
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
We have already demonstrated how to set PDF Document Properties in Java. This article we will show you how to set custom properties for PDF files in Java.
import com.spire.pdf.*;
public class PDFCustomProperties {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String inputPath = "Sample.pdf";
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument(inputPath);
doc.loadFromFile(inputPath);
//Set the custom properties
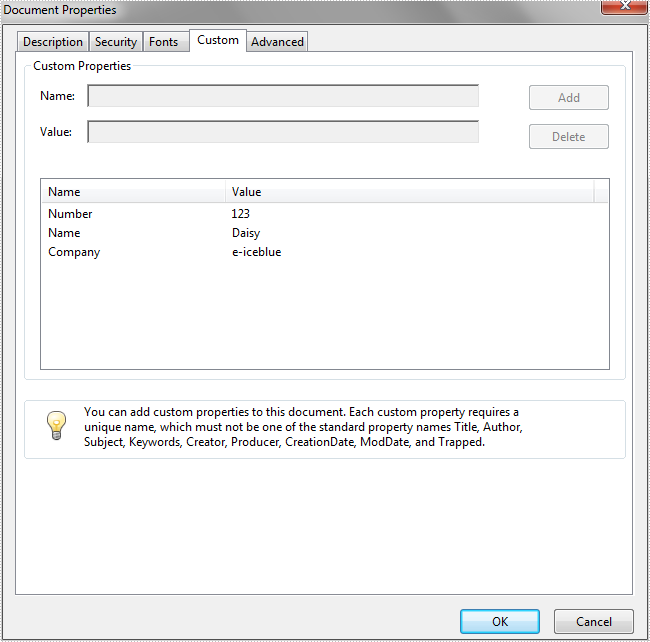
doc.getDocumentInformation().setCustomProperty("Number", "123");
doc.getDocumentInformation().setCustomProperty("Name", "Daisy");
doc.getDocumentInformation().setCustomProperty("Company", "e-iceblue");"
//Save the document to file
doc.saveToFile("Output/result.pdf");
doc.close();
}
}
Effective screenshot after adding custom properties to PDF document:
Java: Create Bulleted or Numbered Lists from Existing Text in Word Documents
2022-07-18 08:26:00 Written by KoohjiA bulleted list is a list with dots in the front and the same indentation for each item, while a numbered list with numbers in the front. Bulleted lists and numbered lists work much better than lengthy text content because, with a well-organized list, readers can easily get the structure and the point of each item. This article shows how to create lists from existing text in Word documents with Spire.Doc for Java.
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>14.1.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Create a Bulleted List and a Numbered List from Existing Text in a Word Document
Spire.Doc for Java provides two methods, ListFormat.applyBulletStyle() and ListFormat.applyNumberedStyle(), to create bulleted and numbered lists.
The detailed steps of creating bulleted and numbered lists are as follows.
- Create an object of Document class.
- Load a Word document from file using Document.loadFromFile() method.
- Get the first section using Document.getSections().get() method.
- Loop through the 4th to 6th paragraphs.
- Apply bulleted list style to these paragraphs using ListFormat.applyBulletStyle() method and set their position using ListFormat.getCurrentListLevel().setNumberPosition() method.
- Loop through the 10th to 12th paragraphs.
- Apply numbered list style to these paragraphs using ListFormat.applyNumberedStyle() method and set their position using ListFormat.getCurrentListLevel().setNumberPosition() method.
- Save the document using Document.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
import com.spire.doc.Section;
import com.spire.doc.documents.Paragraph;
import com.spire.doc.formatting.ListFormat;
public class CreateLists {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create an object of Document class
Document document = new Document();
//Load a Word document from file
document.loadFromFile("C:/Samples/Sample2.docx");
//Get the first section
Section section = document.getSections().get(0);
//Loop through the 4th to the 6th paragraphs
for(int i = 3; i <= 5; i++){
Paragraph para = section.getParagraphs().get(i);
ListFormat listFormat = para.getListFormat();
//Apply bulleted list style
listFormat.applyBulletStyle();
//Set list position
listFormat.getCurrentListLevel().setNumberPosition(-10);
}
//Loop through the 10th to the 12th paragraphs
for(int i = 9; i <= 11; i++){
Paragraph para = section.getParagraphs().get(i);
ListFormat listFormat = para.getListFormat();
//Apply numbered list style
listFormat.applyNumberedStyle();
//Set list position
listFormat.getCurrentListLevel().setNumberPosition(-10);
}
//Save the document
document.saveToFile("CreateLists.docx", FileFormat.Docx_2013);
}
}

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.

Digital signatures play a crucial role in ensuring the authenticity and integrity of PDF documents. Whether you need to sign contracts, legal documents, or financial reports, adding a digital signature helps verify the signer's identity and prevents unauthorized modifications.
In this tutorial, we will explore how to add invisible and visible digital signatures to PDFs using Spire.PDF for Java. We will also cover how to create a signature field for later signing.
- Java Library to Digitally Sign PDF Documents
- Adding an Invisible Digital Signature to a PDF
- Adding a Visible Digital Signature to a PDF
- Creating a Signature Field in a PDF
- Wrap Up
- FAQs
Java Library to Digitally Sign PDF Documents
To work with digital signatures in PDFs, we will use Spire.PDF for Java, a powerful library that allows developers to create, edit, and sign PDF documents programmatically.
Key Features
- Supports PFX certificates for digital signing.
- Allows invisible and visible signatures .
- Enables customization of signature appearance (image, text, details).
- Works with existing PDF forms or creates new signature fields.
Prerequisites
Before you start, ensure you have:
- Java Development Kit (JDK) installed.
- Spire.PDF for Java added to your project.
- A PFX certificate (for signing) and a sample PDF file.
Installation
Download Spire.PDF for Java from our website, and manually import the JAR file into your Java project. If you’re using Maven, add the following code to your project's pom.xml.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.pdf</artifactId>
<version>11.7.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Adding an Invisible Digital Signature to a PDF
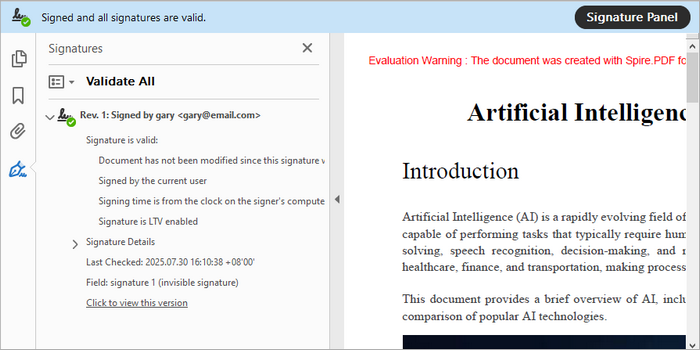
An invisible digital signature embeds cryptographic authentication without displaying a visual element. This is useful for internal verification while keeping the document clean. Below are the steps to add an invisible signature to a PDF using Spire.PDF.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Initialize a PdfDocument object.
- Load the PDF file that you want to sign.
- Use PdfCertificate to load the PFX certificate with password.
- Initialize a PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker object to manage the signing process.
- Use the makeSignature method to embed the signature without visual elements.
- Save the signed PDF to a new file.
Code Example
import com.spire.pdf.PdfDocument;
import com.spire.pdf.interactive.digitalsignatures.PdfCertificate;
import com.spire.pdf.interactive.digitalsignatures.PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker;
public class AddInvisibleSignature {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new PDF document object
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
// Load the input PDF file that needs to be signed
doc.loadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Input.pdf");
// Specify the path to the PFX certificate and its password
String filePath = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/certificate.pfx";
String password = "e-iceblue";
// Load the digital certificate (PFX format) with the given password
PdfCertificate certificate = new PdfCertificate(filePath, password);
// Create a signature maker object to apply the digital signature
PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker signatureMaker = new PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker(doc, certificate);
// Apply an invisible digital signature with the name "signature 1"
signatureMaker.makeSignature("signature 1");
// Save the signed PDF to a new file
doc.saveToFile("Signed.pdf");
// Release resources
doc.dispose();
}
}
Output:
You might also be interested in: How to Verify Signatures in PDF in Java
Adding a Visible Digital Signature to a PDF
A visible digital signature displays signer details (name, reason, image) at a specified location. This is ideal for contracts where visual confirmation is needed. Here’s how to add a visible signature using Spire.PDF.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Create a PdfDocument object and load your target PDF file.
- Load the PFX certificate by initializing the PdfCertificate object.
- Create a PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker instance.
- Define the signer’s name, contact info, and reason for signing.
- Design signature appearance by adding an image, labels, and setting the layout (SignImageAndSignDetail mode).
- Use the makeSignature method to place the signature at the desired coordinates on the PDF.
- Save the signed PDF to a new file.
import com.spire.pdf.PdfDocument;
import com.spire.pdf.PdfPageBase;
import com.spire.pdf.graphics.PdfImage;
import com.spire.pdf.interactive.digitalsignatures.*;
public class AddVisibleSignature {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new PDF document object
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
// Load the input PDF file that needs to be signed
doc.loadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Input.pdf");
// Specify the path to the PFX certificate and its password
String filePath = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/certificate.pfx";
String password = "e-iceblue";
// Load the digital certificate (PFX format) with the given password
PdfCertificate certificate = new PdfCertificate(filePath, password);
// Create a signature maker object to apply the digital signature
PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker signatureMaker = new PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker(doc, certificate);
// Get the pdf signature and set the sign details
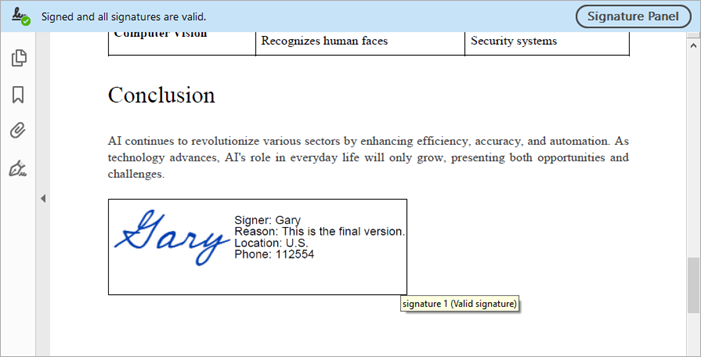
PdfSignature signature = signatureMaker.getSignature();
signature.setName("Gary");
signature.setContactInfo("112554");
signature.setLocation("U.S.");
signature.setReason("This is the final version.");
// Create a signature appearance
PdfSignatureAppearance appearance = new PdfSignatureAppearance(signature);
// Set labels for the signature
appearance.setNameLabel("Signer: ");
appearance.setContactInfoLabel("Phone: ");
appearance.setLocationLabel("Location: ");
appearance.setReasonLabel("Reason: ");
// Load an image
PdfImage image = PdfImage.fromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/signature.png");
// Set the image as the signature image
appearance.setSignatureImage(image);
// Set the graphic mode as SignImageAndSignDetail
appearance.setGraphicMode(GraphicMode.SignImageAndSignDetail);
// Get the last page
PdfPageBase page = doc.getPages().get(doc.getPages().getCount() - 1);
// Add the signature to a specified location of the page
signatureMaker.makeSignature("signature 1", page, 54.0f, 470.0f, 280.0f, 90.0f, appearance);
// Save the signed PDF to a new file
doc.saveToFile("Signed.pdf");
// Release resources
doc.dispose();
}
}
Output:
Creating a Signature Field in a PDF
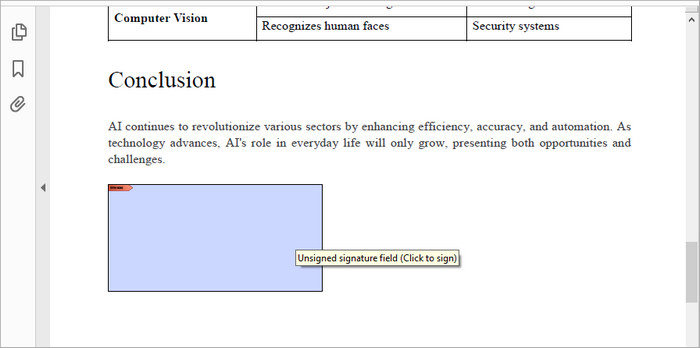
A signature field reserves a space in the PDF for later signing. This is useful for forms or documents that require user signatures. To create a signature field in PDF, follow these steps:
Step-by-Step Guide
- Create a PdfDocument object and load your PDF file.
- Get a specific page (usually last one) where the signature field will be placed.
- Create a PdfSignatureField object for the selected page.
- Customize the field’s appearance by setting border style and color, and field bounds.
- Add the signature field to the document's form.
- Save the updated document to a new PDF file.
Code Example
import com.spire.pdf.PdfDocument;
import com.spire.pdf.fields.PdfBorderStyle;
import com.spire.pdf.fields.PdfHighlightMode;
import com.spire.pdf.fields.PdfSignatureField;
import com.spire.pdf.graphics.PdfRGBColor;
import com.spire.pdf.PdfPageBase;
import java.awt.Rectangle;
public class AddDigitalSignatureField {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Initialize a new PdfDocument object
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
// Load the existing PDF from the specified path
doc.loadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Input.pdf");
// Retrieve the last page of the document
PdfPageBase page = doc.getPages().get(doc.getPages().getCount() - 1);
// Create a signature field on the specified page
PdfSignatureField signatureField = new PdfSignatureField(page, "signature");
// Customize the appearance of the signature field
signatureField.setBorderWidth(1.0f);
signatureField.setBorderStyle(PdfBorderStyle.Solid);
signatureField.setBorderColor(new PdfRGBColor(java.awt.Color.BLACK));
signatureField.setHighlightMode(PdfHighlightMode.Outline);
signatureField.setBounds(new Rectangle(54, 470, 200, 100));
// Enable form creation if none exists in the document
doc.setAllowCreateForm(doc.getForm() == null);
// Add the signature field to the document's form
doc.getForm().getFields().add(signatureField);
// Save the modified document to a new file
doc.saveToFile("SignatureField.pdf");
// Release resources
doc.dispose();
}
}
Output:
Wrap Up
In this tutorial, we explored how to add digital signatures to PDF documents in Java using the Spire.PDF library. We covered the steps for adding both invisible and visible signatures, as well as creating interactive signature fields. With these skills, you can enhance document security and ensure the integrity of your digital communications.
FAQs
Q1. What is a digital signature?
A digital signature is an electronic signature that uses cryptographic techniques to provide proof of the authenticity and integrity of a digital message or document.
Q2. Do I need a special certificate for signing PDFs?
Yes, a valid digital certificate (usually in PFX format) is required to sign PDF documents digitally.
Q3. How do I verify a signed PDF?
You can verify a signed PDF using Adobe Reader or by using Spire.PDF’s PdfSignature.verifySignature() method.
Q4. How can I customize the appearance of my visible digital signature?
With Spire.PDF for Java, you can fully customize visible signatures by:
- Setting text properties (font, color, labels for signer info).
- Adding a signature image (e.g., company logo or scanned handwritten signature).
- Choosing layout modes (SignImageOnly, SignDetail, or SignImageAndSignDetail).
- Adjusting position and dimensions on the page.
Q5. Can I add a timestamp when digitally signing a PDF document?
Yes, you can. Refer to the code:
PdfPKCS7Formatter formatter = new PdfPKCS7Formatter(certificate, false);
formatter.setTimestampService(new TSAHttpService("http://tsa.cesnet.cz:3161/tsa"));
PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker signatureMaker = new PdfOrdinarySignatureMaker(doc, formatter);
signatureMaker.makeSignature("signature 1");
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.PDF for Java without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
