
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
In Microsoft Word, adding, adjusting, and removing page borders is an effective strategy to enhance the aesthetics and professionalism of your documents. The inclusion of borders can lend a page a more refined and dignified appearance, particularly suitable for formal contexts such as reports, certificates, or invitations, conveying a sense of meticulous elegance. By customizing the color, pattern, and thickness of borders, users can ingeniously integrate personal creativity according to the document theme, crafting a unique design style that makes the content more captivating. Conversely, opting to remove borders can achieve a streamlined page layout, effectively eliminating unnecessary visual clutter—a practice especially fitting for those pursuing minimalist aesthetics or aiming to save on printing costs. This article will introduce how to add, modify, or remove Word page borders in Python projects using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your VS Code through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
Python Add Word Page Borders
When setting page borders in a Word document using the Spire.Doc library, you can achieve this by invoking the Section.PageSetup.Borders property. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Use a for loop to iterate through each section (Section) in the document.
- Apply borders to all pages by setting the Section.PageSetup.PageBordersApplyType property to PageBordersApplyType.AllPages.
- Set the page border style using the Secton.PageSetup.Borders.BorderType(BorderStyle.DashDotStroker) method.
- Define the border width using the Section.PageSetup.Borders.LineWidth(2) method.
- Set the border color using the Section.PageSetup.Borders.Color(Color.get_Orange()) method.
- Set the distance between the border and the page content using the Section.PageSetup.Borders.Top.Space, Bottom.Space, Left.Space, and Right.Space properties.
- Save the changes to a Word document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load an existing Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample01.docx")
# Iterate through all sections in the document
for i in range(doc.Sections.Count):
# Set borders for all pages in the current section
doc.Sections.get_Item(i).PageSetup.PageBordersApplyType = PageBordersApplyType.AllPages
# Set border style
doc.Sections.get_Item(i).PageSetup.Borders.BorderType(BorderStyle.DashDotStroker)
# Set border width
doc.Sections.get_Item(i).PageSetup.Borders.LineWidth(2)
# Set border color
doc.Sections.get_Item(i).PageSetup.Borders.Color(Color.get_Orange())
# Set the distance between the top border and page content
doc.Sections.get_Item(i).PageSetup.Borders.Top.Space = 20.0
# Set the distance between the bottom border and page content
doc.Sections.get_Item(i).PageSetup.Borders.Bottom.Space = 20.0
# Set the distance between the left border and page content
doc.Sections.get_Item(i).PageSetup.Borders.Left.Space = 20.0
# Set the distance between the right border and page content
doc.Sections.get_Item(i).PageSetup.Borders.Right.Space = 20.0
# Save the modified document to a new file
doc.SaveToFile("AddWordPageBorders.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
# Release resources used by the Document object
doc.Dispose()

Python Modify Word Page Borders
Leveraging the Spire.Doc library, we can extensively customize the page borders in Word documents, including the style, hue, width, and other visual attributes of the borders. By tweaking these properties, achieving the desired visual presentation becomes effortless. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Retrieve the first section of the document using Document.Sections.get_Item(0).
- Alter the page border style using the Section.PageSetup.Borders.BorderType(BorderStyle.DoubleWave) method.
- Change the color of the page border with the Section.PageSetup.Borders.Color(Color.get_Orange()) method.
- Adjust the width of the page border through the Section.PageSetup.Borders.LineWidth(2) method.
- Save the changes to a Word document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load an existing Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample02.docx")
# Get the first section
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Set border style
section.PageSetup.Borders.BorderType(BorderStyle.DoubleWave)
# Set border color
section.PageSetup.Borders.Color(Color.get_Orange())
# Set border width
section.PageSetup.Borders.LineWidth(2)
# Save the modified document to a new file
doc.SaveToFile("ModifyWordPageBorders.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
# Release resources occupied by the Document object
doc.Dispose()

Python Remove Word Page Borders
To remove page borders in Word, you can use the Section.PageSetup.Borders.BorderType(BorderStyle.none) method. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Use a for loop to iterate through each section (Section) in the document.
- Apply the Section.PageSetup.Borders.BorderType(BorderStyle.none) method to remove the page borders.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load an existing Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample02.docx")
# Iterate through all sections in the document
for i in range(doc.Sections.Count):
# Remove page borders
doc.Sections.get_Item(i).PageSetup.Borders.BorderType(BorderStyle.none)
# Save the modified document to a new file
doc.SaveToFile("RemoveWordPageBorders.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
# Release the resources occupied by the Document object
doc.Dispose()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Charts are an essential tool for visualizing data stored in Excel spreadsheets. Creating charts from your spreadsheet data can reveal trends, patterns, and insights that might be missed in a simple table of numbers. With Spire.Cloud.Excel, an online spreadsheet editor, you can easily convert your Excel data to various types of charts. This guide will walk you through the process of how to convert Excel data with charts online using Spire.Cloud.Excel.
- Spire.Cloud.Excel Spreadsheet Editor
- Chart Types Supported by Spire.Cloud.Excel Spreadsheet Editor
- Convert Excel Data to Charts Online
Spire.Cloud.Excel Spreadsheet Editor
Spire.Cloud.Excel is one of the key components of the Spire.Cloud.Office online suite. This robust online spreadsheet editor empowers users to create, view, edit, convert and collaborate on Excel-compatible spreadsheets directly in their web browsers. It offers a wide range of features, including data analysis tools, formula support, chart creation, and formatting options. With a variety of chart types and customization options, Spire.Cloud.Excel makes data visualization straightforward and effective.
To utilize the services offered by Spire.Cloud.Excel, you first need to install Spire.Cloud.Office on your system:
- Install Spire.Cloud.Office for .NET on Windows
- Install Spire.Cloud.Office for Linux on Ubuntu
- Install Spire.Cloud.Office for Linux on CentOS
After the installation is complete, you can integrate Spire.Cloud.Office in your own web application or visit the example application hosted on port 3000 (as shown in the image below) to explore the editor's functionality.

Chart Types Supported by Spire.Cloud.Excel Spreadsheet Editor
Spire.Cloud.Excel Spreadsheet Editor supports a wide range of chart types, allowing you to choose the best visual representation for your data. Here are some of the chart types you can use:
- Column Chart: Ideal for comparing quantities across different categories. Each category is represented by a vertical bar, making it easy to see differences at a glance. This type of chart is perfect for displaying data like sales figures or population statistics.
- Line Chart: Perfect for showing trends over time. Line charts plot data points connected by a straight line, making them great for tracking changes over periods such as months or years. They are commonly used for financial data, such as stock prices or revenue growth.
- Pie Chart: Useful for displaying proportions and percentages. A pie chart divides a circle into slices to illustrate numerical proportions. Each slice represents a category's contribution to the whole, making it easy to compare parts of a whole.
- Bar Chart: Similar to column charts but with horizontal bars. Bar charts are useful for comparing quantities across categories, especially when the category names are long or there are many categories. They are often used for survey data or inventory levels.
- Area Chart: Great for emphasizing the magnitude of change over time. Area charts are similar to line charts, but the area below the line is filled with color, highlighting the volume of change. They are ideal for showing cumulative totals over time, such as total sales or production levels.
- XY (Scatter) Chart: Used for showing the relationship between two variables. Scatter charts plot individual data points on a grid, with one variable on the x-axis and the other on the y-axis. This type of chart is excellent for identifying correlations or trends between two datasets, such as height versus weight.
- Stock Chart: Suitable for financial data, representing stock prices and market trends. Stock charts can display various financial metrics, such as opening, closing, high, and low prices for a particular period. They are essential for investors and analysts who need to track market movements and make informed decisions.
Each chart type comes with customization options to enhance your data visualization further, allowing you to adjust colors, labels, and other elements to create the most informative and visually appealing charts for your needs.
Convert Excel Data to Chart Online
To convert Excel data to charts online using Spire.Cloud.Excel, you can follow the steps below.
1. Open Your Excel File
- First, you need to upload your Excel file by clicking the "Upload File" button on the example page.

- Once the file is uploaded, click the "Edit" button to open it in the Spire.Cloud.Excel Spreadsheet Editor.
2. Select Your Data
To create a chart, you need to select the data that you want to visualize:
- Click and drag to highlight the cells containing the data you want to include in your chart.
- Ensure you include headers in your selection if you want them to appear in the chart's legend.
3. Insert a Chart
With your data selected, follow these steps to insert a chart:
- Go to the "Insert" tab in the toolbar of Spire.Cloud.Excel Spreadsheet Editor.
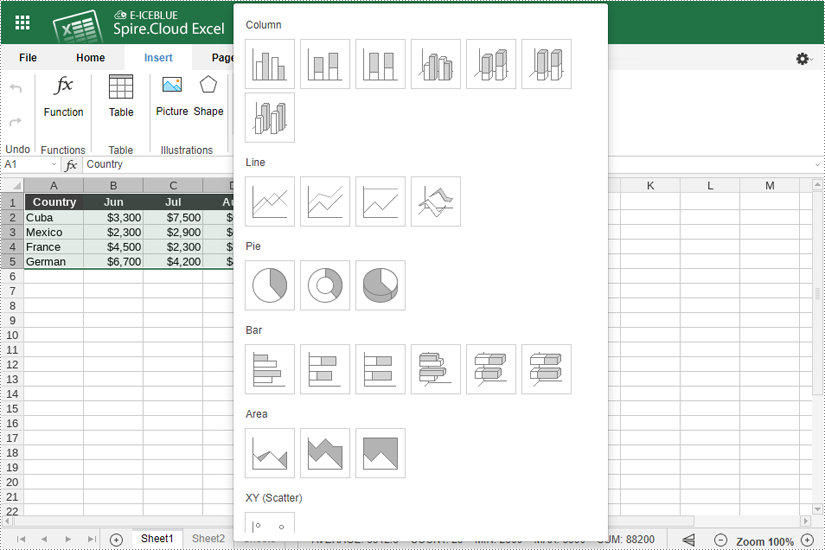
- Click the "Chart" icon. This will open a menu with various chart types. Then Choose the chart type that best represents your data (e.g., bar chart, line chart, pie chart, column chart, XY (scatter chart), area chart).
4. Customize Your Chart
Spire.Cloud.Excel provides numerous options to customize your chart:
- After inserting the chart, click the "Chart Title" to add a title for it.
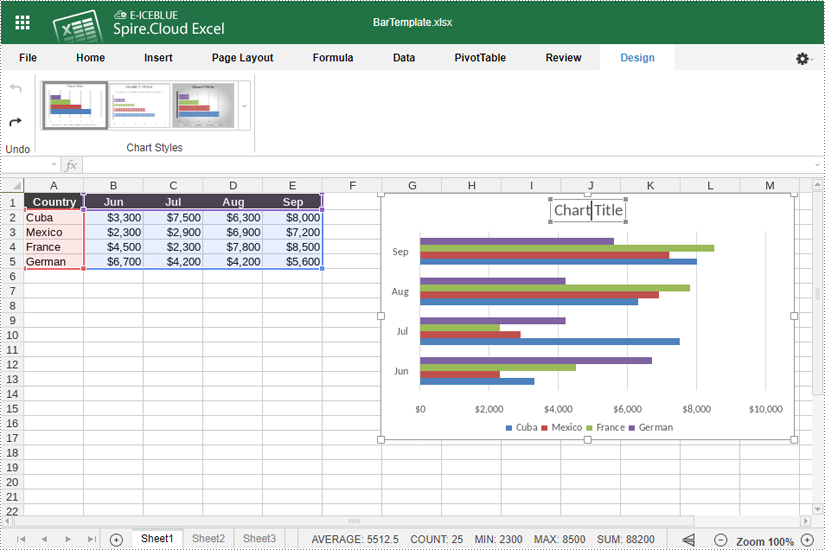
- Right-click the chart and select "Chart Advanced Settings".
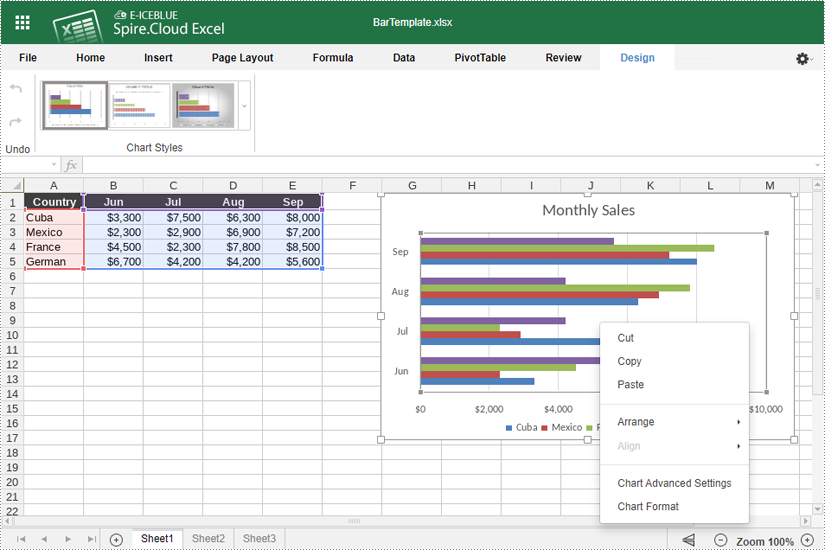
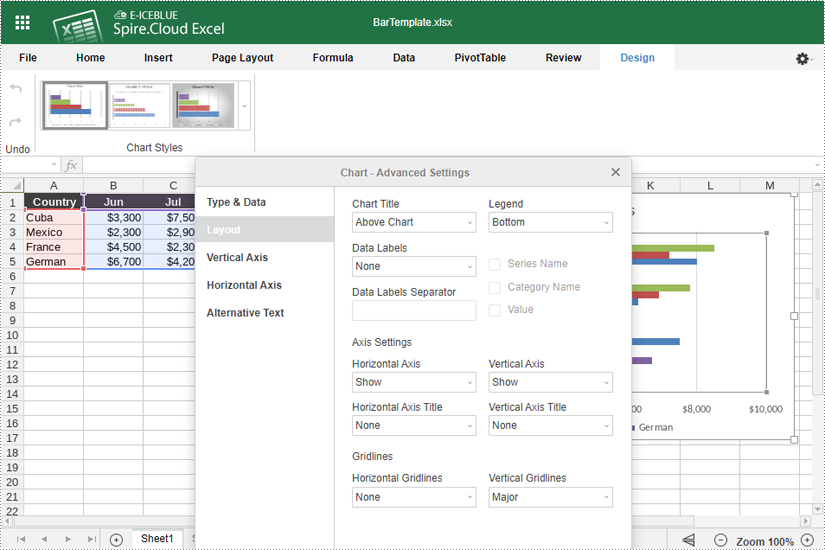
- Use the options available to modify the chart's design, such as changing the chart title and legend position, adding data labels, and adjusting horizontal and vertical axes.
- If you want to change the chart type, right-click the chart and select "Chart Format". Then click "Chart" > "Change Chart Type".
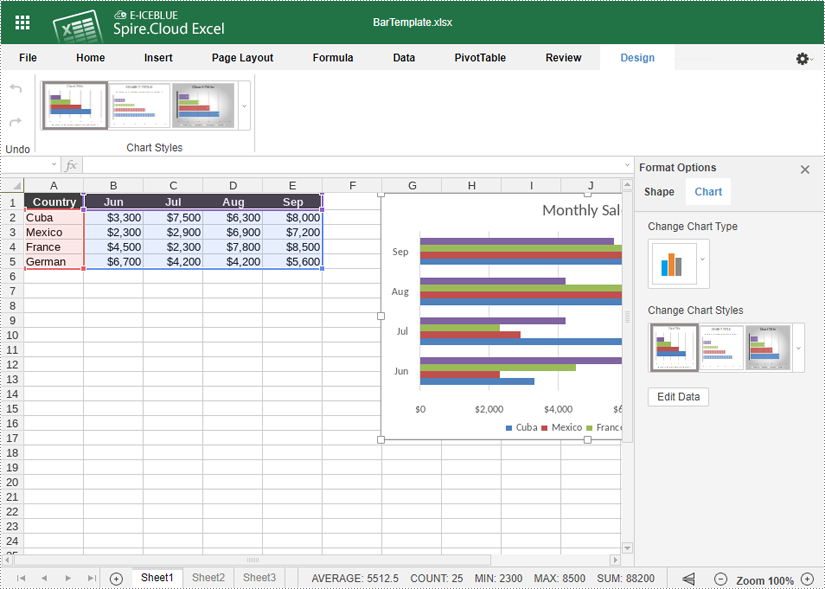
- You can also resize and move the chart within your spreadsheet by clicking and dragging.
5. Save Your Chart
- Once you are satisfied with your chart, you can save your document by pressing "Ctrl + S" or clicking on the "File" menu and selecting "Save" to save your changes.
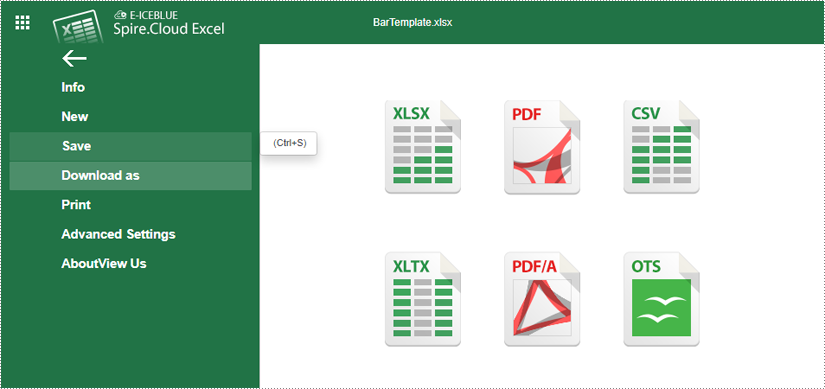
- Your file has been saved and can be accessed on the example page.
Page borders can be a useful design element in Microsoft Word documents. They can help to frame the content and provide a polished, professional. Page borders draw the reader's eye to the main content area and create a sense of structure and cohesion. Conversely, you may want to remove page borders if they are not needed or if they distract from the content.
In this article, you will learn how to add, adjust, and remove page borders in a Word document using Java and Spire.Doc for Java.
- Add Page Borders to a Word Document
- Adjust Page Borders in a Word Document
- Remove Page Borders from a Word Document
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>14.1.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Add Page Borders to a Word Document in Java
Spire.Doc for Java includes the Borders class, which enables developers to manage the page borders in a Word document. This class provides a collection of methods that allow you to control various aspects of the page border, such as the border type, color, and line width.
To add borders to all pages in a Word document using Java, the general steps are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Iterate through the sections in the document.
- Get a specific section.
- Get the PageSetup object of the section.
- Apply borders to all page by passing PageBordersApplyType.All_Pages as the parameter of PageSetup.setPageBordersApplyType() method.
- Get the Borders object using PageSetup.getBorders() method.
- Set the border type, color, line width and other attributes using the methods under the Borders object.
- Save the updated document to a different Word file.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.BorderStyle;
import java.awt.*;
public class AddPageBorder {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load a Word file
doc.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.docx");
// Iterate through the sections in the document
for (int i = 0; i < doc.getSections().getCount(); i++)
{
// Get a specific section
Section section = doc.getSections().get(i);
// Get page setup object
PageSetup pageSetup = section.getPageSetup();
// Apply page border to all pages
pageSetup.setPageBordersApplyType(PageBordersApplyType.All_Pages);
// Set the border type
pageSetup.getBorders().setBorderType(BorderStyle.Dash_Large_Gap);
// Set the border width
pageSetup.getBorders().setLineWidth(2);
// Set the border color
pageSetup.getBorders().setColor(Color.RED);
// Set the spacing between borders and text within them
pageSetup.getBorders().getTop().setSpace(30);
pageSetup.getBorders().getBottom().setSpace(30);
pageSetup.getBorders().getLeft().setSpace(30);
pageSetup.getBorders().getRight().setSpace(30);
}
// Save the updated document to a different file
doc.saveToFile("AddPageBorder.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Dispose resources
doc.dispose();
}
}

Adjust Page Borders in a Word Document in Java
The page borders of an existing Word document can be obtained using the PageSetup.getBorders() method. You can change the appearance of the page borders using the setBorderType(), setColor(), and setLineWidth() methods.
The steps to adjust page borders in a Word document using Java are as follows.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Iterate through the sections in the document.
- Get a specific section.
- Get the PageSetup object of the section.
- Get the Borders object using PageSetup.getBorders() method.
- Set the border type, color, line width and other attributes using the methods under the Borders object.
- Save the updated document to a different Word file.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
import com.spire.doc.PageSetup;
import com.spire.doc.Section;
import com.spire.doc.documents.BorderStyle;
import java.awt.*;
public class AdjustPageBorders {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load a Word file
doc.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Borders.docx");
// Iterate through the sections in the document
for (int i = 0; i < doc.getSections().getCount(); i++)
{
// Get a specific section
Section section = doc.getSections().get(i);
// Get page setup of the section
PageSetup pageSetup = section.getPageSetup();
// Change the border type
section.getPageSetup().getBorders().setBorderType(BorderStyle.Double);
// Change the border color
section.getPageSetup().getBorders().setColor(Color.DARK_GRAY);
// Change the border width
section.getPageSetup().getBorders().setLineWidth(3);
}
// Save the updated document to a different file
doc.saveToFile("AdjustBorder.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Dispose resources
doc.dispose();
}
}

Remove Page Borders from a Word Document in Java
To move page borders from a Word document, pass the BorderStyle.None as the parameter of the Borders.setBorderType() method. By setting the border type as none, you are instructing the document to remove any existing page borders, resulting in a clean, border-free document layout.
The steps to remove page borders from a Word document using Java are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Iterate through the sections in the document.
- Get a specific section.
- Get the PageSetup object of the section.
- Get the Borders object using PageSetup.getBorders() method.
- Set the border type as BorderStyle.None using Borders.setBorderType() method.
- Save the updated document to a different Word file.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
import com.spire.doc.PageSetup;
import com.spire.doc.Section;
import com.spire.doc.documents.BorderStyle;
public class RemovePageBorders {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load a Word file
doc.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Borders.docx");
// Iterate through the sections in the document
for (int i = 0; i < doc.getSections().getCount(); i++)
{
// Get a specific section
Section section = doc.getSections().get(i);
// Get page setup object
PageSetup pageSetup = section.getPageSetup();
// Set the border type to none
pageSetup.getBorders().setBorderType(BorderStyle.None);
}
// Save the updated document to a different file
doc.saveToFile("RemovePageBorders.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Dispose resources
doc.dispose();
}
}

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
