to the VFS and load it into the Document instance
// await wasmModule.FetchFileToVFS('MarkdownExample.md', '', `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/`);
// doc.LoadFromFile({ fileName: 'MarkdownExample.md', fileFormat: wasmModule.FileFormat.Markdown });
// Define the Markdown string
const markdownString = '# Project Aurora: Next-Gen Climate Modeling System *\n' +
'## Overview\n' +
'A next-generation climate modeling platform leveraging AI to predict regional climate patterns with 90%+ accuracy. Built for researchers and policymakers.\n' +
'### Key Features\n' +
'- * Real-time atmospheric pattern recognition\n' +
'- * Carbon sequestration impact modeling\n' +
'- * Custom scenario simulation builder\n' +
'- * Historical climate data cross-analysis\n' +
'\n' +
'## Sample Usage\n' +
'| Command | Description | Example Output |\n' +
'|---------|-------------|----------------|\n' +
'| `region=asia` | Runs climate simulation for Asia | JSON with temperature/precipitation predictions |\n' +
'| `model=co2` | Generates CO2 impact visualization | Interactive 3D heatmap |\n' +
'| `year=2050` | Compares scenarios for 2050 | Tabular data with Δ values |\n' +
'| `format=netcdf` | Exports data in NetCDF format | .nc file with metadata |'
// Write the Markdown string to a file in the VFS
await wasmModule.FS.writeFile('Markdown.md', markdownString, {encoding: 'utf8'})
// Load the Markdown file from the VFS
doc.LoadFromFile({ fileName: 'Markdown.md', fileFormat: wasmModule.FileFormat.Markdown });
// Save the document to a Word file
doc.SaveToFile({fileName: outputFileName, fileFormat: wasmModule.FileFormat.Docx2019});
// Release resources
doc.Dispose();
// Read the Word file
const outputWordFile = await wasmModule.FS.readFile(outputFileName)
// Generate a Blob from the Word file and trigger a download
const blob = new Blob([outputWordFile], { type: 'application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document' });
const url = URL.createObjectURL(blob);
const a = document.createElement("a");
a.href = url;
a.download = outputFileName;
document.body.appendChild(a);
a.click();
document.body.removeChild(a);
URL.revokeObjectURL(url);
}
};
return (
<div style={{ textAlign: 'center', height: '300px' }}>
<h1>Convert Markdown to Word Using JavaScript in React</h1>
<button onClick={ConvertHTMLStringToPDF} disabled={!wasmModule}>
Convert and Download
</button>
</div>
);
}
export default App;

Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for JavaScript without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
In the modern web development landscape, React has become the go-to framework for building dynamic and interactive user interfaces. When it comes to handling PDF documents within a React application, Spire.PDF for JavaScript stands out as a powerful tool.
This guide will walk you through how to integrate Spire.PDF for JavaScript into your React project, explore its benefits, and provide actionable insights to optimize your implementation.
- Benefits of Using Spire.PDF for JavaScript in React
- Set Up Your Environment
- Integrate Spire.PDF for JavaScript in Your Project
- Create and Save PDF Files Using JavaScript
Benefits of Using Spire.PDF for JavaScript in React
React, a widely used JavaScript library for crafting dynamic user interfaces, has become essential in modern web development. In tandem, Spire.PDF for JavaScript is a robust library tailored to enhance PDF document processing in web applications.
By incorporating Spire.PDF for JavaScript into your React project, you can introduce advanced PDF manipulation capabilities to your application. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Effortless PDF Generation: Spire.PDF for JavaScript facilitates the creation and editing of PDF documents directly within React, allowing for efficient management without the need for external applications.
- Cross-Platform Functionality: With Spire.PDF for JavaScript, you can generate PDFs that are accessible across various platforms, enabling users to view and edit documents from any location.
- Comprehensive Features: Spire.PDF for JavaScript provides a wide array of features, including text formatting, image embedding, and annotation capabilities, making it perfect for applications that require detailed PDF manipulation.
- Smooth Integration: Designed to work seamlessly with various JavaScript frameworks, including React, Spire.PDF for JavaScript integrates effortlessly into existing projects, ensuring a smooth development process.
Set Up Your Environment
Step 1. Install React and npm
Download and install Node.js from the official website. Make sure to choose the version that matches your operating system.
After the installation is complete, you can verify that Node.js and npm are working correctly by running the following commands in your terminal:
Step 2. Create a New React Project
Create a new React project named my-app using Create React App from terminal:
npx create-react-app my-app

If your React project is compiled successfully, the app will be served at http://localhost:3000, allowing you to view and test your application in a browser.
To visually browse and manage the files in your project, you can open the project using VS Code.
Integrate Spire.PDF for JavaScript in Your Project
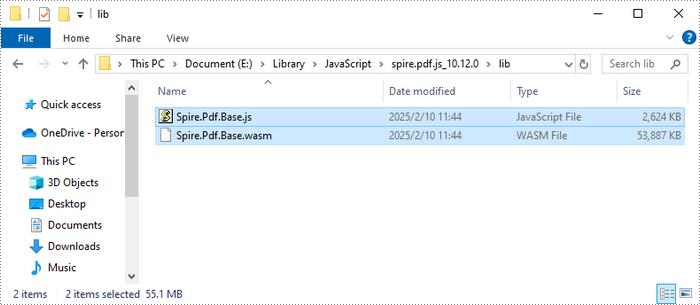
Download Spire.PDF for JavaScript from our website and unzip it to a location on your disk. Inside the lib folder, you will find the Spire.Pdf.Base.js and Spire.Pdf.Base.wasm files.
Alternatively, you can download Spire.PDF for JavaScript using npm. In the terminal within VS Code, run the following command:
npm i spire.pdf

This command will download and install the Spire.PDF package, including all its dependencies. Once the installation is complete, the Spire.Pdf.Base.js and Spire.Pdf.Base.wasm files will be saved in the node_modules/spire.pdf path of your project.
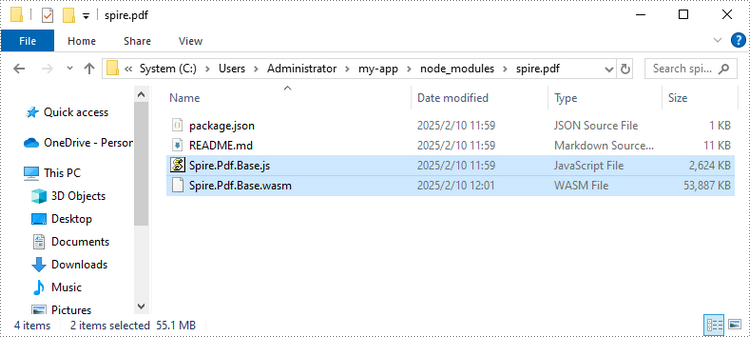
Copy these two files into the "public" folder in your React project.

Add font files you plan to use to the "public" folder in your project. (Not always necessary)
Create and Save PDF Files Using JavaScript
Modify the code in the "App.js" file to generate a PDF file using the WebAssembly (WASM) module. Specifically, utilize the Spire.PDF for JavaScript library for PDF file manipulation.

Here is the entire code:
- JavaScript
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
function App() {
// State to hold the loaded WASM module
const [wasmModule, setWasmModule] = useState(null);
// useEffect hook to load the WASM module when the component mounts
useEffect(() => {
const loadWasm = async () => {
try {
// Access the Module and spirepdf from the global window object
const { Module, spirepdf } = window;
// Set the wasmModule state when the runtime is initialized
Module.onRuntimeInitialized = () => {
setWasmModule(spirepdf);
};
} catch (err) {
// Log any errors that occur during loading
console.error('Failed to load WASM module:', err);
}
};
// Create a script element to load the WASM JavaScript file
const script = document.createElement('script');
script.src = `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/Spire.Pdf.Base.js`;
script.onload = loadWasm;
// Append the script to the document body
document.body.appendChild(script);
// Cleanup function to remove the script when the component unmounts
return () => {
document.body.removeChild(script);
};
}, []);
// Function to create PDF file
const CreatePdfDocument = async () => {
if (wasmModule) {
// Create a new document
const doc= wasmModule.PdfDocument.Create();
// Add a page
let page = doc.Pages.Add();
// Create font and brush
let font = wasmModule.PdfFont.Create(wasmModule.PdfFontFamily.Helvetica, 30);
let brush = wasmModule.PdfSolidBrush.Create({color:wasmModule.Color.get_Blue()});
// Draw text on the page at the specified coordinate
page.Canvas.DrawString({s: 'Hello, World', font: font, brush: brush, x: 10, y: 10});
// Define the output file name
const outputFileName = "output.pdf";
// Save the document to the specified path
doc.SaveToFile({fileName: outputFileName});
// Read the generated PDF file
const modifiedFileArray = wasmModule.FS.readFile(outputFileName);
// Create a Blob object from the PDF file
const modifiedFile = new Blob([modifiedFileArray], { type: 'application/pdf' });
// Create a URL for the Blob
const url = URL.createObjectURL(modifiedFile);
// Create an anchor element to trigger the download
const a = document.createElement('a');
a.href = url;
a.download = outputFileName;
document.body.appendChild(a);
a.click();
document.body.removeChild(a);
URL.revokeObjectURL(url);
// Clean up resources
doc.Dispose();
}
};
return (
<div style={{ textAlign: 'center', height: '300px' }}>
<h1>Create a PDF Document in React</h1>
<button onClick={CreatePdfDocument} disabled={!wasmModule}>
Generate
</button>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Save the changes by clicking "File" - "Save".
Start the development server by entering the following command in the terminal within VS Code:
npm start
Once the React app is successfully compiled, it will open in your default web browser, typically at http://localhost:3000.

Click "Generate," and a "Save As" window will prompt you to save the output file in the designated folder.

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
