Python: Create Various Types of Lists in a Word Document
Lists are a powerful organizational tool that can be used to present information in a structured and easy-to-follow manner. Whether you want to create numbered lists, bulleted lists, or even custom lists with specific formatting, Word provides flexible options to suit your needs. By utilizing different list styles, you can improve the readability and visual appeal of your documents, making it simpler for readers to grasp key points and navigate through the content. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically create various types of lists in a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Create a Numbered List in Word in Python
- Create a Bulleted List in Word in Python
- Create a Multi-Level Numbered List in Word in Python
- Create a Multi-Level Mixed-Type List in Word in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Create a Numbered List in Word in Python
Spire.Doc for Python provides the ListStyle class, which enables you to establish either a numbered list style or a bulleted style. Subsequently, you can utilize the Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method to apply the defined list style to a paragraph. The steps to create a numbered list are as follows.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create an instance of ListStyle class, specifying the list type to Numbered.
- Get a specific level of the list through ListStyle.Levels[index] property, and set the numbering type through ListLevel.PatternType property.
- Add the list style to the document using Document.ListStyles.Add() method.
- Add several paragraphs to the document using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Apply the list style to a specific paragraph using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method.
- Specify the list level through Paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber property.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Create a numbered list style
listStyle = ListStyle(doc, ListType.Numbered)
listStyle.Name = "numberedList"
listStyle.Levels[0].PatternType = ListPatternType.DecimalEnclosedParen
listStyle.Levels[0].TextPosition = 20;
doc.ListStyles.Add(listStyle)
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Required Web Development Skills:")
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 5.0
# Add a paragraph and apply the numbered list style to it
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("HTML")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Add another four paragraphs and apply the numbered list style to them
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("CSS")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("JavaScript")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Python")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("MySQL")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Save the document to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/NumberedList.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
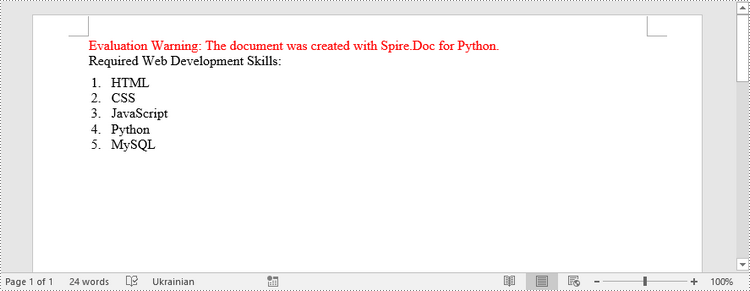
Create a Bulleted List in Word in Python
Creating a bulleted list follows a similar process to creating a numbered list, with the main difference being that you need to specify the list type as "Bulleted" and assign a bullet symbol to it. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create an instance of ListStyle class, specifying the list type to Bulleted.
- Get a specific level of the list through ListStyle.Levels[index] property, and set the bullet symbol through ListLevel.BulletCharacter property.
- Add the list style to the document using Document.ListStyles.Add() method.
- Add several paragraphs to the document using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Apply the list style to a specific paragraph using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method.
- Specify the list level through Paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber property.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Create a bulleted list style
listStyle = ListStyle(doc, ListType.Bulleted)
listStyle.Name = "bulletedList"
listStyle.Levels[0].BulletCharacter = "\u00B7"
listStyle.Levels[0].CharacterFormat.FontName = "Symbol"
listStyle.Levels[0].TextPosition = 20
doc.ListStyles.Add(listStyle)
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Computer Science Subjects:")
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 5.0
# Add a paragraph and apply the bulleted list style to it
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Data Structure")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Add another five paragraphs and apply the bulleted list style to them
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Algorithm")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Computer Networks")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Operating System")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("C Programming")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Theory of Computations")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Save the document to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/BulletedList.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
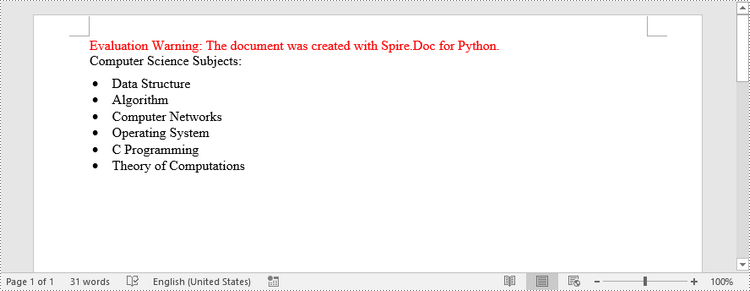
Create a Multi-Level Numbered List in Word in Python
A multi-level list consists of at least two different levels. A certain level of a nested list can be accessed by the ListStyle.Levels[index] property, through which you can set the numbering type and prefix. The following are the steps to create a multi-level numbered list in Word.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create an instance of ListStyle class, specifying the list type to Numbered.
- Get a specific level of the list through ListStyle.Levels[index] property, and set the numbering type and prefix.
- Add the list style to the document using Document.ListStyles.Add() method.
- Add several paragraphs to the document using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Apply the list style to a specific paragraph using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method.
- Specify the list level through Paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber property.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Create a numbered list style, specifying number prefix and pattern type of each level
listStyle = ListStyle(doc, ListType.Numbered)
listStyle.Name = "levelstyle"
listStyle.Levels.get_Item(0).PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic
listStyle.Levels.get_Item(0).TextPosition = 20.0
listStyle.Levels.get_Item(1).NumberPrefix = "%1."
listStyle.Levels.get_Item(1).PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic
listStyle.Levels.get_Item(2).NumberPrefix = "%1.%2."
listStyle.Levels.get_Item(2).PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic
doc.ListStyles.Add(listStyle)
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Here's a Multi-Level Numbered List:")
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 5.0
# Add a paragraph and apply the numbered list style to it
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The first item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Add another five paragraphs and apply the numbered list stype to them
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The second item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The first sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 1
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The second sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ContinueListNumbering()
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle")
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("A sub-sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 2
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The third item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Save the document to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/MultilevelNumberedList.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
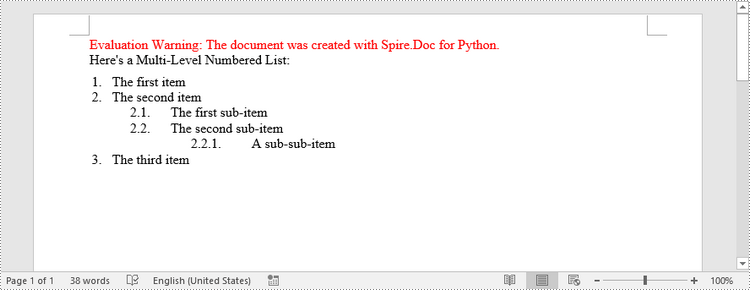
Create a Multi-Level Mixed-Type List in Word in Python
To combine number and symbol bullet points in a multi-level list, create separate list styles (numbered and bulleted) and apply them to different paragraphs. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create a numbered list style and a bulleted list style.
- Add several paragraphs to the document using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Apply different list style to different paragraphs using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Create a numbered list style
numberedListStyle = ListStyle(doc, ListType.Numbered)
numberedListStyle.Name = "numberedStyle"
numberedListStyle.Levels[0].PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic
numberedListStyle.Levels[0].TextPosition = 20
numberedListStyle.Levels[1].PatternType = ListPatternType.LowLetter
doc.ListStyles.Add(numberedListStyle)
# Create a bulleted list style
bulletedListStyle = ListStyle(doc, ListType.Bulleted)
bulletedListStyle.Name = "bulltedStyle"
bulletedListStyle.Levels[2].BulletCharacter = "\u002A"
bulletedListStyle.Levels[2].CharacterFormat.FontName = "Symbol"
doc.ListStyles.Add(bulletedListStyle)
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Here's a Multi-Level Mixed List:")
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 5.0
# Add a paragraph and apply the numbered list style to it
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The first item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedStyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Add the other five paragraphs and apply different list stype to them
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The first sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedStyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 1
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The second sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 1
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedStyle")
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The first sub-sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulltedStyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 2
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The second sub-sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulltedStyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 2
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The second item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedStyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Save the document to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/MultilevelMixedList.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Insert Page Break into Word Documents
A page break is a formatting element used in documents to indicate the end of one page and the beginning of a new page. It is typically represented by a horizontal line or other visual indicator that separates content into different pages. This feature is commonly used when creating lengthy documents such as reports, essays, or books to enhance the overall layout and readability. In this article, you will learn how to how to insert page break into Word documents in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Insert Page Break after a Specific Paragraph
Spire.Doc for Python provides Paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.PageBreak) method to insert a page break after a specific paragraph. The following are detailed steps.
- Create an object of Document class.
- Load a sample file from disk using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first section of this file by Document.Sections[sectionIndex] property.
- Get the second paragraph in the section by Section.Paragraphs[paragraphIndex] property.
- Insert a page break after this paragraph using Paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.PageBreak) method.
- Save the result file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import * from spire.doc.common import * inputFile = "sample.docx" outputFile = "InsertPageBreak.docx" #Create an object of Document class document = Document() #Load a sample file from disk document.LoadFromFile(inputFile) #Insert a page break after this paragraph paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.PageBreak) #Save the result file document.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx2013) document.Close()
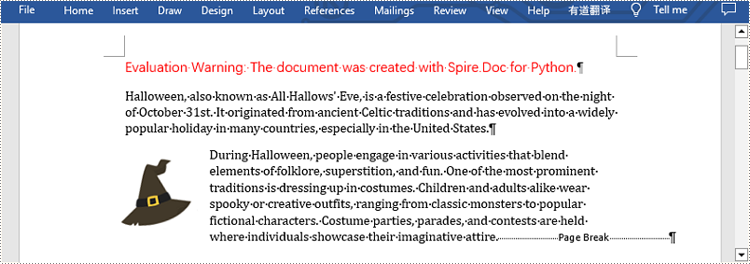
Insert Page Break after a Specific Text
What's more, you are also allowed to insert page break after a specific text by using Paragraph.ChildObjects.Insert() method provided by this library. The following are detailed steps.
- Create an object of Document class.
- Load a sample file from disk using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Find a specific text using Document.FindAllString() method.
- Loop through all searched text and access the text range of it by calling TextSelection.GetAsOneRange() method.
- Get the paragraph where the text range is located by ParagraphBase.OwnerParagraph property.
- Get the position index of the text range in the paragraph using Paragraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf() method.
- Create an object of Break class to create a page break.
- Insert page break after the searched text using Paragraph.ChildObjects.Insert() method.
- Save the result file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
inputFile = "sample.docx"
outputFile = "InsertPageBreakAfterText.docx"
#Create an object of Document class
document = Document()
#Load a sample file from disk
document.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
#Find the specified text
selection = document.FindAllString("fun", True, True)
#Loop through all searched text
for ts in selection:
#Get the text range of the searched text
range = ts.GetAsOneRange()
#Get the paragraph where the text range is located
paragraph = range.OwnerParagraph
#Get the position index of the text range in the paragraph
index = paragraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf(range)
#Create an object of Break class
pageBreak = Break(document, BreakType.PageBreak)
#Insert page break after the searched text
paragraph.ChildObjects.Insert(index + 1, pageBreak)
#Save the result file
document.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx2013)
document.Close()
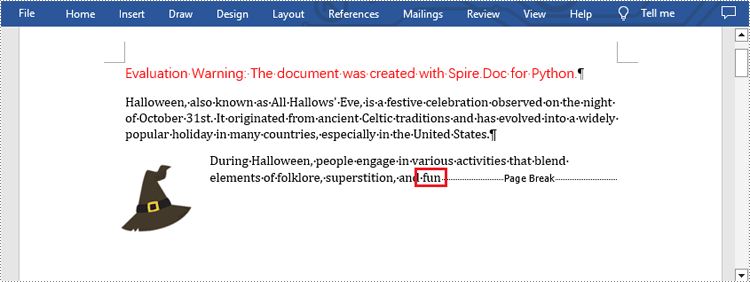
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Add, Replace, or Remove Images in a PDF Document
Alongside textual content, images in a PDF play a crucial role in conveying messages effectively. Being able to manipulate images within a PDF document, such as adding, replacing, or removing them, can be incredibly useful for enhancing the visual appeal, updating outdated graphics, or modifying the document's content. In this article, you will learn how to add, replace, or delete images in a PDF document in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Add an Image to a PDF Document in Python
- Replace an Image in a PDF Document in Python
- Remove an Image from a PDF Document in Python
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Add an Image to a PDF Document in Python
To add an image to a PDF page, you can use the PdfPage.Canvas.DrawImage() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Add a page to the document using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Load an image using PdfImage.FromFile() method.
- Draw the image on the page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawImage() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Set the page margins
doc.PageSettings.SetMargins(30.0, 30.0, 30.0, 30.0)
# Add a page
page = doc.Pages.Add()
# Load an image
image = PdfImage.FromFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/logo.png')
# Specify the size of the image in the document
width = image.Width * 0.70
height = image.Height * 0.70
# Specify the X and Y coordinates where the image will be drawn
x = 10.0
y = 30.0
# Draw the image at a specified location on the page
page.Canvas.DrawImage(image, x, y, width, height)
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("output/AddImage.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
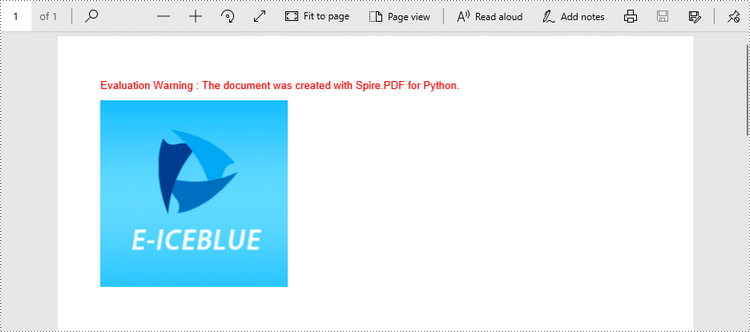
Replace an Image in a PDF Document in Python
Spire.PDF for Python offers the PdfImageHelper class to help us get and deal with the images in a certain page. To replace an image with a new one, you can use the PdfImageHelper.ReplaceImage() method. The following are the steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific page through PdfDocument.Pages[index] property.
- Load an image using PdfImage.FromFile() method.
- Create a PdfImageHelper object, and get the image information from the specified page using PdfImageHelper.GetImagesInfo() method.
- Replace an existing image in the page with the new image using PdfImageHelper.ReplaceImage() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/input.pdf')
# Get the first page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Load an image
image = PdfImage.FromFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/newImage.png')
# Create a PdfImageHelper instance
imageHelper = PdfImageHelper()
# Get the image information from the page
imageInfo = imageHelper.GetImagesInfo(page)
# Replace the first image on the page with the loaded image
imageHelper.ReplaceImage(imageInfo[0], image)
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("output/ReplaceImage.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
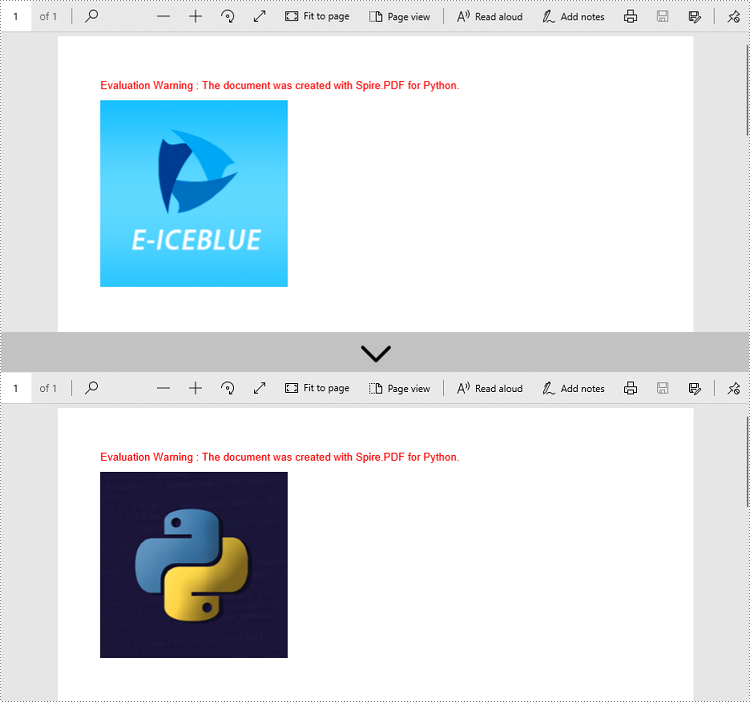
Remove an Image from a PDF Document in Python
To remove a specific image from a page, use the PdfPageBase.DeleteImage(index) method. The following are the steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific page through PdfDocument.Pages[index] property.
- Delete a certain image in the page by its index using PdfPageBase.DeleteImage() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/input.pdf')
# Get the first page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Delete the first image on the page
page.DeleteImage(0)
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile('output/DeleteImage.pdf', FileFormat.PDF)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Extract Text from PDF in Python: A Complete Guide with Practical Code Samples

PDF files are everywhere—from contracts and research papers to eBooks and invoices. While they preserve formatting perfectly, extracting text from PDFs can be challenging, especially with large or complex documents. Manual copying is not only slow but often inaccurate.
Whether you’re a developer automating workflows, a data analyst processing content, or simply someone needing quick text extraction, programmatic methods can save you valuable time and effort.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn how to extract text from PDF files in Python using Spire.PDF for Python — a powerful and easy-to-use PDF processing library. We’ll cover extracting all text, targeting specific pages or areas, ignoring hidden text, and capturing layout details such as text position and size.
Table of Contents
- Why Extract Text from PDF Files
- Install Spire.PDF for Python: Powerful PDF Parser Library
- Extract Text from PDF (Basic Example)
- Advanced Text Extraction Features
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Why Extract Text from PDF Files
Text extraction from PDFs is essential for many use cases, including:
- Automating data entry and document processing
- Enabling full-text search and indexing
- Performing data analysis on reports and surveys
- Extracting content for machine learning and NLP
- Converting PDFs to other editable formats
Install Spire.PDF for Python: Powerful PDF Parser Library
Spire.PDF for Python is a comprehensive and easy-to-use PDF processing library that simplifies all your PDF manipulation needs. It offers advanced text extraction capabilities that work seamlessly with both simple and complex PDF documents.
Installation
The library can be installed easily via pip. Open your terminal and run the following command:
pip install spire.pdf
Need help with the installation? Follow this step-by-step guide: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Extract Text from PDF (Basic Example)
If you just want to quickly read all the text from a PDF, this simple example shows how to do it. It iterates over each page, extracts the full text using PdfTextExtractor, and saves it to a text file with spacing and line breaks preserved.
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Terms of service.pdf')
# Prepare a variable to hold the extracted text
all_text = ""
# Create a PdfTextExtractOptions object
extractOptions = PdfTextExtractOptions()
# Extract all text including whitespaces
extractOptions.IsExtractAllText = True
# Loop through all pages and extract text
for i in range(doc.Pages.Count):
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(i)
textExtractor = PdfTextExtractor(page)
text = textExtractor.ExtractText(extractOptions)
# Append text from each page
all_text += text + "\n"
# Write all extracted text to a file
with open('output/TextOfAllPages.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write(all_text)
Advanced Text Extraction Features
For greater control over what and how text is extracted, Spire.PDF for Python offers advanced options. You can selectively extract content from specific pages or regions, or even with layout details, such as text position and size, to better suit your specific data processing needs.
Retrieve Text from Selected Pages
Instead of processing an entire PDF, you can target specific pages for text extraction. This is especially useful for large documents where only certain sections are relevant for your task.
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Terms of service.pdf')
# Create a PdfTextExtractOptions object and enable full text extraction
extractOptions = PdfTextExtractOptions()
# Extract all text including whitespaces
extractOptions.IsExtractAllText = True
# Get a specific page (e.g., page 2)
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(1)
# Create a PdfTextExtractor object
textExtractor = PdfTextExtractor(page)
# Extract text from the page
text = textExtractor.ExtractText(extractOptions)
# Write the extracted text to a file using UTF-8 encoding
with open('output/TextOfPage.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write(text)

Get Text from Defined Area
When dealing with structured documents like forms or invoices, extracting text from a specific region can be more efficient. You can define a rectangular area and extract only the text within that boundary on the page.
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Terms of service.pdf')
# Get a specific page (e.g., page 2)
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(1)
# Create a PdfTextExtractor object
textExtractor = PdfTextExtractor(page)
# Create a PdfTextExtractOptions object
extractOptions = PdfTextExtractOptions()
# Define the rectangular area to extract text from
# RectangleF(left, top, width, height)
extractOptions.ExtractArea = RectangleF(0.0, 100.0, 890.0, 80.0)
# Extract text from the specified area, keeping white spaces
text = textExtractor.ExtractText(extractOptions)
# Write the extracted text to a file using UTF-8 encoding
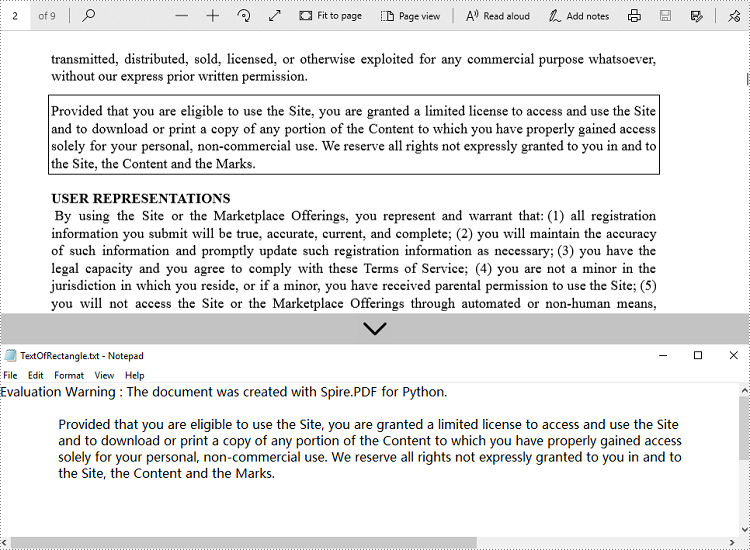
with open('output/TextOfRectangle.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write(text)
Ignore Hidden Text During Extraction
Some PDFs contain hidden or invisible text, often used for accessibility or OCR layers. You can choose to ignore such content during extraction to focus only on what is actually visible to users.
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Terms of service.pdf')
# Create a PdfTextExtractOptions object
extractOptions = PdfTextExtractOptions()
# Ignore hidden text during extraction
extractOptions.IsShowHiddenText = False
# Get a specific page (e.g., page 2)
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(1)
# Create a PdfTextExtractor object
textExtractor = PdfTextExtractor(page)
# Extract text from the page
text = textExtractor.ExtractText(extractOptions)
# Write the extracted text to a file using UTF-8 encoding
with open('output/ExcludeHiddenText.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write(text)
Retrieve Text with Position (Coordinates) and Size Information
For layout-sensitive applications—such as converting PDF content into editable formats or reconstructing page structure—you can extract text along with its position and size. This provides precise control over how content is interpreted and used.
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Terms of service.pdf')
# Loop through all pages of the document
for i in range(doc.Pages.Count):
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Create a PdfTextFinder object for the current page
finder = PdfTextFinder(page)
# Find all text fragments on the page
fragments = finder.FindAllText()
print(f"Page {i + 1}:")
# Loop through all text fragments
for fragment in fragments:
# Extract text content from the current text fragment
text = fragment.Text
# Get bounding rectangles with position and size
rects = fragment.Bounds
print(f'Text: "{text}"')
# Iterate through all rectangles
for rect in rects:
# Print the position and size information of the current rectangle
print(f"Position: ({rect.X}, {rect.Y}), Size: ({rect.Width} x {rect.Height})")
print()
Conclusion
Extracting text from PDF files in Python becomes efficient and flexible with Spire.PDF for Python. Whether you need to process entire documents or extract text from specific pages or regions, Spire.PDF provides a robust set of tools to meet your needs. By automating text extraction, you can streamline workflows, power intelligent search systems, or prepare data for analysis and machine learning.
FAQs
Q1: Can text be extracted from password-protected PDFs?
A1: Yes, Spire.PDF for Python can open and extract text from secured files by providing the correct password when loading the PDF document.
Q2: Is batch text extraction from multiple PDFs supported?
A2: Yes, you can programmatically iterate through a directory of PDF files and apply text extraction to each file efficiently using Spire.PDF for Python.
Q3: Is it possible to extract images or tables from PDFs?
A3: While this guide focuses on text extraction, Spire.PDF for Python also supports image extraction and table extraction.
Q4: Can text be extracted from scanned (image-based) PDFs?
A4: Extracting text from scanned PDFs requires OCR (Optical Character Recognition). Spire.PDF for Python does not include built-in OCR, but you can combine it with an OCR library like Spire.OCR for image-to-text conversion.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.PDF for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Extract Images from PDF in Python – A Complete Guide
PDF files often contain critical embedded images (e.g., charts, diagrams, scanned documents). For developers, knowing how to extract images from PDF in Python allows them to repurpose graphical content for automated report generation or feed these visuals into machine learning models for analysis and OCR tasks.

This article explores how to leverage the Spire.PDF for Python library to extract images from PDF files via Python, covering the following aspects:
- Installation & Environment Setup
- How to Extract Images from PDFs using Python
- Handle Different Image Formats While Extraction
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion (Extract Text and More)
Installation & Environment Setup
Before you start using Spire.PDF for Python to extract images from PDF, make sure you have the following in place:
-
Python Environment: Ensure that you have Python installed on your system. It is recommended to use the latest stable version for the best compatibility and performance.
-
Spire.PDF for Python Library: You need to install the Python PDF SDK, and the easiest way is using pip, the Python package installer.
Open your command prompt or terminal and run the following command:
pip install Spire.PDF
How to Extract Images from PDFs using Python
Example 1: Extract Images from a PDF Page
Here’s a complete Python script to extract and save images from a specified page in PDF:
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("template1.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create a PdfImageHelper instance
imageHelper = PdfImageHelper()
# Get the image information on the page
imageInfo = imageHelper.GetImagesInfo(page)
# Iterate through the image information
for i in range(0, len(imageInfo)):
# Save images to file
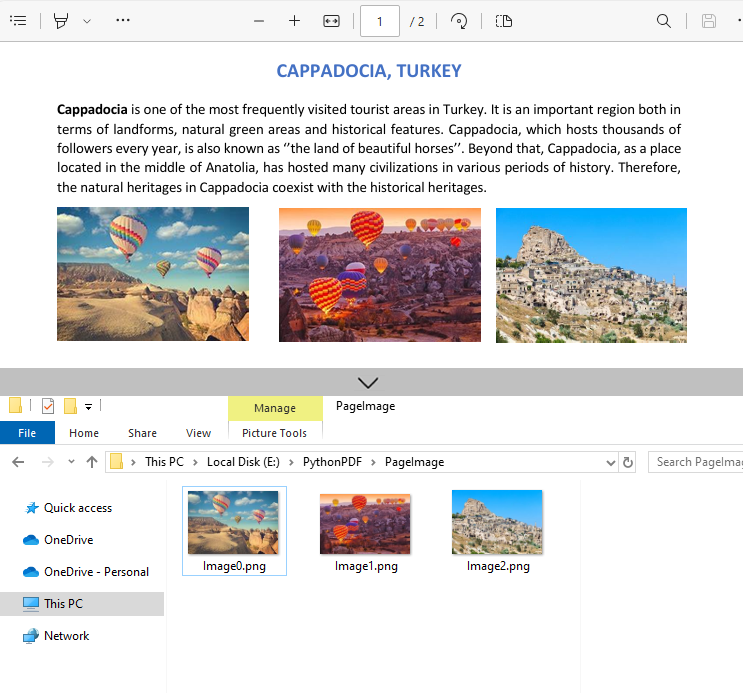
imageInfo[i].Image.Save("PageImage\\Image" + str(i) + ".png")
# Release resources
pdf.Dispose()
Key Steps Explained:
- Load the PDF: Use the LoadFromFile() method to load a PDF file.
- Access a Page: Access a specified PDF page by index.
- Extract Image information:
- Create a PdfImageHelper instance to facilitate image extraction.
- Use the GetImagesInfo() method to retrieve image information from the specified page, and return a list of PdfImageInfo objects.
- Save Images to Files:
- Loops through all detected images on the page
- Use the PdfImageInfo[].Image.Save() method to save the image to disk.
Output:
Example 2: Extract All Images from a PDF File
Building on the single-page extraction method, you can iterate through all pages of the PDF document to extract every embedded image.
Python code example:
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("template1.pdf")
# Create a PdfImageHelper instance
imageHelper = PdfImageHelper()
# Iterate through the pages in the document
for i in range(0, pdf.Pages.Count):
# Get the current page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Get the image information on the page
imageInfo = imageHelper.GetImagesInfo(page)
# Iterate through the image information items
for j in range(0, len(imageInfo)):
# Save the current image to file
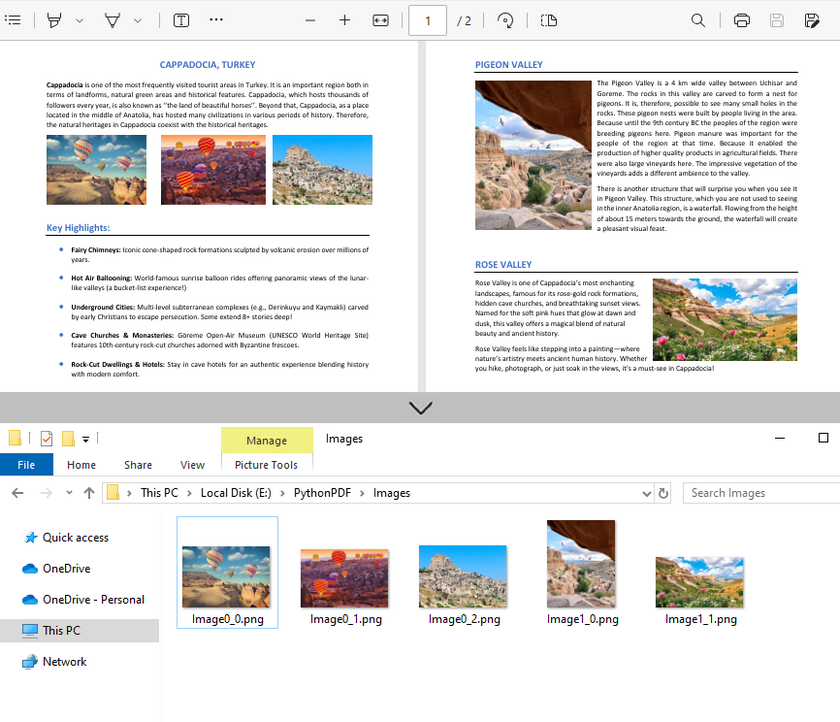
imageInfo[j].Image.Save(f"Images\\Image{i}_{j}.png")
# Release resources
pdf.Close()Output:
Handle Different Image Formats While Extraction
Spire.PDF for Python supports extracting images in various formats such as PNG, JPG/JPEG, BMP, etc. When saving the extracted images, you can choose the appropriate format based on your needs.
Common Image Formats:
| Format | Best Use Cases | PDF Extraction Notes |
|---|---|---|
| JPG/JPEG | Photos, scanned documents | Common in PDFs; quality loss on re-compress |
| PNG | Web graphics, diagrams, screenshots | Preserves transparency; larger file sizes |
| BMP | Windows applications, temp storage | Rare in modern PDFs; avoid for web use |
| TIFF | Archiving, print, OCR input | Ideal for document preservation; multi-page |
| EMF | Windows vector editing | Editable in Illustrator/Inkscape |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Is Spire.PDF for Python a free library?
Spire.PDF for Python offers both free and commercial versions. The free version has limitations, such as a maximum of 10 pages per PDF. For commercial use or to remove these restrictions, you can request a trial license here.
Q2: Can I extract images from a specified page range only?
Yes. Instead of iterating through all pages, specify the page indices you want. For example, to extract images from the pages 2 to 5:
# Extract images from pages 2 to 5
for i in range(1, 4): # Pages are zero-indexed
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Process images as beforeQ3: Is it possible to extract text from images?
Yes. For scanned PDF files, after extracting the images, you can extract the text in the images in conjunction with the Spire.OCR for Python library.
A step-by-step guide: How to Extract Text from Image Using Python (OCR Code Examples)
Conclusion (Extract Text and More)
Spire.PDF simplifies image extraction from PDF in Python with minimal code. By following this guide, you can:
- Extract images from single pages or entire PDF documents.
- Save images from PDF in various formats (PNG, JPG, BMP or TIFF).
As a PDF document can contain different elements, the Python PDF library is also capable of:
Python Image to PDF Conversion: Best Practices and Code Examples

Converting images to PDF programmatically is a common task in document management, as it enhances organization, facilitates sharing, and ensures efficient archiving. By consolidating various image formats into a single PDF document, users can easily manage and distribute their visual content.
In this article, we will explore how to convert a variety of image formats —including PNG , JPEG , TIFF , and SVG —into PDF files using Spire.PDF for Python. We’ll provide detailed instructions and code examples to guide you through the conversion process, highlighting the flexibility and power of this library for handling different image types.
Table of Contents:
- Why Convert Image to PDF?
- Introducing Spire.PDF: Python Image-to-PDF Library
- Convert PNG or JPEG to PDF
- Convert Multi-Page TIFF to PDF
- Convert Scalable SVG to PDF
- Merge Multiple Images into One PDF
- Conclusion
- FAQs
1. Why Convert Image to PDF?
PDFs are preferred for their portability, security, and consistent formatting across devices. Converting images to PDF offers several benefits:
- Preservation of Quality: PDFs retain image resolution, ensuring no loss in clarity.
- Easier Sharing: A single PDF can combine multiple images, simplifying distribution.
- Document Standardization: Converting images to PDF ensures compatibility with most document management systems.
Whether you're archiving scanned documents or preparing a portfolio, converting images to PDF enhances usability.
2. Introducing Spire.PDF: Python Image-to-PDF Library
Spire.PDF for Python is a robust library that enables PDF creation, manipulation, and conversion. Key features include:
- Support for multiple image formats (PNG, JPEG, BMP, SVG, and more).
- Flexible page customization (size, margins, orientation).
- Batch processing and multi-image merging.
- Advanced options like watermarking and encryption (beyond basic conversion).
To install the library, use:
pip install Spire.PDF
3. Convert PNG or JPEG to PDF in Python
3.1 Generate PDF Matching Image Dimensions
To convert a PNG or JPEG image to PDF while preserving its original size, we start by creating a PdfDocument object, which serves as the container for our PDF. We set the page margins to zero, ensuring that the image will fill the entire page.
After loading the image, we obtain its dimensions to create a new page that matches these dimensions. Finally, we draw the image on the page and save the document to a PDF file. This approach guarantees pixel-perfect conversion without resizing or distortion.
The following code demonstrates how to generate a PDF that perfectly matches your image’s size:
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
document = PdfDocument()
# Set the page margins to 0
document.PageSettings.SetMargins(0.0)
# Load an image file
image = PdfImage.FromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\robot.jpg")
# Get the image width and height
imageWidth = image.PhysicalDimension.Width
imageHeight = image.PhysicalDimension.Height
# Add a page that has the same size as the image
page = document.Pages.Add(SizeF(imageWidth, imageHeight))
# Draw image at (0, 0) of the page
page.Canvas.DrawImage(image, 0.0, 0.0)
# Save to file
document.SaveToFile("output/ImageToPdf.pdf")
# Dispose resources
document.Dispose()
Output:

3.2 Custom PDF Layouts and Image Position
To customize the PDF page size and margins, a few modifications to the code are needed. In this example, we set the page size to A4, adjusting the margins accordingly. The image is centered on the page by calculating its position based on the page dimensions. This method creates a more polished layout for the PDF.
The code below shows how to customize PDF settings and position images during conversion:
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
document = PdfDocument()
# Set the page margins to 5
document.PageSettings.SetMargins(5.0)
# Define page size (A4 or custom)
document.PageSettings.Size = PdfPageSize.A4()
# Add a new page to the document
page = document.Pages.Add()
# Load the image from file
image = PdfImage.FromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\robot.jpg")
# Get the image dimensions
imageWidth = image.PhysicalDimension.Width
imageHeight = image.PhysicalDimension.Height
# Calculate centered position for the image
x = (page.GetClientSize().Width - imageWidth) / 2
y = (page.GetClientSize().Height - imageHeight) / 2
# Draw the image at the calculated position
page.Canvas.DrawImage(image, x, y, imageWidth, imageHeight)
# Save to a PDF file
document.SaveToFile("output/ImageToPdf.pdf")
# Release resources
document.Dispose()
Output:

4. Convert Multi-Page TIFF to PDF in Python
TIFF files are widely used for high-resolution images, making them suitable for applications such as document scanning and medical imaging. However, Spire.PDF does not support TIFF images natively. To handle TIFF files, we can use the Python Imaging Library (PIL) , which can be installed with the following command:
pip install Pillow
Using PIL, we can access each frame of a TIFF file, temporarily save it as a PNG, and then draw each PNG onto a PDF. This method ensures that each frame is added as a separate page in the PDF, preserving the original quality and layout.
Here is the code snippet for converting a multi-page TIFF to PDF in Python:
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
from PIL import Image
import io
# Create a PdfDocument object
document = PdfDocument()
# Set the page margins to 0
document.PageSettings.SetMargins(0.0)
# Load a TIFF image
tiff_image = Image.open("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\TIFF.tiff")
# Iterate through the frames in it
for i in range(getattr(tiff_image, 'n_frames', 1)):
# Go to the current frame
tiff_image.seek(i)
# Extract the image of the current frame
frame_image = tiff_image.copy()
# Save the image to a PNG file
frame_image.save(f"temp/output_frame_{i}.png")
# Load the image file to PdfImage
image = PdfImage.FromFile(f"temp/output_frame_{i}.png")
# Get image width and height
imageWidth = image.PhysicalDimension.Width
imageHeight = image.PhysicalDimension.Height
# Add a page to the document
page = document.Pages.Add(SizeF(imageWidth, imageHeight))
# Draw image at (0, 0) of the page
page.Canvas.DrawImage(image, 0.0, 0.0)
# Save the document to a PDF file
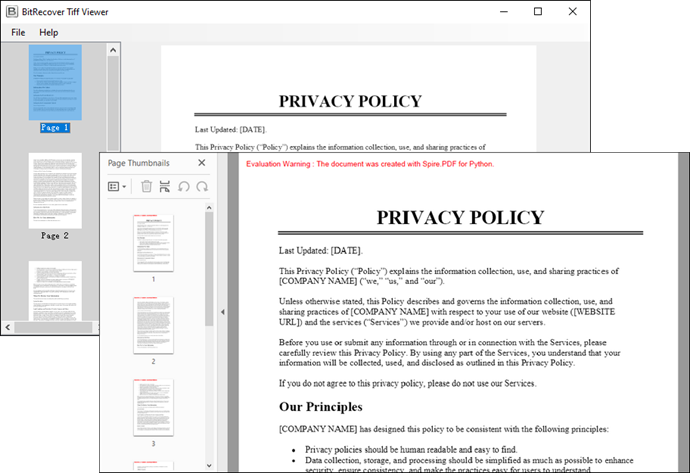
document.SaveToFile("Output/TiffToPdf.pdf",FileFormat.PDF)
# Dispose resources
document.Dispose()
Output:
5. Convert Scalable SVG to PDF in Python
SVG files are vector graphics that provide scalability without loss of quality, making them ideal for web graphics and print media. In this example, we create a PdfDocument object and load an SVG file directly into it. Spire.PDF library efficiently handles the conversion, allowing for quick and straightforward saving of the SVG as a PDF with minimal code.
Below is the code snippet for converting an SVG file to a PDF:
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
document = PdfDocument()
# Load an SVG file
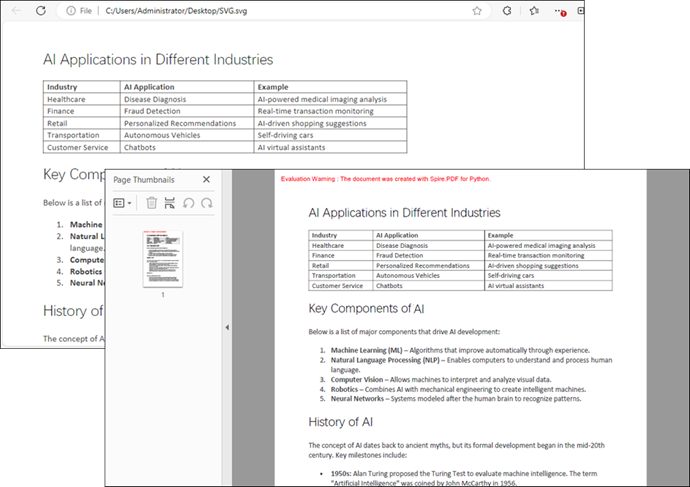
document.LoadFromSvg("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\SVG.svg")
# Save the SVG file to PDF
document.SaveToFile("output/SvgToPdf.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
# Dispose resources
document.Dispose()
Tip : To combine multiple SVG files into a single PDF, convert them separately and then merge the resulting PDFs. For guidance, check out this article: How to Merge PDF Documents in Python.
Output:
6. Merge Multiple Images into One PDF
This process involves iterating through images in a specified directory, loading each one, and creating corresponding pages in the PDF document. Each page is formatted to match the image dimensions, preventing any loss or distortion. Finally, each image is drawn onto its respective page.
Code example for combining a folder of images into a single PDF:
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
import os
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Set the page margins to 0
doc.PageSettings.SetMargins(0.0)
# Get the folder where the images are stored
path = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Images\\"
files = os.listdir(path)
# Iterate through the files in the folder
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path):
for file in files:
# Load a particular image
image = PdfImage.FromFile(os.path.join(root, file))
# Get the image width and height
width = image.PhysicalDimension.Width
height = image.PhysicalDimension.Height
# Add a page that has the same size as the image
page = doc.Pages.Add(SizeF(width, height))
# Draw image at (0, 0) of the page
page.Canvas.DrawImage(image, 0.0, 0.0, width, height)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/CombineImages.pdf")
doc.Dispose()
Output:

7. Conclusion
Converting images to PDF in Python using the Spire.PDF library is a straightforward task that can be accomplished through various methods for different image formats. Whether you need to convert single images, customize layouts, or merge multiple images, Spire.PDF provides the necessary tools to achieve your goals efficiently. With just a few lines of code, you can create high-quality PDFs from images, enhancing your document management capabilities.
8. FAQs
Q1: Can I convert images in bulk using Spire.PDF?
Yes, Spire.PDF allows you to iterate through directories and convert multiple images to a single PDF or individual PDFs, making bulk conversions easy.
Q2: What image formats does Spire.PDF support?
Spire.PDF supports various image formats, including PNG, JPEG, BMP, and SVG, providing versatility for different use cases.
Q3: Can I customize the PDF layout?
Absolutely. You can set margins, page sizes, and positions of images within the PDF for a tailored layout that meets your requirements.
Q4: Does converting an image to PDF reduce its quality?
No - when using Spire.PDF with default settings, the original image data is embedded without compression.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.PDF for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Python: Convert PowerPoint to Images (PNG, JPG, BMP, SVG)
Images are universally compatible and can be easily shared across various platforms, devices, and applications. By converting PowerPoint slides to images, you can distribute your content effortlessly via email, messaging apps, websites, or social media platforms. This makes your presentation accessible to a wider audience and ensures that it can be viewed by anyone, regardless of the software or device they are using. In this article, we will explain how to convert PowerPoint to images in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Convert PowerPoint Presentation to JPG, PNG or BMP Images
- Convert PowerPoint Presentation to JPG, PNG or BMP Images with a Specific Size
- Convert PowerPoint Presentation to SVG Images
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Convert PowerPoint Presentation to JPG, PNG or BMP Images in Python
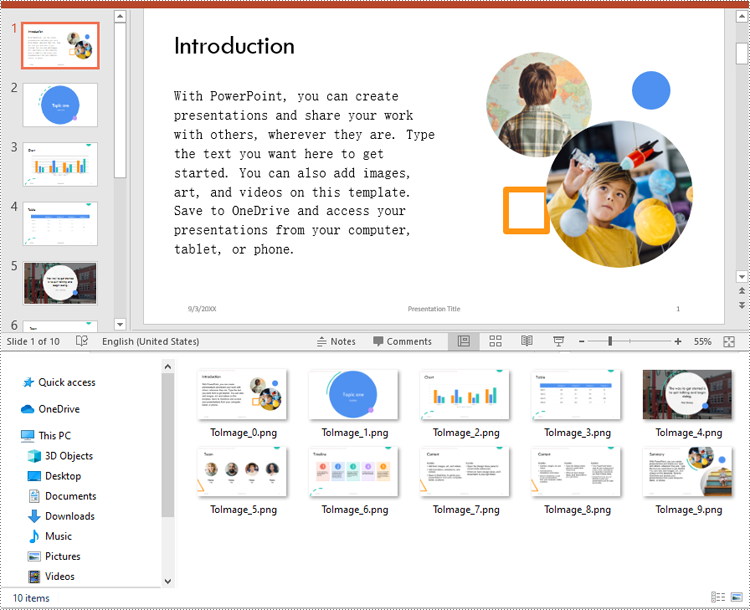
Spire.Presentation for Python offers the ISlide.SaveAsImage() method which enables you to convert the slides in a PowerPoint presentation to image files in formats like PNG, JPG or BMP with ease. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Presentation object.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Loop through the slides in the presentation.
- Save each slide to an image stream using ISlide.SaveAsImage() method.
- Save the image stream to a JPG, PNG or BMP file using Stream.Save() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Loop through the slides in the presentation
for i, slide in enumerate(presentation.Slides):
# Specify the output file name
fileName ="Output/ToImage_" + str(i) + ".png"
# Save each slide as a PNG image
image = slide.SaveAsImage()
image.Save(fileName)
image.Dispose()
presentation.Dispose()
Convert PowerPoint Presentation to JPG, PNG or BMP Images with a Specific Size in Python
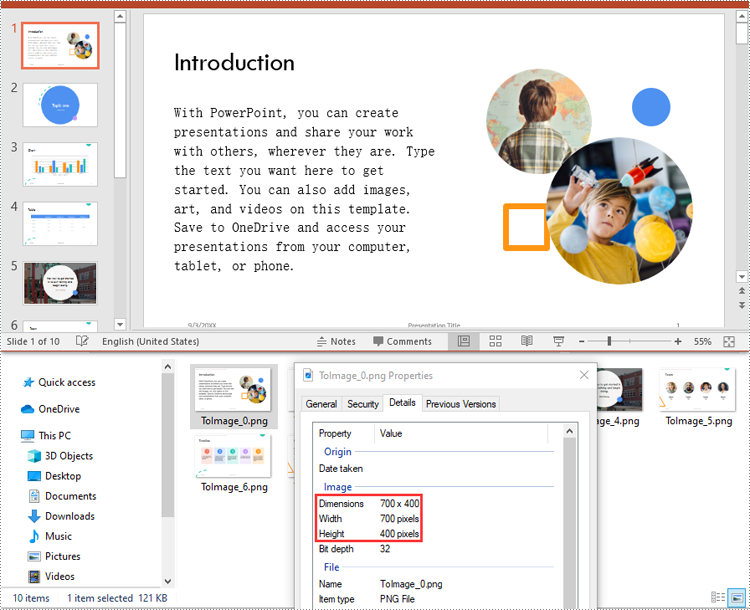
You can convert the slides in a PowerPoint presentation to images with a specific size using ISlide.SaveAsImageByWH() method. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Presentation object.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Loop through the slides in the presentation.
- Save each slide to an image stream using ISlide.SaveAsImageByWH() method.
- Save the image stream to a JPG, PNG or BMP file using Stream.Save() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Loop through the slides in the presentation
for i, slide in enumerate(presentation.Slides):
# Specify the output file name
fileName ="Output/ToImage_" + str(i) + ".png"
# Save each slide to a PNG image with a size of 700 * 400 pixels
slide1 = (ISlide)(slide)
image = slide1.SaveAsImageByWH(700, 400)
image.Save(fileName)
image.Dispose()
presentation.Dispose()
Convert PowerPoint Presentation to SVG Images in Python
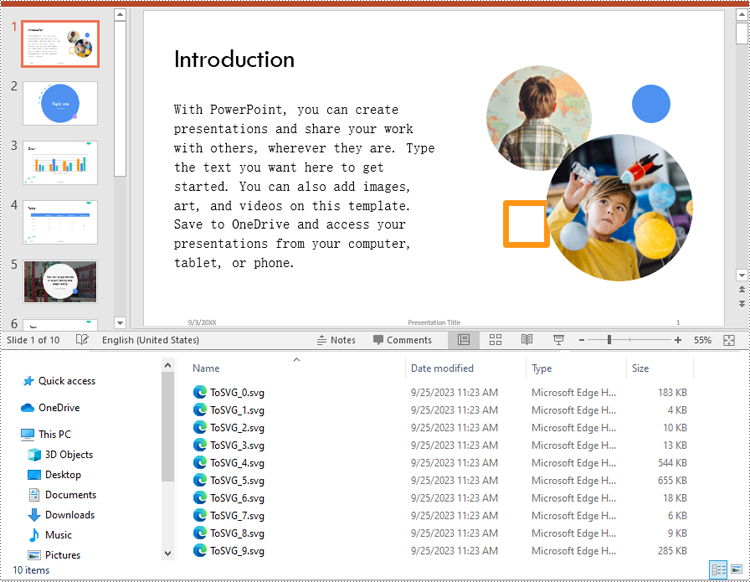
To convert the slides in a PowerPoint presentation to SVG images, you can use the ISlide.SaveToSVG() method. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Presentation object.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Enable the Presentation.IsNoteRetained property to retain notes when converting the presentation to SVG files.
- Loop through the slides in the presentation.
- Save each slide to an SVG stream using ISlide.SaveToSVG() method.
- Save the SVG stream to an SVG file using Stream.Save() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Enable the IsNoteRetained property to retain notes when converting the presentation to SVG files
presentation.IsNoteRetained = True
# Loop through the slides in the presentation
for i, slide in enumerate(presentation.Slides):
# Specify the output file name
fileName = "SVG/ToSVG_" + str(i) + ".svg"
# Save each slide to an SVG image
slide1 = (ISlide)(slide)
svgStream = slide1.SaveToSVG()
svgStream.Save(fileName)
presentation.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Extract Images from PowerPoint Presentations
Extracting images from a PowerPoint presentation is necessary when you need to reuse them elsewhere. By doing so, you gain the flexibility to use these images outside the confines of the original presentation, thus maximizing their value in different projects. This article will demonstrate how to extract images from a PowerPoint document in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Extract Images from a PowerPoint Document in Python
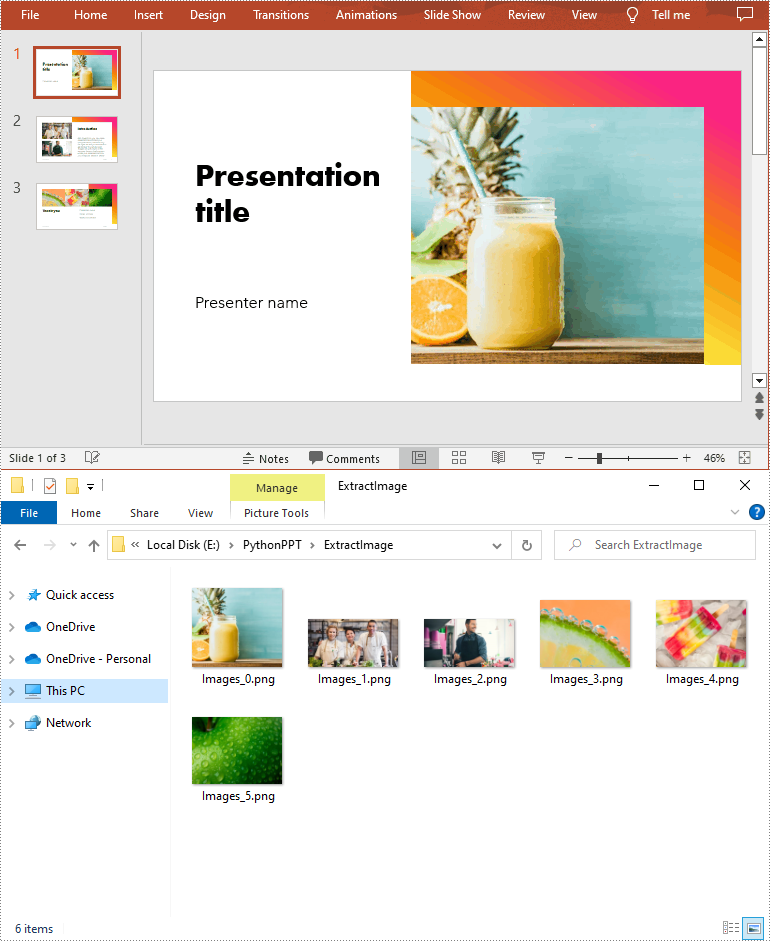
To extract images from an entire PowerPoint presentation, you need to use the Presentation.Images property to get the collection of all the images in the presentation, then iterate through the elements in the collection and call IImageData.Image.Save() method to save each element to an image file. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Presentation instance.
- Load a PowerPoint document using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the collection of all the images in the document using Presentation.Images property.
- Iterate through the elements in the collection, and save each element as an image file using the IImageData.Image.Save() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation instance
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint document
ppt.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx")
# Iterate through all images in the document
for i, image in enumerate(ppt.Images):
# Extract the images
ImageName = "ExtractImage/Images_"+str(i)+".png"
image.Image.Save(ImageName)
ppt.Dispose()
Extract Images from a Presentation Slide in Python
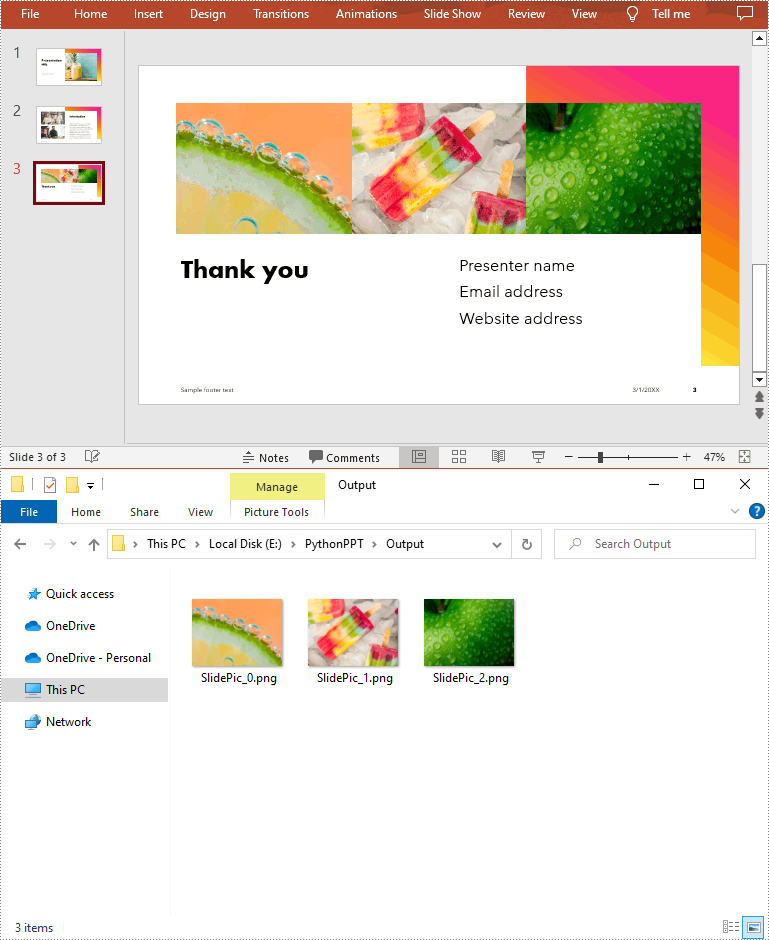
To extract images from a specific slide, you need to iterate through all shapes on the slide and find the shapes that are of SlidePicture or PictureShape type, then use the SlidePicture.PictureFill.Picture.EmbedImage.Image.Save() or PictureShape.EmbedImage.Image.Save() method to save the images to image files. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Presentation instance.
- Load a PowerPoint document using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified slide using Presentation.Slides[int] property.
- Iterate through all shapes on the slide.
- Determine whether the shapes are of SlidePicture or PictureShape type. If so, save the images to image files using SlidePicture.PictureFill.Picture.EmbedImage.Image.Save() or PictureShape.EmbedImage.Image.Save() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation instance
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint document
ppt.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx")
# Get a specified slide
slide = ppt.Slides[2]
i = 0
#Traverse all shapes in the slide
for s in slide.Shapes:
# Determine if the shape is of SlidePicture type
if isinstance(s, SlidePicture):
# If yes, then extract the image
ps = s if isinstance(s, SlidePicture) else None
ps.PictureFill.Picture.EmbedImage.Image.Save("Output/SlidePic_"+str(i)+".png")
i += 1
# Determine if the shape is of PictureShape type
if isinstance(s, PictureShape):
# If yes, then extract the image
ps = s if isinstance(s, PictureShape) else None
ps.EmbedImage.Image.Save("Output/SlidePic_"+str(i)+".png")
i += 1
ppt.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Set a Background Color or Image for PDF
Applying a background color or image to a PDF can be an effective way to enhance its visual appeal, create a professional look, or reinforce branding elements. By adding a background, you can customize the overall appearance of your PDF document and make it more engaging for readers. Whether you want to use a solid color or incorporate a captivating image, this feature allows you to personalize your PDFs and make them stand out. In this article, you will learn how to set a background color or image for a PDF document in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
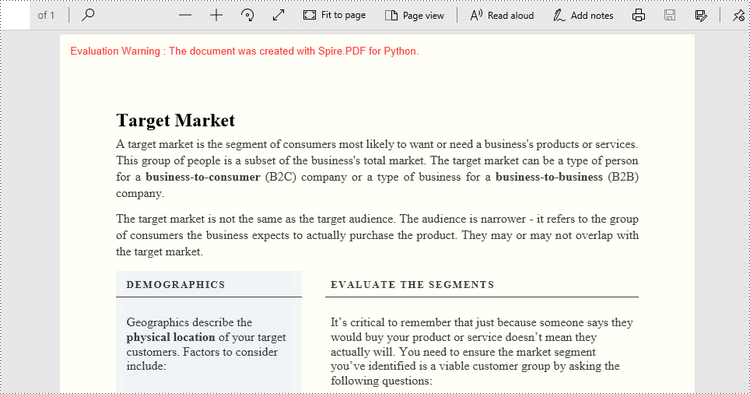
Set a Background Color for PDF in Python
Spire.PDF for Python offers the PdfPageBase.BackgroundColor property to get or set the background color of a certain page. To add a solid color to the background of each page in the document, follow the steps below.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Traverse through the pages in the document, and get a specific page through PdfDocument.Pages[index] property.
- Apply a solid color to the background through PdfPageBase.BackgroundColor property.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.pdf")
# Loop through the pages in the document
for i in range(doc.Pages.Count):
# Get a particular page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Set background color
page.BackgroundColor = Color.get_LightYellow()
# Save the document to a different file
doc.SaveToFile("output/SetBackgroundColor.pdf")
Set a Background Image for PDF in Python
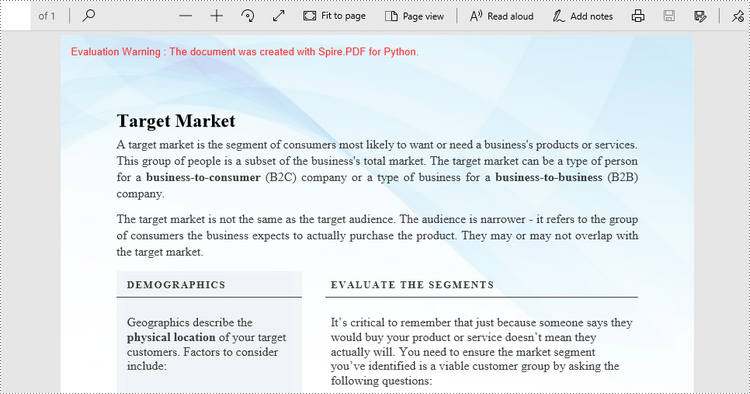
Likewise, an image can be applied to the background of a specific page via PdfPageBase.BackgroundImage property. The steps to set an image background for the entire document are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Traverse through the pages in the document, and get a specific page through PdfDocument.Pages[index] property.
- Apply an image to the background through PdfPageBase.BackgroundImage property.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.pdf")
# Loop through the pages in the document
for i in range(doc.Pages.Count):
# Get a particular page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Set background image
page.BackgroundImage = Stream("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\img.jpg")
# Save the document to a different file
doc.SaveToFile("output/SetBackgroundImage.pdf")
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Rotate PDF Pages
If you receive or download a PDF file and find that some of the pages are displayed in the wrong orientation (e.g., sideways or upside down), rotating the PDF file allows you to correct the page orientation for easier reading and viewing. This article will demonstrate how to programmatically rotate PDF pages using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Rotate a Specific Page in PDF in Python
Rotation is based on 90-degree increments. You can rotate a PDF page by 0/90/180/270 degrees. The following are the steps to rotate a PDF page:
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified page using PdfDocument.Pages[pageIndex] property.
- Get the original rotation angle of the page using PdfPageBase.Rotation.value property.
- Increase the original rotation angle by desired degrees.
- Apply the new rotation angle to the page using PdfPageBase.Rotation property
- Save the result document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Get the original rotation angle of the page
rotation = int(page.Rotation.value)
# Rotate the page 180 degrees clockwise based on the original rotation angle
rotation += int(PdfPageRotateAngle.RotateAngle180.value)
page.Rotation = PdfPageRotateAngle(rotation)
# Save the result document
pdf.SaveToFile("RotatePDFPage.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Rotate All Pages in PDF in Python
Spire.PDF for Python also allows you to loop through each page in a PDF file and then rotate them all. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Loop through each page in the document.
- Get the original rotation angle of the page using PdfPageBase.Rotation.value property.
- Increase the original rotation angle by desired degrees.
- Apply the new rotation angle to the page using PdfPageBase.Rotation property.
- Save the result document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("Input.pdf")
# Loop through each page in the document
for i in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Get the original rotation angle of the page
rotation = int(page.Rotation.value)
# Rotate the page 180 degrees clockwise based on the original rotation angle
rotation += int(PdfPageRotateAngle.RotateAngle180.value)
page.Rotation = PdfPageRotateAngle(rotation)
# Save the result document
pdf.SaveToFile("RotatePDF.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.