
Python (355)
Python: Convert PowerPoint to Images (PNG, JPG, BMP, SVG)
2023-09-27 01:05:46 Written by AdministratorImages are universally compatible and can be easily shared across various platforms, devices, and applications. By converting PowerPoint slides to images, you can distribute your content effortlessly via email, messaging apps, websites, or social media platforms. This makes your presentation accessible to a wider audience and ensures that it can be viewed by anyone, regardless of the software or device they are using. In this article, we will explain how to convert PowerPoint to images in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Convert PowerPoint Presentation to JPG, PNG or BMP Images
- Convert PowerPoint Presentation to JPG, PNG or BMP Images with a Specific Size
- Convert PowerPoint Presentation to SVG Images
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Convert PowerPoint Presentation to JPG, PNG or BMP Images in Python
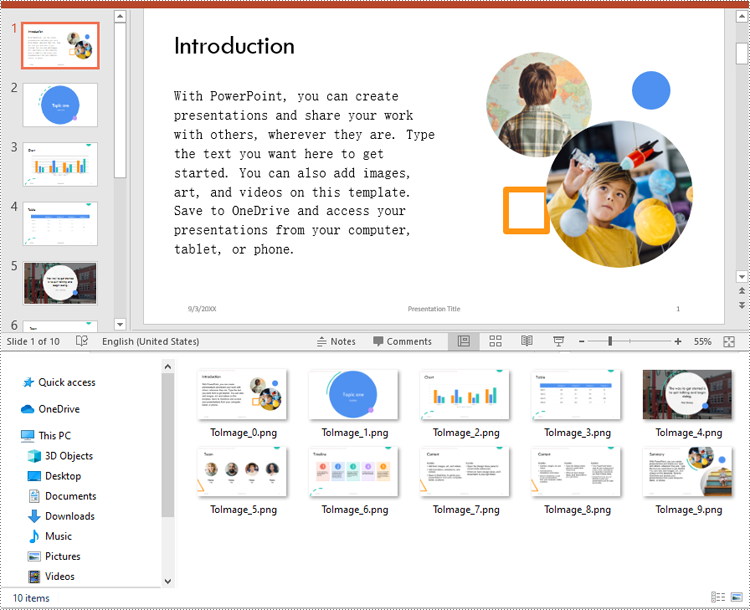
Spire.Presentation for Python offers the ISlide.SaveAsImage() method which enables you to convert the slides in a PowerPoint presentation to image files in formats like PNG, JPG or BMP with ease. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Presentation object.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Loop through the slides in the presentation.
- Save each slide to an image stream using ISlide.SaveAsImage() method.
- Save the image stream to a JPG, PNG or BMP file using Stream.Save() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Loop through the slides in the presentation
for i, slide in enumerate(presentation.Slides):
# Specify the output file name
fileName ="Output/ToImage_" + str(i) + ".png"
# Save each slide as a PNG image
image = slide.SaveAsImage()
image.Save(fileName)
image.Dispose()
presentation.Dispose()
Convert PowerPoint Presentation to JPG, PNG or BMP Images with a Specific Size in Python
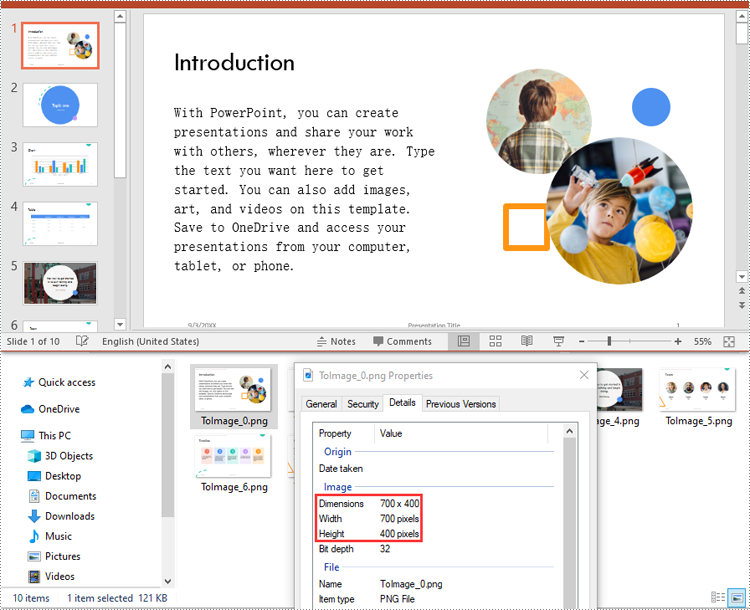
You can convert the slides in a PowerPoint presentation to images with a specific size using ISlide.SaveAsImageByWH() method. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Presentation object.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Loop through the slides in the presentation.
- Save each slide to an image stream using ISlide.SaveAsImageByWH() method.
- Save the image stream to a JPG, PNG or BMP file using Stream.Save() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Loop through the slides in the presentation
for i, slide in enumerate(presentation.Slides):
# Specify the output file name
fileName ="Output/ToImage_" + str(i) + ".png"
# Save each slide to a PNG image with a size of 700 * 400 pixels
slide1 = (ISlide)(slide)
image = slide1.SaveAsImageByWH(700, 400)
image.Save(fileName)
image.Dispose()
presentation.Dispose()
Convert PowerPoint Presentation to SVG Images in Python
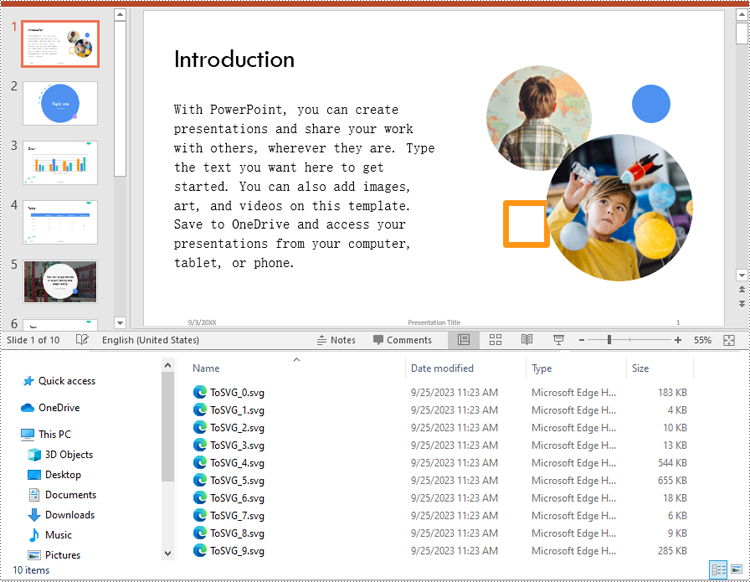
To convert the slides in a PowerPoint presentation to SVG images, you can use the ISlide.SaveToSVG() method. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Presentation object.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Enable the Presentation.IsNoteRetained property to retain notes when converting the presentation to SVG files.
- Loop through the slides in the presentation.
- Save each slide to an SVG stream using ISlide.SaveToSVG() method.
- Save the SVG stream to an SVG file using Stream.Save() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Enable the IsNoteRetained property to retain notes when converting the presentation to SVG files
presentation.IsNoteRetained = True
# Loop through the slides in the presentation
for i, slide in enumerate(presentation.Slides):
# Specify the output file name
fileName = "SVG/ToSVG_" + str(i) + ".svg"
# Save each slide to an SVG image
slide1 = (ISlide)(slide)
svgStream = slide1.SaveToSVG()
svgStream.Save(fileName)
presentation.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Textboxes in Excel provide a flexible way to add textual information or annotations to worksheets, charts, or other objects. They allow users to display explanatory text, labels, or comments that are not directly related to the data itself. In this guide, we will explore how to add, update, and delete textboxes in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Add a Textbox to Excel in Python
- Update a Textbox in Excel in Python
- Delete a Textbox in Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Add a Textbox to Excel in Python
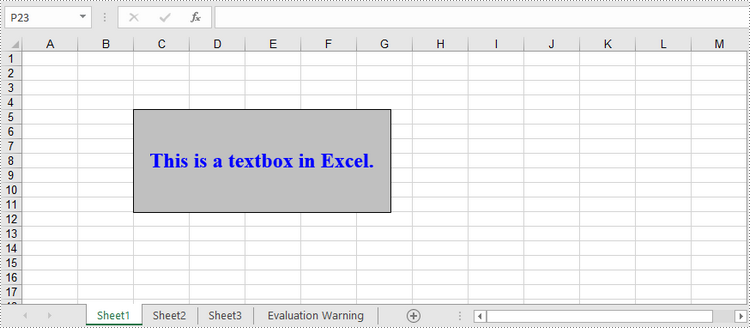
A textbox can be added to the specified location of a worksheet using Worksheet.TextBoxes.AddTextBox() method. The TextBox object has a set of properties that allow you to set the text and formatting of the textbox. The detailed steps to create a textbox using Spire.XLS for Python are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Add a textbox to the worksheet at the specified location using Worksheet.TextBoxes.AddTextBox() method.
- Set text of the textbox through TextBox.Text property.
- Set formatting of the text through other properties under the TextBox object.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add a textbox to the worksheet, specifying location and size
textBox = sheet.TextBoxes.AddTextBox(5, 3, 120, 300)
# Set fill color of the textbox
textBox.Fill.FillType = ShapeFillType.SolidColor
textBox.Fill.ForeKnownColor = ExcelColors.Gray25Percent
# Add text to the textbox and set the text alignment
textBox.Text = "This is a textbox in Excel."
textBox.HAlignment = CommentHAlignType.Center
textBox.VAlignment = CommentVAlignType.Center
# Set font for the text
font = workbook.CreateFont()
font.FontName = "Times New Roman"
font.Size = 18
font.IsBold = True
font.Color = Color.get_Blue()
richText = textBox.RichText
rt = RichText(richText)
rt.SetFont(0, len(textBox.Text) - 1, font)
# Save the workbook to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile('output/InsertTextbox.xlsx', ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Update a Textbox in Excel in Python
A certain textbox can be accessed through Worksheet.TextBoxes[index] property and the text inside the box can be obtained or modified through TextBox.Text property. The following are the steps to update a textbox using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Add a textbox to the worksheet at the specified location using Worksheet.TextBoxes.AddTextBox() method.
- Reset text of the textbox through TextBox.Text property.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile('C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Textbox.xlsx')
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the first textbox
tb = sheet.TextBoxes[0]
# Change the text of textbox
tb.Text = "The text in this textbox was changed."
# Save the workbook to a different Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile('output/UpdateTextbox.xlsx', ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
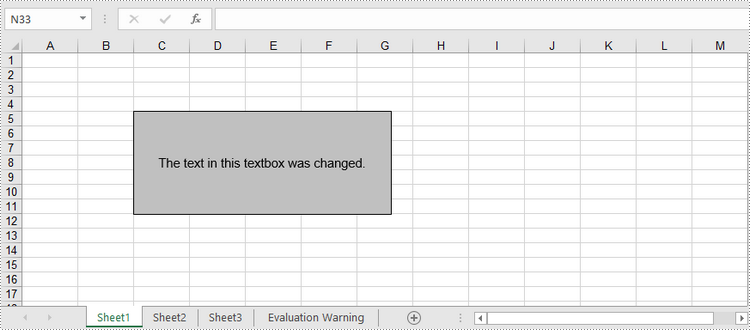
Delete a Textbox in Excel in Python
To remove a specific textbox, you use Worksheet.TextBox[index].Remove() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific sheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Remove a specific textbox by using Worksheet.TextBoxes[index].Remove() method.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile('C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Textbox.xlsx')
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Remove the first textbox
sheet.TextBoxes[0].Remove()
# Save the workbook to a different Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile('output/RemoveTextbox.xlsx', ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Extracting images from a PowerPoint presentation is necessary when you need to reuse them elsewhere. By doing so, you gain the flexibility to use these images outside the confines of the original presentation, thus maximizing their value in different projects. This article will demonstrate how to extract images from a PowerPoint document in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Extract Images from a PowerPoint Document in Python
To extract images from an entire PowerPoint presentation, you need to use the Presentation.Images property to get the collection of all the images in the presentation, then iterate through the elements in the collection and call IImageData.Image.Save() method to save each element to an image file. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Presentation instance.
- Load a PowerPoint document using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the collection of all the images in the document using Presentation.Images property.
- Iterate through the elements in the collection, and save each element as an image file using the IImageData.Image.Save() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation instance
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint document
ppt.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx")
# Iterate through all images in the document
for i, image in enumerate(ppt.Images):
# Extract the images
ImageName = "ExtractImage/Images_"+str(i)+".png"
image.Image.Save(ImageName)
ppt.Dispose()
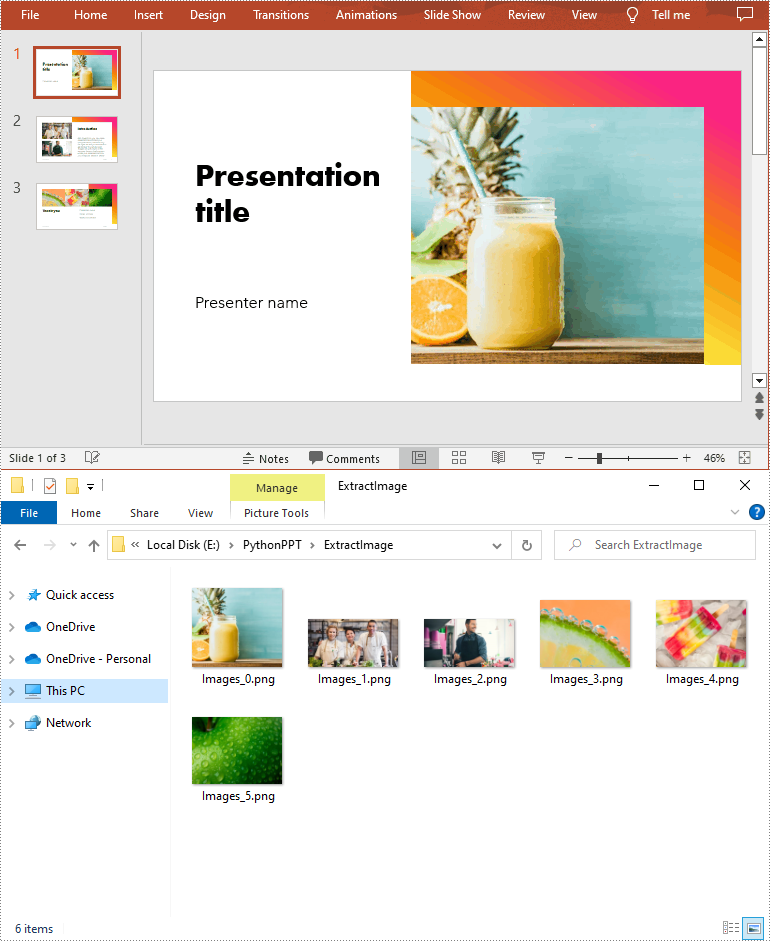
Extract Images from a Presentation Slide in Python
To extract images from a specific slide, you need to iterate through all shapes on the slide and find the shapes that are of SlidePicture or PictureShape type, then use the SlidePicture.PictureFill.Picture.EmbedImage.Image.Save() or PictureShape.EmbedImage.Image.Save() method to save the images to image files. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Presentation instance.
- Load a PowerPoint document using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified slide using Presentation.Slides[int] property.
- Iterate through all shapes on the slide.
- Determine whether the shapes are of SlidePicture or PictureShape type. If so, save the images to image files using SlidePicture.PictureFill.Picture.EmbedImage.Image.Save() or PictureShape.EmbedImage.Image.Save() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation instance
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint document
ppt.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx")
# Get a specified slide
slide = ppt.Slides[2]
i = 0
#Traverse all shapes in the slide
for s in slide.Shapes:
# Determine if the shape is of SlidePicture type
if isinstance(s, SlidePicture):
# If yes, then extract the image
ps = s if isinstance(s, SlidePicture) else None
ps.PictureFill.Picture.EmbedImage.Image.Save("Output/SlidePic_"+str(i)+".png")
i += 1
# Determine if the shape is of PictureShape type
if isinstance(s, PictureShape):
# If yes, then extract the image
ps = s if isinstance(s, PictureShape) else None
ps.EmbedImage.Image.Save("Output/SlidePic_"+str(i)+".png")
i += 1
ppt.Dispose()
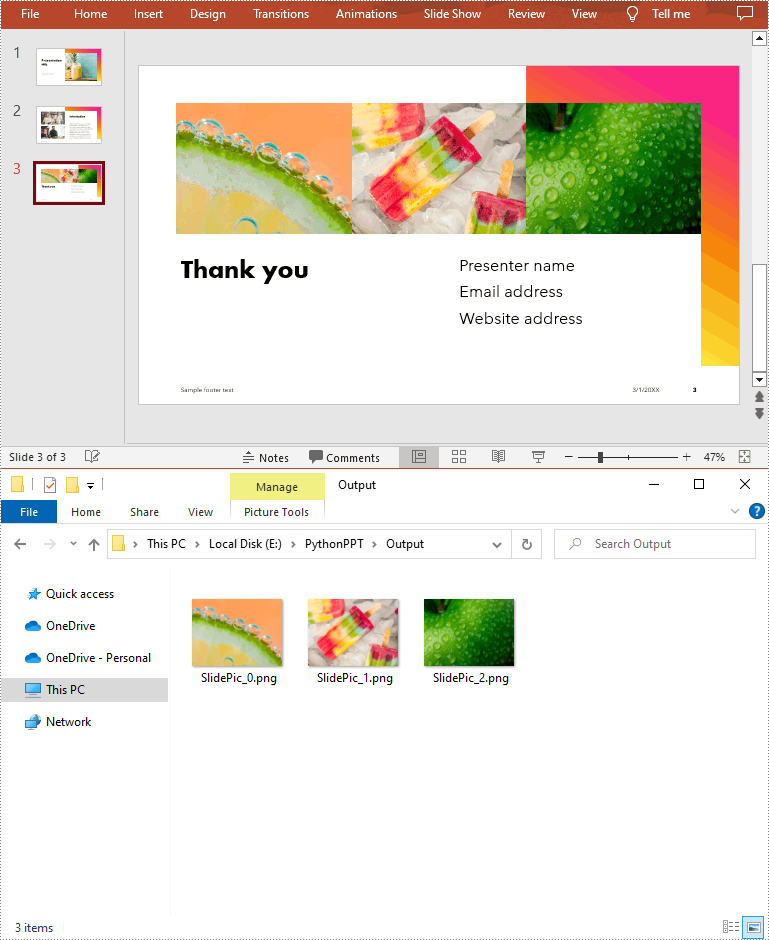
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Proper row height and column width are essential for optimizing data readability and ensuring that all content is fully visible in Excel. While the default row height and column width settings may be suitable in some cases, they may not be sufficient when dealing with lengthy text, large numbers, or complex formulas. In such cases, it becomes necessary to set appropriate row heights and column widths. In this article, we will explain how to set row height and column width in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Set Row Height in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the Worksheet.SetRowHeight() method to set the height for a specific row. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Set the height of a specific row using Worksheet.SetRowHeight() method.
- Save the resulting file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set the height of the first row
worksheet.SetRowHeight(1, 25)
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("SetRowHeight.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Set Column Width in Excel in Python
To set the width of a specific column, you can use the Worksheet.SetColumnWidth() method. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Set the width of a specific column using Worksheet.SetColumnWidth() method.
- Save the resulting file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set the width of the third column
worksheet.SetColumnWidth(3, 15)
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("SetColumnWidth.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
The Find and Replace feature in Word offers a reliable and efficient solution for updating text within your documents. It eliminates the need for exhaustive manual searching and editing by automatically locating and replacing the desired text throughout the entire document. This not only saves time but also guarantees that every instance of the targeted text is updated consistently. In this article, we will demonstrate how to find and replace text in a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Find Text and Replace All Its Instances with New Text
- Find Text and Replace Its First Instance with New Text
- Find and Replace Text Using a Regular Expression
- Find and Replace Text with an Image
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Find Text and Replace All Its Instances with New Text
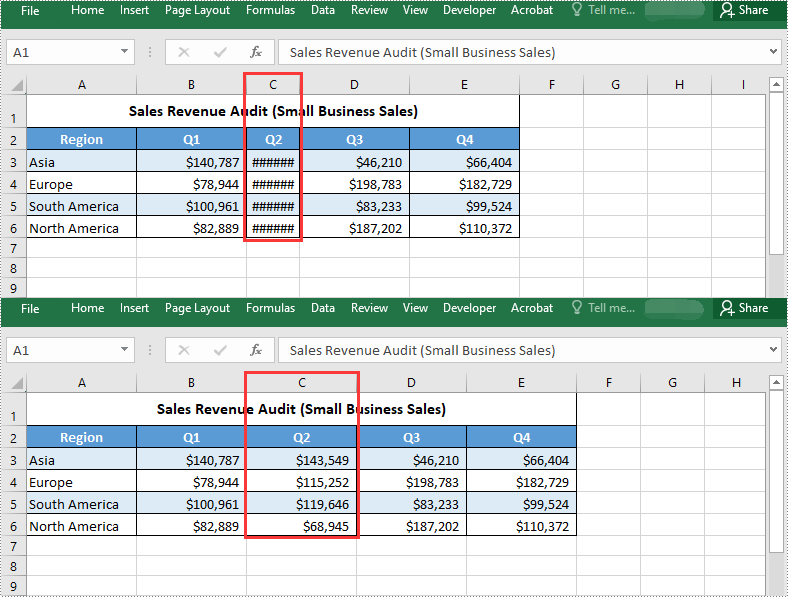
You can find a text and replace all its instances with another text easily using the Document.Replace() method. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Find a specific text and replace all its instances with another text using Document.Replace() method.
- Save the resulting document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Find a specific text and replace all its instances with another text
document.Replace("Spire.Doc", "Eiceblue", False, True)
# Save the resulting document
document.SaveToFile("ReplaceAllOccurrencesOfText.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()
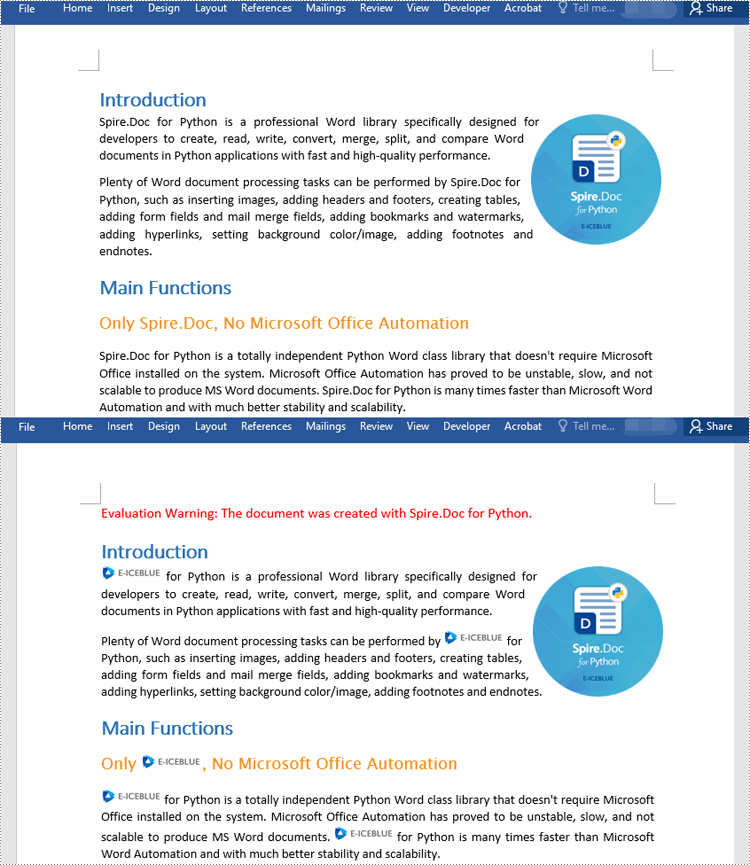
Find Text and Replace Its First Instance with New Text
Spire.Doc for Python provides the Document.ReplaceFirst property which enables you to change the replacement mode from replacing all instances to replacing the first instance. The following steps explain how to find a text and replace its first instance in a Word document:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Change the replacement mode to replace the first instance by setting the Document.ReplaceFirst property as True.
- Replace the first instance of a text with another text using Document.Replace() method.
- Save the resulting document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Change the replacement mode to replace the first match
document.ReplaceFirst = True
# Replace the first instance of a text with another text
document.Replace("Spire.Doc", "Eiceblue", False, True)
# Save the resulting document
document.SaveToFile("ReplaceFirstOccurrenceOfText.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()

Find and Replace Text Using a Regular Expression
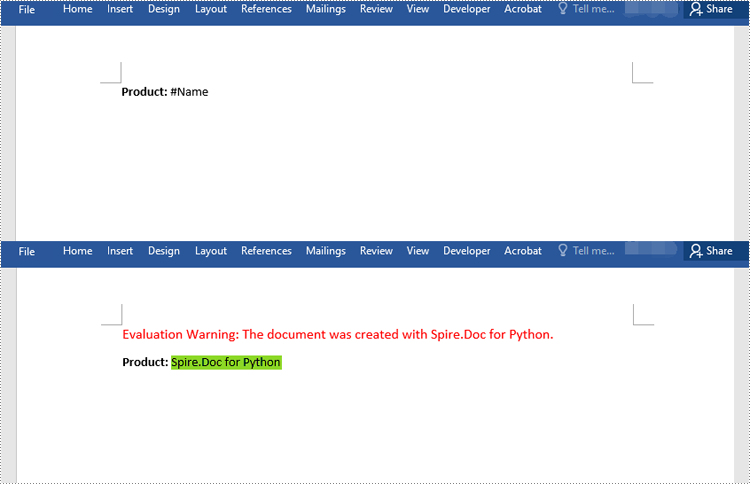
You can replace a text matching a regular expression with new text by passing a Regex object and the new text to the Document.Replace() method as parameters. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a Regex object to match the specific text.
- Replace the text matching the regex with another text using Document.Replace() method.
- Save the resulting document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Sample1.docx")
# Create a regex to match the text that starts with #
regex = Regex("""\\#\\w+\\b""")
# Find the text matching the regex and replace it with another text
document.Replace(regex, "Spire.Doc for Python")
#save the document
document.SaveToFile("ReplaceTextUsingRegex.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()
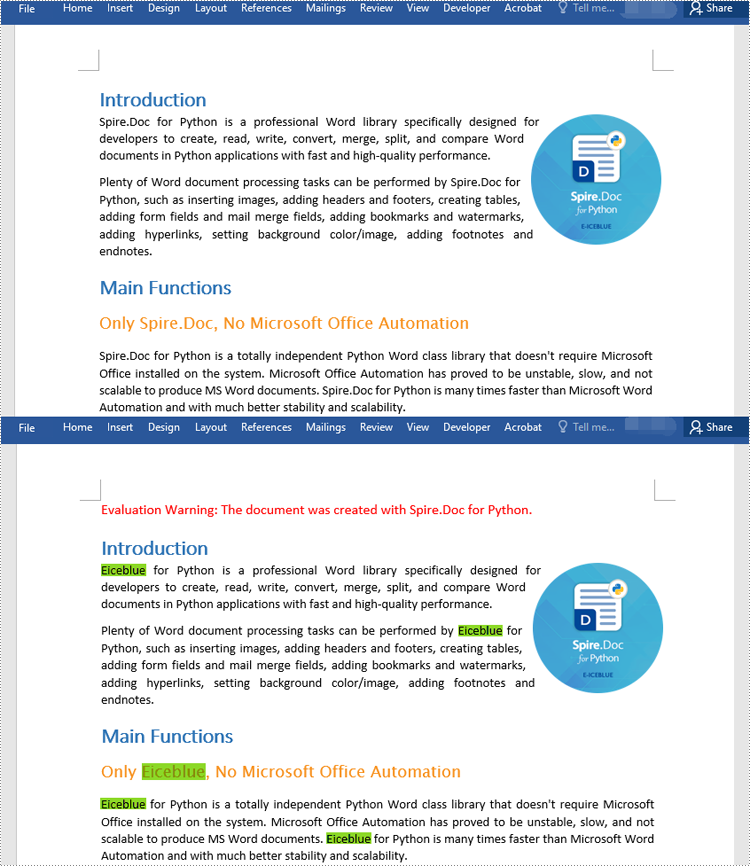
Find and Replace Text with an Image
Spire.Doc for Python doesn't offer a direct method to replace text with image, but you can achieve this by inserting the image at the position of the text and then removing the text from the document. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Find a specific text in the document using Document.FindAllString() method.
- Loop through the found results.
- Create a DocPicture object and load an image using DocPicture.LoadImage() method.
- Get the found text as a single text range and then get the index of the text range in its owner paragraph.
- Insert an image at the position of the text range and then remove the text range from the document.
- Save the resulting document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Find a specific text in the document
selections = document.FindAllString("Spire.Doc", True, True)
index = 0
testRange = None
# Loop through the found results
for selection in selections:
# Load an image
pic = DocPicture(document)
pic.LoadImage("logo.png")
# Get the found text as a single text range
testRange = selection.GetAsOneRange()
# Get the index of the text range in its owner paragraph
index = testRange.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf(testRange)
# Insert an image at the index
testRange.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.Insert(index, pic)
# Remove the text range
testRange.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.Remove(testRange)
# Save the resulting document
document.SaveToFile("ReplaceTextWithImage.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Superscript and subscript are formatting styles used in typography and writing to position characters or numbers above or below the normal line of text. Superscript is a smaller-sized text or symbol that is raised above the baseline. It is commonly used for mathematical exponents, footnotes, and ordinal indicators. Subscript, on the other hand, is a smaller-sized text or symbol that is positioned below the baseline. It is often used for chemical formulas, mathematical expressions and some linguistic notations. These formatting styles can help users distinguish specific elements within text and convey information more effectively. In this article, we will show you how to apply superscript and subscript in Excel by using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Apply Superscript and Subscript in Excel
To apply the superscript or subscript style to specific characters in excel, you need to create a custom font first and set the superscript or subscript property of it. And then assign the font to the specific characters within the cell using CellRange.RichText.SetFont() method provided by Spire.XLS for Python. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Get the first worksheet of it using Workbook.Worksheets[int index] property.
- Get the specific cells using Worksheet.Range[string name] property and add desired text to them.
- Get a cell by using Worksheet.Range[string name] property and add rich text to it by CellRange.RichText.Text property.
- Create a custom font using Workbook.CreateFont() method.
- Enable the subscript property of the font by setting ExcelFont.IsSubscript property to true.
- Assign the font to specific characters of the added rich text in the cell by calling CellRange.RichText.SetFont() method.
- Likewise, get another cell using Worksheet.Range[string name] property and add rich text to it by CellRange.RichText.Text property.
- Create a custom font using Workbook.CreateFont() method.
- Enable the superscript property of the font by setting ExcelFont.IsSuperscript property to true.
- Assign the font to specific characters of the added rich text in the cell by calling CellRange.RichText.SetFont() method.
- Automatically adjust column widths to fit text length using Worksheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
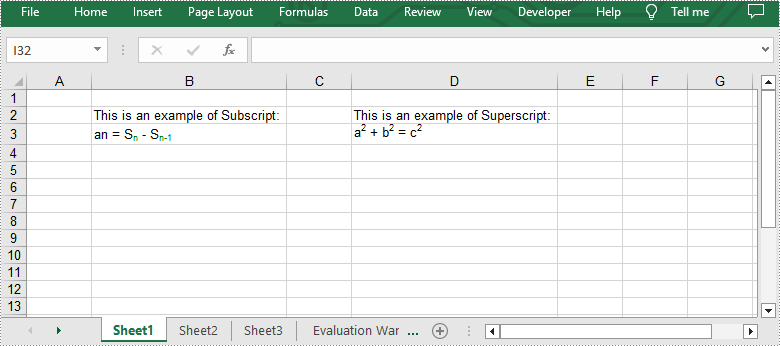
from spire.common import * from spire.xls.common import * outputFile = "ApplySubscriptAndSuperscript.xlsx" #Create an object of Workbook class workbook = Workbook() #Get the first worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] #Add text to the specific cells sheet.Range["B2"].Text = "This is an example of Subscript:" sheet.Range["D2"].Text = "This is an example of Superscript:" #Add rich text to a specific cell range = sheet.Range["B3"] range.RichText.Text = "an = Sn - Sn-1" #Create a custom font font = workbook.CreateFont() #Enable the subscript property of the font by setting the IsSubscript property to "true" font.IsSubscript = True #Set the font color font.Color = Color.get_Green() #Assign the font to specific characters of the added rich text range.RichText.SetFont(6, 6, font) range.RichText.SetFont(11, 13, font) #Add rich text to another cell range = sheet.Range["D3"] range.RichText.Text = "a2 + b2 = c2" #Create a custom font font = workbook.CreateFont() #Enable the superscript property of the font by setting the IsSuperscript property to "true" font.IsSuperscript = True #Assign the font to specific characters of the added rich text range.RichText.SetFont(1, 1, font) range.RichText.SetFont(6, 6, font) range.RichText.SetFont(11, 11, font) #Autofit the column widths sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns() #Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
During the process of document creation, it is common to encounter numerous blank lines. These empty spaces can disrupt the flow of the content, clutter the layout, and undermine the overall aesthetic presentation of the document. In order to optimize the reading experience and ensure a well-structured document, it becomes crucial to eliminate the blank lines. This article will demonstrate how to delete blank lines from Word documents through Python programs using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Remove Blank Lines from Word Documents
Blank lines in a Word document appear as blank paragraphs, which are child objects of sections. Therefore, removing blank lines simply requires iterating through the sections, identifying and deleting empty paragraphs within them. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through each section and each child object of the sections.
- First, check if a child object is of paragraph type. If it is, continue to check if the sub-object is an instance of the "Paragraph" class. If it is, further check if the paragraph has no text. If there is no text, delete the paragraph using Section.Body.ChildObjects.Remove() method.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of the Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Iterate through each section in the document
for i in range(doc.Sections.Count):
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(i)
j = 0
# Iterate through each child object in the section
while j < section.Body.ChildObjects.Count:
# Check if the child object is of type Paragraph
if section.Body.ChildObjects[j].DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Paragraph:
objItem = section.Body.ChildObjects[j]
# Check if the child object is an instance of the Paragraph class
if isinstance(objItem, Paragraph):
paraObj = Paragraph(objItem)
# Check if the paragraph text is empty
if len(paraObj.Text) == 0:
# If the paragraph text is empty, remove the object from the section's child objects list
section.Body.ChildObjects.Remove(objItem)
j -= 1
j += 1
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/RemoveBlankLines.docx")

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Hyperlinks are an essential component of creating dynamic and interactive Word documents. By linking specific text or objects to other documents, web pages, email addresses, or specific locations within the same document, hyperlinks allow users to navigate through information seamlessly. In this article, you will learn how to add or remove hyperlinks in a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Add Hyperlinks to Word in Python
Spire.Doc for Python offers the Paragraph.AppendHyperlink() method to add a web link, an email link, a file link, or a bookmark link to a piece of text or an image inside a paragraph. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section and a paragraph to it.
- Insert a hyperlink based on text using Paragraph.AppendHyerplink(link: str, text: str, type: HyperlinkType) method.
- Add an image to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendPicture() method.
- Insert a hyperlink based on the image using Paragraph.AppendHyerplink(link: str, picture: DocPicture, type: HyperlinkType) method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Word document
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
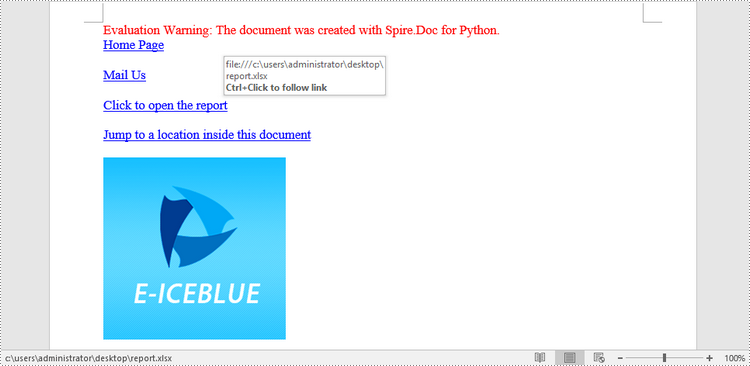
paragraph.AppendHyperlink("https://www-iceblue.com/", "Home Page", HyperlinkType.WebLink)
# Append line breaks
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak)
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak)
# Add an email link
paragraph.AppendHyperlink("mailto:support@e-iceblue.com", "Mail Us", HyperlinkType.EMailLink)
# Append line breaks
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak)
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak)
# Add a file link
filePath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\report.xlsx"
paragraph.AppendHyperlink(filePath, "Click to open the report", HyperlinkType.FileLink)
# Append line breaks
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak)
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak)
# Add another section and create a bookmark
section2 = doc.AddSection()
bookmarkParagrapg = section2.AddParagraph()
bookmarkParagrapg.AppendText("Here is a bookmark")
start = bookmarkParagrapg.AppendBookmarkStart("myBookmark")
bookmarkParagrapg.Items.Insert(0, start)
bookmarkParagrapg.AppendBookmarkEnd("myBookmark")
# Link to the bookmark
paragraph.AppendHyperlink("myBookmark", "Jump to a location inside this document", HyperlinkType.Bookmark)
# Append line breaks
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak)
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak)
# Add an image link
image = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\logo.png"
picture = paragraph.AppendPicture(image)
paragraph.AppendHyperlink("https://www.e-iceblue.com/", picture, HyperlinkType.WebLink)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/CreateHyperlinks.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019);
doc.Dispose()
Remove Hyperlinks from Word in Python
To delete all hyperlinks in a Word document at once, you'll need to find all the hyperlinks in the document and then create a custom method FlattenHyperlinks() to flatten them. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a sample Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Find all the hyperlinks in the document using custom method FindAllHyperlinks().
- Loop through the hyperlinks and flatten all of them using custom method FlattenHyperlinks().
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Find all the hyperlinks in a document
def FindAllHyperlinks(document):
hyperlinks = []
for i in range(document.Sections.Count):
section = document.Sections.get_Item(i)
for j in range(section.Body.ChildObjects.Count):
sec = section.Body.ChildObjects.get_Item(j)
if sec.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Paragraph:
for k in range((sec if isinstance(sec, Paragraph) else None).ChildObjects.Count):
para = (sec if isinstance(sec, Paragraph)
else None).ChildObjects.get_Item(k)
if para.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Field:
field = para if isinstance(para, Field) else None
if field.Type == FieldType.FieldHyperlink:
hyperlinks.append(field)
return hyperlinks
# Flatten the hyperlink fields
def FlattenHyperlinks(field):
ownerParaIndex = field.OwnerParagraph.OwnerTextBody.ChildObjects.IndexOf(
field.OwnerParagraph)
fieldIndex = field.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf(field)
sepOwnerPara = field.Separator.OwnerParagraph
sepOwnerParaIndex = field.Separator.OwnerParagraph.OwnerTextBody.ChildObjects.IndexOf(
field.Separator.OwnerParagraph)
sepIndex = field.Separator.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf(
field.Separator)
endIndex = field.End.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf(field.End)
endOwnerParaIndex = field.End.OwnerParagraph.OwnerTextBody.ChildObjects.IndexOf(
field.End.OwnerParagraph)
FormatFieldResultText(field.Separator.OwnerParagraph.OwnerTextBody,
sepOwnerParaIndex, endOwnerParaIndex, sepIndex, endIndex)
field.End.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(endIndex)
for i in range(sepOwnerParaIndex, ownerParaIndex - 1, -1):
if i == sepOwnerParaIndex and i == ownerParaIndex:
for j in range(sepIndex, fieldIndex - 1, -1):
field.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(j)
elif i == ownerParaIndex:
for j in range(field.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.Count - 1, fieldIndex - 1, -1):
field.OwnerParagraph.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(j)
elif i == sepOwnerParaIndex:
for j in range(sepIndex, -1, -1):
sepOwnerPara.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(j)
else:
field.OwnerParagraph.OwnerTextBody.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(i)
# Convert fields to text range and clear the text formatting
def FormatFieldResultText(ownerBody, sepOwnerParaIndex, endOwnerParaIndex, sepIndex, endIndex):
for i in range(sepOwnerParaIndex, endOwnerParaIndex + 1):
para = ownerBody.ChildObjects[i] if isinstance(
ownerBody.ChildObjects[i], Paragraph) else None
if i == sepOwnerParaIndex and i == endOwnerParaIndex:
for j in range(sepIndex + 1, endIndex):
if isinstance(para.ChildObjects[j], TextRange):
FormatText(para.ChildObjects[j])
elif i == sepOwnerParaIndex:
for j in range(sepIndex + 1, para.ChildObjects.Count):
if isinstance(para.ChildObjects[j], TextRange):
FormatText(para.ChildObjects[j])
elif i == endOwnerParaIndex:
for j in range(0, endIndex):
if isinstance(para.ChildObjects[j], TextRange):
FormatText(para.ChildObjects[j])
else:
for j, unusedItem in enumerate(para.ChildObjects):
if isinstance(para.ChildObjects[j], TextRange):
FormatText(para.ChildObjects[j])
# Format text
def FormatText(tr):
tr.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Black()
tr.CharacterFormat.UnderlineStyle = UnderlineStyle.none
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\test.docx")
# Get all hyperlinks
hyperlinks = FindAllHyperlinks(doc)
# Flatten all hyperlinks
for i in range(len(hyperlinks) - 1, -1, -1):
FlattenHyperlinks(hyperlinks[i])
# Save to a different file
doc.SaveToFile("output/RemoveHyperlinks.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Applying a background color or image to a PDF can be an effective way to enhance its visual appeal, create a professional look, or reinforce branding elements. By adding a background, you can customize the overall appearance of your PDF document and make it more engaging for readers. Whether you want to use a solid color or incorporate a captivating image, this feature allows you to personalize your PDFs and make them stand out. In this article, you will learn how to set a background color or image for a PDF document in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Set a Background Color for PDF in Python
Spire.PDF for Python offers the PdfPageBase.BackgroundColor property to get or set the background color of a certain page. To add a solid color to the background of each page in the document, follow the steps below.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Traverse through the pages in the document, and get a specific page through PdfDocument.Pages[index] property.
- Apply a solid color to the background through PdfPageBase.BackgroundColor property.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.pdf")
# Loop through the pages in the document
for i in range(doc.Pages.Count):
# Get a particular page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Set background color
page.BackgroundColor = Color.get_LightYellow()
# Save the document to a different file
doc.SaveToFile("output/SetBackgroundColor.pdf")
Set a Background Image for PDF in Python
Likewise, an image can be applied to the background of a specific page via PdfPageBase.BackgroundImage property. The steps to set an image background for the entire document are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Traverse through the pages in the document, and get a specific page through PdfDocument.Pages[index] property.
- Apply an image to the background through PdfPageBase.BackgroundImage property.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.pdf")
# Loop through the pages in the document
for i in range(doc.Pages.Count):
# Get a particular page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Set background image
page.BackgroundImage = Stream("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\img.jpg")
# Save the document to a different file
doc.SaveToFile("output/SetBackgroundImage.pdf")
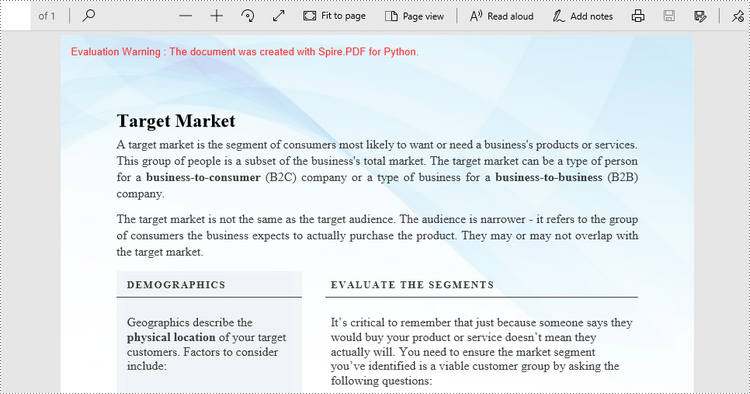
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
If you receive or download a PDF file and find that some of the pages are displayed in the wrong orientation (e.g., sideways or upside down), rotating the PDF file allows you to correct the page orientation for easier reading and viewing. This article will demonstrate how to programmatically rotate PDF pages using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Rotate a Specific Page in PDF in Python
Rotation is based on 90-degree increments. You can rotate a PDF page by 0/90/180/270 degrees. The following are the steps to rotate a PDF page:
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified page using PdfDocument.Pages[pageIndex] property.
- Get the original rotation angle of the page using PdfPageBase.Rotation.value property.
- Increase the original rotation angle by desired degrees.
- Apply the new rotation angle to the page using PdfPageBase.Rotation property
- Save the result document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Get the original rotation angle of the page
rotation = int(page.Rotation.value)
# Rotate the page 180 degrees clockwise based on the original rotation angle
rotation += int(PdfPageRotateAngle.RotateAngle180.value)
page.Rotation = PdfPageRotateAngle(rotation)
# Save the result document
pdf.SaveToFile("RotatePDFPage.pdf")
pdf.Close()
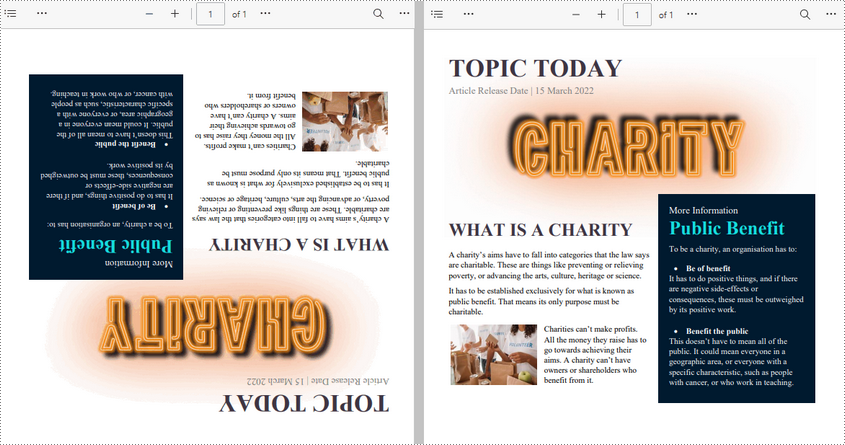
Rotate All Pages in PDF in Python
Spire.PDF for Python also allows you to loop through each page in a PDF file and then rotate them all. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Loop through each page in the document.
- Get the original rotation angle of the page using PdfPageBase.Rotation.value property.
- Increase the original rotation angle by desired degrees.
- Apply the new rotation angle to the page using PdfPageBase.Rotation property.
- Save the result document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("Input.pdf")
# Loop through each page in the document
for i in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Get the original rotation angle of the page
rotation = int(page.Rotation.value)
# Rotate the page 180 degrees clockwise based on the original rotation angle
rotation += int(PdfPageRotateAngle.RotateAngle180.value)
page.Rotation = PdfPageRotateAngle(rotation)
# Save the result document
pdf.SaveToFile("RotatePDF.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
