
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Spire.Doc for JavaScript is an independent Word API that allows developers to integrate Microsoft Word document creation capabilities into their JavaScript applications, without installing Microsoft Word on either development or target systems.
It is a trustworthy MS Word API for JavaScript that can apply multiple Word document processing tasks. Spire.Doc for JavaScript supports Word 97-2003 /2007/2010/2013/2016/2019, and it has the capability of converting them to other common formats, like XML, RTF, TXT, EMF, HTML, ODT, Markdown, and vice versa. Moreover, it supports converting Word Doc/Docx to PDF, images (PNG, JPEG), PostScript, OFD, XPS, EPUB, PCL (Printer Command Language), and RTF to PDF/HTML, HTML to PDF/Image, Markdown to PDF in high quality.
In Excel, copying rows, columns, and cells is a fundamental operation that allows users to replicate data efficiently across different parts of a worksheet or between multiple worksheets. Understanding how to programmatically copy rows, columns, and cells in Excel can significantly streamline your data manipulation tasks, especially when working with large datasets or automating repetitive tasks. In this article, you will learn how to copy rows, columns and cells in Excel with formatting in Java using Spire.XLS for Java.
- Copy Rows in Excel with Formatting in Java
- Copy Columns in Excel with Formatting in Java
- Copy Cells in Excel with Formatting in Java
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Copy Rows in Excel with Formatting in Java
The Worksheet.copyRow(CellRange sourceRow, Worksheet destSheet, int destRowIndex, EnumSet<CopyRangeOptions> copyOptions) method in Spire.XLS for Java is used to duplicate rows either within the same worksheet or across different worksheets. The CopyRangeOptions parameter in this method gives developers the ability to control what aspects of the row are copied, such as all flags, conditional formatting, data validations, or just the formula values.
The following steps demonstrate how to copy rows with formatting between different worksheets using Spire.XLS for Java.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get the source worksheet and the destination worksheet using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get(index) method.
- Get the desired row that you want to copy using the Worksheet.getRows()[index] method.
- Copy the row and its formatting from the source worksheet to the destination worksheet using the Worksheet.copyRow(CellRange sourceRow, Worksheet destSheet, int destRowIndex, EnumSet<CopyRangeOptions> copyOptions) method.
- Copy the column widths of cells in the source row to the corresponding cells in the destination row.
- Save the workbook to a file using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
import java.util.EnumSet;
public class CopyRows {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("ContactList.xlsx");
// Get the source worksheet
Worksheet sheet1 = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get the destination worksheet
Worksheet sheet2 = workbook.getWorksheets().get(1);
// Get the desired row that you want to copy
CellRange row = sheet1.getRows()[0];
// Copy the row from the source worksheet to the first row of the destination worksheet
sheet1.copyRow(row, sheet2, 1, EnumSet.of(CopyRangeOptions.All));
int columns = sheet1.getColumns().length;
// Copy the column widths of the cells in the source row to the corresponding cells in the destination row
for (int i = 0; i < columns; i++)
{
double columnWidth = row.getColumns()[i].getColumnWidth();
sheet2.getRows()[0].getColumns()[i].setColumnWidth(columnWidth);
}
// Save the workbook to a file
workbook.saveToFile("CopyRow.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.dispose();
}
}
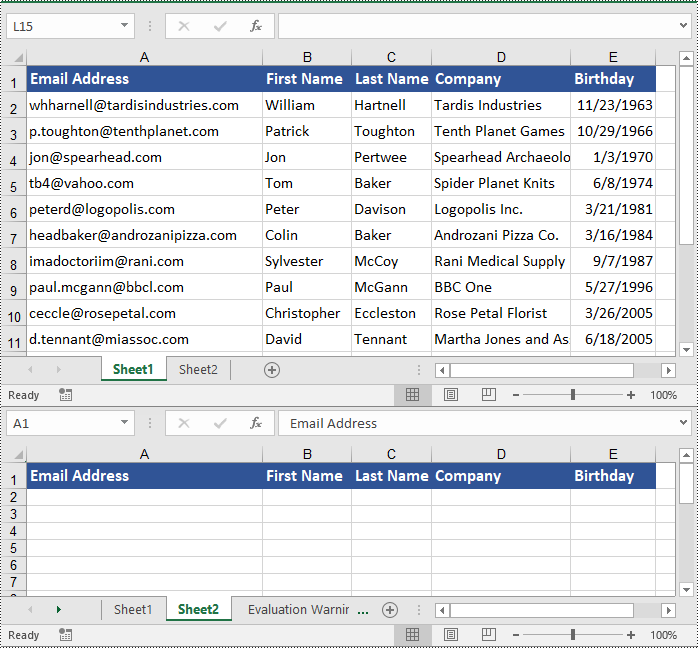
Copy Columns in Excel with Formatting in Java
To copy columns in Excel while preserving their formatting, use the Worksheet.copyColumn(CellRange sourceColumn, Worksheet destSheet, int destColIndex, EnumSet<CopyRangeOptions> copyOptions) method. The detailed steps are outlined below.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get the source worksheet and the destination worksheet using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get(index) method.
- Get the desired column that you want to copy using the Worksheet.getColumns()[index] method.
- Copy the column and its formatting from the source worksheet to the destination worksheet using the Worksheet.copyColumn(CellRange sourceColumn, Worksheet destSheet, int destColIndex, EnumSet<CopyRangeOptions> copyOptions) method.
- Copy the row heights of cells in the source column to the corresponding cells in the destination column.
- Save the workbook to a file using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
import java.util.EnumSet;
public class CopyColumns {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("ContactList.xlsx");
// Get the source worksheet
Worksheet sheet1 = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get the destination worksheet
Worksheet sheet2 = workbook.getWorksheets().get(1);
// Get the desired column that you want to copy
CellRange column = sheet1.getColumns()[0];
// Copy the column from the source worksheet to the first column of the destination worksheet
sheet1.copyColumn(column, sheet2, 1, EnumSet.of(CopyRangeOptions.All));
int rows = column.getRows().length;
// Copy the row heights of cells in the source column to the corresponding cells in the destination column
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
double rowHeight = column.getRows()[i].getRowHeight();
sheet2.getColumns()[0].getRows()[i].setRowHeight(rowHeight);
}
// Save the workbook to a file
workbook.saveToFile("CopyColumn.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.dispose();
}
}

Copy Cells in Excel with Formatting in Java
Spire.XLS for Java also allows developers to copy cell ranges with formatting using the CellRange.copy(CellRange destRange, EnumSet<CopyRangeOptions> copyOptions) method. The detailed steps are provided below.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get the source worksheet and the destination worksheet using the Workbook.getWorksheets().get(index) method.
- Get the source cell range and the destination cell range using the Worksheet.getCellRange() method.
- Copy the source cell range and its formatting from the source worksheet to the destination cell range in the destination worksheet using the CellRange.copy(CellRange destRange, EnumSet<CopyRangeOptions> copyOptions) method.
- Copy the row heights and column widths of the source cell range to the destination cell range.
- Save the workbook to a file using the Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
import java.util.EnumSet;
public class CopyCells {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel file
workbook.loadFromFile("ContactList.xlsx");
// Get the source worksheet
Worksheet sheet1 = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Get the destination worksheet
Worksheet sheet2 = workbook.getWorksheets().get(1);
// Get the source cell range
CellRange range1 = sheet1.getCellRange("A1:E7");
// Get the destination cell range
CellRange range2 = sheet2.getCellRange("A1:E7");
// Copy the source cell range from the source worksheet to the destination cell range in the destination worksheet
range1.copy(range2, EnumSet.of(CopyRangeOptions.All));
// Copy the row heights and column widths of the source cell range to the destination cell range
for (int i = 0; i < range1.getRows().length; i++)
{
CellRange row = range1.getRows()[i];
for (int j = 0; j < row.getColumns().length; j++)
{
CellRange column = row.getColumns()[j];
range2.getRows()[i].getColumns()[j].setColumnWidth(column.getColumnWidth());
range2.getRows()[i].setRowHeight(row.getRowHeight());
}
}
// Save the workbook to a file
workbook.saveToFile("CopyCells.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Add, Extract and Remove Custom Document Properties in Word Documents
2024-12-23 01:00:11 Written by AdministratorCustom document properties are user-defined fields within a Word document that store specific metadata. Unlike standard properties, such as title, author, or subject, which are predefined by Microsoft Word, these custom properties provide users with the flexibility to define and manage additional metadata fields according to their specific requirements. In this article, we will demonstrate how to add, extract, and remove custom document properties in Word documents in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Add Custom Document Properties to Word in Python
- Extract Custom Document Properties in Word in Python
- Remove Custom Document Properties from Word in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Add Custom Document Properties to Word in Python
Spire.Doc for Python provides the CustomDocumentProperties.Add() method, which enables developers to assign different types of values, such as text, time, numeric, or yes or no, to the custom properties of a Word document. The steps below demonstrate how to add custom document properties with different types of values to a Word document using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Initialize an instance of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the custom document properties of the document through the Document.CustomDocumentProperties property.
- Add custom document properties with different data types to the document using the CustomDocumentProperties.Add(name, value) method.
- Save the result document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Example.docx")
# Add custom document properties with different types of values to the document
customProperties = document.CustomDocumentProperties
customProperties.Add("DocumentCategory", String("Technical Report"))
customProperties.Add("RevisionNumber", Int32(5))
customProperties.Add("LastReviewedDate", DateTime(2024, 12, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0))
customProperties.Add("RequiresFollowUp", Boolean(False))
# Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("AddCustomDocumentProperties.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()

Extract Custom Document Properties in Word in Python
Extracting custom document properties allows developers to access metadata for further analysis, reporting, or integration into other applications. Spire.Doc for Python makes it simple to retrieve the details of these properties using the CustomDocumentProperty.Name and CustomDocumentProperty.Value properties. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Initialize an instance of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the custom document properties of the document through the Document.CustomDocumentProperties property.
- Iterate through the custom document properties.
- Extract the name and value of each custom document property.
- Save the extracted data to a text file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("AddCustomDocumentProperties.docx")
# Open a text file to save the extracted custom properties
with open("ExtractedCustomProperties.txt", "w") as output_file:
# Iterate through all custom document properties
for i in range(document.CustomDocumentProperties.Count):
# Extract the name and value of each custom property
property_name = document.CustomDocumentProperties.get_Item(i).Name
property_value = document.CustomDocumentProperties.get_Item(i).Value
# Write the property details to the text file
output_file.write(f"{property_name}: {property_value}\n")
document.Close()
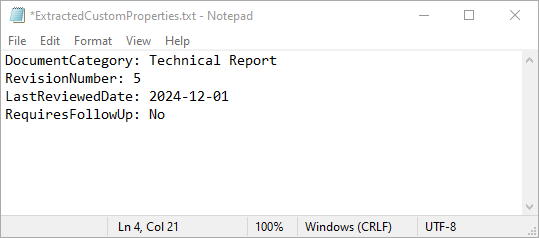
Remove Custom Document Properties from Word in Python
Cleaning up custom document properties is crucial for maintaining confidentiality, reducing file size, and ensuring metadata does not contain outdated or irrelevant information. Spire.Doc for Python allows developers to remove custom properties from a Word document using the DocumentProperties.Remove() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Initialize an instance of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the custom document properties of the document through the Document.CustomDocumentProperties property.
- Iterate through the custom document properties.
- Remove each custom document property through its name using the DocumentProperties.Remove() method.
- Save the result document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("AddCustomDocumentProperties.docx")
# Iterate through all custom document properties
customProperties = document.CustomDocumentProperties
for i in range(customProperties.Count - 1, -1, -1):
# Remove each custom document property by its name
customProperties.Remove(customProperties[i].Name)
# Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("RemoveCustomDocumentProperties.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.



