Java: Find and Extract Hyperlinks in Word Documents
Hyperlinks in Word documents can lead readers to a webpage, an external file, an email address, and a specific place of the document being read. They are commonly used in Word documents for their convenience. This article will teach you how to use Spire.Doc for Java to find and extract hyperlinks in Word documents, including hypertexts and links.
- Find and Extract a Specified Hyperlink in a Word Document
- Find and Extract All the Hyperlinks in a Word Document
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>14.1.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
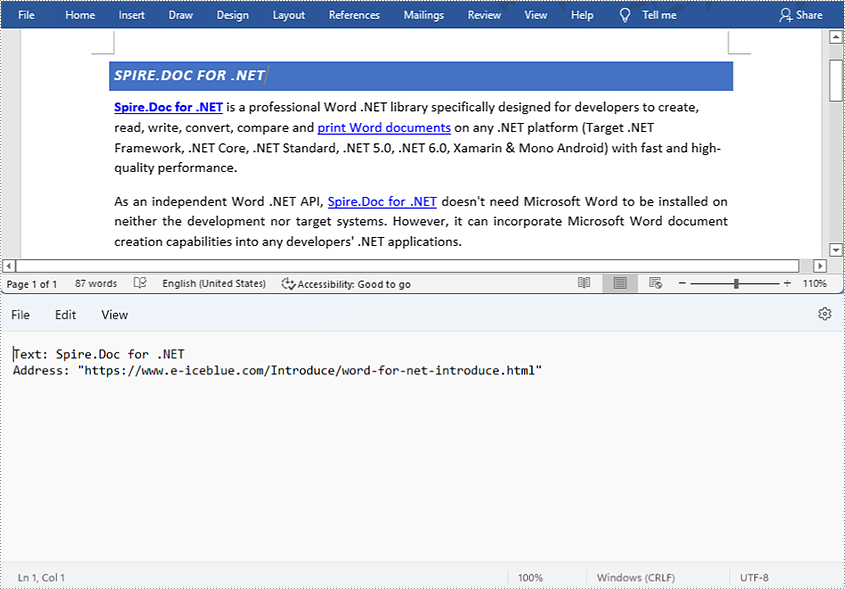
Find and Extract a Specified Hyperlink in a Word Document
The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document instance and load a Word document from disk using Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Create an object of ArrayList<Field>.
- Iterate through the items in the sections to find all hyperlinks.
- Get the text of the first hyperlink using Field.get().getFieldText() method and get its link using Field.get().getValue() method.
- Save the text and the link of the first hyperlink to a TXT file using custom method writeStringToText().
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
import com.spire.doc.fields.Field;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class findHyperlinks {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//Create a Document instance and load a Word document from file
String input = "D:/testp/test.docx";
Document doc = new Document();
doc.loadFromFile(input);
//Create an object of ArrayList
ArrayListField> hyperlinks = new ArrayList();
//Iterate through the items in the sections to find all hyperlinks
for (Section section : (IterableSection>) doc.getSections()) {
for (DocumentObject object : (IterableDocumentObject>) section.getBody().getChildObjects()) {
if (object.getDocumentObjectType().equals(DocumentObjectType.Paragraph)) {
Paragraph paragraph = (Paragraph) object;
for (DocumentObject cObject : (IterableDocumentObject>) paragraph.getChildObjects()) {
if (cObject.getDocumentObjectType().equals(DocumentObjectType.Field)) {
Field field = (Field) cObject;
if (field.getType().equals(FieldType.Field_Hyperlink)) {
hyperlinks.add(field);
}
}
}
}
}
}
//Get the text and the address of the first hyperlink
String hyperlinksText = hyperlinks.get(0).getFieldText();
String hyperlinkAddress = hyperlinks.get(0).getValue();
//Save the text and the link of the first hyperlink to a TXT file
String output = "D:/javaOutput/HyperlinkTextAndLink.txt";
writeStringToText("Text:\r\n" + hyperlinksText+ "\r\n" + "Link:\r\n" + hyperlinkAddress, output);
}
//Create a method to write the text and link of hyperlinks to a TXT file
public static void writeStringToText(String content, String textFileName) throws IOException {
File file = new File(textFileName);
if (file.exists())
{
file.delete();
}
FileWriter fWriter = new FileWriter(textFileName, true);
try {
fWriter.write(content);
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fWriter.flush();
fWriter.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
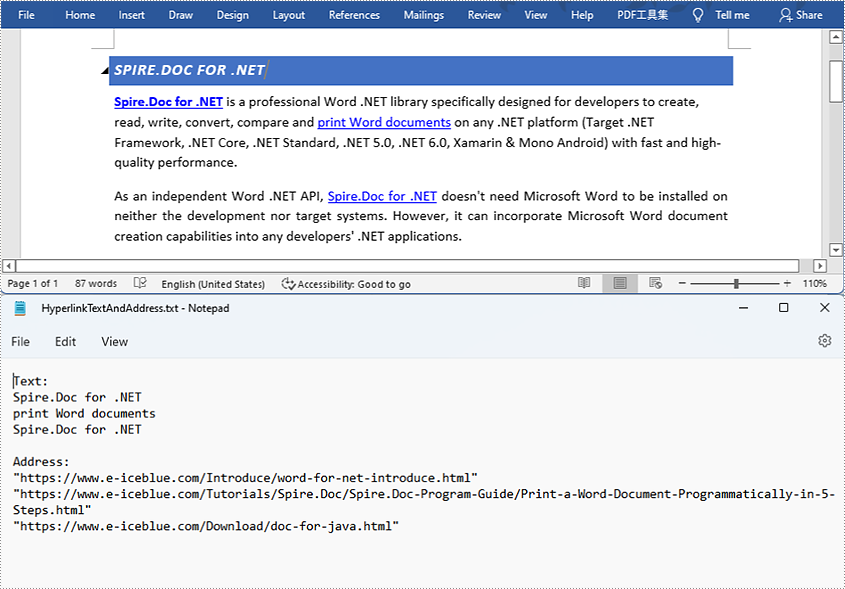
Find and Extract All the Hyperlinks in a Word Document
The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Document instance and load a Word document from disk using Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Create an object of ArrayList<Field>.
- Iterate through the items in the sections to find all hyperlinks.
- Get the texts of the hyperlinks using Field.get().getFieldText() method and get their links using Field.get().getValue() method.
- Save the text and the links of the hyperlinks to a TXT file using custom method writeStringToText().
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
import com.spire.doc.fields.Field;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class findHyperlinks {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//Create a Document instance and load a Word document from file
String input = "D:/testp/test.docx";
Document doc = new Document();
doc.loadFromFile(input);
//Create an object of ArrayList
ArrayListField> hyperlinks = new ArrayList();
String hyperlinkText = "";
String hyperlinkAddress = "";
//Iterate through the items in the sections to find all hyperlinks
for (Section section : (IterableSection>) doc.getSections()) {
for (DocumentObject object : (IterableDocumentObject>) section.getBody().getChildObjects()) {
if (object.getDocumentObjectType().equals(DocumentObjectType.Paragraph)) {
Paragraph paragraph = (Paragraph) object;
for (DocumentObject cObject : (IterableDocumentObject>) paragraph.getChildObjects()) {
if (cObject.getDocumentObjectType().equals(DocumentObjectType.Field)) {
Field field = (Field) cObject;
if (field.getType().equals(FieldType.Field_Hyperlink)) {
hyperlinks.add(field);
}
}
}
}
}
}
//Save the texts and the links of the hyperlinks to a TXT file
String output = "D:/javaOutput/HyperlinksTextsAndLinks.txt";
writeStringToText("Text:\r\n " + hyperlinkText + "\r\n" + "Link:\r\n" + hyperlinkAddress + "\r\n", output);
}
//Create a method to write the text and link of hyperlinks to a TXT file
public static void writeStringToText(String content, String textFileName) throws IOException {
File file = new File(textFileName);
if (file.exists())
{
file.delete();
}
FileWriter fWriter = new FileWriter(textFileName, true);
try {
fWriter.write(content);
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fWriter.flush();
fWriter.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Java: Remove Hyperlinks in Word Documents
Hyperlinks usually appear on texts. By clicking on a hyperlink, we can access a website, a document, an email address, or other elements. Some Word documents, especially those that are generated from web content, may contain irritating hyperlinks, such as advertisements. This article shows you how to programmatically remove one hyperlink or all hyperlinks in a Word document using Spire.Doc for Java.
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>14.1.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
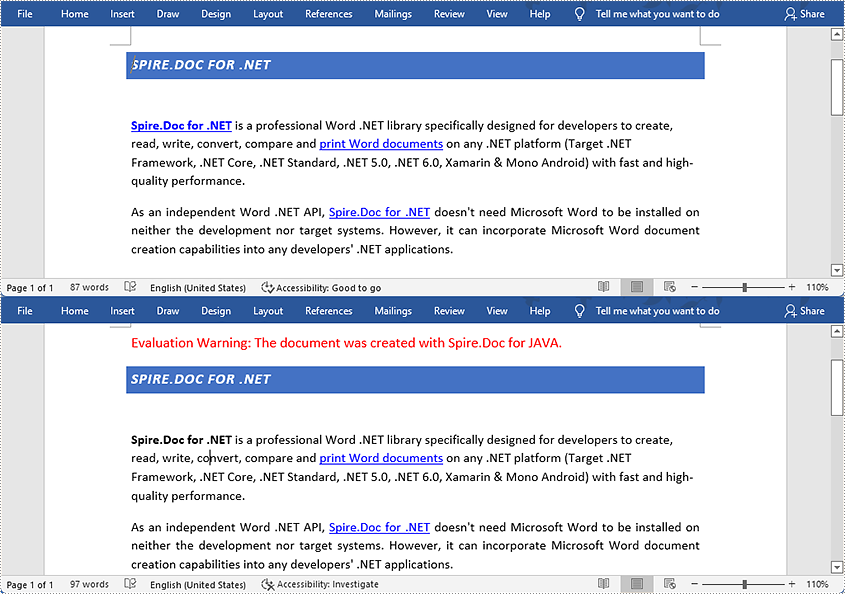
Remove a Specified Hyperlink in a Word Document
The detailed steps to remove a specified hyperlink in a Word file are as follows:
- Create a Document object and load a Word document from disk using Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Find all the hyperlinks using custom method FindAllHyperlinks().
- Flatten the first hyperlink using custom method FlattenHyperlinks().
- Save the document using Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.DocumentObjectType;
import com.spire.doc.documents.Paragraph;
import com.spire.doc.documents.UnderlineStyle;
import com.spire.doc.fields.Field;
import com.spire.doc.fields.TextRange;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class removeHyperlink {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a Document object and load a Word document from disk
String input = "D:/testp/test.docx";
Document doc = new Document();
doc.loadFromFile(input);
//Find all hyperlinks
ArrayList<Field> hyperlinks = FindAllHyperlinks(doc);
//Flatten the first hyperlink
FlattenHyperlinks(hyperlinks.get(0));
//Save the document to file
String output = "D:/javaOutput/RemoveHyperlinks.docx";
doc.saveToFile(output, FileFormat.Docx);
}
//Iterate through the items in the sections to find all hyperlinks
for (Section section : (Iterable<Section>)document.getSections())
{
for (DocumentObject object : (Iterable<DocumentObject>)section.getBody().getChildObjects())
{
if (object.getDocumentObjectType().equals(DocumentObjectType.Paragraph))
{
Paragraph paragraph = (Paragraph) object;
for (DocumentObject cObject : (Iterable<DocumentObject>)paragraph.getChildObjects())
{
Paragraph paragraph = (Paragraph) object;
for (DocumentObject cObject : (Iterable)paragraph.getChildObjects())
{
if (cObject.getDocumentObjectType().equals(DocumentObjectType.Field))
{
Field field = (Field) cObject;
if (field.getType().equals(FieldType.Field_Hyperlink))
{
hyperlinks.add(field);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return hyperlinks;
}
//Create a method FlattenHyperlinks() to flatten the hyperlink field
public static void FlattenHyperlinks(Field field)
{
int ownerParaIndex = field.getOwnerParagraph().getOwnerTextBody().getChildObjects().indexOf(field.getOwnerParagraph());
int fieldIndex = field.getOwnerParagraph().getChildObjects().indexOf(field);
Paragraph sepOwnerPara = field.getSeparator().getOwnerParagraph();
int sepOwnerParaIndex = field.getSeparator().getOwnerParagraph().getOwnerTextBody().getChildObjects().indexOf(field.getSeparator().getOwnerParagraph());
int sepIndex = field.getSeparator().getOwnerParagraph().getChildObjects().indexOf(field.getSeparator());
int endIndex = field.getEnd().getOwnerParagraph().getChildObjects().indexOf(field.getEnd());
int endOwnerParaIndex = field.getEnd().getOwnerParagraph().getOwnerTextBody().getChildObjects().indexOf(field.getEnd().getOwnerParagraph());
FormatFieldResultText(field.getSeparator().getOwnerParagraph().getOwnerTextBody(), sepOwnerParaIndex, endOwnerParaIndex, sepIndex, endIndex);
field.getEnd().getOwnerParagraph().getChildObjects().removeAt(endIndex);"
for (int i = sepOwnerParaIndex; i >= ownerParaIndex; i--)
{
if (i == sepOwnerParaIndex && i == ownerParaIndex)
{
for (int j = sepIndex; j >= fieldIndex; j--)
{
field.getOwnerParagraph().getChildObjects().removeAt(j);
}
}
else if (i == ownerParaIndex)
{
for (int j = field.getOwnerParagraph().getChildObjects().getCount() - 1; j >= fieldIndex; j--)
{
field.getOwnerParagraph().getChildObjects().removeAt(j);
}
}
else if (i == sepOwnerParaIndex)
{
for (int j = sepIndex; j >= 0; j--)
{
sepOwnerPara.getChildObjects().removeAt(j);
}
}
else
{
field.getOwnerParagraph().ownerTextBody().getChildObjects().removeAt(i);
}
}
}
//Create a method FormatFieldResultText() to remove the font color and underline format of the hyperlinks
private static void FormatFieldResultText(Body ownerBody, int sepOwnerParaIndex, int endOwnerParaIndex, int sepIndex, int endIndex)
{
for (int i = sepOwnerParaIndex; i <= endOwnerParaIndex; i++)
{
Paragraph para = (Paragraph) ownerBody.getChildObjects().get(i);
if (i == sepOwnerParaIndex && i == endOwnerParaIndex)
{
for (int j = sepIndex + 1; j < endIndex; j++)
{
FormatText((TextRange)para.getChildObjects().get(j));
}
}
else if (i == sepOwnerParaIndex)
{
for (int j = sepIndex + 1; j < para.getChildObjects().getCount(); j++)
{
FormatText((TextRange)para.getChildObjects().get(j));
}
}
else if (i == endOwnerParaIndex)
{
for (int j = 0; j < endIndex; j++)
{
FormatText((TextRange)para.getChildObjects().get(j));
}
}
else
{
for (int j = 0; j < para.getChildObjects().getCount(); j++)
{
FormatText((TextRange)para.getChildObjects().get(j));
}
}
}
}
//Create a method FormatText() to change the color of the text to black and remove the underline
private static void FormatText(TextRange tr)
{
//Set the text color to black
tr.getCharacterFormat().setTextColor(Color.black);
//Set the text underline style to none
tr.getCharacterFormat().setUnderlineStyle(UnderlineStyle.None);
}
}
Remove All the Hyperlinks in a Word Document
The detailed steps to remove all the hyperlinks in a Word file are as follows:
- Create a Document object and load a Word document from disk using Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Find all the hyperlinks using custom method FindAllHyperlinks().
- Loop through the hyperlinks, and invoke the custom method FlattenHyperlinks() to flatten the specific hyperlink.
- Save the document using Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.DocumentObjectType;
import com.spire.doc.documents.Paragraph;
import com.spire.doc.documents.UnderlineStyle;
import com.spire.doc.fields.Field;
import com.spire.doc.fields.TextRange;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class removeHyperlink {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a Document object and load a Word document from disk
String input = "D:/testp/test.docx";
Document doc = new Document();
doc.loadFromFile(input);
//Find all the hyperlinks
ArrayList<Field> hyperlinks = FindAllHyperlinks(doc);
//Loop through the hyperlinks, and flatten the specific hyperlink.
for (int i = hyperlinks.size() -1; i >= 0; i--)
{
FlattenHyperlinks(hyperlinks.get(i));
}
//Save the document to file
String output = "D:/javaOutput/RemoveHyperlinks.docx";
doc.saveToFile(output, FileFormat.Docx);
}
//Create a method FindAllHyperlinks() to get all the hyperlinks from the sample document
private static ArrayList FindAllHyperlinks(Document document)
{
ArrayListField> hyperlinks = new ArrayList();
//Iterate through the items in the sections to find all hyperlinks
for (Section section : (Iterable<Section>)document.getSections())
{
for (DocumentObject object : (Iterable<DocumentObject>)section.getBody().getChildObjects())
{
if (object.getDocumentObjectType().equals(DocumentObjectType.Paragraph))
{
Paragraph paragraph = (Paragraph) object;
for (DocumentObject cObject : (Iterable<DocumentObject>)paragraph.getChildObjects())
{
if (cObject.getDocumentObjectType().equals(DocumentObjectType.Field))
{
Field field = (Field) cObject;
if (field.getType().equals(FieldType.Field_Hyperlink))
{
hyperlinks.add(field);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return hyperlinks;
}
//Create a method FlattenHyperlinks() to flatten the hyperlink field
public static void FlattenHyperlinks(Field field)
{
int ownerParaIndex = field.getOwnerParagraph().getOwnerTextBody().getChildObjects().indexOf(field.getOwnerParagraph());
int fieldIndex = field.getOwnerParagraph().getChildObjects().indexOf(field);
Paragraph sepOwnerPara = field.getSeparator().getOwnerParagraph();
int sepOwnerParaIndex = field.getSeparator().getOwnerParagraph().getOwnerTextBody().getChildObjects().indexOf(field.getSeparator().getOwnerParagraph());
int sepIndex = field.getSeparator().getOwnerParagraph().getChildObjects().indexOf(field.getSeparator());
int endIndex = field.getEnd().getOwnerParagraph().getChildObjects().indexOf(field.getEnd());
int endOwnerParaIndex = field.getEnd().getOwnerParagraph().getOwnerTextBody().getChildObjects().indexOf(field.getEnd().getOwnerParagraph());
FormatFieldResultText(field.getSeparator().getOwnerParagraph().getOwnerTextBody(), sepOwnerParaIndex, endOwnerParaIndex, sepIndex, endIndex);
field.getEnd().getOwnerParagraph().getChildObjects().removeAt(endIndex);"
for (int i = sepOwnerParaIndex; i >= ownerParaIndex; i--)
{
if (i == sepOwnerParaIndex && i == ownerParaIndex)
{
for (int j = sepIndex; j >= fieldIndex; j--)
{
field.getOwnerParagraph().getChildObjects().removeAt(j);
}
}
else if (i == ownerParaIndex)
{
for (int j = field.getOwnerParagraph().getChildObjects().getCount() - 1; j >= fieldIndex; j--)
{
field.getOwnerParagraph().getChildObjects().removeAt(j);
}
}
else if (i == sepOwnerParaIndex)
{
for (int j = sepIndex; j >= 0; j--)
{
sepOwnerPara.getChildObjects().removeAt(j);
}
}
else
{
field.getOwnerParagraph().ownerTextBody().getChildObjects().removeAt(i);
}
}
}
//Create a method FormatFieldResultText() to format the texts
private static void FormatFieldResultText(Body ownerBody, int sepOwnerParaIndex, int endOwnerParaIndex, int sepIndex, int endIndex)
{
for (int i = sepOwnerParaIndex; i <= endOwnerParaIndex; i++)
{
Paragraph para = (Paragraph) ownerBody.getChildObjects().get(i);
if (i == sepOwnerParaIndex && i == endOwnerParaIndex)
{
for (int j = sepIndex + 1; j < endIndex; j++)
{
FormatText((TextRange)para.getChildObjects().get(j));
}
}
else if (i == sepOwnerParaIndex)
{
for (int j = sepIndex + 1; j < para.getChildObjects().getCount(); j++)
{
FormatText((TextRange)para.getChildObjects().get(j));
}
}
else if (i == endOwnerParaIndex)
{
for (int j = 0; j < endIndex; j++)
{
FormatText((TextRange)para.getChildObjects().get(j));
}
}
else
{
for (int j = 0; j < para.getChildObjects().getCount(); j++)
{
FormatText((TextRange)para.getChildObjects().get(j));
}
}
}
}
//Create a method FormatText() to change the color of the text to black and remove the underline
private static void FormatText(TextRange tr)
{
//Set the text color to black
tr.getCharacterFormat().setTextColor(Color.black);
//Set the text underline style to none
tr.getCharacterFormat().setUnderlineStyle(UnderlineStyle.None);
}
}

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Java: Find Text and Add Hyperlinks for Them in PDF
A hyperlink refers to an icon, graphic, or text that links to another file or object. It is one of the most commonly used features for manipulating documents. Spire.PDF for Java supports creating a new PDF document and adding various hyperlinks to it, including ordinary links, hypertext links, email links and document links. This article will show you how to add hyperlinks to specific text in an existing PDF.
Install Spire.PDF for Java
First of all, you need to add the Spire.Pdf.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.pdf</artifactId>
<version>11.12.16</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
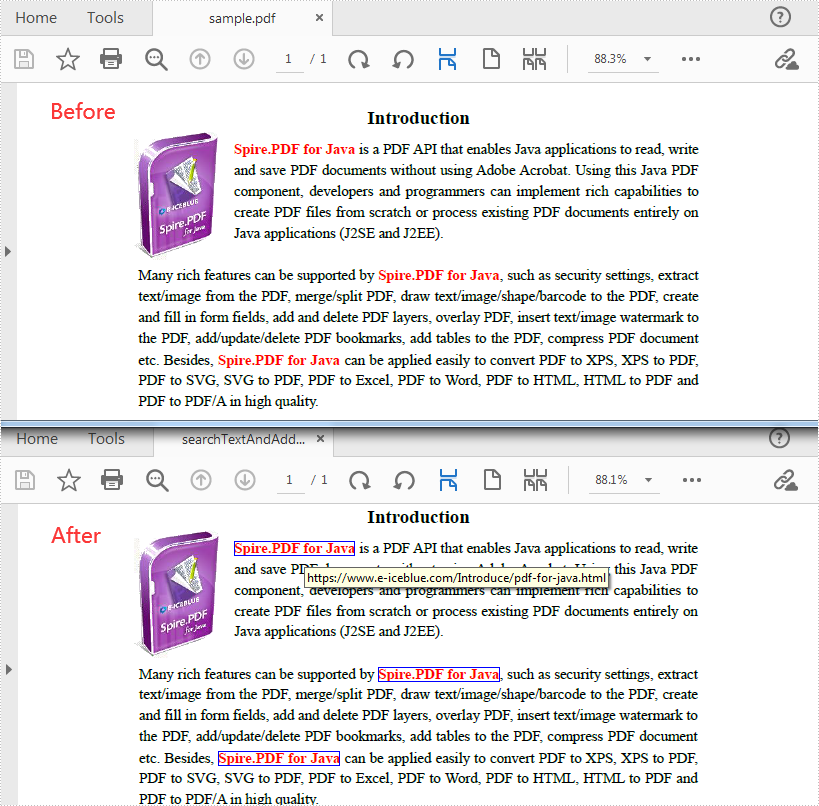
Find Text and Add Hyperlinks for Them in PDF
With Spire PDF for Java, you can find all matched text in a specific PDF page and add hyperlinks to them. Here are the detailed steps to follow.
- Create a PdfDocument instance and load a sample PDF document using PdfDocument.loadFromFile()method.
- Get a specific page of the document using PdfDocument.getPages().get() method.
- Find all matched text in the page using PdfPageBase.findText(String searchPatternText, boolean isSearchWholeWord) method, and return a PdfTextFindCollection object.
- Create a PdfUriAnnotation instance based on the bounds of a specific find result.
- Set a URL address for the annotation using PdfUriAnnotation.set(String value) method and set its border and color as well.
- Add the URL annotation to the PDF annotation collection as a new annotation using PdfPageBase.getAnnotationWidget().add() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.pdf.*;
import com.spire.pdf.annotations.*;
import com.spire.pdf.general.find.*;
import com.spire.pdf.graphics.PdfRGBColor;
import java.awt.*;
public class SearchTextAndAddHyperlink {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a PdfDocument instance
PdfDocument pdf = new PdfDocument();
//Load a sample PDF document
pdf.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Test1\\Desktop\\sample.pdf");
//Get the first page
PdfPageBase page = pdf.getPages().get(0);
// Find all matched strings and return the reesult oject
ListPdfTextFragment> results = null;
PdfTextFindOptions findOptions = new PdfTextFindOptions();
findOptions.setTextFindParameter(EnumSet.of(TextFindParameter.WholeWord));
//loop through the find collection
for(PdfTextFragment find : results)
{
// Create a PdfUriAnnotation instance to add hyperlinks for the searched text
Rectangle2D[] linkBounds = find.getBounds();
PdfUriAnnotation uri = new PdfUriAnnotation(linkBounds[0]);
uri.setUri("https://www.e-iceblue.com/Introduce/pdf-for-java.html");
uri.setBorder(new PdfAnnotationBorder(1f));
uri.setColor(new PdfRGBColor(Color.blue));
page.getAnnotationsWidget().add(uri);
}
//Save the document
pdf.saveToFile("output/searchTextAndAddHyperlink.pdf");
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Add Multiline Watermarks to PowerPoint in Java
This article demonstrates how to add multiline watermarks to a PowerPoint slide using Spire.Presentation for Java. To add watermarks to all slides, use one more for loop outside the two for loops in the following code snippet.
import com.spire.presentation.*;
import com.spire.presentation.Presentation;
import com.spire.presentation.drawing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
//Create a Presentation object
Presentation presentation = new Presentation();
//Load the sample PowerPoint file
presentation.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Spire.Presentation.pptx");
//Specify watermark text
String watermarkText = "E-iceblue";
//Get the size of the watermark text
Image image = new BufferedImage(1, 1, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_ARGB);
Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D) image.getGraphics();
Font font = new Font("Arial", Font.BOLD, 20);
g2d.setFont(font);
FontMetrics fm = g2d.getFontMetrics();
Rectangle2D strSize = fm.getStringBounds(watermarkText, g2d);
//Initialize x and y coordinate
float x = 30;
float y = 80;
for (int rowNum = 0; rowNum < 4; rowNum++) {
for (int colNum = 0; colNum < 5; colNum++) {
//Add a rectangle shape
Rectangle2D rect = new Rectangle2D.Float(x, y, (float) strSize.getWidth() + 10, (float) strSize.getHeight());
IAutoShape shape = presentation.getSlides().get(0).getShapes().appendShape(ShapeType.RECTANGLE, rect);
//Set the style of the shape
shape.getFill().setFillType(FillFormatType.NONE);
shape.getShapeStyle().getLineColor().setColor(new Color(1, 1, 1, 0));
shape.setRotation(-45);
shape.getLocking().setSelectionProtection(true);
shape.getLine().setFillType(FillFormatType.NONE);
//Add watermark text to the shape
shape.getTextFrame().setText(watermarkText);
PortionEx textRange = shape.getTextFrame().getTextRange();
//Set the style of the text range
textRange.getFill().setFillType(FillFormatType.SOLID);
textRange.getFill().getSolidColor().setColor(Color.pink);
textRange.setLatinFont(new TextFont(font.getName()));
textRange.setFontMinSize(font.getSize());
x += (100 + strSize.getWidth());
}
x = 30;
y += (100 + strSize.getHeight());
}
//Save the document
presentation.saveToFile("output/Watermark.pptx", FileFormat.PPTX_2013);
Verify If a Word Document is Password Protected in Java
This article demonstrates how to verify if a Word document is password protected or not using Spire.Doc for Java.
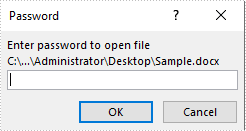
The following image shows that the input Word document is protected with password:
import com.spire.doc.Document;
public class DetectIfWordIsPasswordProtected {
public static void main(String []args){
//Detect if the Word document is password protected
boolean isPasswordProtected = Document.isEncrypted("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Sample.docx");
if(isPasswordProtected)
{
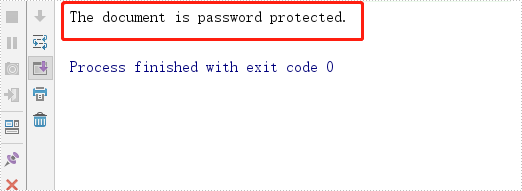
System.out.println("The document is password protected.");
}
else
{
System.out.println("The document is not password protected.");
}
}
}
Output:
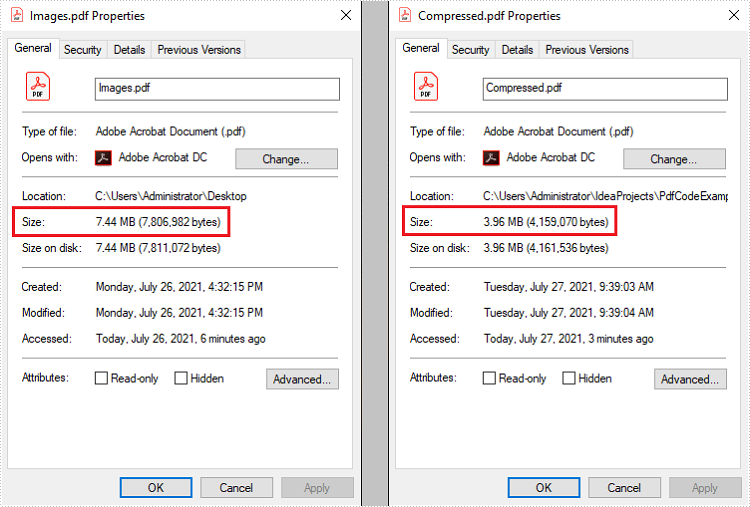
Compress High-resolution Images in PDF in Java
This article demonstrates how to compress high-resolution images of a PDF document using Spire.PDF for Java. Images in low-resolution will not be compressed anymore.
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//Load the sample PDF document
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Images.pdf");
//Set IncrementalUpdate to false
doc.getFileInfo().setIncrementalUpdate(false);
//Declare a PdfPageBase variable
PdfPageBase page;
// Create the PdfImageHelper object
PdfImageHelper imageHelper = new PdfImageHelper();
//Loop through the pages
for (int i = 0; i < doc.getPages().getCount(); i++) {
//Get the specific page
page = doc.getPages().get(i);
if (page != null) {
if(page.getImagesInfo() != null){
//Loop through the images in the page
for (PdfImageInfo info : imageHelper.getImagesInfo(page))
//Use tryCompressImage method the compress high-resolution images
info.tryCompressImage();
}
}
}
//Save to file
doc.saveToFile("output/Compressed.pdf");
}
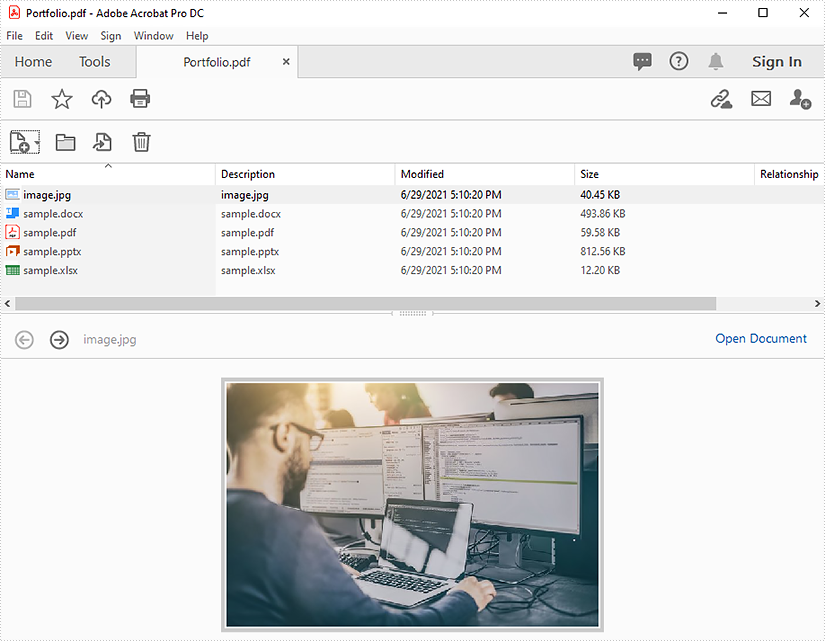
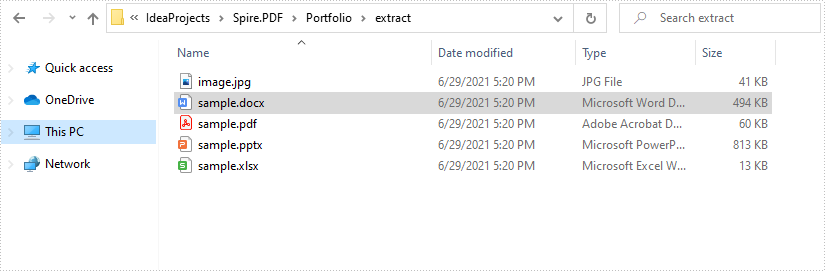
Extract Files from PDF Portfolio in Java
This article demonstrates how to extract files from a PDF portfolio in Java using Spire.PDF for Java.
The input PDF:
import com.spire.pdf.PdfDocument;
import com.spire.pdf.attachments.PdfAttachment;
import java.io.*;
public class ReadPortfolio {
public static void main(String []args) throws IOException {
//Create a PdfDocument instance
PdfDocument pdf = new PdfDocument();
//Load the PDF file
pdf.loadFromFile("Portfolio.pdf");
//Loop through the attachments in the file
for(Object obj : pdf.getAttachments()) {
PdfAttachment attachment = (PdfAttachment) obj;
//Extract files
String fileName = attachment.getFileName();
OutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("extract/" + fileName);
fos.write(attachment.getData());
}
pdf.dispose();
}
}
Output:
C#/VB.NET: Add or Remove Digital Signatures in PowerPoint
A digital signature is a modern alternative to signing documents manually on paper with pen. It uses an advanced mathematical technique to check the authenticity and integrity of digital documents, which guarantees that the contents in a digital document comes from the signer and has not been altered since then. Sometimes PowerPoint documents that contain confidential information may require a signature. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically add or remove digital signatures in PowerPoint using Spire.Presentation for .NET.
- Add a Digital Signature to PowerPoint in C# and VB.NET
- Remove All Digital Signatures from PowerPoint in C# and VB.NET
Install Spire.Presentation for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Presentation for.NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Presentation
Add a Digital Signature to PowerPoint in C# and VB.NET
To add a digital signature, you'll need to have a valid signature certificate first. Then you can digitally sign a PowerPoint document with the certificate using Presentation.AddDigitalSignature (X509Certificate2 certificate, string comments, DateTime signTime) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Presentation instance.
- Load a sample PowerPoint document using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Initializes an instance of X509Certificate2 class with the certificate file name and password.
- Add a digital signature to the PowerPoint document using Presentation.AddDigitalSignature (X509Certificate2 certificate, string comments, DateTime signTime) method.
- Save result document using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Presentation;
using System;
namespace AddDigitalSignature
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Presentation instance
Presentation ppt = new Presentation();
//Load a PowerPoint document
ppt.LoadFromFile("Input.pptx");
//Add a digital signature
ppt.AddDigitalSignature("gary.pfx", "e-iceblue", "test", DateTime.Now);
//Save the result document
ppt.SaveToFile("AddDigitalSignature_result.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("AddDigitalSignature_result.pptx");
//Dispose
ppt.Dispose();
}
}
}
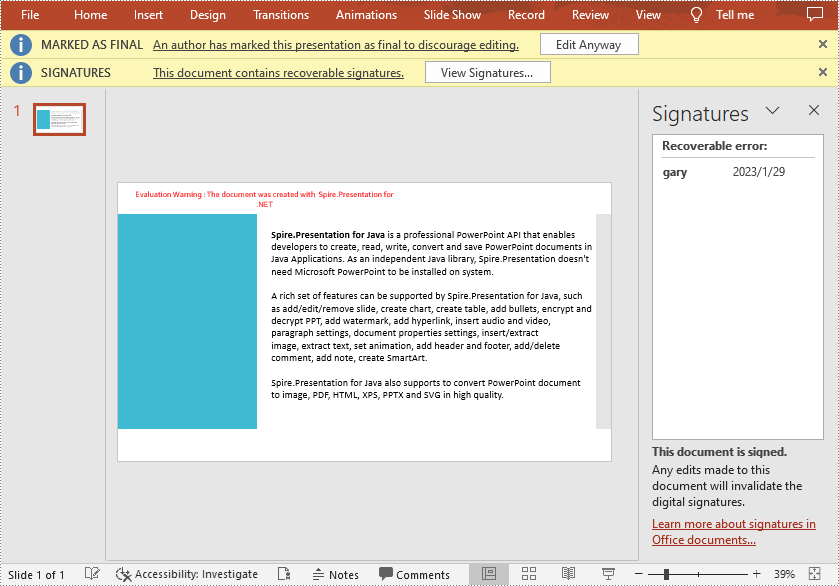
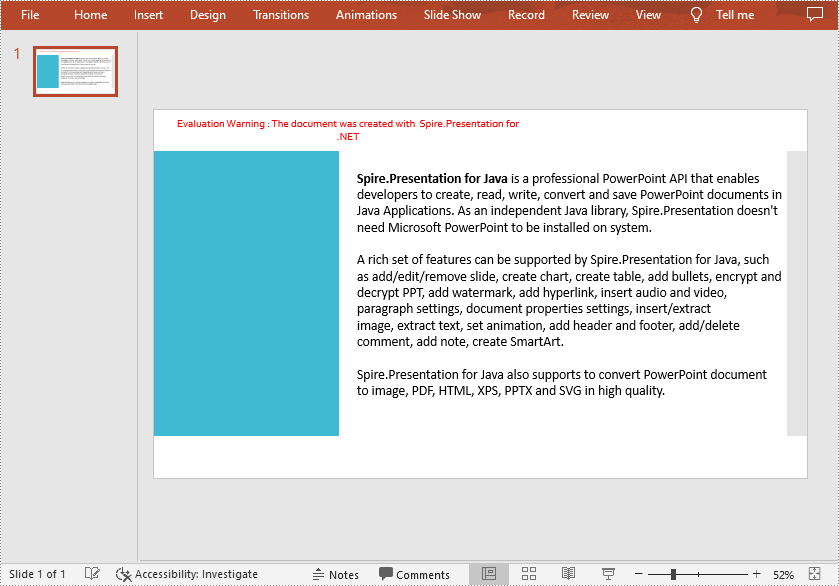
Remove All Digital Signatures from PowerPoint in C# and VB.NET
At some point you may need to remove the digital signatures from a PowerPoint document. Spire.Presentation for .NET provides the Presentation.RemoveAllDigitalSignatures() method to remove all digital signatures at once. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Presentation instance.
- Load a sample PowerPoint document using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Determine if the document contains digital signatures using Presentation.IsDigitallySigned property.
- Remove all digital signatures from the document using Presentation.RemoveAllDigitalSignatures() method.
- Save the result document using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Presentation;
namespace RemoveDigitalSignature
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Presentation instance
Presentation ppt = new Presentation();
//Load a PowerPoint document
ppt.LoadFromFile("AddDigitalSignature.pptx");
//Detect if the document is digitally signed
if (ppt.IsDigitallySigned == true)
{
//Remove all digital signatures
ppt.RemoveAllDigitalSignatures();
}
//Save the result document
ppt.SaveToFile("RemoveDigitalSignature.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Download PDF Document from URL in C#/VB.NET
This article shows you how to download a PDF document from an URL using Spire.PDF with C# and VB.NET.
using System.IO;
using System.Net;
using Spire.Pdf;
namespace DownloadPdfFromUrl
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a PdfDocument object
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
//Create a WebClient object
WebClient webClient = new WebClient();
//Download data from URL and save as memory stream
using (MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream(webClient.DownloadData("https://www.e-iceblue.com/article/toDownload.pdf")))
{
//Load the stream
doc.LoadFromStream(ms);
}
//Save to PDF file
doc.SaveToFile("result.pdf", FileFormat.PDF);
}
}
}
Imports System.IO
Imports System.Net
Imports Spire.Pdf
Namespace DownloadPdfFromUrl
Class Program
Shared Sub Main(ByVal args() As String)
'Create a PdfDocument object
Dim doc As PdfDocument = New PdfDocument()
'Create a WebClient object
Dim webClient As WebClient = New WebClient()
'Download data from URL and save as memory stream
Dim pdfData As Byte() = webClient.DownloadData(""https://www.e-iceblue.com/article/toDownload.pdf"")
Using ms As New MemoryStream(pdfData)
'Load the stream
doc.LoadFromStream(ms)
End Using
'Save to PDF file
doc.SaveToFile(""result.pdf"", FileFormat.PDF)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Java: Get Coordinates of Text or Images in PDF
Getting the coordinates of text or images in a PDF helps accurately identify elements, making it easier to extract content. This is especially important for data analysis, where specific information needs to be pulled from complicated layouts. Additionally, knowing these coordinates allows users to add notes, marks, or stamps in the right places, improving document interactivity and collaboration by letting them highlight important sections or add comments exactly where they're needed.
In this article, you will learn how to get coordinates of the specified text or image in a PDF document using Java and Spire.PDF for Java library.
Install Spire.PDF for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Pdf.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.pdf</artifactId>
<version>11.12.16</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Coordinate System in Spire.PDF
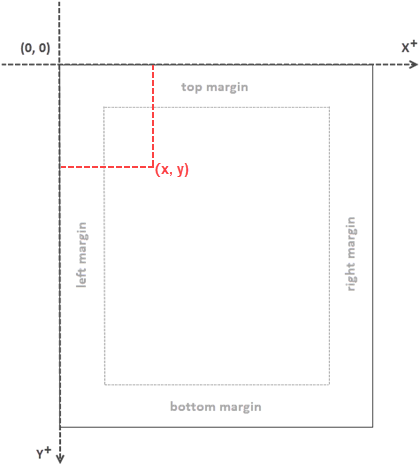
When utilizing Spire.PDF for Java to work with an existing PDF document, it's important to note that the coordinate system's origin is positioned at the top-left corner of the page. The x-axis extends to the right, and the y-axis extends downward, as illustrated below.
Get Coordinates of the Specified Text in PDF
To start, you can use the PdfTextFinder.find() method to search for all occurrences of the specified text on the page, which results in a list of PdfTextFragment. After that, you can retrieve the coordinates of the first occurrence of the text using the PdfTextFragment.getPositions() method.
The steps to get coordinates of the specified text in PDF are as follows:
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific page using PdfDocument.getPages().get() method.
- Search for all occurrences of the specified text on the page using PdfTextFinder.find() method and return results in a list of PdfTextFragment.
- Access a specific PdfTextFragment in the list, and get the coordinates of the fragment using PdfTextFragment.getPositions() method.
- Java
import com.spire.pdf.PdfDocument;
import com.spire.pdf.PdfPageBase;
import com.spire.pdf.texts.PdfTextFindOptions;
import com.spire.pdf.texts.PdfTextFinder;
import com.spire.pdf.texts.PdfTextFragment;
import com.spire.pdf.texts.TextFindParameter;
import java.awt.geom.Point2D;
import java.util.EnumSet;
import java.util.List;
public class GetTextCoordinates {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a PdfDocument object
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
// Load a PDF file
doc.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.pdf");
// Get a specific page
PdfPageBase page = doc.getPages().get(0);
// Create a PdfTextFinder object
PdfTextFinder finder = new PdfTextFinder(page);
// Set the find options
PdfTextFindOptions options = new PdfTextFindOptions();
options.setTextFindParameter(EnumSet.of(TextFindParameter.IgnoreCase));
finder.setOptions(options);
// Find all instances of the text
List fragments = finder.find("Personal Data");
// Get a specific text fragment
PdfTextFragment fragment = (PdfTextFragment)fragments.get(0);
// Get the positions of the text (If the text spans multiple lines, there will be more than one position)
Point2D[] positions = fragment.getPositions();
// Get its first position
double x = positions[0].getX();
double y = positions[0].getY();
// Print result
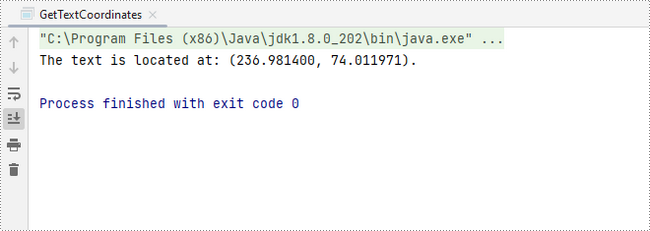
System.out.println(String.format("The text is located at: (%f, %f).",x,y));
}
}
Get Coordinates of the Specified Image in PDF
To begin, you can use the PdfImageHelper.getImagesInfo() method to retrieve information about all images on the specified page, storing the results in an array of PdfImageInfo. Next, you can obtain the X and Y coordinates of a specific image using the PdfImageInfo.getBounds().getX() and PdfImageInfo.getBounds().getY() methods.
The steps to get coordinates of the specified image in PDF are as follows:
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific page using PdfDocument.getPages().get() method.
- Retrieve all the image information on the page using PdfImageHelper.getImagesInfo() method and return results in an array of PdfImageInfo.
- Get X and Y coordinates of a specific image using PdfImageInfo.getBounds().getX() and PdfImageInfo.getBounds().getY() methods
- Java
import com.spire.pdf.PdfDocument;
import com.spire.pdf.PdfPageBase;
import com.spire.pdf.utilities.PdfImageHelper;
import com.spire.pdf.utilities.PdfImageInfo;
public class GetImageCoordinates {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a PdfDocument object
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
// Load a PDF file
doc.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input2.pdf");
// Get a specific page
PdfPageBase page = doc.getPages().get(0);
// Create a PdfImageHelper object
PdfImageHelper helper = new PdfImageHelper();
// Get image information from the page
PdfImageInfo[] imageInfo = helper.getImagesInfo(page);
// Get X, Y coordinates of the first image
double x = imageInfo[0].getBounds().getX();
double y = imageInfo[0].getBounds().getY();
// Print result
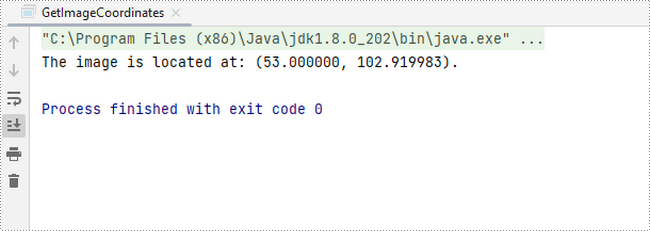
System.out.println(String.format("The image is located at: (%f, %f).",x,y));
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.