
Python (355)
SmartArt in Microsoft PowerPoint is a valuable tool that allows users to create visually appealing diagrams, charts, and graphics to represent information or concepts. It provides a quick and easy way to transform plain text into visually engaging visuals, making it easier for the audience to understand and remember the information being presented. In this article, we will demonstrate how to create, read and delete SmartArt in a PowerPoint in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Create SmartArt in PowerPoint in Python
- Read SmartArt in PowerPoint in Python
- Delete SmartArt from PowerPoint in Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Create SmartArt in PowerPoint in Python
Spire.Presentation for Python provides the ISlide.Shapes.AppendSmartArt() method to add a SmartArt graphic to a specific slide of a PowerPoint presentation. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified slide by its index using Presentation.Slides[index] property.
- Insert a SmartArt graphic into the specified slide using ISlide.Shapes.AppendSmartArt() method.
- Set the style and color of the SmartArt using ISmartArt.Style and ISmartArt.ColorStyle properties.
- Loop through the nodes in the SmartArt and remove all default nodes using ISmartArt.Nodes.RemoveNode() method.
- Add a node to the SmartArt using ISmartArt.Nodes.AddNode() method.
- Add two sub-nodes to the node using ISmartArtNode.ChildNodes.AddNode() method.
- Add two sub-nodes to the first sub-node and the second sub-node respectively using ISmartArtNode.ChildNodes.AddNode() method.
- Add text to each node and sub-node using ISmartArtNode.TextFrame.Text property, and then set the font size for the text using ISmartArtNode.TextFrame.TextRange.FontHeight property.
- Save the resulting presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Get the first slide
slide = presentation.Slides[0]
# Add a SmartArt (Organization Chart) to the slide
smartArt = slide.Shapes.AppendSmartArt(200, 60, 500, 430, SmartArtLayoutType.OrganizationChart)
# Set style and color for the SmartArt
smartArt.Style = SmartArtStyleType.ModerateEffect
smartArt.ColorStyle = SmartArtColorType.ColorfulAccentColors5to6
# Remove the default nodes from the SmartArt
list = []
for node in smartArt.Nodes:
list.append(node)
for subnode in list:
smartArt.Nodes.RemoveNode(subnode)
# Add a node to the SmartArt
node = smartArt.Nodes.AddNode()
# Add two sub-nodes to the node
subNode1 = node.ChildNodes.AddNode()
subNode2 = node.ChildNodes.AddNode()
# Add two sub-nodes to the first sub-node
subsubNode1 = subNode1.ChildNodes.AddNode()
subsubNode2 = subNode1.ChildNodes.AddNode()
# Add two sub-nodes to the second sub-node
subsubNode3 = subNode2.ChildNodes.AddNode()
subsubNode4 = subNode2.ChildNodes.AddNode()
# Set text and font size for the node and sub-nodes
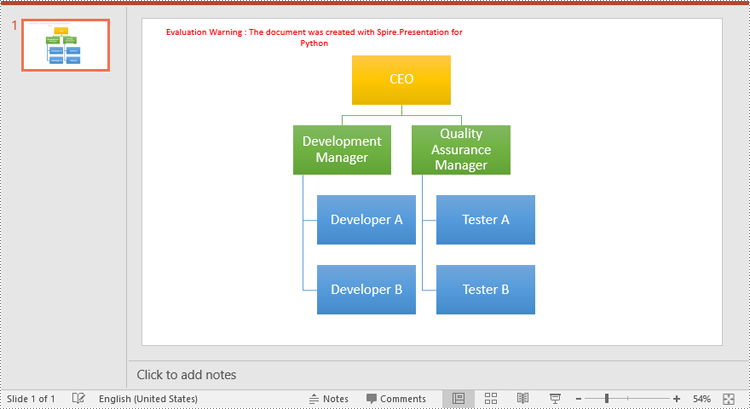
node.TextFrame.Text = "CEO"
node.TextFrame.TextRange.FontHeight = 14.0
subNode1.TextFrame.Text = "Development Manager"
subNode1.TextFrame.TextRange.FontHeight = 12.0
subNode2.TextFrame.Text = "Quality Assurance Manager"
subNode2.TextFrame.TextRange.FontHeight = 12.0
subsubNode1.TextFrame.Text = "Developer A"
subsubNode1.TextFrame.TextRange.FontHeight = 12.0
subsubNode2.TextFrame.Text = "Developer B"
subsubNode2.TextFrame.TextRange.FontHeight = 12.0
subsubNode3.TextFrame.Text = "Tester A"
subsubNode3.TextFrame.TextRange.FontHeight = 12.0
subsubNode4.TextFrame.Text = "Tester B"
subsubNode4.TextFrame.TextRange.FontHeight = 12.0
# Save the resulting presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("InsertSmartArt.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
presentation.Dispose()
Read SmartArt in PowerPoint in Python
To read the text of SmartArt graphics on a PowerPoint slide, you need to find the SmartArt shapes on the slide, then loop through all nodes of each SmartArt shape, and finally retrieve the text of each node through the ISmartArtNode.TextFrame.Text property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific slide using Presentation.Slides[index] property.
- Create a list to store the extracted text.
- Loop through all the shapes on the slide.
- Check if the shapes are of ISmartArt type. If the result is True, loop through all the nodes of each SmartArt shape, then retrieve the text from each node through ISmartArtNode.TextFrame.Text property and append the text to the list.
- Write the text in the list into a text file.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("InsertSmartArt.pptx")
# Get the first slide
slide = presentation.Slides[0]
# Create a list to store the extracted text
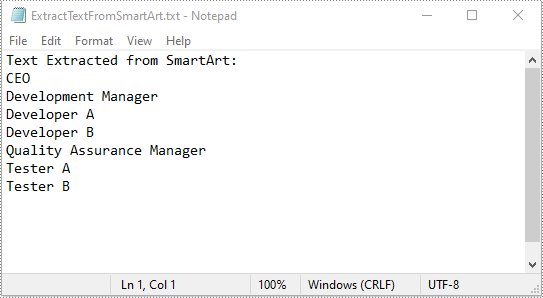
str = []
str.append("Text Extracted from SmartArt:")
# Loop through the shapes on the slide and find the SmartArt shapes
for shape in slide.Shapes:
if isinstance(shape, ISmartArt):
smartArt = shape
# Extract text from the SmartArt shapes and append the text to the list
for node in smartArt.Nodes:
str.append(node.TextFrame.Text)
# Write the text in the list into a text file
with open("ExtractTextFromSmartArt.txt", "w", encoding = "utf-8") as text_file:
for text in str:
text_file.write(text + "\n")
presentation.Dispose()
Delete SmartArt from PowerPoint in Python
To delete SmartArt graphics from a PowerPoint slide, you need to loop through all the shapes on the slide, find the SmartArt shapes and then delete them from the slide using ISlide.Shapes.Remove() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific slide using Presentation.Slides[index] property.
- Create a list to store the SmartArt shapes.
- Loop through all the shapes on the slide.
- Check if the shapes are of ISmartArt type. If the result is True, append them to the list.
- Loop through the SmartArt shapes in the list, then remove them from the slide one by one using ISlide.Shapes.Remove() method.
- Save the resulting presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("InsertSmartArt.pptx")
# Get the first slide
slide = presentation.Slides[0]
# Create a list to store the SmartArt shapes
list = []
# Loop through all the shapes on the slide
for shape in slide.Shapes:
# Find the SmartArt shapes and append them to the list
if isinstance (shape, ISmartArt):
list.append(shape)
# Remove the SmartArt from the slide
for smartArt in list:
slide.Shapes.Remove(smartArt)
# Save the resulting presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("DeleteSmartArt.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
presentation.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Pivot tables provide a flexible way to organize, manipulate, and summarize data from different perspectives, enabling users to gain valuable insights and make informed decisions. With pivot tables, you can easily rearrange and summarize data based on various criteria, such as categories, dates, or numerical values. This feature is particularly useful when dealing with complex datasets or when you need to compare and analyze data from different angles. In this article, you will learn how to create or operate pivot tables in an Excel document using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Pivot Table in Excel in Python
- Sort Pivot Table by Column Values in Python
- Expand or Collapse Rows in Pivot Table in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Create a Pivot Table in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python offers the PivotTable class to work with pivot tables in an Excel document. To create a pivot table based on the data in an existing Excel worksheet, follow the steps below.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Specify the range of cells on which the pivot table will be created using Worksheet.Range property
- Create an object of PivotCache using Workbook.PivotCaches.Add() method.
- Add a pivot table to the worksheet using Worksheet.PivotTables.Add() method.
- Add fields to rows area.
- Add fields to values area.
- Save the result document using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load a sample Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Data.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
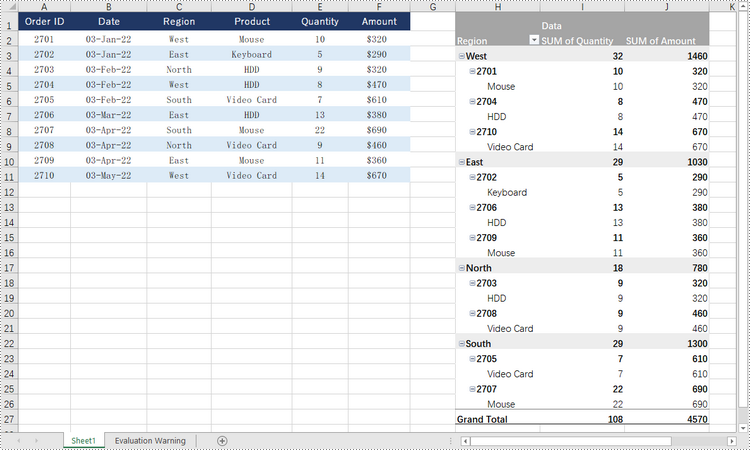
# Select the data source range
cellRange = sheet.Range["C1:F11"]
piVotCache = workbook.PivotCaches.Add(cellRange)
# Add a PivotTable to the worksheet and set the location and cache of it
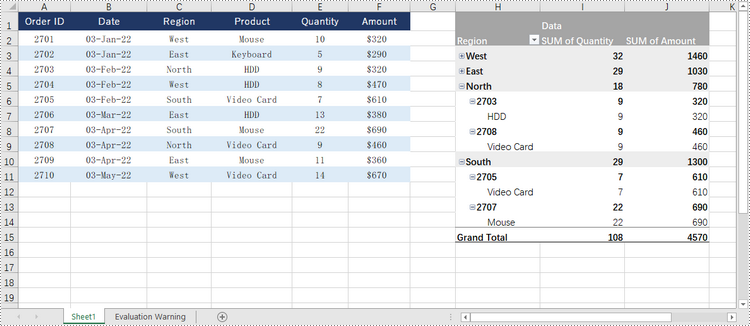
pivotTable = sheet.PivotTables.Add("Pivot Table", sheet.Range["H1"], piVotCache)
# Add "Region" and "Product" fields to rows area
regionField = pivotTable.PivotFields["Region"]
regionField.Axis = AxisTypes.Row
pivotTable.Options.RowHeaderCaption = "Region"
productField = pivotTable.PivotFields["Product"]
productField.Axis = AxisTypes.Row
# Add "Quantity" and "Amount" fields to values area
pivotTable.DataFields.Add(pivotTable.PivotFields["Quantity"], "SUM of Quantity", SubtotalTypes.Sum)
pivotTable.DataFields.Add(pivotTable.PivotFields["Amount"], "SUM of Amount", SubtotalTypes.Sum)
# Apply a built-in style to the pivot table
pivotTable.BuiltInStyle = PivotBuiltInStyles.PivotStyleMedium11
# Set column width
sheet.SetColumnWidth(8, 16);
sheet.SetColumnWidth(9, 16);
sheet.SetColumnWidth(10, 16);
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("output/PivotTable.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
Sort Pivot Table by Column Values in Python
A specific field can be accessed through the PivotTable.PivotFields[index] property, and then you can set its sort type using the PivotField.SortType property. The following are the steps to sort pivot table by the values of a specific field.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific pivot table from the worksheet through Worksheet.PivotTables[index] property.
- Get a specific field through PivotTable.PivotFields[fieldName] property.
- Sort data in the field through PivotField.SortType property.
- Save the workbook to a different file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\PivotTable.xlsx");
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the specified pivot table
pivotTable = sheet.PivotTables[0]
# Get the specified field
idField = pivotTable.PivotFields["Order ID"]
# Sort data in the column of "Order ID" field
idField.SortType = PivotFieldSortType.Descending
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("output/SortData.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
Expand or Collapse Rows in Pivot Table in Python
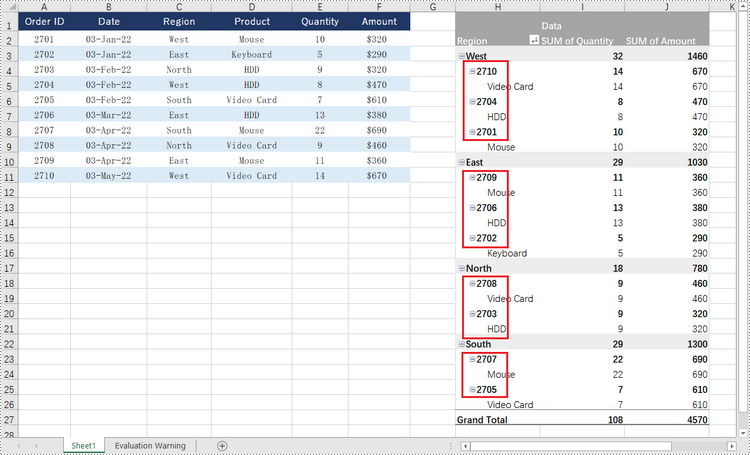
To collapse the details under a certain pivot field, use PivotField.HideItemDetail(string itemValue, bool isHiddenDetail) method and set the second parameter to true; to show the details, set the second parameter to false. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific pivot table from the worksheet through Worksheet.PivotTables[index] property.
- Get a specific field through PivotTable.PivotFields[fieldName] property.
- Collapse or expand rows of the field using PivotField.HideItemDetail(string itemValue, bool isHiddenDetail) method.
- Save the workbook to a different file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load a sample Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\PivotTable.xlsx");
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the specified pivot table
pivotTable = sheet.PivotTables[0]
# Get the specified field
regoinField = pivotTable.PivotFields["Region"]
# Hide details under the selected item of the region
regoinField.HideItemDetail("West", True)
regoinField.HideItemDetail("East", True)
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("output/CollapseRows.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Comments are invaluable tools for collaboration and feedback in Word documents, allowing users to provide insights, suggestions, clarification, and discussions. Whether the goal is to share ideas, respond to existing comments, or remove outdated feedback, mastering the efficient handling of Word document comments can significantly enhance document workflow. This article aims to show how to add, delete, or reply to comments in Word documents using Spire.Doc for Python in Python programs.
- Add Comments to a Paragraph in Word Documents using Python
- Add Comments to Text in Word Documents using Python
- Remove Comments from Word Documents using Python
- Reply to Comments in Word Documents using Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Add Comments to a Paragraph in Word Documents using Python
Spire.Doc for Python provides the Paragraph.AppendComment() method to add a comment to a specified paragraph. And the range of text corresponding to the comment needs to be controlled using the comment start marks and end marks. The detailed steps to add comments on paragraphs are as follows:
- Create an object of Document class and load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first section using Document.Sections.get_Item() method.
- Get the first paragraph in the section using Section.Paragraphs.get_Item() method.
- Add a comment to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendComment() method.
- Set the author the comment through Comment.Format.Author property.
- Create a comment start mark and an end mark and set them as the start and end marks of the created comment though CommentMark.CommentId property.
- Insert the comment start mark and end mark at the beginning and end of the paragraph respectively using Paragraph.ChildObjects.Insert() method.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document class and load a Word document
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Get the first section
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get the forth paragraph
paragraph = section.Paragraphs.get_Item(4)
# Add a comment to the paragraph
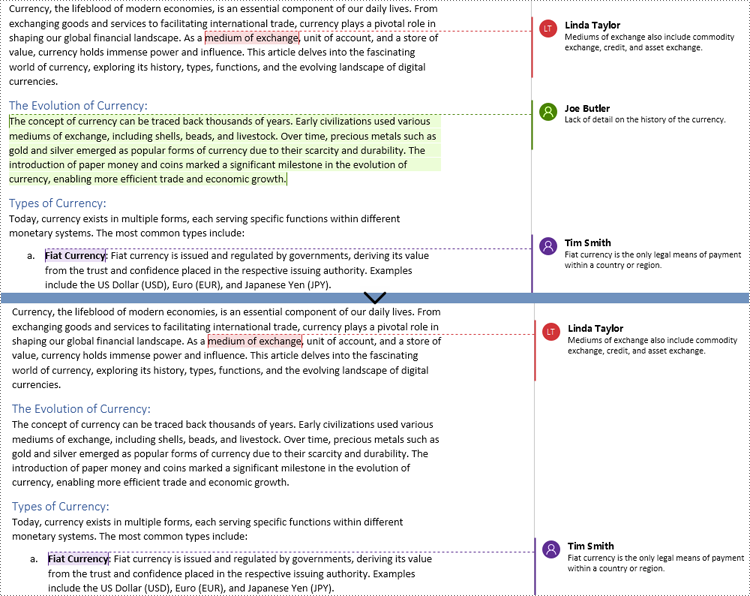
comment = paragraph.AppendComment("Lack of detail on the history of the currency.")
# Set the author of the comment
comment.Format.Author = "Joe Butler"
# Create a comment start mark and an end mark and set them as the start and end marks of the created comment
commentStart = CommentMark(doc, CommentMarkType.CommentStart)
commentEnd = CommentMark(doc, CommentMarkType.CommentEnd)
commentStart.CommentId = comment.Format.CommentId
commentEnd.CommentId = comment.Format.CommentId
# Insert the comment start mark and end mark at the beginning and end of the paragraph respectively
paragraph.ChildObjects.Insert(0, commentStart)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(commentEnd)
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/CommentOnParagraph.docx")
doc.Close()

Add Comments to Text in Word Documents using Python
Spire.Doc for Python also supports finding specified text and adding comments to it. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Document class and load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Find the text to comment on using Document.FindString() method.
- Create an object of Comment class, set the comment content through Comment.Body.AddParagraph().Text property, and set the author of the comment through Comment.Format.Author property.
- Get the text as one text range using TextSelection.GetAsOneRange() method and get the paragraph the text belongs to through TextRange.OwnerParagraph property.
- Insert the comment after the found text using Paragraph.ChildObjects.Insert() method.
- Create a comment start mark and an end mark and set them as the start and end marks of the created comment though CommentMark.CommentId property.
- Insert the comment start mark and end mark before and after found text respectively using Paragraph.ChildObjects.Insert() method.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document class and load a Word document
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Find the text to comment on
text = doc.FindString("medium of exchange", True, True)
# Create a comment and set the content and author of the comment
comment = Comment(doc)
comment.Body.AddParagraph().Text = "Fiat currency is the only legal means of payment within a country or region."
comment.Format.Author = "Linda Taylor"
# Get the found text as a text range and get the paragraph it belongs to
range = text.GetAsOneRange()
paragraph = range.OwnerParagraph
# Add the comment to the paragraph
paragraph.ChildObjects.Insert(paragraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf(range) + 1, comment)
# Create a comment start mark and an end mark and set them as the start and end marks of the created comment
commentStart = CommentMark(doc, CommentMarkType.CommentStart)
commentEnd = CommentMark(doc, CommentMarkType.CommentEnd)
commentStart.CommentId = comment.Format.CommentId
commentEnd.CommentId = comment.Format.CommentId
# Insert the created comment start and end tags before and after the found text respectively
paragraph.ChildObjects.Insert(paragraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf(range), commentStart)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Insert(paragraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf(range) + 1, commentEnd)
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile ("output/CommentOnText.docx")
doc.Close()

Remove Comments from Word Documents using Python
Spire.Doc for Python provides the Document.Comments.RemoveAt() method that can be used to remove a specified comment and the Document.Clear() method that can remove all comments. The detailed steps for removing comments are as follows:
- Create an object of Document class and load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Delete a specific comment using Document.Comments.RemoveAt() method or delete all the comments using Document.Comments.Clear() method.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document class and load a Word document
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample1.docx")
# Remove the second comment
doc.Comments.RemoveAt(1)
# Remove all comments
#doc.Comments.Clear()
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/RemoveComments.docx")
doc.Close()
Reply to Comments in Word Documents using Python
Spire.Doc for Python allows users to reply to a comment by setting a comment as a reply to another comment using Comment.ReplyToComment(Comment) method. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Document class and load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a comment using Document.Comments.get_Item() method.
- Create a comment and set its content and author through Comment.Body.AddParagraph().Text property and Comment.Format.Author property.
- Set the created comment as a reply to the obtained comment using Comment.ReplyToComment() method.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document class and load a Word document
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("output/CommentOnParagraph.docx")
# Get a comment
comment = doc.Comments.get_Item(0)
# Create a reply comment and set the content and author of it
reply = Comment(doc)
reply.Body.AddParagraph().Text = "We will give more details about the history of the currency."
reply.Format.Author = "Moris Peter"
# Set the created comment as a reply to obtained comment
comment.ReplyToComment(reply)
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/ReplyToComments.docx")
doc.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Textboxes are versatile tools in Microsoft Word, allowing you to insert and position text or other elements anywhere on a page, giving you the power to create eye-catching flyers, brochures, or reports. Whether you're looking to emphasize a particular section of text, place captions near images, or simply add a decorative touch, the capacity to manipulate textboxes offers a practical and aesthetic advantage in document design. In this article, you will learn how to add or remove textboxes in a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Add a Textbox to a Word Document in Python
Spire.Doc for Python provides the Paragraph.AppendTextBox() method to insert a textbox in a specified paragraph. The content and formatting of the textbox can be set through the properties under the TextBox object. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first section and add a paragraph to the section using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Add a text box to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendTextBox() method.
- Get the format of the textbox using TextBox.Format property, and then set the textbox's wrapping type, position, border color and fill color using the properties of TextBoxFormat Class.
- Add a paragraph to the textbox using TextBox.Body.AddParagraph() method.
- Add an image to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendPicture() method.
- Add text to the textbox using Paragraph.AppendText() method
- Save the document to a different file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/input3.docx")
# Insert a textbox and set its wrapping style
textBox = document.Sections[0].Paragraphs[0].AppendTextBox(135, 300)
textBox.Format.TextWrappingStyle = TextWrappingStyle.Square
# Set the position of the textbox
textBox.Format.HorizontalOrigin = HorizontalOrigin.RightMarginArea
textBox.Format.HorizontalPosition = -145.0
textBox.Format.VerticalOrigin = VerticalOrigin.Page
textBox.Format.VerticalPosition = 120.0
# Set the border style and fill color of the textbox
textBox.Format.LineColor = Color.get_DarkBlue()
textBox.Format.FillColor = Color.get_LightGray()
# Insert an image to textbox as a paragraph
para = textBox.Body.AddParagraph();
picture = para.AppendPicture("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Wikipedia_Logo.png")
# Set alignment for the paragraph
para.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
# Set the size of the inserted image
picture.Height = 90.0
picture.Width = 90.0
# Insert text to textbox as the second paragraph
textRange = para.AppendText("Wikipedia is a free encyclopedia, written collaboratively by the people who use it. "
+ "Since 2001, it has grown rapidly to become the world's largest reference website, "
+ "with 6.7 million articles in English attracting billions of views every month.")
# Set alignment for the paragraph
para.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
# Set the font of the text
textRange.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Times New Roman"
textRange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12.0
textRange.CharacterFormat.Italic = True
# Save the result file
document.SaveToFile("output/AddTextBox.docx", FileFormat.Docx)

Remove a Textbox from a Word Document in Python
Spire.Doc for Python provides the Document.TextBoxes.RemoveAt(int index) method to delete a specified textbox. To delete all textboxes from a Word document, you can use the Document.TextBoxes.Clear() method. The following example shows how to remove the first textbox from a Word document.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove the first text box using Document.TextBoxes.RemoveAt(int index) method.
- Save the document to another file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document .LoadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/TextBox.docx")
# Remove the first textbox
document .TextBoxes.RemoveAt(0)
# Remove all textboxes
# document.TextBoxes.Clear()
# Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("output/RemoveTextbox.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Pages are the most fundamental components of a PDF document. If you want to add new information or supplemental material to an existing PDF, it is necessary to add new pages. Conversely, if there are some pages that contain incorrect or irrelevant content, you can remove them to create a more professional document. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically add or delete pages in PDF using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
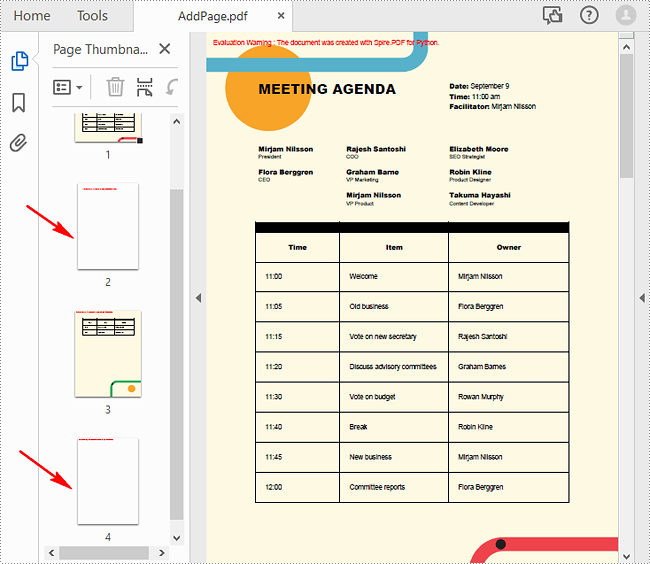
Add Empty Pages to a PDF Document in Python
With Spire.PDF for Python, you can easily add a blank page to a specific position or to the end of the document using PdfDocument.Pages.Insert() or PdfDocument.Pages.Add(SizeF, PdfMargins) methods. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a sample PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a new blank page and insert it into a specific position of the document using PdfDocument.Pages.Insert() method.
- Create another new blank page with the specified size and margins, and then append it to the end of the document using PdfDocument.Pages.Add(SizeF, PdfMargins) method.
- Save the result document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("Test.pdf")
# Insert a blank page to the document as the second page
pdf.Pages.Insert(1)
# Add an empty page to the end of the document
pdf.Pages.Add(PdfPageSize.A4(), PdfMargins(0.0, 0.0))
# Save the result document
pdf.SaveToFile("AddPage.pdf")
pdf.Close()
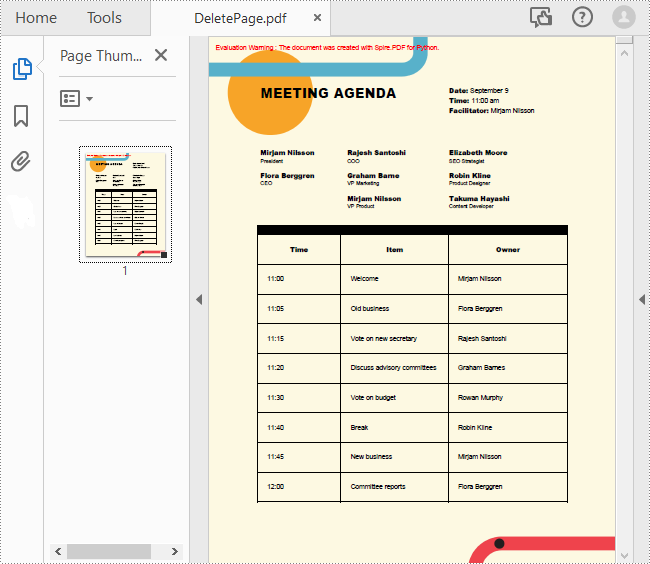
Delete an Existing Page in a PDF Document in Python
To remove a specified page from a PDF, you can use the PdfDocument.Pages.RemoveAt() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a sample PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove a specified page from the document using PdfDocument.Pages.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the result document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("Test.pdf")
# Delete the second page of the document
pdf.Pages.RemoveAt(1)
# Save the result document
pdf.SaveToFile("DeletePage.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Stamps are a powerful tool in PDF documents that allow users to mark and annotate specific areas or sections of a PDF file. Often used for approval, review, or to indicate a specific status, stamps can greatly enhance collaboration and document management. In PDF, stamps can take various forms, such as a simple checkmark, a customized graphic, a date and time stamp, or even a signature. In this article, you will learn how to add image stamps and dynamic stamps to a PDF document in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Add an Image Stamp to PDF Documents in Python
Spire.PDF for Python offers the PdfRubberStampAnnotation class to represent a rubber stamp in a PDF document. In order to create the appearance of a rubber stamp, the PdfTemplate class is used. The PdfTemplate is a piece of canvas on which you can draw whatever information you want, such as text, images, date, and time.
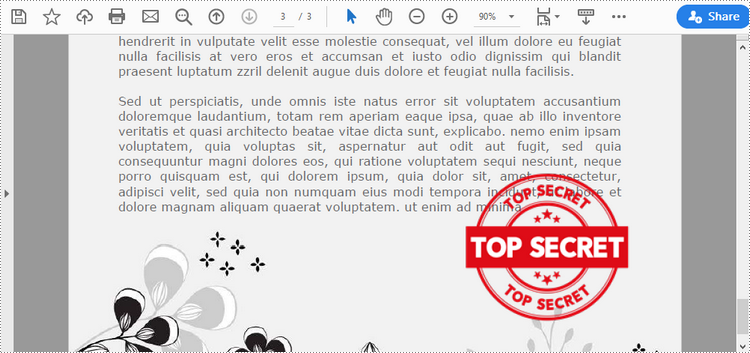
Image stamps can include logos, signatures, watermarks, or any other custom graphics that you want to overlay onto your PDFs. The main steps to add an image stamp to PDF using Spire.PDF for Python are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Load an image that you want to stamp on PDF using PdfImage.FromFile() method.
- Create a PdfTemplate object with the dimensions of the image.
- Draw the image on the template using PdfTemplate.Graphics.DrawImage() method.
- Create a PdfRubberStampAnnotation object, and set the template as its appearance.
- Add the stamp to a specific PDF page using PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.Add() method.
- Save the document to a different file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.pdf")
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(2)
# Load an image file
image = PdfImage.FromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\secret.png")
# Get the width and height of the image
width = (float)(image.Width)
height = (float)(image.Height)
# Create a PdfTemplate object based on the size of the image
template = PdfTemplate(width, height, True)
# Draw image on the template
template.Graphics.DrawImage(image, 0.0, 0.0, width, height)
# Create a rubber stamp annotation, specifying its location and position
rect = RectangleF((float) (page.ActualSize.Width - width - 50), (float) (page.ActualSize.Height - height - 40), width, height)
stamp = PdfRubberStampAnnotation(rect)
# Create a PdfAppearance object
pdfAppearance = PdfAppearance(stamp)
# Set the template as the normal state of the appearance
pdfAppearance.Normal = template
# Apply the appearance to the stamp
stamp.Appearance = pdfAppearance
# Add the stamp annotation to PDF
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(stamp)
# Save the file
doc.SaveToFile("output/ImageStamp.pdf")
doc.Close()
Add a Dynamic Stamp to PDF in Python
Unlike static stamps, dynamic stamps can contain variable information such as the date, time, or user input. The following are the steps to create a dynamic stamp in PDF using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a PdfTemplate object with desired size.
- Draw strings on the template using PdfTemplate.Graphics.DrawString() method.
- Create a PdfRubberStampAnnotation object, and set the template as its appearance.
- Add the stamp to a specific PDF page using PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.Add() method.
- Save the document to a different file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.pdf")
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(2)
# Create a PdfTemplate object
template = PdfTemplate(220.0, 50.0, True)
# Create two fonts
font1 = PdfTrueTypeFont("Elephant", 16.0, 0, True)
font2 = PdfTrueTypeFont("Times New Roman", 10.0, 0, True)
# Create a solid brush and a gradient brush
solidBrush = PdfSolidBrush(PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue()))
rectangle1 = RectangleF(PointF(0.0, 0.0), template.Size)
linearGradientBrush = PdfLinearGradientBrush(rectangle1, PdfRGBColor(Color.get_White()), PdfRGBColor(Color.get_LightBlue()), PdfLinearGradientMode.Horizontal)
# Create a pen
pen = PdfPen(solidBrush)
# Create a rounded rectangle path
CornerRadius = 10.0
path = PdfPath()
path.AddArc(template.GetBounds().X, template.GetBounds().Y, CornerRadius, CornerRadius, 180.0, 90.0)
path.AddArc(template.GetBounds().X + template.Width - CornerRadius, template.GetBounds().Y, CornerRadius, CornerRadius, 270.0, 90.0)
path.AddArc(template.GetBounds().X + template.Width - CornerRadius, template.GetBounds().Y + template.Height - CornerRadius, CornerRadius, CornerRadius, 0.0, 90.0)
path.AddArc(template.GetBounds().X, template.GetBounds().Y + template.Height - CornerRadius, CornerRadius, CornerRadius, 90.0, 90.0)
path.AddLine(template.GetBounds().X, template.GetBounds().Y + template.Height - CornerRadius, template.GetBounds().X, template.GetBounds().Y + CornerRadius / 2)
# Draw path on the template
template.Graphics.DrawPath(pen, path)
template.Graphics.DrawPath(linearGradientBrush, path)
# Draw text on the template
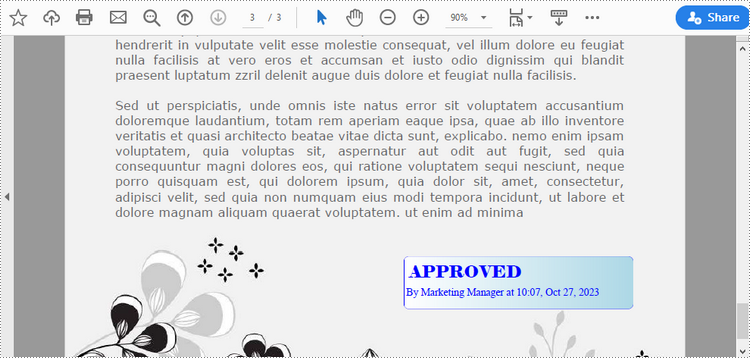
string1 = "APPROVED\n"
string2 = "By Marketing Manager at " + DateTime.get_Now().ToString("HH:mm, MMM dd, yyyy")
template.Graphics.DrawString(string1, font1, solidBrush, PointF(5.0, 5.0))
template.Graphics.DrawString(string2, font2, solidBrush, PointF(2.0, 28.0))
# Create a rubber stamp, specifying its size and location
rectangle2 = RectangleF((float) (page.ActualSize.Width - 220.0 - 50.0), (float) (page.ActualSize.Height - 50.0 - 100.0), 220.0, 50.0)
stamp = PdfRubberStampAnnotation(rectangle2)
# Create a PdfAppearance object and apply the template as its normal state
apprearance = PdfAppearance(stamp)
apprearance.Normal = template
# Apply the appearance to stamp
stamp.Appearance = apprearance
# Add the stamp annotation to annotation collection
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(stamp)
# Save the file
doc.SaveToFile("output/DynamicStamp.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Create Various Types of Lists in a Word Document
2023-10-27 00:57:31 Written by AdministratorLists are a powerful organizational tool that can be used to present information in a structured and easy-to-follow manner. Whether you want to create numbered lists, bulleted lists, or even custom lists with specific formatting, Word provides flexible options to suit your needs. By utilizing different list styles, you can improve the readability and visual appeal of your documents, making it simpler for readers to grasp key points and navigate through the content. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically create various types of lists in a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Create a Numbered List in Word in Python
- Create a Bulleted List in Word in Python
- Create a Multi-Level Numbered List in Word in Python
- Create a Multi-Level Mixed-Type List in Word in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Create a Numbered List in Word in Python
Spire.Doc for Python provides the ListStyle class, which enables you to establish either a numbered list style or a bulleted style. Subsequently, you can utilize the Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method to apply the defined list style to a paragraph. The steps to create a numbered list are as follows.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create an instance of ListStyle class, specifying the list type to Numbered.
- Get a specific level of the list through ListStyle.Levels[index] property, and set the numbering type through ListLevel.PatternType property.
- Add the list style to the document using Document.ListStyles.Add() method.
- Add several paragraphs to the document using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Apply the list style to a specific paragraph using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method.
- Specify the list level through Paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber property.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Create a numbered list style
listStyle = doc.Styles.Add(ListType.Numbered,"numberedList")
Levels = listStyle.ListRef.Levels
Levels[0].PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic
Levels[0].TextPosition = 20
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
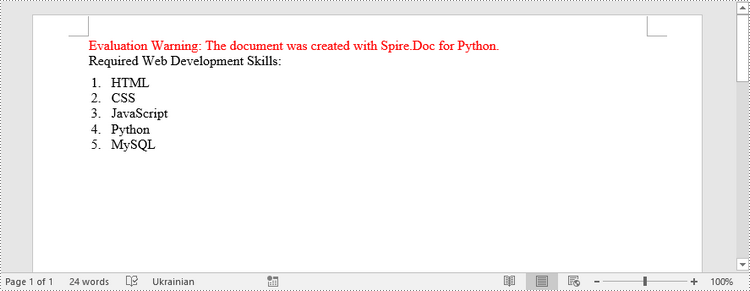
paragraph.AppendText("Required Web Development Skills:")
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 5.0
# Add a paragraph and apply the numbered list style to it
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("HTML")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Add another four paragraphs and apply the numbered list style to them
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("CSS")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("JavaScript")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Python")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("MySQL")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Save the document to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/NumberedList.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
Create a Bulleted List in Word in Python
Creating a bulleted list follows a similar process to creating a numbered list, with the main difference being that you need to specify the list type as "Bulleted" and assign a bullet symbol to it. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create an instance of ListStyle class, specifying the list type to Bulleted.
- Get a specific level of the list through ListStyle.Levels[index] property, and set the bullet symbol through ListLevel.BulletCharacter property.
- Add the list style to the document using Document.ListStyles.Add() method.
- Add several paragraphs to the document using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Apply the list style to a specific paragraph using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method.
- Specify the list level through Paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber property.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Create a bulleted list style
listStyle = doc.Styles.Add(ListType.Bulleted,"bulletedList")
Levels = listStyle.ListRef.Levels
Levels[0].BulletCharacter = "\u00B7"
Levels[0].CharacterFormat.FontName = "Symbol"
Levels[0].TextPosition = 20
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
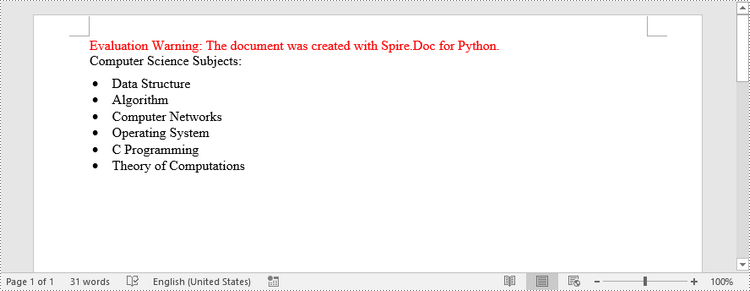
paragraph.AppendText("Computer Science Subjects:")
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 5.0
# Add a paragraph and apply the bulleted list style to it
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Data Structure")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Add another five paragraphs and apply the bulleted list style to them
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Algorithm")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Computer Networks")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Operating System")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("C Programming")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Theory of Computations")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Save the document to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/BulletedList.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
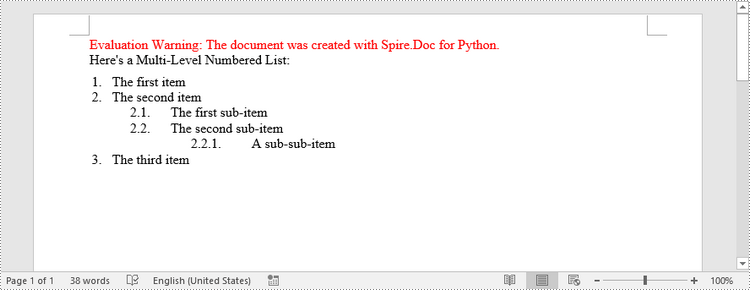
Create a Multi-Level Numbered List in Word in Python
A multi-level list consists of at least two different levels. A certain level of a nested list can be accessed by the ListStyle.Levels[index] property, through which you can set the numbering type and prefix. The following are the steps to create a multi-level numbered list in Word.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create an instance of ListStyle class, specifying the list type to Numbered.
- Get a specific level of the list through ListStyle.Levels[index] property, and set the numbering type and prefix.
- Add the list style to the document using Document.ListStyles.Add() method.
- Add several paragraphs to the document using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Apply the list style to a specific paragraph using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method.
- Specify the list level through Paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber property.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Create a numbered list style, specifying number prefix and pattern type of each level
listStyle = doc.Styles.Add(ListType.Numbered,"levelstyle")
Levels = listStyle.ListRef.Levels
Levels[0].PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic
Levels[0].TextPosition = 20.0
Levels[1].NumberPrefix = "%1."
Levels[1].PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic
Levels[2].NumberPrefix = "%1.%2."
Levels[2].PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Here's a Multi-Level Numbered List:")
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 5.0
# Add a paragraph and apply the numbered list style to it
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The first item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Add another five paragraphs and apply the numbered list stype to them
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The second item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The first sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 1
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The second sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ContinueListNumbering()
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle")
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("A sub-sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 2
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The third item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Save the document to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/MultilevelNumberedList.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
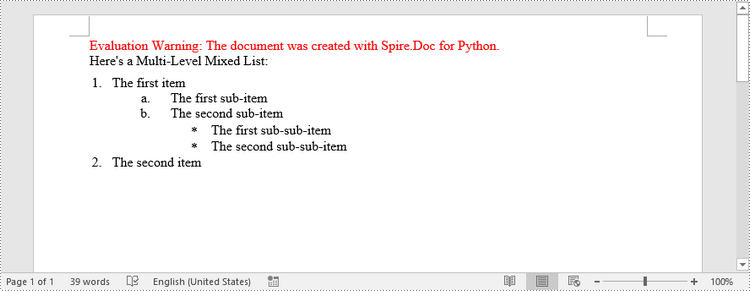
Create a Multi-Level Mixed-Type List in Word in Python
To combine number and symbol bullet points in a multi-level list, create separate list styles (numbered and bulleted) and apply them to different paragraphs. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create a numbered list style and a bulleted list style.
- Add several paragraphs to the document using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Apply different list style to different paragraphs using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Create a numbered list style
numberList = doc.Styles.Add(ListType.Numbered, "numberedStyle")
Levels = numberList.ListRef.Levels
Levels[0].PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic
Levels[0].TextPosition = 20
Levels[1].PatternType = ListPatternType.LowLetter
# Create a bulleted list style
bulletedListStyle = doc.Styles.Add(ListType.Bulleted, "bulletedStyle")
Levels = bulletedListStyle.ListRef.Levels
Levels[2].BulletCharacter = "\u002A"
Levels[2].CharacterFormat.FontName = "Symbol"
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Here's a Multi-Level Mixed List:")
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 5.0
# Add a paragraph and apply the numbered list style to it
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The first item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedStyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Add the other five paragraphs and apply different list stype to them
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The first sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedStyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 1
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The second sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 1
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedStyle")
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The first sub-sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedStyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 2
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The second sub-sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedStyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 2
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The second item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedStyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Save the document to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/MultilevelMixedList.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
By default, Excel uses column letters and row numbers to refer to cells and ranges (for example, A1, B2:C5). While this approach is functional, it can become inconvenient, particularly when dealing with large datasets or complex formulas. Named ranges provide a solution to this problem by allowing users to assign custom names to cells or ranges, making them easier to identify, reference, and work with. In this article, we will explain how to create, edit and delete named ranges in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Named Range in Excel in Python
- Edit an Existing Named Range in Excel in Python
- Delete a Named Range from Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Create a Named Range in Excel in Python
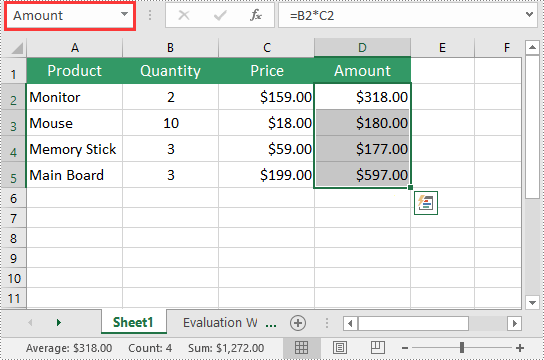
You can use the Workbook.NameRanges.Add() method provided by Spire.XLS for Python to add a named range to an Excel workbook. Once the named range is added, you can define the cell or range of cells it refers to using the INamedRange.RefersToRange property.
The following steps explain how to create a named range in Excel using Spire.XLS for Python:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel workbook using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add a named range to the workbook using the Workbook.NameRanges.Add() method.
- Get a specific worksheet in the workbook using the Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Set the cell range that the named range refers to using the INamedRange.RefersToRange property.
- Save the resulting file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel workbook
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Add a named range to the workbook
namedRange = workbook.NameRanges.Add("Amount")
# Get a specific worksheet in the workbook
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set the cell range that the named range references
namedRange.RefersToRange = sheet.Range["D2:D5"]
# Save the resulting file to a specific location
workbook.SaveToFile("CreateNamedRange.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Edit an Existing Named Range in Excel in Python
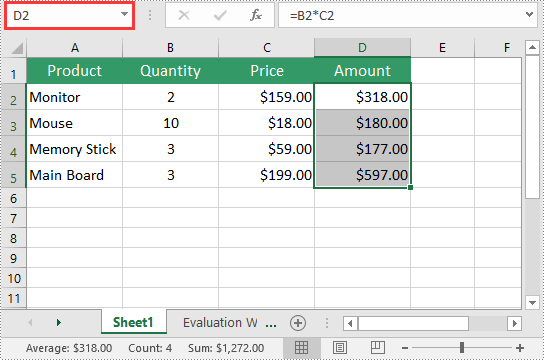
After you've created a named range, you may want to modify its name or adjust the cells it refers to.
The following steps explain how to modify the name and cell references of an existing named range in Excel using Spire.XLS for Python:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel workbook using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific named range in the workbook using the Workbook.NameRanges[] property.
- Modify the name of the named range using the INamedRange.Name property.
- Modify the cells that the named range refers to using the INamedRange.RefersToRange property.
- Save the resulting file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel workbook
workbook.LoadFromFile("CreateNamedRange.xlsx")
# Get the first named range in the workbook
namedRange = workbook.NameRanges[0]
# Change the name of the named range
namedRange.Name = "MonitorAmount"
# Change the cell range that the named range references
namedRange.RefersToRange = workbook.Worksheets[0].Range["D2"]
# Save the resulting file to a specific location
workbook.SaveToFile("ModifyNamedRange.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()

Delete a Named Range from Excel in Python
If you have made significant changes to the structure or layout of your spreadsheet, it might be necessary to delete a named range that is no longer relevant or accurate.
The following steps explain how to delete a named range from Excel using Spire.XLS for Python:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel workbook using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove a specific named range by its index or name using the Workbook.NameRanges.RemoveAt() or Workbook.NameRanges.Remove() method.
- Save the resulting file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel workbook
workbook.LoadFromFile("CreateNamedRange.xlsx")
# Remove the first named range by its index
workbook.NameRanges.RemoveAt(0)
# Remove the first named range by its name
# workbook.NameRanges.Remove("Amount");
# Save the resulting file to a specific location
workbook.SaveToFile("RemoveNamedRange.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
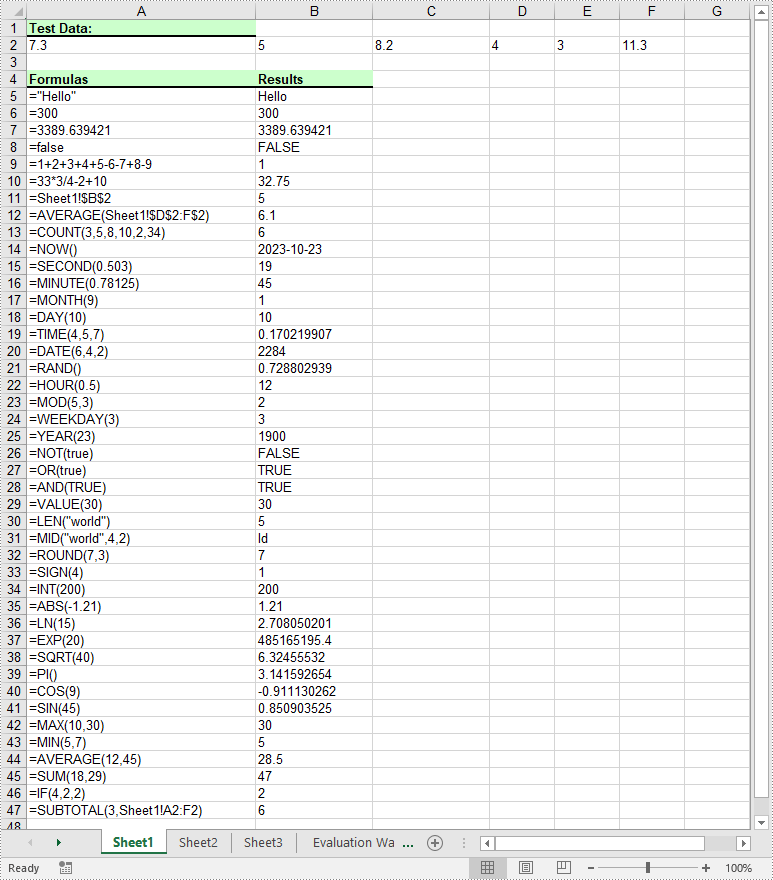
Formulas in Excel are equations or expressions that perform calculations on data within a spreadsheet. They allow you to perform basic arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, as well as more advanced functions like statistical analysis, date and time calculations, and logical evaluations. By incorporating formulas into your Excel spreadsheets, you can save time, eliminate errors, and gain valuable insights from your data. In this article, we will demonstrate how to add or read formulas in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Add Formulas to Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python offers the Worksheet.Range[rowIndex, columnIndex].Formula property to add formulas to specific cells in an Excel worksheet. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using the Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Add some text and numeric data to specific cells of the worksheet using the Worksheet.Range[rowIndex, columnIndex].Text and Worksheet.Range[rowIndex, columnIndex].NumberValue properties.
- Add text and formulas to specific cells of the worksheet using the Worksheet.Range[rowIndex, columnIndex].Text and Worksheet.Range[rowIndex, columnIndex].Formula properties.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Declare two variables: currentRow, currentFormula
currentRow = 1
currentFormula = ""
# Add text to the worksheet and set cell style
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "Test Data:"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Style.Font.IsBold = True
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Style.FillPattern = ExcelPatternType.Solid
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightGreen1
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Medium
currentRow += 1
# Add some numeric data to the worksheet
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].NumberValue = 7.3
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].NumberValue = 5
sheet.Range[currentRow, 3].NumberValue = 8.2
sheet.Range[currentRow, 4].NumberValue = 4
sheet.Range[currentRow, 5].NumberValue = 3
sheet.Range[currentRow, 6].NumberValue = 11.3
currentRow += 2
# Add text to the worksheet and set cell style
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "Formulas"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Text = "Results"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1, currentRow, 2].Style.Font.IsBold = True
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1, currentRow, 2].Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightGreen1
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1, currentRow, 2].Style.FillPattern = ExcelPatternType.Solid
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1, currentRow, 2].Style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Medium
currentRow += 1
# Add text and formulas to the worksheet
# Str
currentFormula = "=\"Hello\""
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# Int
currentFormula = "=300"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# Float
currentFormula = "=3389.639421"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# Bool
currentFormula = "=false"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# Expressions
currentFormula = "=1+2+3+4+5-6-7+8-9"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
currentFormula = "=33*3/4-2+10"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# Cell reference
currentFormula = "=Sheet1!$B$2"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# Functions
# AVERAGE
currentFormula = "=AVERAGE(Sheet1!$D$2:F$2)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# COUNT
currentFormula = "=COUNT(3,5,8,10,2,34)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# NOW
currentFormula = "=NOW()"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Style.NumberFormat = "yyyy-MM-DD"
currentRow += 1
# SECOND
currentFormula = "=SECOND(0.503)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# MINUTE
currentFormula = "=MINUTE(0.78125)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# MONTH
currentFormula = "=MONTH(9)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# DAY
currentFormula = "=DAY(10)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# TIME
currentFormula = "=TIME(4,5,7)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# DATE
currentFormula = "=DATE(6,4,2)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# RAND
currentFormula = "=RAND()"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# HOUR
currentFormula = "=HOUR(0.5)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# MOD
currentFormula = "=MOD(5,3)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# WEEKDAY
currentFormula = "=WEEKDAY(3)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# YEAR
currentFormula = "=YEAR(23)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# NOT
currentFormula = "=NOT(true)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# OR
currentFormula = "=OR(true)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# AND
currentFormula = "=AND(TRUE)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# VALUE
currentFormula = "=VALUE(30)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# LEN
currentFormula = "=LEN(\"world\")"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# MID
currentFormula = "=MID(\"world\",4,2)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# ROUND
currentFormula = "=ROUND(7,3)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# SIGN
currentFormula = "=SIGN(4)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# INT
currentFormula = "=INT(200)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# ABS
currentFormula = "=ABS(-1.21)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# LN
currentFormula = "=LN(15)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# EXP
currentFormula = "=EXP(20)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# SQRT
currentFormula = "=SQRT(40)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# PI
currentFormula = "=PI()"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# COS
currentFormula = "=COS(9)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# SIN
currentFormula = "=SIN(45)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# MAX
currentFormula = "=MAX(10,30)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# MIN
currentFormula = "=MIN(5,7)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# AVERAGE
currentFormula = "=AVERAGE(12,45)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# SUM
currentFormula = "=SUM(18,29)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# IF
currentFormula = "=IF(4,2,2)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# SUBTOTAL
currentFormula = "=SUBTOTAL(3,Sheet1!A2:F2)"
sheet.Range[currentRow, 1].Text = "'" + currentFormula
sheet.Range[currentRow, 2].Formula = currentFormula
currentRow += 1
# Set width of the 1st, 2nd and 3rd columns
sheet.SetColumnWidth(1, 32)
sheet.SetColumnWidth(2, 16)
sheet.SetColumnWidth(3, 16)
# Create a cell style
style = workbook.Styles.Add("Style")
# Set the horizontal alignment as left
style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left
# Apply the style to the worksheet
sheet.ApplyStyle(style)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("AddFormulas.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Read Formulas in Excel in Python
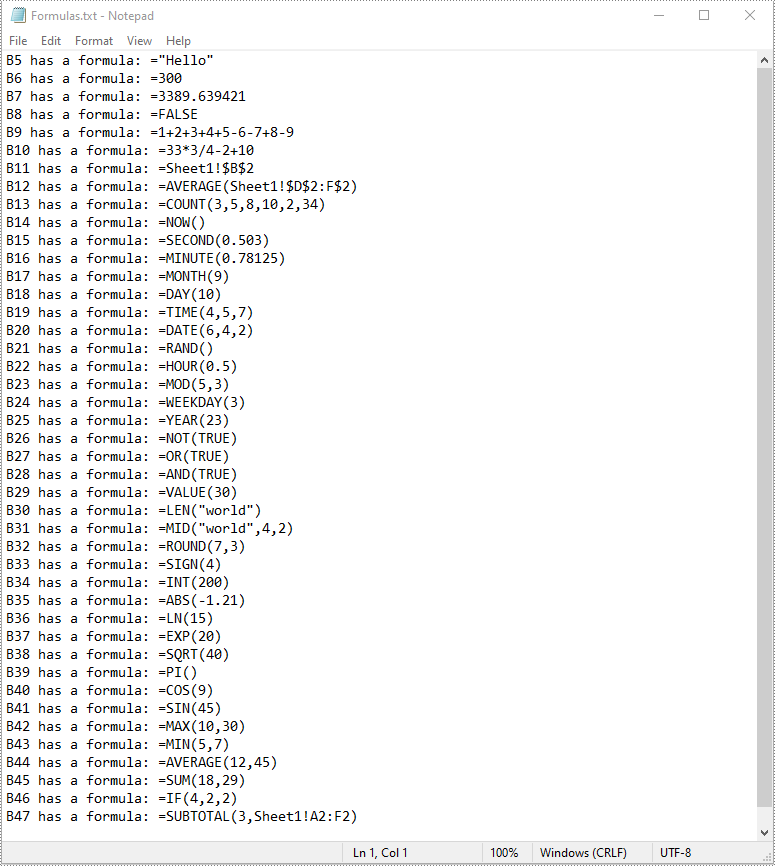
To read formulas in an Excel worksheet, you need to loop through all the cells in the worksheet, after that, find the cells containing formulas using the Cell.HasFormula property, and then get the formulas of the cells using the CellRange.Formula property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using the Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Get the used range of the worksheet using the Worksheet.AllocatedRange property.
- Create an empty list.
- Loop through all the cells in the used range.
- Find the cells containing formulas using the Cell.HasFormula property.
- Get the names and the formulas of the cells using the CellRange.RangeAddressLocal and CellRange.Formula properties.
- Append the cell names and formulas to the list.
- Write the items in the list into a text file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("AddFormulas.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the used range of the worksheet
usedRange = sheet.AllocatedRange
# Create an empty list
list = []
# Loop through the cells in the used range
for cell in usedRange:
# Check if the cell has a formula
if(cell.HasFormula):
# Get the cell name
cellName = cell.RangeAddressLocal
# Get the formula
formula = cell.Formula
# Append the cell name and formula to the list
list.append(cellName + " has a formula: " + formula)
# Write the items in the list into a text file
with open("Formulas.txt", "w", encoding = "utf-8") as text_file:
for item in list:
text_file.write(item + "\n")
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Images have the power to captivate audiences and enhance their understanding of your content. By adding relevant and visually appealing images to your PowerPoint presentations, you can effectively convey complex ideas and make your presentations more memorable and impactful. In this article, we will explain how to add images to PowerPoint presentations in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Add an Image to a Slide in Python
Spire.Presentation for Python offers the ISlide.Shapes.AppendEmbedImageByPath() method to add an image to a specific slide. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific slide by its index through Presentation.Slides[index] property.
- Add an image to the slide using ISlide.Shapes.AppendEmbedImageByPath() method.
- Save the resulting presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import * import math from spire.presentation import * inputFile = "Input.pptx" outputFile = "AddImageToSlide.pptx" # Create an object of the Presentation class presentation = Presentation() # Load a PowerPoint presentation presentation.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get the first slide slide = presentation.Slides[0] # Insert an image into the slide imageFile = "Image.png" left = math.trunc(presentation.SlideSize.Size.Width / float(2)) - 280 rect1 = RectangleF.FromLTRB (left, 140, 120 + left, 260) image = slide.Shapes.AppendEmbedImageByPath (ShapeType.Rectangle, imageFile, rect1) image.Line.FillType = FillFormatType.none # Save the resulting presentation presentation.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Pptx2010) presentation.Dispose()
Add an Image to a Slide Master in Python
A slide master is the top-level slide that governs the formatting and styling of all other slides within the presentation. When you make changes to the slide master, such as adding a logo, modifying the background or changing the font styles, those changes are automatically applied to all slides based on that slide master. If you want an image to appear on all your slides, you can add it to the slide master.
Spire.Presentation for Python offers the IMasterSlide.Shapes.AppendEmbedImageByPath() method to add an image to a slide master. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific slide master by its index through Presentation.Masters[index] property.
- Add an image to the slide master using IMasterSlide.Shapes.AppendEmbedImageByPath() method.
- Save the resulting presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import * import math from spire.presentation import * inputFile = "Input1.pptx" outputFile = "AddImageToSlideMaster.pptx" # Create an object of the Presentation class presentation = Presentation() # Load a PowerPoint presentation presentation.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get the first slide master master = presentation.Masters[0] # Insert an image into the slide master imageFile = "Logo.png" rect1 = RectangleF.FromLTRB (40, 40, 80, 80) image = master.Shapes.AppendEmbedImageByPath (ShapeType.Rectangle, imageFile, rect1) image.Line.FillType = FillFormatType.none # Save the resulting presentation presentation.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Pptx2010) presentation.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
