
Python (355)
SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) is an XML-based vector image format that describes two-dimensional graphics using geometric shapes, text, and other graphical elements. SVG files can be easily scaled without losing image quality, which makes them ideal for various purposes such as web design, illustrations, and animations. In certain situations, you may encounter the need to convert PDF files to SVG format. In this article, we will explain how to convert PDF to SVG in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Convert a PDF File to SVG in Python
- Convert a PDF File to SVG with Custom Width and Height in Python
- Convert Specific Pages of a PDF File to SVG in Python
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Convert a PDF File to SVG in Python
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename:str, fileFormat:FileFormat) method to convert each page of a PDF file to a separate SVG file. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load a sample PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Convert each page of the PDF file to SVG using PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename:str, fileFormat:FileFormat) method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create an object of the PdfDocument class
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Save each page of the file to a separate SVG file
doc.SaveToFile("PdfToSVG/ToSVG.svg", FileFormat.SVG)
# Close the PdfDocument object
doc.Close()
Convert a PDF File to SVG with Custom Width and Height in Python
The PdfDocument.PdfConvertOptions.SetPdfToSvgOptions(wPixel:float, hPixel:float) method provided by Spire.PDF for Python allows you to specify the width and height of the SVG files converted from PDF. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load a sample PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Specify the width and height of the output SVG files using PdfDocument.PdfConvertOptions.SetPdfToSvgOptions(wPixel:float, hPixel:float) method.
- Convert each page of the PDF file to SVG using PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename:str, fileFormat:FileFormat) method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create an object of the PdfDocument class
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Specify the width and height of output SVG files
doc.ConvertOptions.SetPdfToSvgOptions(800.0, 1200.0)
# Save each page of the file to a separate SVG file
doc.SaveToFile("PdfToSVGWithCustomWidthAndHeight/ToSVG.svg", FileFormat.SVG)
# Close the PdfDocument object
doc.Close()
Convert Specific Pages of a PDF File to SVG in Python
The PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename:str, startIndex:int, endIndex:int, fileFormat:FileFormat) method provided by Spire.PDF for Python allows you to convert specific pages of a PDF file to SVG files. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load a sample PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Convert specific pages of the PDF file to SVG using PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename:str, startIndex:int, endIndex:int, fileFormat:FileFormat) method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create an object of the PdfDocument class
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Save specific pages of the file to SVG files
doc.SaveToFile("PdfPagesToSVG/ToSVG.svg", 1, 2, FileFormat.SVG)
# Close the PdfDocument object
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Add, Replace, or Remove Images in a PDF Document
2023-10-17 00:46:55 Written by AdministratorAlongside textual content, images in a PDF play a crucial role in conveying messages effectively. Being able to manipulate images within a PDF document, such as adding, replacing, or removing them, can be incredibly useful for enhancing the visual appeal, updating outdated graphics, or modifying the document's content. In this article, you will learn how to add, replace, or delete images in a PDF document in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Add an Image to a PDF Document in Python
- Replace an Image in a PDF Document in Python
- Remove an Image from a PDF Document in Python
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Add an Image to a PDF Document in Python
To add an image to a PDF page, you can use the PdfPage.Canvas.DrawImage() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Add a page to the document using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Load an image using PdfImage.FromFile() method.
- Draw the image on the page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawImage() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Set the page margins
doc.PageSettings.SetMargins(30.0, 30.0, 30.0, 30.0)
# Add a page
page = doc.Pages.Add()
# Load an image
image = PdfImage.FromFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/logo.png')
# Specify the size of the image in the document
width = image.Width * 0.70
height = image.Height * 0.70
# Specify the X and Y coordinates where the image will be drawn
x = 10.0
y = 30.0
# Draw the image at a specified location on the page
page.Canvas.DrawImage(image, x, y, width, height)
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("output/AddImage.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
Replace an Image in a PDF Document in Python
Spire.PDF for Python offers the PdfImageHelper class to help us get and deal with the images in a certain page. To replace an image with a new one, you can use the PdfImageHelper.ReplaceImage() method. The following are the steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific page through PdfDocument.Pages[index] property.
- Load an image using PdfImage.FromFile() method.
- Create a PdfImageHelper object, and get the image information from the specified page using PdfImageHelper.GetImagesInfo() method.
- Replace an existing image in the page with the new image using PdfImageHelper.ReplaceImage() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/input.pdf')
# Get the first page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Load an image
image = PdfImage.FromFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/newImage.png')
# Create a PdfImageHelper instance
imageHelper = PdfImageHelper()
# Get the image information from the page
imageInfo = imageHelper.GetImagesInfo(page)
# Replace the first image on the page with the loaded image
imageHelper.ReplaceImage(imageInfo[0], image)
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("output/ReplaceImage.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
Remove an Image from a PDF Document in Python
To remove a specific image from a page, use the PdfPageBase.DeleteImage(index) method. The following are the steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific page through PdfDocument.Pages[index] property.
- Delete a certain image in the page by its index using PdfPageBase.DeleteImage() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/input.pdf')
# Get the first page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Delete the first image on the page
page.DeleteImage(0)
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile('output/DeleteImage.pdf', FileFormat.PDF)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Modifying the font in a Word document can significantly impact its visual appearance and overall readability. Whether you want to enhance the document's style or align it with specific formatting requirements, changing the font is a straightforward process that allows you to customize your text. In this article, you will learn how to change font of a paragraph or a piece of text in a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Change the Font of a Paragraph in Python
Using Spire.Doc for Python, you can create a ParagraphStyle object which defines the font information that can be applied to a certain paragraph. The following are the steps to change the font of a paragraph.
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section through Document.Sections[index] property.
- Get a specified paragraph that you want to change the font through Section.Paragraphs[index] property.
- Create a ParagraphStyle instance, specifying the font name, font color and font style through the properties under it.
- Add the style to the document using Document.Styles.Add() method.
- Apply the style to the paragraph using Paragraph.ApplyStyle() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/input.docx')
# Get the first section
section = document.Sections[0]
# Get a specific paragraph
paragraph = section.Paragraphs[2]
# Create a paragraph style
style = ParagraphStyle(document)
style.Name = 'NewStyle'
style.CharacterFormat.Bold = True
style.CharacterFormat.Italic = True
style.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Red()
style.CharacterFormat.FontName = 'Cambria'
document.Styles.Add(style)
# Apply the style to the paragraph
paragraph.ApplyStyle(style.Name)
# Save the result document
document.SaveToFile('output/ChangeFontOfParagraph.docx', FileFormat.Docx)
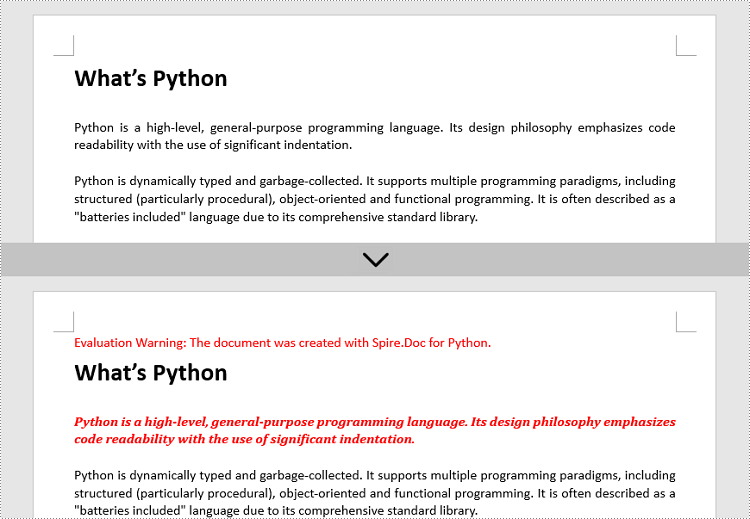
Change the Font of Specific Text in Python
To change the font of specific text (letter, phrase or sentence) in a Word document, you need first to find the text from the document and then set a different color or font style for it. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Find the text that you want to change font color using Document.FindAllString() method.
- Loop through all occurrences of the searched text and change the font color or style for each occurrence through the properties under TextSelection.GetAsOneRange().CharacterFormat object.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/input.docx')
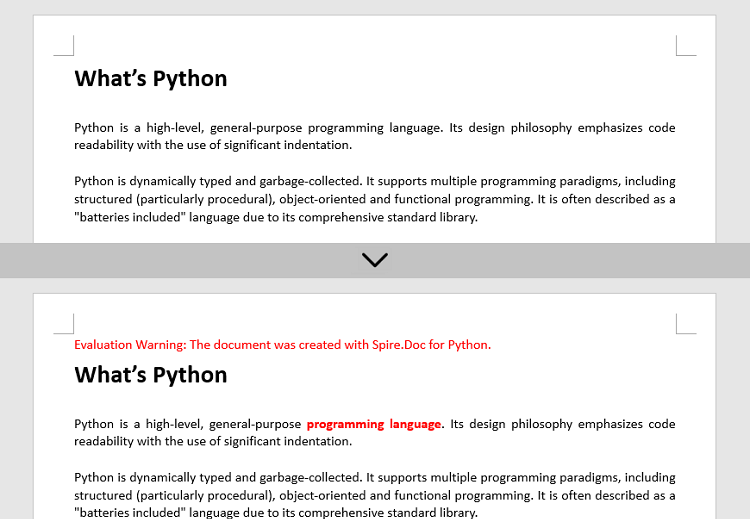
# Find the text that you want to change font
textSelections = document.FindAllString('programming language', False, True)
# Change the font style of the text
for selection in textSelections:
selection.GetAsOneRange().CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Red()
selection.GetAsOneRange().CharacterFormat.Bold = True
# Save the result document
document.SaveToFile('output/ChangeFontOfText.docx', FileFormat.Docx)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
A workbook can consist of one or more worksheets, and each worksheet is independent. When dealing with an existing Excel file or creating a new Excel file from scratch, we can add worksheets as needed to better manage and analyze data. In this article, we will show you how to add worksheets to Excel programmatically by using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Add a Worksheet to an Existing Excel file
- Add a Worksheet to a New Excel file
- Add Multiple Worksheets to a New Excel file
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Add a Worksheet to an Existing Excel file
Spire.XLS for Python allows users to add a new worksheet to an existing Excel file by using Workbook.Worksheets.Add(sheetName) method. The following are detailed steps.
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
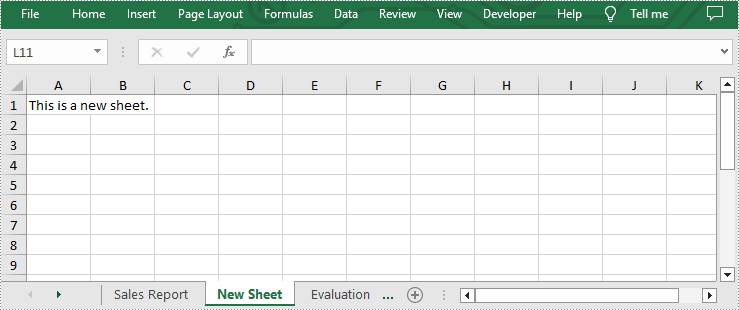
- Add a new sheet to this file using Workbook.Worksheets.Add(sheetName) method.
- Add desired text to cell A1 by Worksheet.Range[cellName].Text property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
inputFile = "sample.xlsx"
outputFile = "AddWorksheet.xlsx"
#Create an object of Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
#Load an Excel file from disk
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
#Add a new worksheet to this file
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("New Sheet")
#Add desired text to cell A1
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "This is a new sheet."
#Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Add a Worksheet to a New Excel file
In addition to adding worksheets to existing Excel files, you can also add worksheets to a newly created Excel files with the same method. You just need to clear the default worksheet before adding by calling Workbook.Worksheets.Clear() method. The following are detailed steps.
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Clear the default worksheets using Workbook.Worksheets.Clear() method.
- Add a new sheet to the new workbook by using Workbook.Worksheets.Add(sheetName) method.
- Add desired text to cell A1 by Worksheet.Range[cellName].Text property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
outputFile = "AddWorksheet.xlsx"
#Create an object of Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
#Clear the default sheets
workbook.Worksheets.Clear()
#Add a new worksheet to the new file
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("New Sheet")
#Add desired text to cell A1
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "This is a new sheet."
#Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
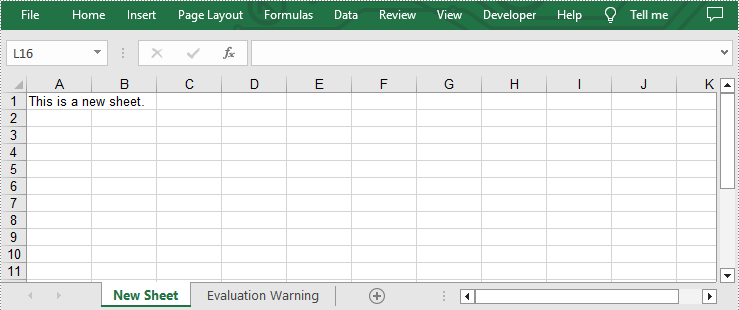
Add Multiple Worksheets to a New Excel file
If you want to add multiple worksheets to a newly created Excel file, you can use Workbook.CreateEmptySheets(sheetCount) method to add a specified number of worksheets. The following are detailed steps.
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Add three sheets to this file by using Workbook.CreateEmptySheets(sheetCount) method.
- Loop through the added worksheets and add text to cell A1 in each worksheet by Worksheet.Range[cellName].Text property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
outputFile = "AddWorksheet.xlsx"
#Create an object of Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
#Add three sheets to this file
sheetCount = 3
workbook.CreateEmptySheets(sheetCount)
#Loop through the added worksheets
for i in range(sheetCount):
#Add text to cell A1 in each worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[i]
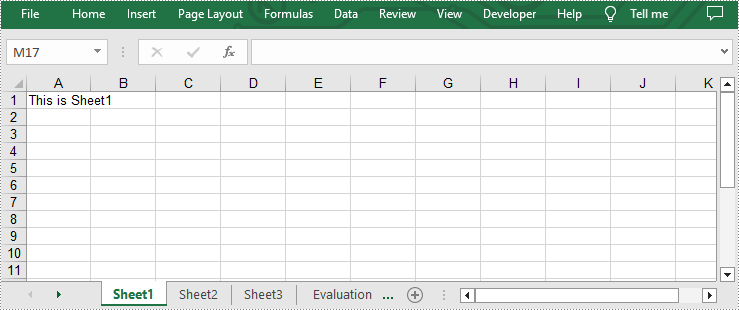
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "This is Sheet{}".format(i+1)
#Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Hiding and showing slides are two practical features in PowerPoint that allow you to control the visibility of slides during a slideshow. Hiding slides is useful when you want to skip certain slides or temporarily remove them from the presentation without deleting them. Whereas showing slides is helpful when you want to re-display the hidden slides. In this article, we will demonstrate how to hide and show slides in a PowerPoint presentation in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Hide a Specific Slide in PowerPoint in Python
- Show a Hidden Slide in PowerPoint in Python
- Show All Hidden Slides in PowerPoint in Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Hide a Specific Slide in PowerPoint in Python
Spire.Presentation for Python provides the ISlide.Hidden property to control the visibility of a slide during a slideshow. If you don’t want a certain slide to be shown, you can hide this slide by setting the ISlide.Hidden property as True. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific slide using Presentation.Slides[index] property.
- Hide the slide by setting the ISlide.Hidden property as True.
- Save the resulting presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
ppt.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Get the second slide and hide it
slide = ppt.Slides[1]
slide.Hidden = True
# Save the resulting presentation to a new .pptx file
ppt.SaveToFile("HideSlide.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
ppt.Dispose()
Show a Hidden Slide in PowerPoint in Python
To show a hidden slide, you can set the ISlide.Hidden property as False. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific slide using Presentation.Slides[index] property.
- Unhide the slide by setting the ISlide.Hidden property as False.
- Save the resulting presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
ppt.LoadFromFile("HideSlide.pptx")
# Get the second slide and unhide it
slide = ppt.Slides[1]
slide.Hidden = False
# Save the resulting presentation to a new .pptx file
ppt.SaveToFile("ShowSlide.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
ppt.Dispose()
Show All Hidden Slides in PowerPoint in Python
To show all hidden slides in a PowerPoint presentation, you need to loop through all the slides in the presentation, then find the hidden slides and unhide them by setting the ISlide.Hidden property as False. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Loop through the slides in the presentation.
- Check whether the current slide is hidden or not using ISlide.Hidden property. If the result is true, unhide the slide by setting the ISlide.Hidden property as False.
- Save the resulting presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
ppt.LoadFromFile("Sample2.pptx")
# Loop through each slide in the presentation
for i in range(ppt.Slides.Count):
slide = ppt.Slides[i]
# Check if the slide is hidden
if(slide.Hidden):
# Unhide the slide
slide.Hidden = False
# Save the resulting presentation to a new .pptx file
ppt.SaveToFile("ShowAllHidenSlides.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
ppt.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.

Converting Word documents (DOCX or DOC) to HTML format is essential when you want to display formatted content on web pages, import legacy documents into content management systems, or generate web previews for DOCX files. HTML’s universal browser compatibility makes it an ideal format for sharing content online.
This guide shows how to convert Word to HTML in Python using Spire.Doc for Python. It covers both basic and advanced conversion techniques with practical examples, helping you handle diverse conversion needs.
Table of Contents
- Why Convert Word to HTML
- Install Word to HTML Converter in Python
- How to Convert Word to HTML Using Python
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Why Convert Word to HTML?
Here are some typical scenarios where converting Word to HTML is beneficial:
- Web publishing: Display Word content in a browser without requiring users to download the document.
- CMS integration: Import Word-based articles into a web-based content system.
- Content preview: Generate HTML previews for Word attachments or document archives.
- Email rendering: Convert DOCX content into HTML-friendly formats for email templates.
Install Word to HTML Converter in Python
Spire.Doc for Python is a professional library designed for Word document processing and conversion. It provides a reliable way to export Word documents to HTML while preserving accurate formatting and layout. 
Benefits of Using Spire.Doc for Word-to-HTML Conversion
- Accurate formatting: Preserves fonts, colors, styles, tables, and images.
- No Office dependency: Does not require Microsoft Word or Office Interop.
- Supports DOCX and DOC: Compatible with both modern and legacy Word formats.
- Customizable output: Fine-tune HTML export settings, including image embedding and CSS styling.
Installation
Install the library from PyPI using the following command:
pip install spire.doc
Need help with the installation? Check this step-by-step guide: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows.
How to Convert Word to HTML Using Python
This section demonstrates how to convert Word documents to HTML using Spire.Doc for Python. First, you'll see a quick example using default settings for fast export. Then, you'll learn how to customize the HTML output with advanced options.
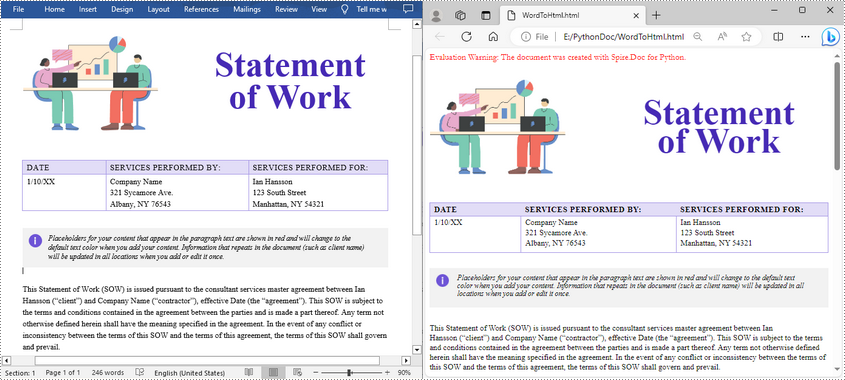
Quick Conversion with Default Settings
The following code snippet shows how to save a Word document to HTML format using the default export settings. It’s suitable for simple use cases where no customization is needed.
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Load a doc or docx document
document.LoadFromFile("Statement.docx")
# Save the document to HTML format
document.SaveToFile("WordToHtml.html", FileFormat.Html)
document.Close()
Advanced Conversion Options
You can customize the HTML export to suit your needs by configuring options such as including headers and footers, linking to an external CSS stylesheet, choosing whether to embed images or save them separately, and exporting form fields as plain text. The example below shows how to set these options.
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Load a .docx or .doc document
document.LoadFromFile("Statement.docx")
# Control whether to include headers and footers in the exported HTML
document.HtmlExportOptions.HasHeadersFooters = False
# Specify the name of the CSS file to use for styling the exported HTML
document.HtmlExportOptions.CssStyleSheetFileName = "sample.css"
# Set the CSS stylesheet type to external, so the HTML file links to the specified CSS file instead of embedding styles inline
document.HtmlExportOptions.CssStyleSheetType = CssStyleSheetType.External
# Configure image export: do not embed images inside HTML, save them to a separate folder
document.HtmlExportOptions.ImageEmbedded = False
document.HtmlExportOptions.ImagesPath = "Images/"
# Export form fields as plain text instead of interactive form elements
document.HtmlExportOptions.IsTextInputFormFieldAsText = True
# Save the document as an HTML file
document.SaveToFile("ToHtmlExportOption.html", FileFormat.Html)
document.Close()
Conclusion
Spire.Doc for Python delivers high-fidelity Word-to-HTML conversions without requiring Microsoft Word. Whether for quick exports or customized HTML output, it provides a versatile, dependable solution.
Beyond HTML conversion, Spire.Doc supports a wide range of Word automation tasks such as document merging, text replacement, and PDF conversion, empowering developers to build robust document processing pipelines. To explore these capabilities further, check out the full Python Word programming guide and start enhancing your document workflows today.
FAQs
Q1: Can Spire.Doc convert both DOC and DOCX files to HTML?
A1: Yes, it supports exporting both legacy DOC and modern DOCX formats.
Q2: Is Microsoft Word required for conversion?
A2: No, Spire.Doc works independently without needing Microsoft Word or Office Interop.
Q3: Can images be embedded directly in the HTML instead of saved separately?
A3: Yes, you can embed images directly into the HTML output by setting ImageEmbedded to True. This ensures that all images are included within the HTML file itself, without creating separate image files or folders.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Adding and deleting slides in PowerPoint are essential actions that allow presenters to control the structure and content of their presentations. Adding slides provides the opportunity to expand and enhance the presentation by introducing new topics or providing supporting information. On the other hand, deleting slides helps streamline the presentation by removing redundant, repetitive, or irrelevant content. In this article, we will demonstrate how to add or delete slides in a PowerPoint Presentation in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Add a New Slide at the End of the PowerPoint Document in Python
- Insert a New Slide Before a Specific Slide in PowerPoint in Python
- Delete a Specific Slide from a PowerPoint Document in Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Add a New Slide at the End of the PowerPoint Document in Python
Spire.Presentation for Python provides the Presentation.Slides.Append() method to add a new slide after the last slide of a PowerPoint presentation. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add a new blank slide at the end of the presentation using Presentation.Slides.Append() method.
- Save the result presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Add a new slide at the end of the presentation
presentation.Slides.Append()
# Save the result presentation to a .pptx file
presentation.SaveToFile("AddSlide.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
presentation.Dispose()
Insert a New Slide Before a Specific Slide in PowerPoint in Python
You can use the Presentation.Slides.Insert() method to insert a new slide before a specific slide of a PowerPoint presentation. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Insert a blank slide before a specific slide using Presentation.Slides.Insert() method.
- Save the result presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Insert a blank slide before the second slide
presentation.Slides.Insert(1)
# Save the result presentation to a .pptx file
presentation.SaveToFile("InsertSlide.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
presentation.Dispose()
Delete a Specific Slide from a PowerPoint Document in Python
To delete a specific slide from a PowerPoint presentation, you can use the Presentation.Slides.RemoveAt() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove a specific slide from the presentation using Presentation.Slides.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the result presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Remove the first slide
presentation.Slides.RemoveAt(0)
# Save the result presentation to a .pptx file
presentation.SaveToFile("RemoveSlide.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
presentation.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Setting proper margins is an essential step in creating professional Word documents. Margins may seem like a small detail, but they play a vital role in improving the readability and visual appeal of a document. By defining the space around content, margins help maintain a consistent and balanced layout, prevent text from being truncated, and make documents look more organized and aesthetically pleasing. This article will show how to use Spire.Doc for Python to set page margins for Word documents through Python programs.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Set the Page Margins of a Word Document
Spire.Doc for Python provides properties under the Margins class that can be used to set margins for each side of a document separately or to set the same margins for all sides. One important thing to note is that the margins are set based on sections. For consistent margins throughout the document, it is necessary to iterate through each section of the document to set the margins. Below are the detailed steps for setting page margins:
- Create an object of Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Loop through the sections of the document.
- Get a section using Document.Sections.get_Item() method.
- Get the margins of the section using Section.PageSetup.Margins property.
- Set the top, bottom, left, and right margin using property under Margins class.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Loop thorugh the sections of document
for i in range(doc.Sections.Count):
# Get a section
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(i)
# Get the margins of the section
margins = section.PageSetup.Margins
# Set the top, bottom, left, and right margins
margins.Top = 17.9
margins.Bottom = 17.9
margins.Left = 20.9
margins.Right = 20.9
# margins.All = 17.9
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/SetPageMargins.docx", FileFormat.Auto)

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Extract Text from PDF in Python: A Complete Guide with Practical Code Samples
2023-10-09 01:26:32 Written by Administrator
PDF files are everywhere—from contracts and research papers to eBooks and invoices. While they preserve formatting perfectly, extracting text from PDFs can be challenging, especially with large or complex documents. Manual copying is not only slow but often inaccurate.
Whether you’re a developer automating workflows, a data analyst processing content, or simply someone needing quick text extraction, programmatic methods can save you valuable time and effort.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn how to extract text from PDF files in Python using Spire.PDF for Python — a powerful and easy-to-use PDF processing library. We’ll cover extracting all text, targeting specific pages or areas, ignoring hidden text, and capturing layout details such as text position and size.
Table of Contents
- Why Extract Text from PDF Files
- Install Spire.PDF for Python: Powerful PDF Parser Library
- Extract Text from PDF (Basic Example)
- Advanced Text Extraction Features
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Why Extract Text from PDF Files
Text extraction from PDFs is essential for many use cases, including:
- Automating data entry and document processing
- Enabling full-text search and indexing
- Performing data analysis on reports and surveys
- Extracting content for machine learning and NLP
- Converting PDFs to other editable formats
Install Spire.PDF for Python: Powerful PDF Parser Library
Spire.PDF for Python is a comprehensive and easy-to-use PDF processing library that simplifies all your PDF manipulation needs. It offers advanced text extraction capabilities that work seamlessly with both simple and complex PDF documents.
Installation
The library can be installed easily via pip. Open your terminal and run the following command:
pip install spire.pdf
Need help with the installation? Follow this step-by-step guide: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Extract Text from PDF (Basic Example)
If you just want to quickly read all the text from a PDF, this simple example shows how to do it. It iterates over each page, extracts the full text using PdfTextExtractor, and saves it to a text file with spacing and line breaks preserved.
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Terms of service.pdf')
# Prepare a variable to hold the extracted text
all_text = ""
# Create a PdfTextExtractOptions object
extractOptions = PdfTextExtractOptions()
# Extract all text including whitespaces
extractOptions.IsExtractAllText = True
# Loop through all pages and extract text
for i in range(doc.Pages.Count):
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(i)
textExtractor = PdfTextExtractor(page)
text = textExtractor.ExtractText(extractOptions)
# Append text from each page
all_text += text + "\n"
# Write all extracted text to a file
with open('output/TextOfAllPages.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write(all_text)
Advanced Text Extraction Features
For greater control over what and how text is extracted, Spire.PDF for Python offers advanced options. You can selectively extract content from specific pages or regions, or even with layout details, such as text position and size, to better suit your specific data processing needs.
Retrieve Text from Selected Pages
Instead of processing an entire PDF, you can target specific pages for text extraction. This is especially useful for large documents where only certain sections are relevant for your task.
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Terms of service.pdf')
# Create a PdfTextExtractOptions object and enable full text extraction
extractOptions = PdfTextExtractOptions()
# Extract all text including whitespaces
extractOptions.IsExtractAllText = True
# Get a specific page (e.g., page 2)
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(1)
# Create a PdfTextExtractor object
textExtractor = PdfTextExtractor(page)
# Extract text from the page
text = textExtractor.ExtractText(extractOptions)
# Write the extracted text to a file using UTF-8 encoding
with open('output/TextOfPage.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write(text)

Get Text from Defined Area
When dealing with structured documents like forms or invoices, extracting text from a specific region can be more efficient. You can define a rectangular area and extract only the text within that boundary on the page.
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Terms of service.pdf')
# Get a specific page (e.g., page 2)
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(1)
# Create a PdfTextExtractor object
textExtractor = PdfTextExtractor(page)
# Create a PdfTextExtractOptions object
extractOptions = PdfTextExtractOptions()
# Define the rectangular area to extract text from
# RectangleF(left, top, width, height)
extractOptions.ExtractArea = RectangleF(0.0, 100.0, 890.0, 80.0)
# Extract text from the specified area, keeping white spaces
text = textExtractor.ExtractText(extractOptions)
# Write the extracted text to a file using UTF-8 encoding
with open('output/TextOfRectangle.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write(text)
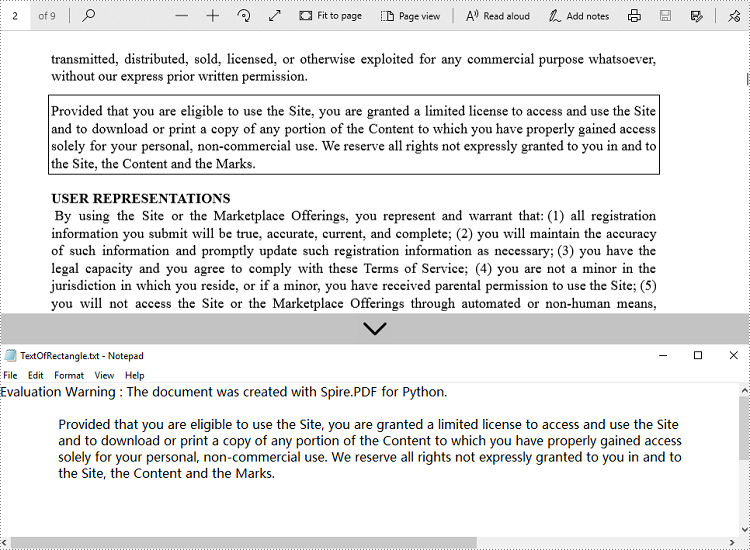
Ignore Hidden Text During Extraction
Some PDFs contain hidden or invisible text, often used for accessibility or OCR layers. You can choose to ignore such content during extraction to focus only on what is actually visible to users.
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Terms of service.pdf')
# Create a PdfTextExtractOptions object
extractOptions = PdfTextExtractOptions()
# Ignore hidden text during extraction
extractOptions.IsShowHiddenText = False
# Get a specific page (e.g., page 2)
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(1)
# Create a PdfTextExtractor object
textExtractor = PdfTextExtractor(page)
# Extract text from the page
text = textExtractor.ExtractText(extractOptions)
# Write the extracted text to a file using UTF-8 encoding
with open('output/ExcludeHiddenText.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write(text)
Retrieve Text with Position (Coordinates) and Size Information
For layout-sensitive applications—such as converting PDF content into editable formats or reconstructing page structure—you can extract text along with its position and size. This provides precise control over how content is interpreted and used.
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Terms of service.pdf')
# Loop through all pages of the document
for i in range(doc.Pages.Count):
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Create a PdfTextFinder object for the current page
finder = PdfTextFinder(page)
# Find all text fragments on the page
fragments = finder.FindAllText()
print(f"Page {i + 1}:")
# Loop through all text fragments
for fragment in fragments:
# Extract text content from the current text fragment
text = fragment.Text
# Get bounding rectangles with position and size
rects = fragment.Bounds
print(f'Text: "{text}"')
# Iterate through all rectangles
for rect in rects:
# Print the position and size information of the current rectangle
print(f"Position: ({rect.X}, {rect.Y}), Size: ({rect.Width} x {rect.Height})")
print()
Conclusion
Extracting text from PDF files in Python becomes efficient and flexible with Spire.PDF for Python. Whether you need to process entire documents or extract text from specific pages or regions, Spire.PDF provides a robust set of tools to meet your needs. By automating text extraction, you can streamline workflows, power intelligent search systems, or prepare data for analysis and machine learning.
FAQs
Q1: Can text be extracted from password-protected PDFs?
A1: Yes, Spire.PDF for Python can open and extract text from secured files by providing the correct password when loading the PDF document.
Q2: Is batch text extraction from multiple PDFs supported?
A2: Yes, you can programmatically iterate through a directory of PDF files and apply text extraction to each file efficiently using Spire.PDF for Python.
Q3: Is it possible to extract images or tables from PDFs?
A3: While this guide focuses on text extraction, Spire.PDF for Python also supports image extraction and table extraction.
Q4: Can text be extracted from scanned (image-based) PDFs?
A4: Extracting text from scanned PDFs requires OCR (Optical Character Recognition). Spire.PDF for Python does not include built-in OCR, but you can combine it with an OCR library like Spire.OCR for image-to-text conversion.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.PDF for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
PDF files often contain critical embedded images (e.g., charts, diagrams, scanned documents). For developers, knowing how to extract images from PDF in Python allows them to repurpose graphical content for automated report generation or feed these visuals into machine learning models for analysis and OCR tasks.

This article explores how to leverage the Spire.PDF for Python library to extract images from PDF files via Python, covering the following aspects:
- Installation & Environment Setup
- How to Extract Images from PDFs using Python
- Handle Different Image Formats While Extraction
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion (Extract Text and More)
Installation & Environment Setup
Before you start using Spire.PDF for Python to extract images from PDF, make sure you have the following in place:
-
Python Environment: Ensure that you have Python installed on your system. It is recommended to use the latest stable version for the best compatibility and performance.
-
Spire.PDF for Python Library: You need to install the Python PDF SDK, and the easiest way is using pip, the Python package installer.
Open your command prompt or terminal and run the following command:
pip install Spire.PDF
How to Extract Images from PDFs using Python
Example 1: Extract Images from a PDF Page
Here’s a complete Python script to extract and save images from a specified page in PDF:
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("template1.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create a PdfImageHelper instance
imageHelper = PdfImageHelper()
# Get the image information on the page
imageInfo = imageHelper.GetImagesInfo(page)
# Iterate through the image information
for i in range(0, len(imageInfo)):
# Save images to file
imageInfo[i].Image.Save("PageImage\\Image" + str(i) + ".png")
# Release resources
pdf.Dispose()
Key Steps Explained:
- Load the PDF: Use the LoadFromFile() method to load a PDF file.
- Access a Page: Access a specified PDF page by index.
- Extract Image information:
- Create a PdfImageHelper instance to facilitate image extraction.
- Use the GetImagesInfo() method to retrieve image information from the specified page, and return a list of PdfImageInfo objects.
- Save Images to Files:
- Loops through all detected images on the page
- Use the PdfImageInfo[].Image.Save() method to save the image to disk.
Output:
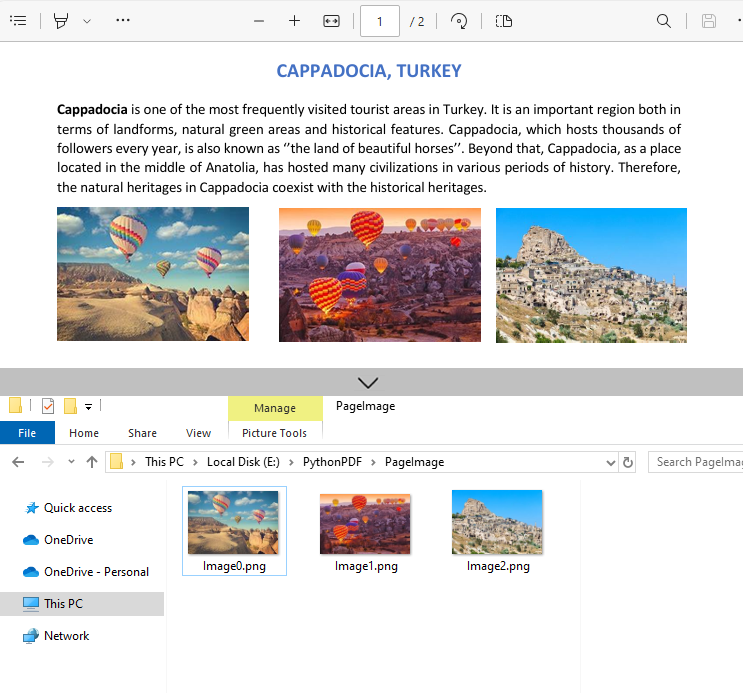
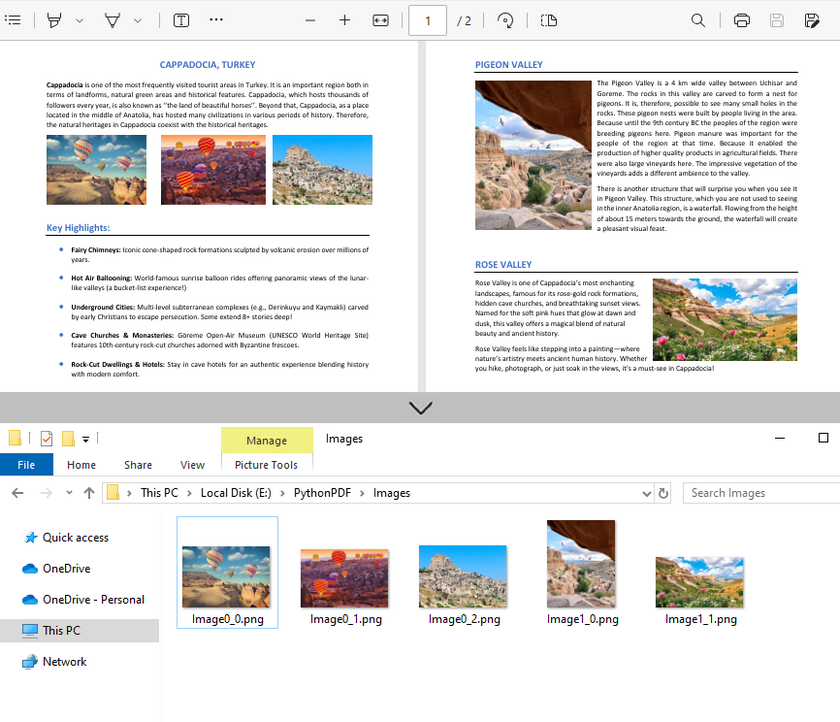
Example 2: Extract All Images from a PDF File
Building on the single-page extraction method, you can iterate through all pages of the PDF document to extract every embedded image.
Python code example:
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("template1.pdf")
# Create a PdfImageHelper instance
imageHelper = PdfImageHelper()
# Iterate through the pages in the document
for i in range(0, pdf.Pages.Count):
# Get the current page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Get the image information on the page
imageInfo = imageHelper.GetImagesInfo(page)
# Iterate through the image information items
for j in range(0, len(imageInfo)):
# Save the current image to file
imageInfo[j].Image.Save(f"Images\\Image{i}_{j}.png")
# Release resources
pdf.Close()Output:
Handle Different Image Formats While Extraction
Spire.PDF for Python supports extracting images in various formats such as PNG, JPG/JPEG, BMP, etc. When saving the extracted images, you can choose the appropriate format based on your needs.
Common Image Formats:
| Format | Best Use Cases | PDF Extraction Notes |
|---|---|---|
| JPG/JPEG | Photos, scanned documents | Common in PDFs; quality loss on re-compress |
| PNG | Web graphics, diagrams, screenshots | Preserves transparency; larger file sizes |
| BMP | Windows applications, temp storage | Rare in modern PDFs; avoid for web use |
| TIFF | Archiving, print, OCR input | Ideal for document preservation; multi-page |
| EMF | Windows vector editing | Editable in Illustrator/Inkscape |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Is Spire.PDF for Python a free library?
Spire.PDF for Python offers both free and commercial versions. The free version has limitations, such as a maximum of 10 pages per PDF. For commercial use or to remove these restrictions, you can request a trial license here.
Q2: Can I extract images from a specified page range only?
Yes. Instead of iterating through all pages, specify the page indices you want. For example, to extract images from the pages 2 to 5:
# Extract images from pages 2 to 5
for i in range(1, 4): # Pages are zero-indexed
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Process images as beforeQ3: Is it possible to extract text from images?
Yes. For scanned PDF files, after extracting the images, you can extract the text in the images in conjunction with the Spire.OCR for Python library.
A step-by-step guide: How to Extract Text from Image Using Python (OCR Code Examples)
Conclusion (Extract Text and More)
Spire.PDF simplifies image extraction from PDF in Python with minimal code. By following this guide, you can:
- Extract images from single pages or entire PDF documents.
- Save images from PDF in various formats (PNG, JPG, BMP or TIFF).
As a PDF document can contain different elements, the Python PDF library is also capable of:
