
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Apart from creating chart with continuous data range, Spire.XLS also supports to create chart with discontinuous data range by calling the XlsRange.AddCombinedRange(CellRange cr) method. This example explains a quick solution of how to achieve this task in C# with the help of Spire.XLS.
For demonstration, here we used a template excel document, in which you can see there are some blank rows among the data, in other words, the data range is discontinuous.
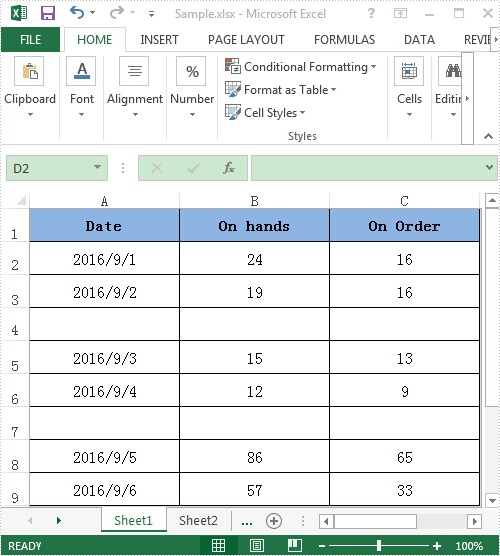
Here comes to the detail steps:
Step 1: Instantiate a Wordbook object, load the excel document and get its first worksheet.
Workbook book = new Workbook();
book.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = book.Worksheets[0];
Step 2: Add a column chart to the first worksheet and set the position of the chart.
Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered); chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false; //Set chart position chart.LeftColumn = 5; chart.TopRow = 1; chart.RightColumn = 13; chart.BottomRow = 10;
Step 3: Add two series to the chart, set data source for category labels and values of the series with discontinuous data range.
//Add the first series var cs1 = (ChartSerie)chart.Series.Add(); //Set name of the serie cs1.Name = sheet.Range["B1"].Value; //Set data source for Category Labels and Values of the serie with discontinuous data range cs1.CategoryLabels = sheet.Range["A2:A3"].AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["A5:A6"]).AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["A8:A9"]); cs1.Values = sheet.Range["B2:B3"].AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["B5:B6"]).AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["B8:B9"]); //Specify the serie type cs1.SerieType = ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered; //Add the second series var cs2 = (ChartSerie)chart.Series.Add(); cs2.Name = sheet.Range["C1"].Value; cs2.CategoryLabels = cs2.CategoryLabels = sheet.Range["A2:A3"].AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["A5:A6"]).AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["A8:A9"]); cs2.Values = sheet.Range["C2:C3"].AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["C5:C6"]).AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["C8:C9"]); cs2.SerieType = ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered;
Step 4: Save the excel document.
book.SaveToFile("Result.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2010);
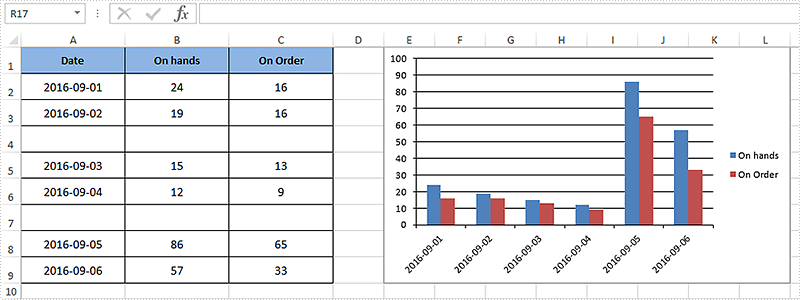
After executing the above example code, a column chart with discontinuous data range was added to the worksheet as shown below.
Full code:
using Spire.Xls;
using Spire.Xls.Charts;
namespace Assign_discontinuous_range_for_chart
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Workbook book = new Workbook();
book.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = book.Worksheets[0];
Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered);
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false;
chart.LeftColumn = 5;
chart.TopRow = 1;
chart.RightColumn = 13;
chart.BottomRow = 10;
var cs1 = (ChartSerie)chart.Series.Add();
cs1.Name = sheet.Range["B1"].Value;
cs1.CategoryLabels = sheet.Range["A2:A3"].AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["A5:A6"]).AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["A8:A9"]);
cs1.Values = sheet.Range["B2:B3"].AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["B5:B6"]).AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["B8:B9"]);
cs1.SerieType = ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered;
var cs2 = (ChartSerie)chart.Series.Add();
cs2.Name = sheet.Range["C1"].Value;
cs2.CategoryLabels = sheet.Range["A2:A3"].AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["A5:A6"]).AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["A8:A9"]);
cs2.Values = sheet.Range["C2:C3"].AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["C5:C6"]).AddCombinedRange(sheet.Range["C8:C9"]);
cs2.SerieType = ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered;
chart.ChartTitle = string.Empty;
book.SaveToFile("Result.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("Result.xlsx");
}
}
}
Set Different Header or Footer for Odd and Even Pages in Excel in C#, VB.NET
2016-09-22 00:59:10 Written by KoohjiHeaders or footers are added to a worksheet to deliver some extra information about each page. By default, the headers or footers on odd and even pages are the same. However, we are able to set different headers or footers for odd and even pages to display different information.
Following sections demonstrate how to create different odd and even page headers/footers using Spire.XLS.
Code Snippet:
Step 1: Initialize an instance of Workbook and get the first worksheet.
Workbook wb = new Workbook(); Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
Step 2: Set the value of DifferentOddEven as 1, which indicates that headers/footers for odd and even pages are different.
sheet.PageSetup.DifferentOddEven = 1;
Step 3: Set header and footer string for odd pages, and format the string.
sheet.PageSetup.OddHeaderString = "&\"Arial\"&12&B&KFFC000Odd_Header"; sheet.PageSetup.OddFooterString = "&\"Arial\"&12&B&KFFC000Odd_Footer";
Step 4: Set different header and footer string for even pages, and format the string with different color.
sheet.PageSetup.EvenHeaderString = "&\"Arial\"&12&B&KFF0000Even_Header"; sheet.PageSetup.EvenFooterString = "&\"Arial\"&12&B&KFF0000Even_Footer";
Step 5: Save the file.
wb.SaveToFile("OddEvenHeaderFooter.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
Output:
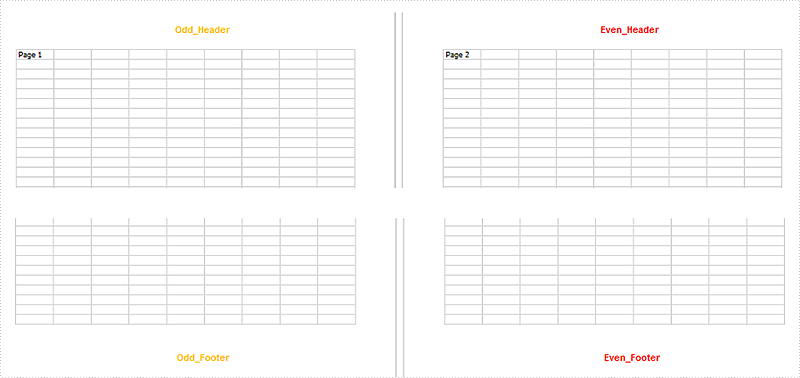
Full Code:
using Spire.Xls;
namespace SetDifferentHeaderorFooter
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Page 1";
sheet.Range["J1"].Text = "Page 2";
sheet.PageSetup.DifferentOddEven = 1;
sheet.PageSetup.OddHeaderString = "&\"Arial\"&12&B&KFFC000Odd_Header";
sheet.PageSetup.OddFooterString = "&\"Arial\"&12&B&KFFC000Odd_Footer";
sheet.PageSetup.EvenHeaderString = "&\"Arial\"&12&B&KFF0000Even_Header";
sheet.PageSetup.EvenFooterString = "&\"Arial\"&12&B&KFF0000Even_Footer";
wb.SaveToFile("OddEvenHeaderFooter.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Xls
Namespace SetDifferentHeaderorFooter
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
Dim wb As New Workbook()
Dim sheet As Worksheet = wb.Worksheets(0)
sheet.Range("A1").Text = "Page 1"
sheet.Range("J1").Text = "Page 2"
sheet.PageSetup.DifferentOddEven = 1
sheet.PageSetup.OddHeaderString = "&""Arial""&12&B&KFFC000Odd_Header"
sheet.PageSetup.OddFooterString = "&""Arial""&12&B&KFFC000Odd_Footer"
sheet.PageSetup.EvenHeaderString = "&""Arial""&12&B&KFF0000Even_Header"
sheet.PageSetup.EvenFooterString = "&""Arial""&12&B&KFF0000Even_Footer"
wb.SaveToFile("OddEvenHeaderFooter.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
To make the text within a cell diverse, we can apply different font to different range of characters. Spire.XLS also provides the ability to apply multiple fonts in a single cell by using RichText.SetFont() method. This article presents how to create different fonts in a workbook and apply them to a certain cell in C# and VB.NET.
Code Snippet:
Step 1: Initialize an instance of Workbook class and get the first worksheet.
Workbook wb = new Workbook(); Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
Step 2: Create a font object in workbook, setting the font color, size and type.
ExcelFont font1 = wb.CreateFont(); font1.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightBlue; font1.IsBold = true; font1.Size = 10;
Step 3: Create another font object specifying its properties.
ExcelFont font2 = wb.CreateFont(); font2.KnownColor = ExcelColors.Red; font2.IsBold = true; font2.IsItalic = true; font2.FontName = "Times New Roman"; font2.Size = 11;
Step 4: Write a RichText string to the cell 'A1', and set the font for the specific range of characters using RichText.SetFont() method.
RichText richText = sheet.Range["A1"].RichText; richText.Text = "This document was created with Spire.XLS for .NET."; richText.SetFont(0, 29, font1); richText.SetFont(31, 48, font2);
Step 5: Save the file.
wb.SaveToFile("MultiFonts.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
Output:
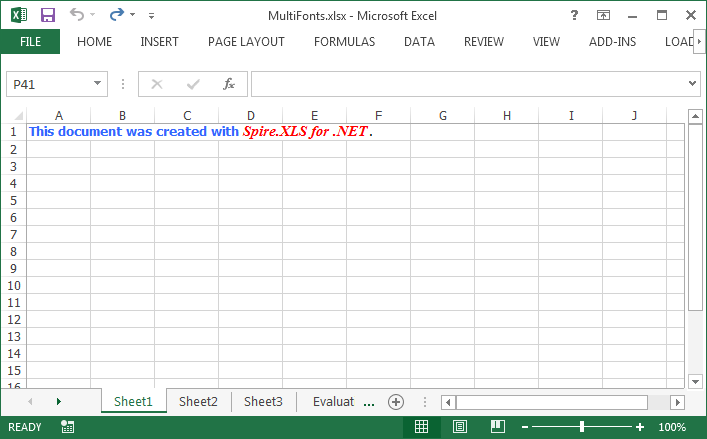
Full Code:
using Spire.Xls;
namespace ApplyMutipleFont
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
ExcelFont font1 = wb.CreateFont();
font1.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightBlue;
font1.IsBold = true;
font1.Size = 10;
ExcelFont font2 = wb.CreateFont();
font2.KnownColor = ExcelColors.Red;
font2.IsBold = true;
font2.IsItalic = true;
font2.FontName = "Times New Roman";
font2.Size = 11;
RichText richText = sheet.Range["A1"].RichText;
richText.Text = "This document was created with Spire.XLS for .NET.";
richText.SetFont(0, 29, font1);
richText.SetFont(31, 48, font2);
wb.SaveToFile("MultiFonts.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Xls
Namespace ApplyMutipleFont
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
Dim wb As New Workbook()
Dim sheet As Worksheet = wb.Worksheets(0)
Dim font1 As ExcelFont = wb.CreateFont()
font1.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightBlue
font1.IsBold = True
font1.Size = 10
Dim font2 As ExcelFont = wb.CreateFont()
font2.KnownColor = ExcelColors.Red
font2.IsBold = True
font2.IsItalic = True
font2.FontName = "Times New Roman"
font2.Size = 11
Dim richText As RichText = sheet.Range("A1").RichText
richText.Text = "This document was created with Spire.XLS for .NET."
richText.SetFont(0, 29, font1)
richText.SetFont(31, 48, font2)
wb.SaveToFile("MultiFonts.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
