
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Charts and shapes in Excel are vital tools for clear and effective data presentation. Sometimes, it's beneficial to convert these visual elements into images. Perhaps you need to include a specific chart in a report or presentation outside of Excel. Or maybe you want to use an Excel-created infographic on your company's website. Regardless of the use case, knowing how to export these visuals as standalone image files can be invaluable. In this guide, we will explore how to convert charts and shapes in Excel to images in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Convert a Specific Chart in an Excel Worksheet to Image in Python
- Convert All Charts in an Excel Worksheet to Images in Python
- Convert a Chart Sheet in Excel to Image in Python
- Convert Shapes in Excel to Images in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Convert a Specific Chart in an Excel Worksheet to Image in Python
Spire.XLS for Python offers the Workbook.SaveChartAsImage(worksheet: Worksheet, chartIndex: int) method, allowing you to convert a specific chart within a worksheet into an image stream. This image stream can then be saved as an image file in various formats, including PNG, JPG, BMP, and more. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet in the file using the Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Save a specific chart in the worksheet to an image stream using the Workbook.SaveChartAsImage(worksheet: Worksheet, chartIndex: int) method.
- Save the image stream to an image file using the Stream.Save() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Charts.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Save the first chart in the worksheet to an image stream
image_stream = workbook.SaveChartAsImage(sheet, 0)
# Save the image stream to a PNG image file
image_stream.Save("Output/chart.png")
workbook.Dispose()
Convert All Charts in an Excel Worksheet to Images in Python
To convert all charts in an Excel worksheet to images, you can use the Workbook.SaveChartAsImage(worksheet: Worksheet) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet in the file using the Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Save all charts in the worksheet to a list of image streams using the Workbook.SaveChartAsImage(worksheet: Worksheet) method.
- Iterate through the image streams in the list and save them to separate image files.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Charts.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
image_streams = []
# Save the charts in the worksheet to a list of image streams
image_streams = workbook.SaveChartAsImage(sheet)
# Save the image streams to PNG image files
for i, image_stream in enumerate(image_streams):
image_stream.Save(f"Output/chart-{i}.png")
workbook.Dispose()
Convert a Chart Sheet in Excel to Image in Python
In Microsoft Excel, a chart sheet is a special type of sheet that is dedicated to displaying a single chart or graph. You can convert a chart sheet in an Excel workbook to an image using the Workbook.SaveChartAsImage(chartSheet: ChartSheet) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific chart sheet in the file using the Workbook.Chartsheets[] property.
- Save the chart sheet to an image stream using the Workbook.SaveChartAsImage(chartSheet: ChartSheet) method.
- Save the image stream to an image file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("ChartSheet.xlsx")
# Get the first chart sheet
chart_sheet = workbook.Chartsheets[0]
# Save the chart sheet to an image stream
image_stream = workbook.SaveChartAsImage(chart_sheet)
# Save the image stream to a PNG image file
image_stream.Save("Output/chartSheet.png")
workbook.Dispose()
Convert Shapes in Excel to Images in Python
In addition to converting charts or chart sheets to images, you can also convert shapes in an Excel worksheet to images by using the XlsShape.SaveToImage() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet in the file using the Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Iterate through all the shapes in the worksheet.
- Typecast the shape to an XlsShape object.
- Save the shape to an image stream using the XlsShape.SaveToImage() method.
- Save the image stream to an image file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Shapes.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Iterate through all the shapes in the worksheet
for i, shape in enumerate(sheet.PrstGeomShapes):
xls_shape = XlsShape(shape)
# Save the shape to an image stream
image_stream = shape.SaveToImage()
# Save the image stream to a PNG image file
image_stream.Save(f"Output/shape_{i}.png")
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Create and Execute Conditional Mail Merges in Word Documents
2024-08-09 00:54:29 Written by KoohjiConditional mail merge in Word documents is a powerful method for personalized communication at scale. Unlike other mail merges that apply the same template to all recipients, conditional mail merge allows users to customize content based on specific criteria or conditions, ensuring that each recipient receives information that is directly relevant to them. By leveraging Python, users can automate the creation and execution of conditional mail merges.
This article will show how to create and execute conditional mail merges in Word documents through Python code using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Create Conditional Mail Merge in a Word Document with Python
- Execute Conditional Mail Merge in a Word Document with Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Create Conditional Mail Merge in a Word Document with Python
A conditional mail merge uses an If field containing a mail merge field, which alters the merge results based on the data. To add a conditional mail merge to a Word document, insert an If field, then include a mail merge field within the If field’s code, and finish by adding the field end mark to complete the setup. The condition is controlled by the code within the If field.
The detailed steps for adding a conditional mail merge to a Word document are as follows:
- Create an instance of the Document class to generate a Word document.
- Add a section to the document and configure the page setup.
- Create paragraph styles, add paragraphs, and set their formats.
- Create an IfField object, set its starting code through the IfField.Code property, and insert it into a paragraph using the Paragraph.Items.Add() method.
- Append a mail merge field to the paragraph using the Paragraph.AppendField() method.
- Append the remaining code to the paragraph using the Paragraph.AppendText() method.
- Append a field end mark to end the If field using the Paragraph.AppendFieldMark() method.
- Set the end mark as the end mark of the If field through the IfField.End property.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
# Create an instance of Document
doc = Document()
# Add a section to the document
section = doc.AddSection()
# Set the page size and margins
section.PageSetup.PageSize = PageSize.A4()
section.PageSetup.Margins.All = 50
# Create a paragraph style
style = ParagraphStyle(doc)
style.Name = "Style1"
style.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
style.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 14
style.ParagraphFormat.BeforeSpacing = 5
style.ParagraphFormat.AfterSpacing = 10
doc.Styles.Add(style)
# Add paragraphs and set the style
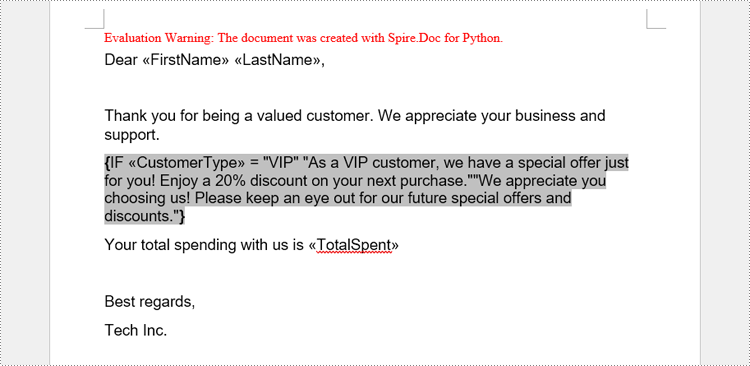
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Dear ")
paragraph.AppendField("FirstName", FieldType.FieldMergeField)
paragraph.AppendText(" ")
paragraph.AppendField("LastName", FieldType.FieldMergeField)
paragraph.AppendText(",")
paragraph.ApplyStyle(style.Name)
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("\r\nThank you for being a valued customer. We appreciate your business and support.")
paragraph.ApplyStyle(style.Name)
# Add an If field to a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
ifField = IfField(doc)
ifField.Type = FieldType.FieldIf
ifField.Code = "IF "
paragraph.Items.Add(ifField)
# Add a mail merge field in the code of the If field
paragraph.AppendField("CustomerType", FieldType.FieldMergeField)
paragraph.AppendText(" = ")
paragraph.AppendText("\"VIP\"")
paragraph.AppendText(" \"As a VIP customer, we have a special offer just for you! Enjoy a 20% discount on your next "
"purchase.\"")
paragraph.AppendText("\"We appreciate you choosing us! Please keep an eye out for our future special offers and "
"discounts.\"")
# Add a field end mark at the end to end the If field
endIf = paragraph.AppendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.FieldEnd)
ifField.End = endIf
paragraph.ApplyStyle(style.Name)
# Add paragraphs and set the style
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Your total spending with us is ")
paragraph.AppendField("TotalSpent", FieldType.FieldMergeField)
paragraph.ApplyStyle(style.Name)
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("\r\nBest regards,\r\nTech Inc.")
paragraph.ApplyStyle(style.Name)
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/ConditionalMailMerge.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
Execute Conditional Mail Merge in a Word Document with Python
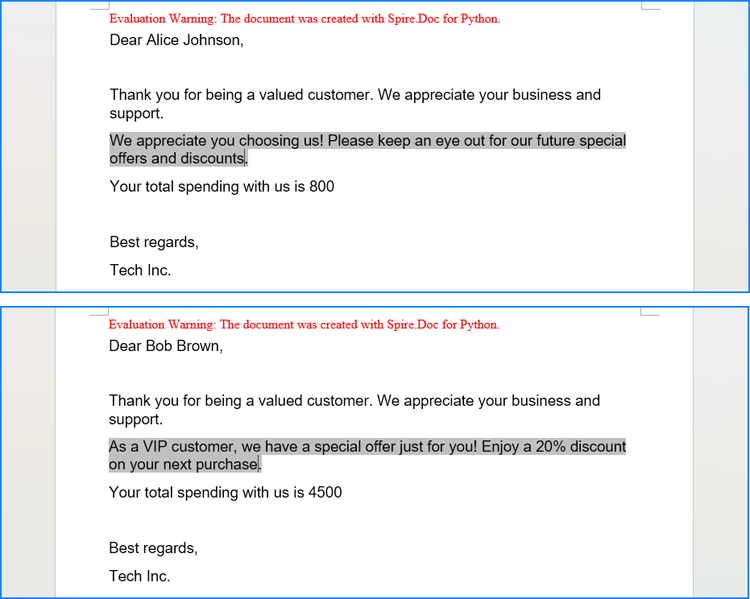
The Document.MailMerge.Execute(fieldNames: list[str], fieldValues: list[str]) method provided by Spire.Doc for Python allows for mail merge operations within Word documents. After the merge, you can update the results of conditional mail merges by setting the Document.IsUpdateFields property to True. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Read the data in the table used for the merge as a two-dimensional list.
- Iterate through the data rows, skipping the header:
- Create an instance of the Document class and load the Word document to be merged.
- Get the names of the mail merge fields as a list using the Document.MailMerge.GetMergeFieldNames() method.
- Execute the mail merge with the data using the Document.MailMerge.Execute() method.
- Update the If field by setting the Document.IsUpdateFields property to True.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
import csv
# Read the data from a CSV file
data = []
with open("Customers.csv", "r") as csvfile:
read = csv.reader(csvfile)
for row in read:
data.append(row)
# Iterate through the data rows by skipping the header
for i in range(1, len(data)):
# Create an instance of Document and load a Word document
doc = Document("output/ConditionalMailMerge.docx")
# Get the field names from the document
fieldNames = doc.MailMerge.GetMergeFieldNames()
# Execute the mail merge
doc.MailMerge.Execute(fieldNames, data[i])
# Update the If field
doc.IsUpdateFields = True
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile(f"output/Customers/{data[i][0]} {data[i][1]}.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Managing PDF documents often involves removing annotations. Whether you're preparing documents for a presentation, sharing the final files with clients when questions are settled down, or archiving important records, deleting annotations can be essential.
Spire.PDF for Python allows users to delete annotations from PDFs in Python efficiently. Follow the instructions below to clean up your PDF files seamlessly.
- Delete Specified Annotations
- Delete All Annotations from a Page
- Delete All Annotations from the PDF Document
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install it, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows.
Delete Specified Annotations from PDF in Python
To delete a specified annotation from PDF documents, you need to target the annotation to be removed at first. Then you can remove it by calling the Page.AnnotationsWidget.RemoveAt() method offered by Spire.PDF for Python. This section will guide you through the whole process step by step.
Steps to remove an annotation from a page:
- Create a new PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document from files using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the specific page of the PDF with PdfDocument.Pages.get_Item() method.
- Delete the annotation from the page by calling Page.AnnotationsWidget.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the resulting document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
Here's the code example for you to refer to:
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a new PDF document
doc = PdfDocument()
# Open the PDF document to be modified from the disk
doc.LoadFromFile("sample1.pdf")
# Get the first page of the document
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Remove the 2nd annotation from the page
page.AnnotationsWidget.RemoveAt(1)
# Save the PDF document
doc.SaveToFile("output/delete_2nd_annotation.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Close()
Delete All Annotations from a PDF Page in Python
The Pages.AnnotationsWidget.Clear() method provided by Spire.PDF for Python helps you to complete the task of removing each annotation from a page. This part will demonstrate how to delete all annotations from a page in Python with a detailed guide and a code example.
Steps to delete all annotations from a page:
- Create an instance of the PdfDocument class.
- Read the PDF document from the disk by PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove annotations on the page using Pages.AnnotationsWidget.Clear() method.
- Write the document to disk with PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
Below is the code example of deleting annotations from the first page:
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a new PDF document
document = PdfDocument()
# Load the file from the disk
document.LoadFromFile("sample1.pdf")
# Remove all annotations from the first page
document.Pages[0].AnnotationsWidget.Clear()
# Save the document
document.SaveToFile("output/delete_annotations_page.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
document.Close()
Delete All Annotations of PDF Documents in Python
Removing all annotations from a PDF document involves retrieving the annotations first, which means you need to loop through each page to ensure that every annotation is deleted. The section will introduce how to accomplish the task in Python, providing detailed steps and an example to assist in cleaning up PDF documents.
Steps to remove all annotations of the whole PDF document:
- Instantiate a PdfDocument object.
- Open the document from files using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Loop through pages of the PDF document.
- Get each page of the PDF document with PdfDocument.Pages.get_Item() method.
- Remove all annotations from each page using Page.AnnotationsWidget.Clear() method.
- Save the document to your local file with PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
Here is the example for reference:
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create an object of PDF class
document = PdfDocument()
# Load the file to be operated from the disk
document.LoadFromFile("sample1.pdf")
# Loop through all pages in the PDF document
for i in range(document.Pages.Count):
# Get a specific page
page = document.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Remove all annotations from the page
page.AnnotationsWidget.Clear()
# Save the resulting document
document.SaveToFile("output/delete_all_annotations.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
document.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
