
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
XML is often used for data interchange between different systems, while Excel is a widely recognized format for data analysis and reporting. By converting XML data to Excel, you can leverage Excel's powerful features to analyze and visualize the data more effectively. This conversion process is essential in various industries, including finance, healthcare, and e-commerce.
In this article, you will learn how to convert XML to Excel and PDF in C# using Spire.XLS for .NET.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Understanding XML Structure: Elements, Attributes, and Data
Before converting XML to Excel, it's crucial to understand the structure of XML files. XML is a markup language that uses tags to define elements, attributes, and data. Here’s a breakdown of these components:
- Elements: These are the building blocks of XML. They are defined by start and end tags and can contain data or other elements.
<person>
<name>John Doe</name>
<age>30</age>
</person>
- Attributes: These provide additional information about elements. They are specified within the start tag of an element.
<person id="1">
<name>John Doe</name>
<age>30</age>
</person>
- Data: This is the content enclosed within the start and end tags of an element.
Understanding these components will help you map XML data to Excel effectively.
Convert XML to Excel in C#
In .NET, you can use the System.Xml.Linq namespace, which provides classes for working with XML files. The primary class used is XDocument, which allows you to load, navigate, and manipulate XML documents effortlessly.
Here's an example:
- C#
using System;
using System.Xml.Linq;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// Load the XML file
XDocument doc = XDocument.Load("data.xml");
XElement root = doc.Root;
// Iterate through elements
foreach (XElement person in root.Elements("person"))
{
string name = person.Element("name")?.Value;
string age = person.Element("age")?.Value;
// Output the name and age
Console.WriteLine($"Name: {name}, Age: {age}");
}
}
}
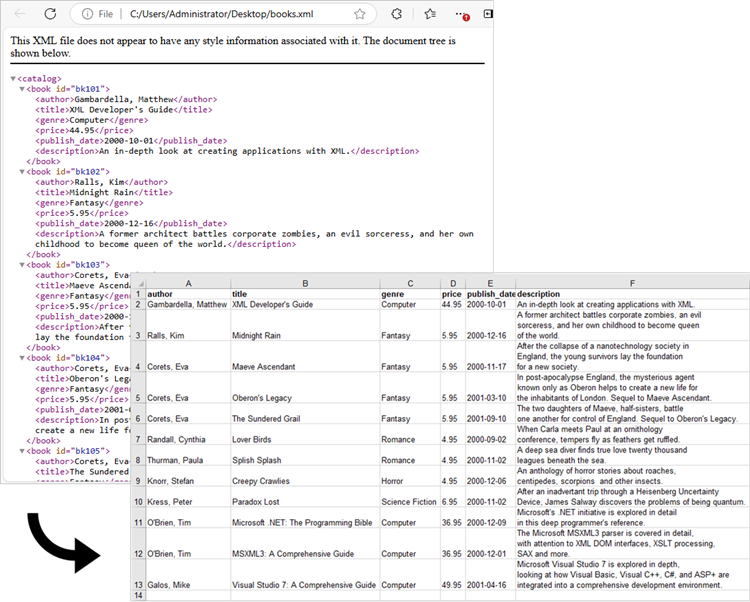
After parsing the XML data, the next step is to map it to an Excel worksheet. You can use Spire.XLS for .NET to create a new workbook, input data into specific cells, and apply various styles and formatting options. These include auto-fitting column widths, adjusting text alignment, and making the header bold.
To convert XML to Excel in C#, follow these steps:
- Utilize the System.Xml.Linq library to extract data from the XML file.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Add a worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets.Add() method.
- Write the extracted data into the worksheet cells using the Worksheet.SetValue() method.
- Apply styles and formatting to enhance the appearance of the worksheet.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
The following code demonstrates an efficient and advanced method for reading data from XML and importing it into an Excel file.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Xml.Linq;
namespace ConvertXmlToExcel
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Remove default worksheets
workbook.Worksheets.Clear();
// Add a worksheet and name it
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("Books");
// Load an XML file
XDocument xmlDoc = XDocument.Load(@"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Books.xml");
XElement xmlRoot = xmlDoc.Root;
// Get the first "book" element
XElement firstBook = xmlRoot.Element("book");
// Extract header information and convert it into a list
var headers = firstBook.Elements().ToList();
// Write header to Excel
for (int colIndex = 0; colIndex < headers.Count; colIndex++)
{
string headerText = headers[colIndex].Name.LocalName;
worksheet.SetValue(1, colIndex + 1, headerText);
}
// Write other data to Excel by iterating over each book element and each data node within it
int rowIndex = 2;
foreach (XElement book in xmlRoot.Elements("book"))
{
var dataNodes = book.Elements().ToList();
for (int colIndex = 0; colIndex < dataNodes.Count; colIndex++)
{
string value = dataNodes[colIndex].Value;
worksheet.SetValue(rowIndex, colIndex + 1, value);
}
rowIndex++;
}
// Set column width
worksheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns();
// Set alignment
worksheet.AllocatedRange.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left;
// Set font style
worksheet.Range["A1:F1"].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
// Save the workbook to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/XmlToExcel.xlsx");
// Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
Convert XML to PDF in C#
The previous example effectively imports data from an XML file into an Excel worksheet. This worksheet can subsequently be converted to a PDF file using the Worksheet.SaveToPdf() method. To ensure a well-structured PDF, you may want to adjust page layout settings, such as margins and the preservation of gridlines, during the conversion process.
Here are the steps to convert XML to PDF using C#:
- Use the System.Xml.Linq library to retrieve data from the XML file.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Add a worksheet with the Workbook.Worksheets.Add() method.
- Populate the worksheet cells with data extracted from the XML file using the Worksheet.SetValue() method.
- Apply styles and formatting to improve the worksheet's appearance.
- Configure page settings using properties from the PageSetup object, accessible via Worksheet.PageSetup.
- Save the worksheet as a PDF file using the Worksheet.SaveToPdf() method.
The following code snippet illustrates how to import data from XML into a worksheet and then save that worksheet as a PDF file.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using Spire.Xls.Core;
using System.Xml.Linq;
namespace ConvertXmlToPdf
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Remove default worksheets
workbook.Worksheets.Clear();
// Add a worksheet and name it
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("Books");
// Load an XML file
XDocument xmlDoc = XDocument.Load(@"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Books.xml");
XElement xmlRoot = xmlDoc.Root;
// Get the first "book" element
XElement firstBook = xmlRoot.Element("book");
// Extract header information and convert it into a list
var headers = firstBook.Elements().ToList();
// Write header to Excel
for (int colIndex = 0; colIndex < headers.Count; colIndex++)
{
string headerText = headers[colIndex].Name.LocalName;
worksheet.SetValue(1, colIndex + 1, headerText);
}
// Write other data to Excel by iterating over each book element and each data node within it
int rowIndex = 2;
foreach (XElement book in xmlRoot.Elements("book"))
{
var dataNodes = book.Elements().ToList();
for (int colIndex = 0; colIndex < dataNodes.Count; colIndex++)
{
string value = dataNodes[colIndex].Value;
worksheet.SetValue(rowIndex, colIndex + 1, value);
}
rowIndex++;
}
// Set column width
worksheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns();
// Set alignment
worksheet.AllocatedRange.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left;
// Set font style
worksheet.Range["A1:F1"].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
// Fit worksheet on one page
workbook.ConverterSetting.SheetFitToPage = true;
// Get the PageSetup object
PageSetup pageSetup = worksheet.PageSetup;
// Set page margins
pageSetup.TopMargin = 0.3;
pageSetup.BottomMargin = 0.3;
pageSetup.LeftMargin = 0.3;
pageSetup.RightMargin = 0.3;
// Preserve gridlines
pageSetup.IsPrintGridlines = true;
// Save the worksheet to a PDF file
worksheet.SaveToPdf("output/XmlToPdf.pdf");
// Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Efficiently integrating data between systems is vital for boosting productivity and informed decision-making. A common task in this area is transferring data between Excel and databases. Importing Excel files into a database enables businesses to utilize powerful features like efficient queries, transaction support, and concurrency control, which Excel lacks. Conversely, exporting database data to Excel allows for detailed analysis, reporting, and sharing in a widely used and familiar format. In this article, we will explore how to import Excel data into databases and export data from databases into Excel files using Spire.XLS for .NET with C#.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Import Excel Data into Databases with C#
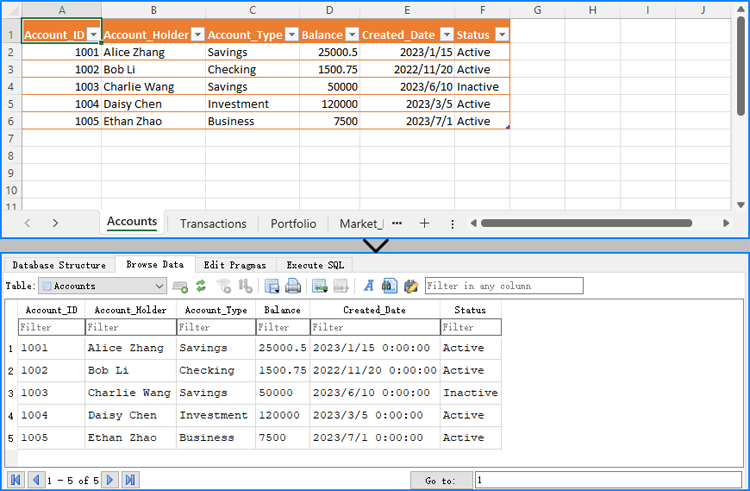
With the help of Spire.XLS for .NET, we can use the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method to load an Excel file and then access the cell data using CellRange.Value property. Subsequently, we can utilize the relevant database operation modules, such as the System.Data.SQLite module for SQLite, to write the data into the database. This approach enables the seamless import of data from an Excel file into a database.
The following steps and code use SQLite as an example to demonstrate how to import Excel data into a database using C#:
- Define the path for the Excel file and the output database.
- Create an instance of Workbook class and load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a new SQLite database or connect to an existing database.
- Iterate through each worksheet in the workbook and create a table in the database for each worksheet.
- Get the cells in the first row through Worksheet.Rows.CellList property.
- Iterate through the cells to get their values through CellRange.Value property, and use these values as the column names of the database table.
- Iterate through the rest rows and cells, and insert them as values into the database.
- Close the database connection and release resources.
- C#
using System.Data.SQLite;
using Spire.Xls;
namespace ExcelToSQLite
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Excel file path
string excelFilePath = "Sample.xlsx";
// SQLite database path
string sqliteFilePath = "output/Database.db";
// Open the Excel file
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile(excelFilePath);
// If the database file doesn't exist, create it
if (!File.Exists(sqliteFilePath))
{
SQLiteConnection.CreateFile(sqliteFilePath);
Console.WriteLine("A new SQLite database file has been created: output.db");
}
// Create SQLite connection
using (SQLiteConnection connection = new SQLiteConnection($"Data Source={sqliteFilePath};Version=3;"))
{
connection.Open();
// Iterate through each worksheet
foreach (Worksheet sheet in workbook.Worksheets)
{
string tableName = sheet.Name;
// Get the first row as column names
var columns = sheet.Rows[0].CellList;
string createTableQuery = $"CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS [{tableName}] (";
foreach (var column in columns)
{
createTableQuery += $"[{column.Value}] TEXT,";
}
createTableQuery = createTableQuery.TrimEnd(',') + ");";
// Create table
using (SQLiteCommand createTableCommand = new SQLiteCommand(createTableQuery, connection))
{
createTableCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
// Insert data
for (int i = 1; i < sheet.Rows.Length; i++) // Skip the first row
{
var row = sheet.Rows[i];
string insertQuery = $"INSERT INTO [{tableName}] VALUES (";
foreach (var cell in row.CellList)
{
insertQuery += $"'{cell.Value?.Replace("'", "''")}',"; // Prevent SQL injection
}
insertQuery = insertQuery.TrimEnd(',') + ");";
using (SQLiteCommand insertCommand = new SQLiteCommand(insertQuery, connection))
{
insertCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
}
connection.Close();
workbook.Dispose();
}
Console.WriteLine("Excel data has been successfully written to the new SQLite database!");
}
}
}
Export Data from Databases into Excel Files with C#
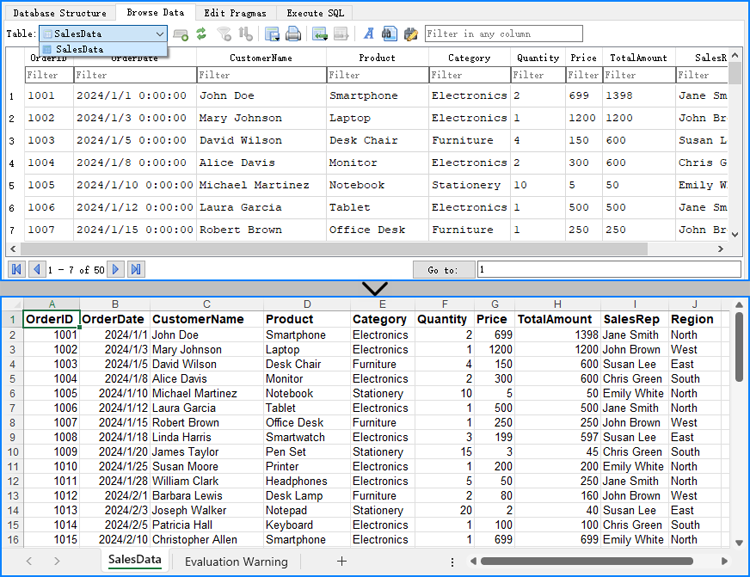
Similarly, we can use the database handling module to read data from the database. Then, by creating a Workbook object, we can generate an Excel file and use the CellRange.Value property to write the data into the Excel file. This allows us to export data from the database to an Excel file.
The following steps and code use an SQLite database as an example to demonstrate how to export data from a database to an Excel file.
- Define the path for the database and the output Excel file.
- Create a Workbook instance to create a new Excel workbook and clear the default worksheets using Workbook.Worksheets.Clear() method.
- Connect to the database and get all the table names.
- Create a worksheet for each table with the table names as sheet names using Workbook.Worksheets.Add() method.
- Get the column names in the tables and write them to the first row of the worksheet through Worksheet.Range[].Value property.
- Get the data in the table and write it to the worksheet sequentially through Worksheet.Range[].Value property.
- Format the worksheet through CellRange.Style property if needed.
- Close the database connection and save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using System.Data;
using System.Data.SQLite;
using Spire.Xls;
namespace SQLiteToExcel
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// SQLite database path
string sqliteFilePath = "Sample.db";
// Excel file path
string excelFilePath = "output/DatabaseToExcel.xlsx";
// Create a new Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Clear the default worksheet
workbook.Worksheets.Clear();
// Create SQLite connection
using (SQLiteConnection connection = new SQLiteConnection($"Data Source={sqliteFilePath};Version=3;"))
{
connection.Open();
// Get all table names
DataTable tables = connection.GetSchema("Tables");
// Iterate through each table
foreach (DataRow tableRow in tables.Rows)
{
string tableName = tableRow["TABLE_NAME"].ToString();
// Create a new worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add(tableName);
// Get table data
string selectQuery = $"SELECT * FROM [{tableName}]";
using (SQLiteCommand command = new SQLiteCommand(selectQuery, connection))
{
using (SQLiteDataReader reader = command.ExecuteReader())
{
// Get column names and write them in the first row
for (int col = 0; col < reader.FieldCount; col++)
{
sheet.Range[1, col + 1].Value = reader.GetName(col);
}
// Set the font style for the header
sheet.Rows[0].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
sheet.Rows[0].Style.Font.Size = 12;
// Write data rows
int rowIndex = 2;
while (reader.Read())
{
for (int col = 0; col < reader.FieldCount; col++)
{
sheet.Range[rowIndex, col + 1].Value = reader.GetValue(col).ToString();
// Auto-fit column width
sheet.AutoFitColumn(col + 1);
}
// Set the font style for data rows
sheet.Rows[rowIndex - 1].Style.Font.Size = 11;
rowIndex++;
}
}
}
}
connection.Close();
}
// Save the Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile(excelFilePath);
workbook.Dispose();
Console.WriteLine("Data has been successfully exported to the Excel file!");
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
How to Integrate Spire.Doc for JavaScript in a Node.js Project
2024-12-09 08:31:04 Written by KoohjiDocument processing is an essential feature in many modern web applications, enabling tasks such as report generation and data management. Node.js, known for its non-blocking I/O model and extensive ecosystem, provides a powerful platform for backend development. By integrating Spire.Doc for JavaScript, you can streamline the creation and manipulation of Word documents effortlessly.
This guide will take you through the steps to integrate Spire.Doc for JavaScript into your Node.js projects, from initial setup to a basic usage example.
- Benefits of Using Spire.Doc for JavaScript in Node.js Projects
- Set Up Your Environment
- Integrate Spire.Doc for JavaScript in Your Project
- Create and Save Word Files Using JavaScript
Benefits of Using Spire.Doc for JavaScript in Node.js Projects
Node.js is a powerful runtime environment that allows developers to build scalable network applications using JavaScript. Spire.Doc for JavaScript, on the other hand, is a versatile library designed to manipulate Word documents within JavaScript environments. It provides a wide range of features, including document creation, editing, conversion, and more, making it a valuable tool for developers working with document-based applications.
Integrating Spire.Doc for JavaScript into your Node.js project offers numerous benefits, including:
- Efficient Document Management: Easily create, edit, and manage Word documents without the need for Microsoft Word.
- Scalability: Leverage Node.js's non-blocking I/O model to handle large volumes of document processing tasks efficiently.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Use Spire.Doc for JavaScript across various platforms, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Ease of Integration: Seamlessly integrate Spire.Doc for JavaScript with other Node.js libraries and tools.
These benefits make Spire.Doc for JavaScript an ideal choice for developers looking to enhance their Node.js projects with robust document processing capabilities.
Set Up Your Environment
Step 1
Download and install Node.js from the official website. Make sure to choose the version that matches your operating system.
After the installation is complete, you can verify that Node.js and npm are installed correctly, along with the version numbers, by entering the following commands in CMD:
node -v npm -v
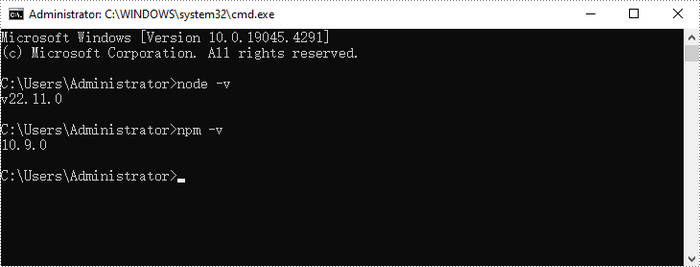
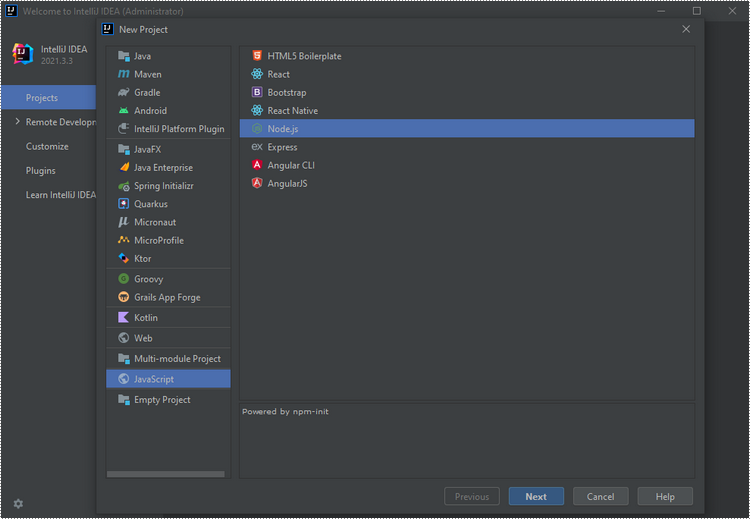
Step 2
Create a Node.js project in your IntelliJ IDEA.
Install Jest in your project to write and run tests for your code, by running the following command in Terminal:
npm install --save-dev jest
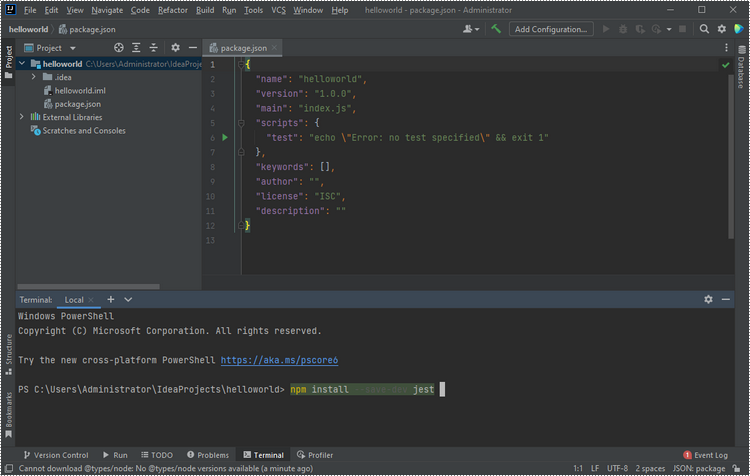
Create a JavaScript file named "jest.config.js" in your project, and include the following configuration in it.
module.exports = {
testTimeout: 20000,
testEnvironment: 'node',
transform: {},
testMatch: ['<rootDir>/*.js'],
moduleFileExtensions: [ 'json', 'node', 'tsx', 'ts', 'js', 'jsx','mjs'],
};
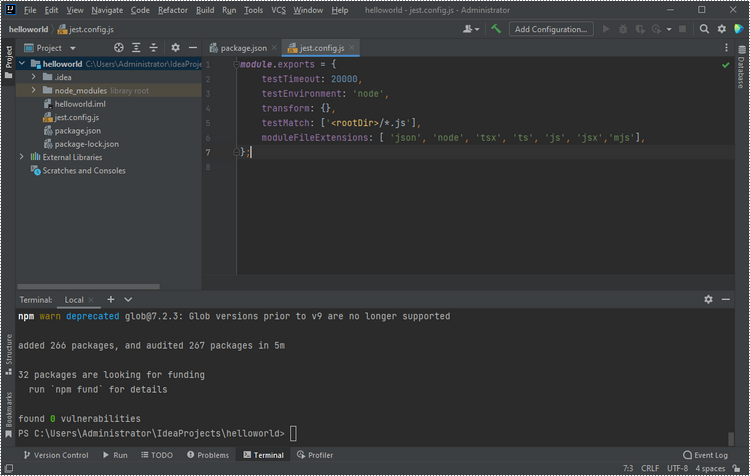
Add a "fonts" folder and a "lib" folder to your project.
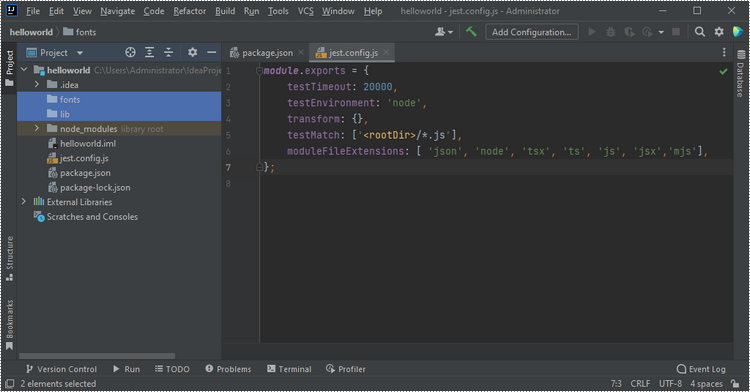
Integrate Spire.Doc for JavaScript in Your Project
Download Spire.Doc for JavaScript and unzip it to a location on your disk. Inside the lib folder, you will find the Spire.Doc.Base.js and Spire.Doc.Base.wasm files.
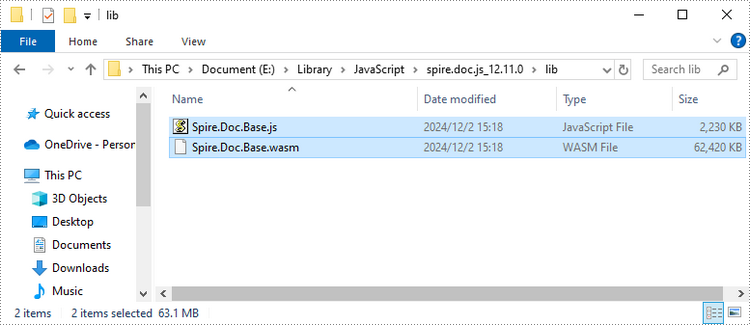
Copy these two files into the "lib" folder in your Node.js project.
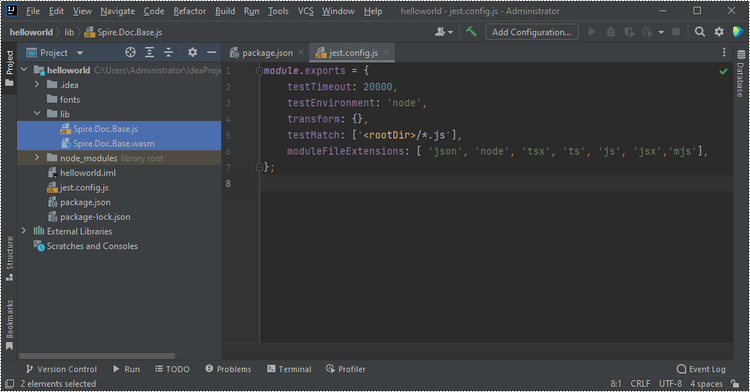
Place the font files you plan to use into the "fonts" folder in your project.
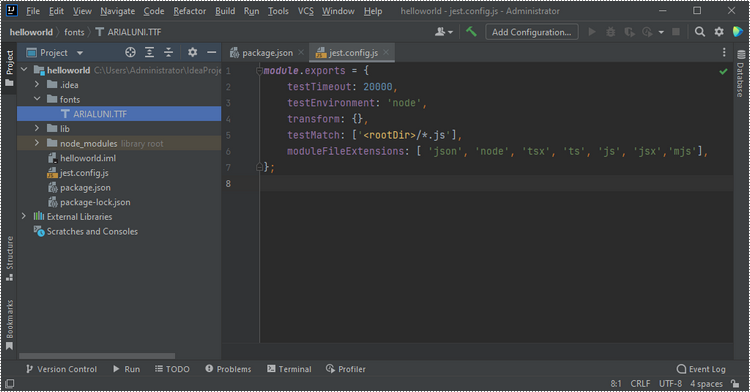
Create and Save Word Files Using JavaScript
Add a JavaScript file in your project to generate a simple Word document from JavaScript code.
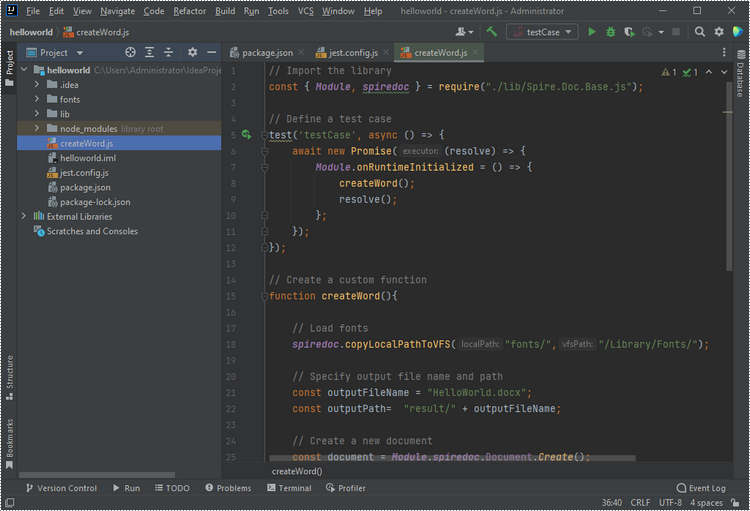
Here is the entire JavaScript code:
- JavaScript
// Import the library
const { Module, spiredoc } = require("./lib/Spire.Doc.Base.js");
// Define a test case
test('testCase', async () => {
await new Promise((resolve) => {
Module.onRuntimeInitialized = () => {
createWord();
resolve();
};
});
});
// Create a custom function
function createWord(){
// Load fonts
spiredoc.copyLocalPathToVFS("fonts/","/Library/Fonts/");
// Specify output file name and path
const outputFileName = "HelloWorld.docx";
const outputPath= "result/" + outputFileName;
// Create a new document
const document = Module.spiredoc.Document.Create();
// Add a section
let section = document.AddSection();
// Add a paragraph
let paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
// Append text to the paragraph
paragraph.AppendText("Hello, World!");
// Save the document to a Word file
document.SaveToFile({fileName: outputFileName, fileFormat: spiredoc.FileFormat.Docx2013,
});
spiredoc.copyFileFromFSToLocalStorage(outputFileName, outputPath);
// Dispose resources
document.Dispose();
}
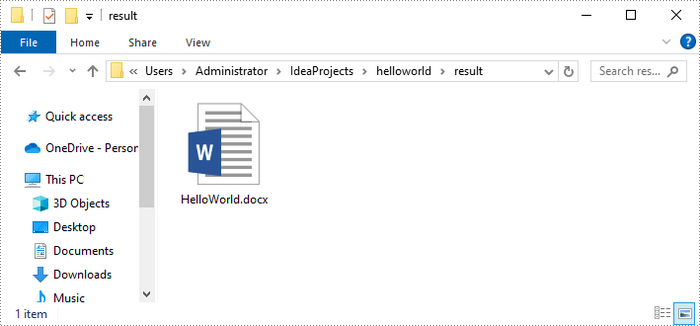
Once you run the code, you will find the generated Word file in the designated file path.
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
