
Knowledgebase (2310)
Children categories
How to Integrate Spire.PDFViewer for MAUI in .NET Project
2025-09-05 02:36:38 Written by AdministratorSpire.PDFViewer for MAUI is a dedicated PDF viewing component tailored for .NET Multi-platform App UI (MAUI) frameworks. This guide will show you how to configure it in your .NET MAUI project, including environment setup, product installation, and core PDF viewing feature implementation.
1. Prerequisites & Environment Setup
Ensure your development environment meets the following requirements before you begin.
1.1 Required Software
- IDE: Visual Studio 2022 (version 17.8 or later) for Windows, or Visual Studio 2022 for Mac (version 17.6 or later).
- Target Frameworks:
- Android 5.0 (API 21) or higher
- Windows 11, or Windows 10 Version 1809 or higher
1.2 Install the .NET MAUI Workload
The .NET Multi-platform App UI development workload is mandatory for MAUI projects. Follow these steps to install it:
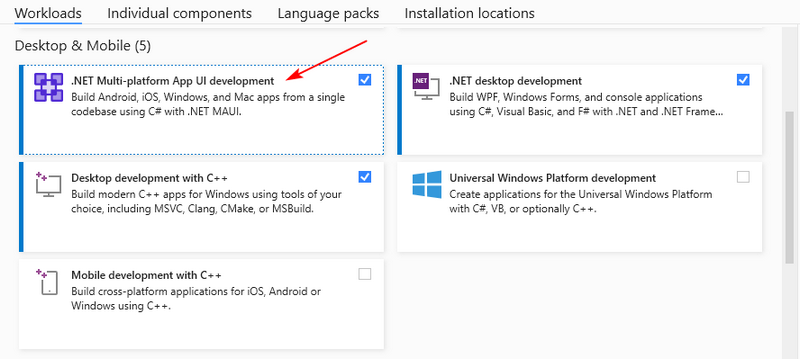
- Open Visual Studio Installer:
- Search for "Visual Studio Installer" in your Start Menu (usually under the "Visual Studio 2022" folder).
- Alternatively, open Visual Studio, go to “Tools > Get Tools and Features”.
- Modify Your Installation:
- Click "Modify" next to your Visual Studio 2022 edition.
- Navigate to the "Workloads" tab.
- Check the box for ".NET Multi-platform App UI development".
- Ensure the optional components you need are selected.
- Click "Modify" to start the installation
2. Create a New .NET MAUI Project
After installing MAUI, follow these steps to create a new .NET MAUI project:
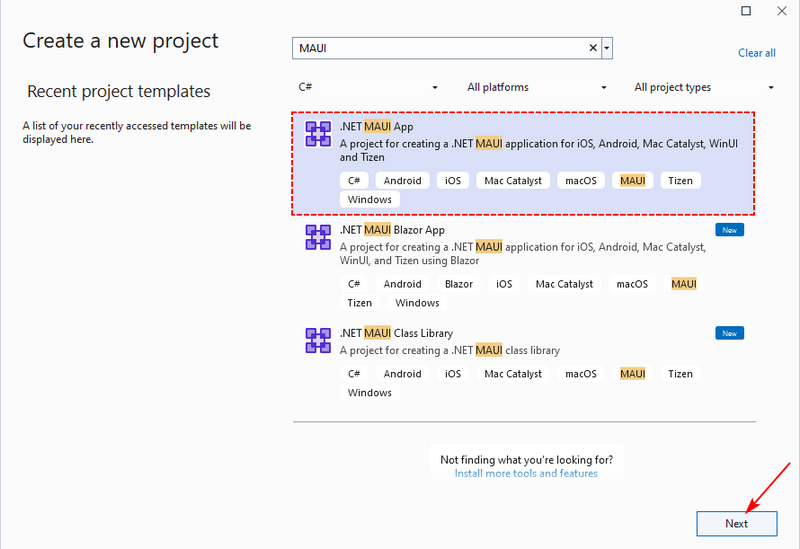
2.1 Select the Project Template
- Open Visual Studio and click “Create a new project”.
- Search for "MAUI" and select the .NET MAUI App template (C#).
- Click “Next” to proceed.
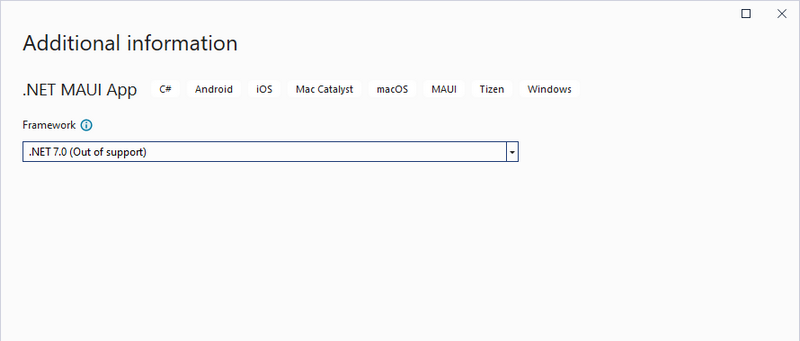
2.2 Configure Project Details
- Enter a project name (e.g., "PdfViewerMauiApp") and choose a Save location.
- Next, select .NET 7.0 or later (e.g., .NET 8.0) as the target framework.
- Click “Create” to generate the project.
3. Install Spire.PDFViewer and Dependencies
To implement the PDF viewer in .NET MAUI, you need to install the dependent NuGet packages and add Spire.PDFViewer DLLs.
3.1 Install Dependent NuGet Packages
- Go to “Tools > NuGet Package Manager > Package Manager Console”.
- Run the following command to install all required packages at once:
Install-Package Microsoft.Win32.Registry -Version 5.0.0
Install-Package System.Security.Permissions -Version 4.7.0
Install-Package System.Text.Encoding.CodePages -Version 4.7.0
Install-Package System.Security.Cryptography.Pkcs -Version 4.7.0
Install-Package System.Security.Cryptography.Xml -Version 4.7.1
Install-Package HarfBuzzSharp -Version 8.3.0.1
Install-Package SkiaSharp -Version 3.116.1
Install-Package SkiaSharp.Views.Maui.Controls -Version 2.88.5
Install-Package System.Buffers -Version 4.5.1
Install-Package System.Memory -Version 4.5.5
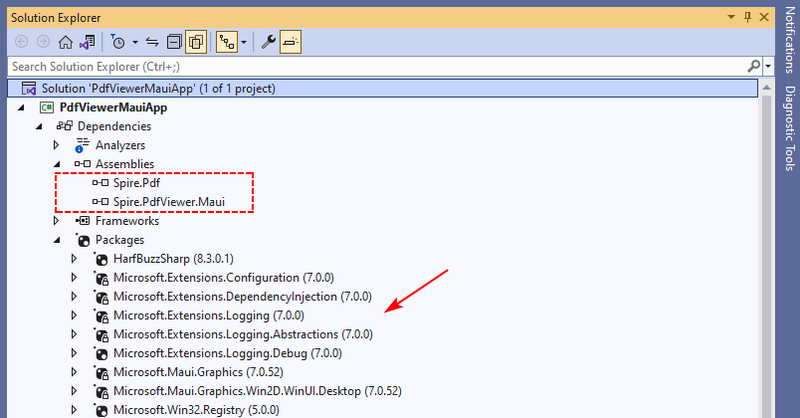
3.2 Add Spire.PDFViewer DLLs
- Download the Spire.PdfViewer package from the official website.
- Unzip the downloaded file to a specified file path.
- In Visual Studio’s Solution Explorer, right-click the project > Add > Project Reference.
- Click “Browse”, navigate to the unzipped folder (BIN\NET7.0\windows10.0.19041.0), and add both:
- Spire.PdfViewer.Maui.dll
- Spire.Pdf.dll
3.3 Restrict Target Platform to Windows
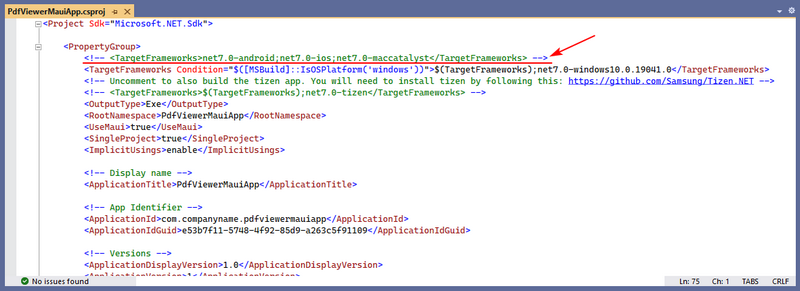
Currently, the Spire.PDFViewer for MAUI only supports the Windows platform. Therefore, it’s necessary to modify the project file (.csproj) to remove non-Windows target frameworks:
- In Solution Explorer, right-click the project and select “Edit Project File”.
- Locate the
<TargetFrameworks>element and delete or comment out this line. - Save the file (Ctrl+S) and reload the project when prompted by Visual Studio.
4. Add PDF Viewer to the Project
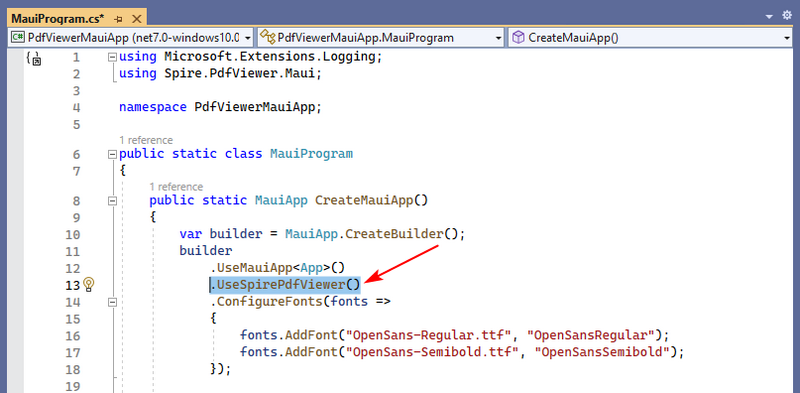
4.1 Initialize Spire.PDFViewer
In “MauiProgram.cs”, add the .UseSpirePdfViewer() method in the MauiAppBuilder chain:
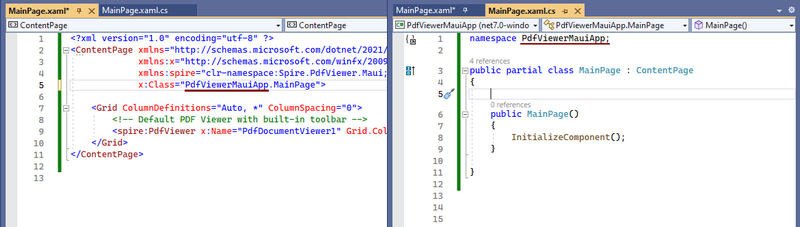
4.2 Option 1: Use the Default PDF Viewer UI
For a quick setup with a pre-built toolbar (supports loading, zooming, and searching), use the minimal XAML configuration:
- Replace the default XAML content of “MainPage.xaml” with the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<ContentPage xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:spire="clr-namespace:Spire.PdfViewer.Maui;assembly=Spire.PdfViewer.Maui"
x:Class="PdfViewerMauiApp.MainPage"> <!-- Modify “PdfViewerMauiApp” to match your project name -->
<Grid ColumnDefinitions="Auto, *" ColumnSpacing="0">
<!-- Default PDF Viewer with built-in toolbar -->
<spire:PdfViewer x:Name="PdfDocumentViewer1" Grid.Column="1" />
</Grid>
</ContentPage>
- Open “MainPage.xaml.cs” and ensure the namespace matches your project name:
namespace PdfViewerMauiApp; // Match the project name in the x:Class value
public partial class MainPage : ContentPage
{
public MainPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
}
When you run the project, a PDF viewer with a built-in toolbar (Home, Zoom, Find) will appear. You can load PDFs directly via the toolbar and use its default features.

4.3 Option 2: Customize the UI Layout & Functionality
For a tailored experience (e.g., a dedicated "Load PDF" button or page navigation), design a custom layout and implement core logic.
Step 1: Design the Custom UI (MainPage.xaml)
Replace the default XAML content of “MainPage.xaml” with a two-column grid (left: control panel; right: PDF viewer):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<ContentPage xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:spire="clr-namespace:Spire.PdfViewer.Maui;assembly=Spire.PdfViewer.Maui"
x:Class="PdfViewerMauiApp.MainPage"> <!-- Modify “PdfViewerMauiApp” to match your project name -->
<Grid ColumnDefinitions="Auto, *" ColumnSpacing="0">
<!-- Left Control Panel -->
<VerticalStackLayout Grid.Column="0" WidthRequest="220"
Padding="10" Spacing="10">
<!-- Button to load PDF files -->
<Button Text="Load PDF File"
Clicked="LoadFromFile_Clicked"
HeightRequest="40"/>
<!-- Page Navigation: Entry + Button -->
<HorizontalStackLayout Spacing="10">
<Entry x:Name="pageEntry"
WidthRequest="100"
HeightRequest="40"
Keyboard="Numeric"
Placeholder="Page Number"/>
<Button Text="Go To"
Clicked="GoPages_Clicked"
WidthRequest="80"
HeightRequest="40"/>
</HorizontalStackLayout>
<Label x:Name="lbl1" HeightRequest="30"/>
</VerticalStackLayout>
<!-- Right PDF Viewing Area -->
<spire:PdfDocumentViewer x:Name="PdfDocumentViewer1" Grid.Column="1" />
</Grid>
</ContentPage>
Step 2: Add Functionality (MainPage.xaml.cs)
Add event handlers in “MainPage.xaml.cs” to enable PDF loading and page navigation:
namespace PdfViewerMauiApp; // Match your project name
public partial class MainPage : ContentPage
{
public MainPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
// Click event for the Load PDF File button
private async void LoadFromFile_Clicked(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
// Restrict file picker to PDF files only
var result = await FilePicker.PickAsync(new PickOptions
{
FileTypes = FilePickerFileType.Pdf,
PickerTitle = "Choose a PDF file"
});
if (result != null)
{
// Load the PDF file from the selected path
PdfDocumentViewer1.LoadFromFile(result.FullPath);
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Display error message
lbl1.Text = $"Loading failed: {ex.Message}";
}
}
// Click event for page navigation button
private void GoPages_Clicked(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (int.TryParse(pageEntry.Text, out int pageNumber) && pageNumber > 0)
{
// Verify that the page number is within the valid range.
if (pageNumber <= PdfDocumentViewer1.PageCount)
{
// Jump to a specific page number
PdfDocumentViewer1.GotoPage(pageNumber, true);
lbl1.Text = $"Navigated to Page: {pageNumber}/{PdfDocumentViewer1.PageCount}";
}
else
{
lbl1.Text = $"Out of Range (Max Page: {PdfDocumentViewer1.PageCount})";
}
}
else
{
lbl1.Text = "Please enter a valid page number.";
}
}
}
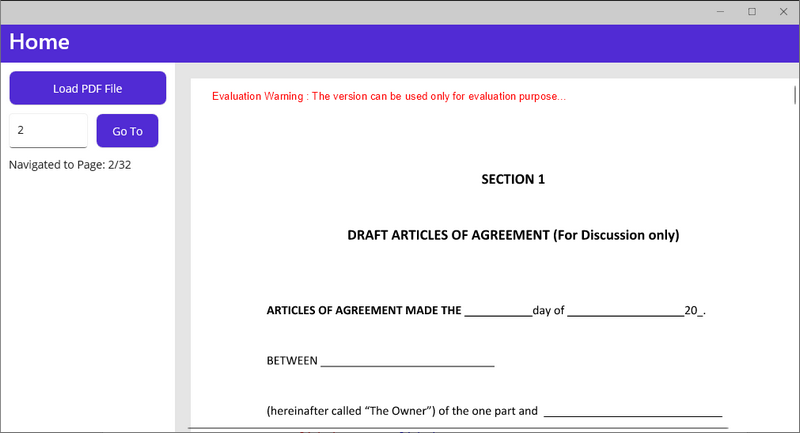
Step 3: Run the Project
Run the application, and test the PDF viewer functionality:
-
Click “Load PDF File” to select and open a PDF.
-
Enter a page number and click “Go To” to navigate to that page.
Integrating Spire.PDFViewer into a .NET MAUI project enables developers to quickly add robust, user-friendly PDF viewing capabilities, including document loading, page navigation, and built-in/ custom UI controls. By following the steps outlined here, developers can avoid common pitfalls (e.g., version mismatches, missing dependencies) and deploy a functional PDF viewer in minimal time.
How to Convert Markdown to HTML in Python: Step-by-Step Guide
2025-09-05 02:05:04 Written by Administrator
Markdown (.md) is widely used in web development, documentation, and technical writing. Its simple syntax makes content easy to write and read. However, web browsers do not render Markdown directly. Converting Markdown to HTML ensures your content is structured, readable, and compatible with web platforms.
In this step-by-step guide, you will learn how to efficiently convert Markdown (.md) files into HTML using Python and Spire.Doc for Python, complete with practical code examples, clear instructions, and best practices for both single-file and batch conversions.
Table of Contents
- What is Markdown
- Why Convert Markdown to HTML
- Introducing Spire.Doc for Python
- Step-by-Step Guide: Converting Markdown to HTML in Python
- Automating Batch Conversion
- Best Practices for Markdown to HTML Conversion
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Markdown?
Markdown is a lightweight markup language designed for readability and ease of writing. Unlike HTML, which can be verbose and harder to write by hand, Markdown uses simple syntax to indicate headings, lists, links, images, and more.
Example Markdown:
# This is a Heading
This is a paragraph with \*\*bold text\*\* and \*italic text\*.
- Item 1
- Item 2
Even in its raw form, Markdown is easy to read, which makes it popular for documentation, blogging, README files, and technical writing.
For more on Markdown syntax, see the Markdown Guide.
Why Convert Markdown to HTML?
While Markdown is excellent for authoring content, web browsers cannot render it natively. Converting Markdown to HTML allows you to:
- Publish content on websites – Most CMS platforms require HTML for web pages.
- Enhance styling – HTML supports CSS and JavaScript for advanced formatting and interactivity.
- Maintain compatibility – HTML is universally supported by browsers, ensuring content displays correctly everywhere.
- Integrate with web frameworks – Frameworks like React, Vue, and Angular require HTML as the base for rendering components.
Introducing Spire.Doc for Python
Spire.Doc for Python is a robust library for handling multiple document formats. It supports reading and writing Word documents, Markdown files, and exporting content to HTML. The library allows developers to convert Markdown directly to HTML with minimal code, preserving proper formatting and structure.
In addition to HTML, Spire.Doc for Python also allows you to convert Markdown to Word in Python or convert Markdown to PDF in Python, making it particularly useful for developers who want a unified tool for handling Markdown across different output formats.
Benefits of Using Spire.Doc for Python for Markdown to HTML Conversion
- Easy-to-use API – Simple, intuitive methods that reduce development effort.
- Accurate formatting – Preserves all Markdown elements such as headings, lists, links, and emphasis in HTML.
- No extra dependencies – Eliminates the need for manual parsing or third-party libraries.
- Flexible usage – Supports both single-file conversion and automated batch processing.
Step-by-Step Guide: Converting Markdown to HTML in Python
Now that you understand the purpose and benefits of converting Markdown to HTML, let’s walk through a clear, step-by-step process to transform your Markdown files into structured, web-ready HTML.
Step 1: Install Spire.Doc for Python
First, ensure that Spire.Doc for Python is installed in your environment. You can install it directly from PyPI using pip:
pip install spire.doc
Step 2: Prepare Your Markdown File
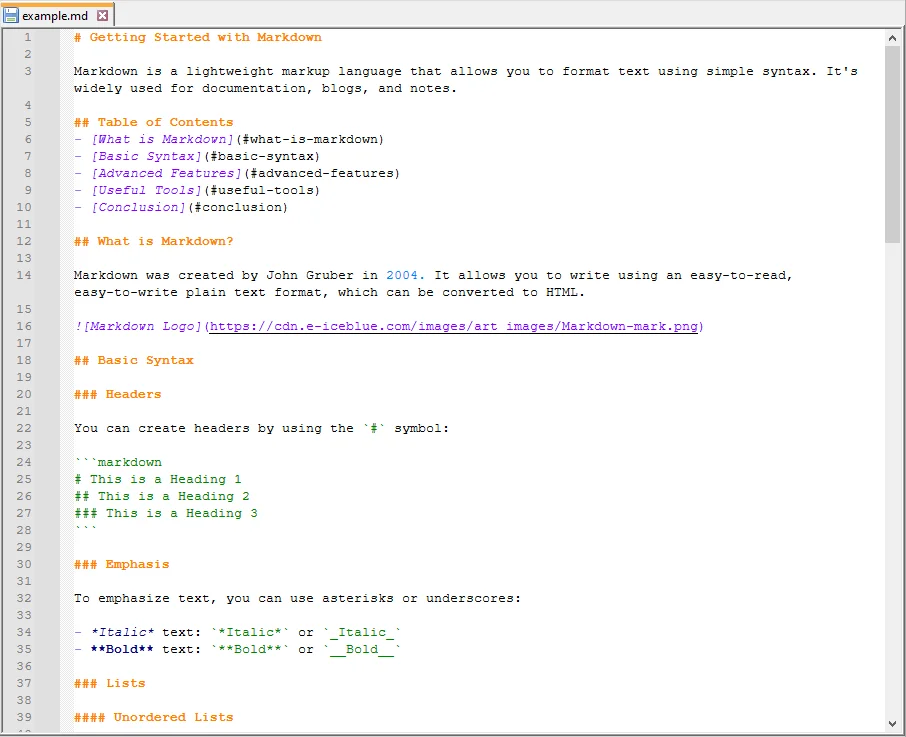
Next, create a sample Markdown file that you want to convert. For example, example.md:
Step 3: Write the Python Script
Now, write a Python script that loads the Markdown file and converts it to HTML:
from spire.doc import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load the Markdown file
doc.LoadFromFile("example.md", FileFormat.Markdown)
# Save the document as HTML
doc.SaveToFile("example.html", FileFormat.Html)
# Close the document
doc.Close()
Explanation of the code:
- Document() initializes a new document object.
- LoadFromFile("example.md", FileFormat.Markdown) loads the Markdown file into memory.
- SaveToFile("example.html", FileFormat.Html) converts the loaded content into HTML and saves it to disk.
- doc.Close() ensures resources are released properly, which is particularly important when processing multiple files or running batch operations.
Step 4: Verify the HTML Output
Finally, open the generated example.html file in a web browser or HTML editor. Verify that the Markdown content has been correctly converted.

Automating Batch Conversion
You can convert multiple Markdown files in a folder automatically:
import os
from spire.doc import *
# Set the folder containing Markdown files
input_folder = "markdown_files"
# Set the folder where HTML files will be saved
output_folder = "html_files"
# Create the output folder if it doesn't exist
os.makedirs(output_folder, exist_ok=True)
# Loop through all files in the input folder
for filename in os.listdir(input_folder):
# Process only Markdown files
if filename.endswith(".md"):
# Create a new Document object for each file
doc = Document()
# Load the Markdown file into the Document object
doc.LoadFromFile(os.path.join(input_folder, filename), FileFormat.Markdown)
# Construct the output file path by replacing .md extension with .html
output_file = os.path.join(output_folder, filename.replace(".md", ".html"))
# Save the loaded Markdown content as HTML
doc.SaveToFile(output_file, FileFormat.Html)
# Close the document to release resources
doc.Close()
This approach allows you to process multiple Markdown files efficiently and generate corresponding HTML files automatically.
Best Practices for Markdown to HTML Conversion
While the basic steps are enough to complete a Markdown-to-HTML conversion, following a few best practices will help you avoid common pitfalls, improve compatibility, and ensure your output is both clean and professional:
- Use proper Markdown syntax – Ensure headings, lists, links, and emphasis are correctly written.
- Use UTF-8 Encoding: Always save your Markdown files in UTF-8 encoding to avoid issues with special characters or non-English text.
- Batch Processing: If you need to convert multiple files, wrap your script in a loop and process entire folders. This saves time and ensures consistent formatting across documents.
- Enhance Styling: Remember that HTML gives you the flexibility to add CSS and JavaScript for custom layouts, responsive design, and interactivity—something not possible in raw Markdown.
Conclusion
Converting Markdown to HTML using Python with Spire.Doc is simple, reliable, and efficient. It preserves formatting, supports automation, and produces clean HTML output ready for web use. By following this guide, you can implement a smooth Markdown to HTML workflow for both single documents and batch operations.
FAQs
Q1: Can I convert multiple Markdown files to HTML in Python?
A1: Yes, you can automate batch conversions by iterating through Markdown files in a directory and applying the conversion logic to each file.
Q2: Will the HTML preserve all Markdown formatting?
A2: Yes, Spire.Doc effectively preserves all essential Markdown formatting, including headings, lists, bold and italic text, links, and more.
Q3: Is there a way to handle images in Markdown during conversion?
A3: Yes, Spire.Doc supports the conversion of images embedded in Markdown, ensuring they are included in the resulting HTML.
Q4: Do I need additional libraries besides Spire.Doc?
A4: No additional libraries are required. Spire.Doc for Python provides a comprehensive solution for converting Markdown to HTML without any external dependencies.
Q5: Can I use the generated HTML in web frameworks?
A5: Yes, the HTML produced is fully compatible with popular web frameworks such as React, Vue, and Angular, making integration seamless.
C# Write to Excel Guide: Insert Data into Worksheets Easily
2025-09-04 09:05:06 Written by Administrator
Excel remains one of the most widely used tools for managing and analyzing data due to its powerful features and user-friendly interface. In C# applications, developers often need to generate reports, export database results, or automate tasks by writing directly to Excel files.
To achieve this efficiently, developers often turn to third-party libraries. Spire.XLS for .NET makes it simple to write to Excel programmatically without relying on Microsoft Excel. With Spire.XLS, you can insert text, numbers, dates, formulas, or even bulk datasets such as arrays, DataTables, and lists into Excel worksheets. This provides a fast, flexible, and reliable way to automate Excel writing in C# applications.
On this page:
- Getting Started with Spire.XLS for .NET
- How to Create a New Excel File in C#
- Write Different Data Types to Excel Cells
- Write Bulk Data to Excel Sheets
- Save and Export Excel Files
- Common Issues and Solutions
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Getting Started with Spire.XLS for .NET
What’s Spire.XLS for .NET
Spire.XLS for .NET is a professional .NET Excel library developed by E-iceblue. It allows developers to write to Excel files in C# and perform a wide range of operations including creating, editing, reading, and exporting Excel documents—without requiring Microsoft Excel to be installed.
Key features include:
- Write and update Excel files programmatically.
- Support for Excel formats (XLS, XLSX, CSV, ODS).
- Advanced features such as formulas, charts, pivot tables, and data validation.
- Export Excel to PDF, HTML, and image formats.
- High performance with large datasets, suitable for desktop, server, and web applications.
How to Install Spire.XLS for .NET
Option 1: Install via NuGet (recommended)
- Open Visual Studio.
- Navigate to Tools > NuGet Package Manager > Manage NuGet Packages for Solution.
- Search for Spire.XLS and install it.
Or, install it directly using the Package Manager Console :
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Option 2: Manual installation
- Download the Spire.XLS package from our official website
- Add a reference to Spire.Xls.dll in your project.
Once installed, you’re ready to start writing to Excel in C#.
How to Create a New Excel File in C#
The first step is to create a new workbook and add a worksheet. Here’s how:
using Spire.Xls;
namespace CreateNewExcel
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new workbook
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Remove default worksheets
workbook.Worksheets.Clear();
// Add a worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("Report");
// Save the empty Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("NewExcelFile.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
At this point, you have created an empty Excel file with a worksheet named “Report”. Next, let’s write data into it.
Write Different Data Types to Excel Cells in C#
Spire.XLS allows you to write various data types directly to Excel cells. Below are common examples:
Write Text Values
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Hello Excel!";
Write Numeric Values
sheet.Range["A2"].NumberValue = 123.45;
Write Date and Time
sheet.Range["A3"].DateTimeValue = DateTime.Now;
sheet.Range["A3"].NumberFormat = "yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm";
Write Boolean Values
sheet.Range["A4"].BooleanValue = true;
Write TimeSpan Values
sheet.Range["A5"].TimeSpanValue = new TimeSpan(2, 30, 0); // 2 hours 30 minutes;
sheet.Range["A5"].NumberFormat = "[h]:mm:ss";
Insert Formulas
sheet.Range["A6"].Formula = "=SUM(A2,100)";
Insert HTML Formatted Strings
string htmlText = "<span style=\"font-family: Times New Roman; color: blue; font-size: 15pt;\">Hello
<strong>Spire.XLS</strong></span>";
sheet.Range["A7"].HtmlString = htmlText;
Write General Values Without Specific Type
sheet.Range["A8"].Value = "General Value";
Output:

You might also be interested in: How to Read Excel Files in C#
Write Bulk Data to Excel Sheets in C#
When dealing with larger datasets, writing values cell by cell isn’t efficient. Spire.XLS provides methods to insert arrays , and DataTables directly. Other data structures can be converted to arrays or DataTables before being written to the Excel sheet.
Write Arrays to Excel
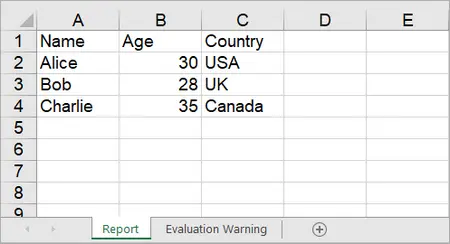
Spire.XLS provides the Worksheet.InsertArray(string[] stringArray, int firstRow, int firstColumn, bool isVertical) method, allowing developers to insert one-dimensional or two-dimensional arrays into a specified range of cells in a worksheet.
string[,] data = {
{ "Name", "Age", "Country" },
{ "Alice", "30", "USA" },
{ "Bob", "28", "UK" },
{ "Charlie", "35", "Canada" }
};
sheet.InsertArray(data, 1, 1);
Output:
Write DataTables to Excel
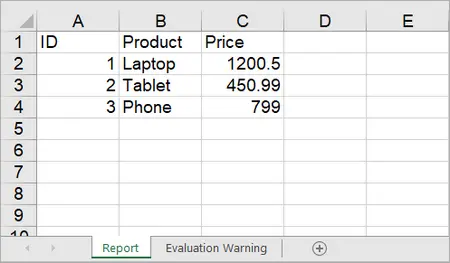
To import data from a DataTable to a worksheet, use the Worksheet.InsertDataTable(DataTable dataTable, bool columnHeaders, int firstRow, int firstColumn, bool transTypes) method.
using System.Data;
DataTable dt = new DataTable();
dt.Columns.Add("ID", typeof(int));
dt.Columns.Add("Product", typeof(string));
dt.Columns.Add("Price", typeof(double));
// Add rows
dt.Rows.Add(1, "Laptop", 1200.5);
dt.Rows.Add(2, "Tablet", 450.99);
dt.Rows.Add(3, "Phone", 799.0);
// Insert DataTable starting at cell A1
sheet.InsertDataTable(dt, true, 1, 1, true);
Output:
On the contrary, you can export data from Excel to DataTable by using the ExportDataTable method of the Worksheet class.
Write Lists to Excel
While Spire.XLS does not provide a direct method for writing lists to Excel, you can convert lists to a DataTable and then use the InsertDataTable method to write the DataTable to Excel.
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Data;
namespace WriteListToExcel
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Remove default worksheets
workbook.Worksheets.Clear();
// Add a worksheet and name it
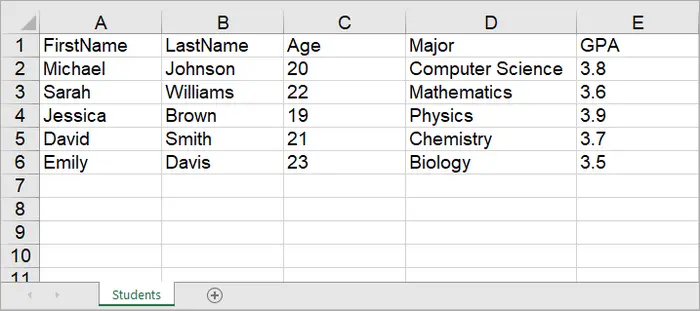
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("Students");
// Create a list with student data
List<Student> students = new List<Student>
{
new Student("Michael", "Johnson", 20, "Computer Science", 3.8),
new Student("Sarah", "Williams", 22, "Mathematics", 3.6),
new Student("Jessica", "Brown", 19, "Physics", 3.9),
new Student("David", "Smith", 21, "Chemistry", 3.7),
new Student("Emily", "Davis", 23, "Biology", 3.5)
};
// Convert the list to DataTable
DataTable dataTable = ConvertListToDataTable(students);
// Write DataTable to the worksheet
worksheet.InsertDataTable(dataTable, true, 1, 1, true);
// Set column width
worksheet.AllocatedRange.ColumnWidth = 12;
// Align content to left
worksheet.AllocatedRange.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left;
// Save to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("InsertStudents.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
// Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose();
}
static DataTable ConvertListToDataTable(List<Student> students)
{
DataTable dataTable = new DataTable();
// Add columns
dataTable.Columns.Add("FirstName", typeof(string));
dataTable.Columns.Add("LastName", typeof(string));
dataTable.Columns.Add("Age", typeof(int));
dataTable.Columns.Add("Major", typeof(string));
dataTable.Columns.Add("GPA", typeof(double));
// Add rows
foreach (var student in students)
{
DataRow row = dataTable.NewRow();
row["FirstName"] = student.FirstName;
row["LastName"] = student.LastName;
row["Age"] = student.Age;
row["Major"] = student.Major;
row["GPA"] = student.GPA;
dataTable.Rows.Add(row);
}
return dataTable;
}
}
class Student
{
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public string Major { get; set; }
public double GPA { get; set; }
public Student(string firstName, string lastName, int age, string major, double gpa)
{
FirstName = firstName;
LastName = lastName;
Age = age;
Major = major;
GPA = gpa;
}
}
}
Output:
Save and Export Excel Files
After writing data, you’ll want to save or export the Excel file. Spire.XLS supports multiple formats including XLSX, CSV, and PDF .
// Save as XLSX
workbook.SaveToFile("Output.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
// Save as CSV
workbook.SaveToFile("Output.csv", ",", Encoding.UTF8);
// Export as PDF
workbook.SaveToFile("Output.pdf", FileFormat.PDF);
For web applications, you can also save to a MemoryStream :
using (MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream())
{
workbook.SaveToStream(ms, FileFormat.Version2016);
// Write to Response in ASP.NET if needed
}
Common Issues and Solutions
1. Incorrect Date or Time Format
Issue: Dates/times appear as serial numbers.
Solution :
- Apply a proper number format to the cell:
sheet.Range["A1"].DateTimeValue = DateTime.Now;
sheet.Range["A1"].NumberFormat = "yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm";
2. Data Overwriting or Misaligned
Issue : Writing arrays or DataTables overwrites existing data unintentionally.
Solution :
- Check firstRow and firstColumn parameters in InsertArray() or InsertDataTable().
- Use separate worksheets or offset ranges if necessary.
3. Large Dataset Performance Issues
Issue : Writing thousands of rows is slow.
Solution :
- Use bulk writing methods instead of looping cell by cell.
- Apply styles after inserting data to avoid repeated formatting overhead.
4. Formula Not Calculating Correctly
Issue : Excel formulas inserted via sheet.Range["A1"].Formula do not return expected results.
Solution :
- Ensure the formula syntax is correct for Excel (e.g., =SUM(A2:A10)).
- Call workbook.CalculateAllValue() to update all formulas before saving if needed.
Conclusion
Writing to Excel in C# doesn’t have to be complex. With Spire.XLS for .NET , you can seamlessly write different data types—whether individual values or large datasets—into Excel worksheets. The library also provides support for styling, formulas, and advanced formatting, ensuring your Excel files are not only accurate but also presentation-ready.
By using efficient bulk-writing techniques like arrays and DataTables, you can handle both small and large data operations with ease. If your goal is to write to Excel files quickly and reliably , Spire.XLS gives you the tools you need—without the overhead of Microsoft Excel.
FAQs
Q1. Can I write to an existing Excel file with Spire.XLS?
Yes. Use workbook.LoadFromFile("file.xlsx") to open an existing file, then modify and save it.
Q2. Does Spire.XLS require Microsoft Excel to be installed?
No. It’s a standalone library that works without Excel.
Q3. Can Spire.XLS handle large Excel files with thousands of rows?
Yes. It’s optimized for high performance with large datasets.
Q4. How do I format cells while writing data?
You can style cells using properties like font, color, borders, and alignment:
sheet.Range["A1"].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
sheet.Range["A1"].Style.Color = Color.Yellow;
sheet.Range["A1"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left;
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.XLS for .NET without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
