
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Formatting plays a crucial role in making your Excel spreadsheets clean, organized, and visually appealing. Often, you may want to apply the same formatting to multiple cells or ranges in your workbook. Instead of manually formatting each cell individually, Excel provides a convenient feature called "Copy Cell Formatting" that allows you to quickly replicate the formatting from one cell to others.
Here in this article, you will learn how to programmatically copy cell formatting in Excel using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your system through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Copy Formatting from One Cell to Another in Python
You can access a specific cell by using the Worksheet.Range[row:int, column:int] property. The formatting of that cell can be retrieved through the CellRange.Style property, and this formatting can then be applied to a different cell.
The steps to copy formatting from one to cell to anther are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document from a give path.
- Get a specific worksheet within the workbook.
- Get a specific cell through Worksheet.Range[row:int, column:int] property.
- Get the cell formatting through CellRange.Style property, and apply it to another cell through the same property.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
This code example loads an existing Excel document, copies the formatting (style) from the cells in the second column to the cells in the fourth column for rows 2 through 14, and then saves the modified workbook to a new Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Loop through the selected rows
for i in range(2, 15):
# Get style (formatting) of a specific cell
style = worksheet.Range[i, 2].Style
# Apply the style to a different cell
worksheet.Range[i, 4].Style = style
# Save the workbook to file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/CopyFormatting.xlsx",ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
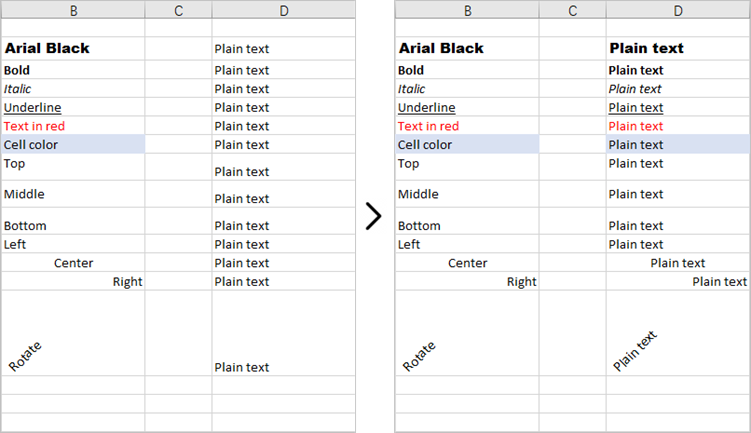
Copy Formatting from One Cell to a Cell Range in Python
Once you get the style (formatting) of a certain cell, you can apply it to a cell rang which is retrieved through the Worksheet.Range[row:int, column:int, endRow:int, endColumn:int] property.
Here are the steps to copy formatting from once cell to a cell range.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document from a give path.
- Get a specific worksheet within the workbook.
- Get a specific cell through Worksheet.Range[row:int, column:int] property.
- Get the formatting of the cell through CellRange.Style property.
- Get a cell range through Worksheet.Range[row:int, column:int, endRow:int, endColumn:int] property.
- Apply the formatting to the cell range through CellRange.Style property.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
This code example loads an existing Excel document, retrieves the style of a cell located in the third row and first column, and then applies that style to a range of cells from the third row, fourth column to the fourth row, sixth column.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get style (formatting) of a specific cell
style = worksheet.Range[3, 1].Style
# Apply the style to a cell range
worksheet.Range[3, 4, 4, 6].Style = style
# Save the workbook to file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/ApplyFormatToCellRange.xlsx",ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
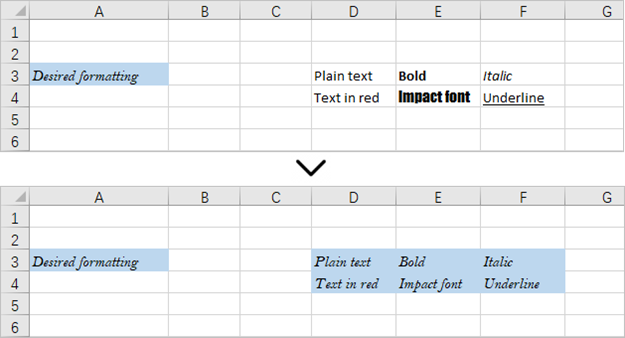
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
C#: Extract Text from Images using the New Model of Spire.OCR for .NET
2024-07-18 01:09:12 Written by AdministratorSpire.OCR for .NET offers developers a new model to extract text from images. In this article, we will demonstrate how to extract text from images in C# using the new model of Spire.OCR for .NET.
The detailed steps are as follows.
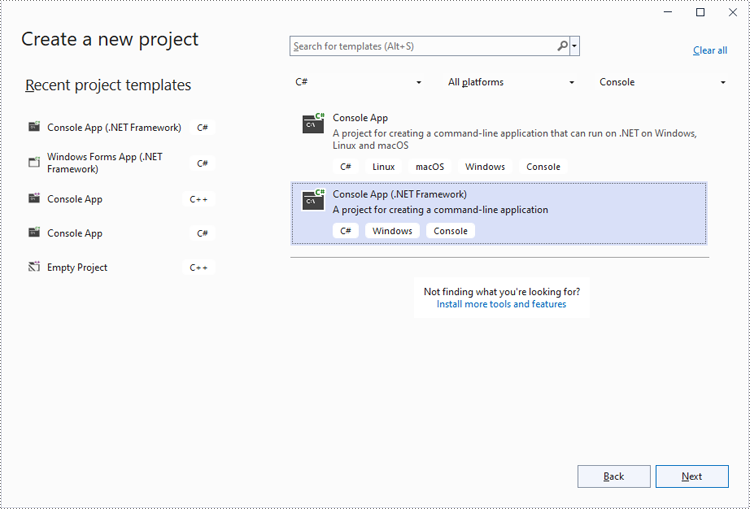
Step 1: Create a Console App (.NET Framework) in Visual Studio.
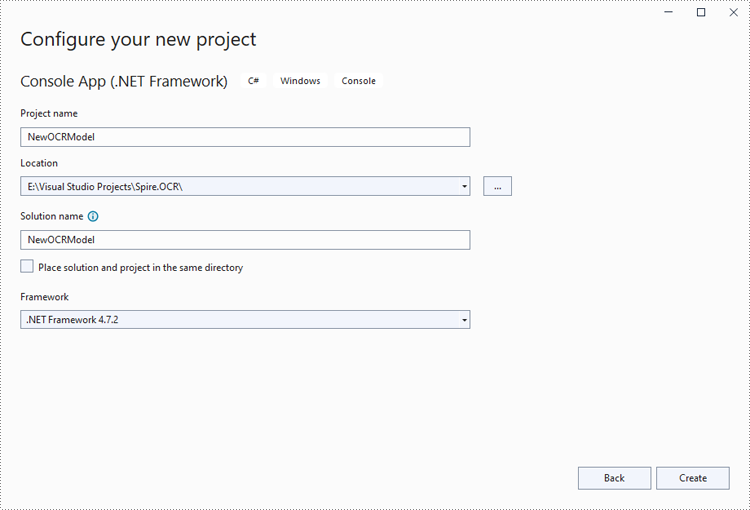
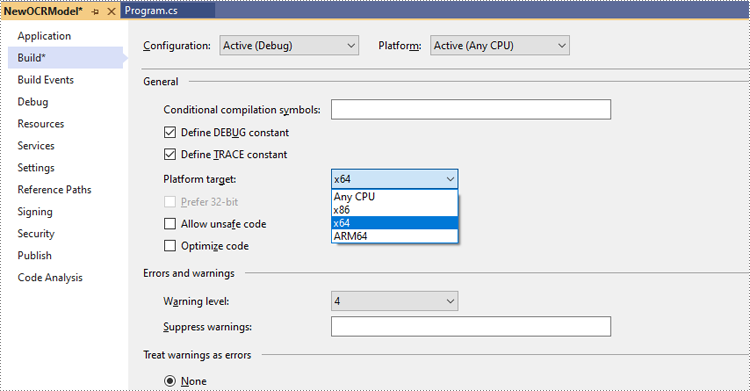
Step 2: Change the platform target of the application to x64.
In the application's Solution Explorer, right-click on the project's name and then select "Properties".
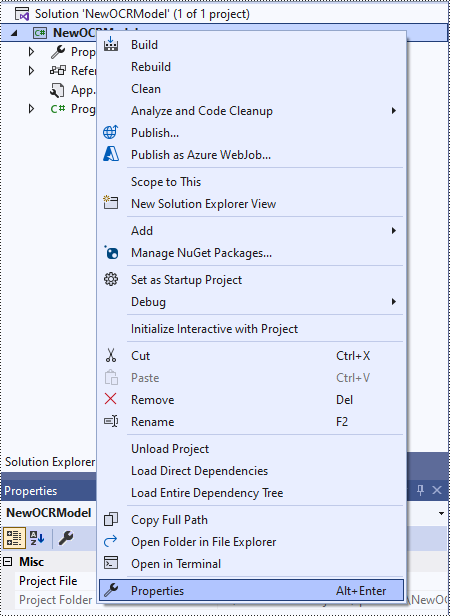
Change the platform target of the application to x64. This step must be performed since Spire.OCR only supports 64-bit platforms.
Step 3: Install Spire.OCR for .NET in your application.
Install Spire.OCR for .NET through NuGet by executing the following command in the NuGet Package Manager Console:
Install-Package Spire.OCR
Step 4: Download the new model of Spire.OCR for .NET.
Download the model that fits in with your operating system from one of the following links.
Then extract the package and save it to a specific directory on your computer. In this example, we saved the package to "D:\".
Step 5: Use the new model of Spire.OCR for .NET to extract text from images in C#.
The following code example shows how to extract text from an image using C# and the new model of Spire.OCR for .NET:
- C#
using Spire.OCR;
using System.IO;
namespace NewOCRModel
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Set license key
// Spire.OCR.License.LicenseProvider.SetLicenseKey("your-license-key");
// Create an instance of the OcrScanner class
OcrScanner scanner = new OcrScanner();
// Create an instance of the ConfigureOptions class to set up the scanner configuration
ConfigureOptions configureOptions = new ConfigureOptions();
// Set the path to the new model
configureOptions.ModelPath = "D:\\win-x64";
// Set the language for text recognition. The default is English.
// Supported languages include English, Chinese, Chinesetraditional, French, German, Japanese, and Korean.
configureOptions.Language = "English";
// Apply the configuration options to the scanner
scanner.ConfigureDependencies(configureOptions);
// Extract text from an image
scanner.Scan("test.png");
//Save the extracted text to a text file
string text = scanner.Text.ToString();
File.WriteAllText("Output.txt", text);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
When creating a new PDF document, you can add information about the company, icons, and page numbers as the header and footer to enhance the appearance and professionalism of PDF documents.
This detailed guide will introduce how to add a header and footer when creating a new PDF Document in Python with Spire.PDF for Python effortlessly. Read on.
- Add Header with Python When Creating a PDF Document
- Add Footer with Python When Creating a PDF Document
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows.
Background Knowledge
Spire.PDF for Python offers the PdfPageTemplateElement class for defining page template elements. It provides users with PdfPageTemplateElement.Graphics.DrawString(), PdfPageTemplateElement.Graphics.DrawLine(), PdfPageTemplateElement.Graphics.DrawImage(), and more to draw text, lines, and images. Furthermore, Spire.PDF for Python supports drawing automatic fields like PdfPageCountField and PdfPageNumberField to the template element by PdfGraphicsWidget.Draw() method.
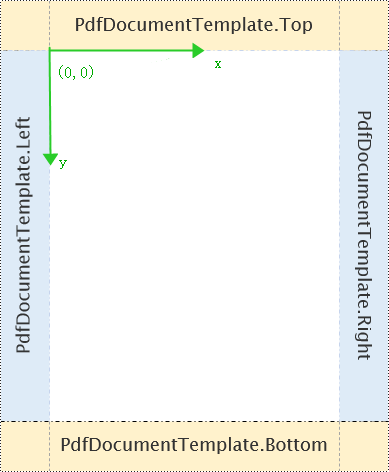
To draw content on the PdfPageTemplateElement template element, the coordinate system settings are as follows:
- The coordinates system's origin is positioned at the top left corner of the template.
- The x-axis extends to the right, and the y-axis extends downward.
Spire.PDF for Python provides PdfDocumentTemplate class to design the entire page templates of a PDF. The defined PdfPageTemplateElement page template elements above can be applied to the PdfDocumentTemplate page template directly.
PdfDocumentTemplate can apply one or more PdfPageTemplateElement page template elements. For example, apply them to PdfDocumentTemplate.Top and PdfDocumentTemplate.Bottom page templates to create a header and footer in the PDF.
The new page generated by Spire.PDF contains margins by default. The initialization coordinates for the PdfDocumentTemplate page template are set as follows:
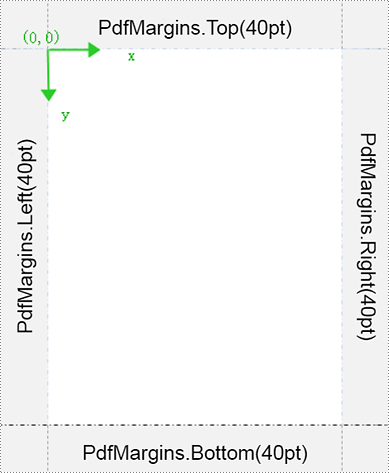
Content cannot be drawn in the margins. To apply PdfPageTemplateElement to PdfDocumentTemplate for the header and footer, you can reset the PDF margins to 0. This way, the coordinate system of the PdfDocumentTemplate page template on the new page will adjust based on the size set by the PdfPageTemplateElement. For example:
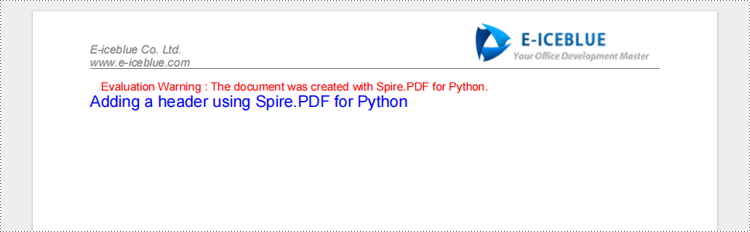
Add a Header with Python When Creating a PDF Document
The following explains how to add text, images, and lines to the header using Spire.PDF for Python when creating a new PDF.
Part 1: Design the header template elements by customizing the CreateHeaderTemplate() method.
- Create PdfPageTemplateElement objects.
- Set the font, brush, pen, and text alignment format for drawing the content of the header by defining PdfTrueTypeFont, PdfBrushes, PdfPen, and PdfTextAlignment.
- Load images to be drawn in the header with PdfImage.FromFile() method.
- Draw text, lines, and images at specified positions in the header template elements using PdfPageTemplateElement.Graphics.DrawString(), PdfPageTemplateElement.Graphics.DrawLine(), and PdfPageTemplateElement.Graphics.DrawImage() methods.
Part 2: Create PDF document objects and call the custom method above to add the header
- Create a new PdfDocument object.
- Set page size by PdfDocoment.PageSettings.Size. Reset the top, bottom, left, and right margins to 0 using PageSettings.Margins.
- Create a new PdfMargins object to set the sizes of the header, the footer, and the left and right templates.
- Call the custom method CreateHeaderTemplate() to add a header.
- Add pages using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Define PdfTrueTypeFont and PdfBrushes to set font and brushes for drawing the main content.
- Draw content in the specified area on the newly created page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Save the resulting file with PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Define CreateHeaderTemplate()
def CreateHeaderTemplate(doc, pageSize, margins):
#Create a header template with a specified size
headerSpace = PdfPageTemplateElement(pageSize.Width, margins.Top)
headerSpace.Foreground = True
doc.Template.Top = headerSpace
# Initialize the x and y coordinate points
x = margins.Left
y = 0.0
# Set font, brush, pen, and ext alignment format
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 10.0, PdfFontStyle.Italic, True)
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Gray()
pen = PdfPen(PdfBrushes.get_Gray(), 1.0)
leftAlign = PdfTextAlignment.Left
# Load the header image and get its height and width values
headerImage = PdfImage.FromFile("E:\Administrator\Python1\header.png")
width = headerImage.Width
height = headerImage.Height
unitCvtr = PdfUnitConvertor()
pointWidth = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(width, PdfGraphicsUnit.Pixel, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point)
pointFeight = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(height, PdfGraphicsUnit.Pixel, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point)
# Draw a header image at the specified position
headerSpace.Graphics.DrawImage(headerImage, headerSpace.Width-x-pointWidth, headerSpace.Height-pointFeight)
# Draw the header text at the specified place
headerSpace.Graphics.DrawString("E-iceblue Co. Ltd.\nwww.e-iceblue.com", font, brush, x, headerSpace.Height-font.Height*2, PdfStringFormat(leftAlign))
# Draw the header line at the specified position
headerSpace.Graphics.DrawLine(pen, x, margins.Top, pageSize.Width - x, margins.Top)
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Set the page size and margins
pageSize =PdfPageSize.A4()
doc.PageSettings.Size = pageSize
doc.PageSettings.Margins = PdfMargins(0.0)
# Create a new PdfMargins object to set the size of the header, footer, and left and right templates
margins = PdfMargins(50.0, 50.0, 50.0, 50.0)
doc.Template.Left = PdfPageTemplateElement(margins.Left, pageSize.Height-margins.Bottom-margins.Top)
doc.Template.Right = PdfPageTemplateElement(margins.Right, pageSize.Height-margins.Bottom-margins.Top)
doc.Template.Bottom = PdfPageTemplateElement(pageSize.Width, margins.Bottom)
# Call CreateHeaderTemplate() to add a header
CreateHeaderTemplate(doc, pageSize, margins)
# Add pages according to the settings above
page = doc.Pages.Add()
# Define the font and brush to be used for the page content
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 14.0, PdfFontStyle.Regular, True)
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Blue()
# Draw text on the page
text = "Adding a header using Spire.PDF for Python"
page.Canvas.DrawString(text, font, brush, 0.0, 20.0)
# Save the document as PDF
doc.SaveToFile("output/result.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
# Dispose document objects
doc.Close()
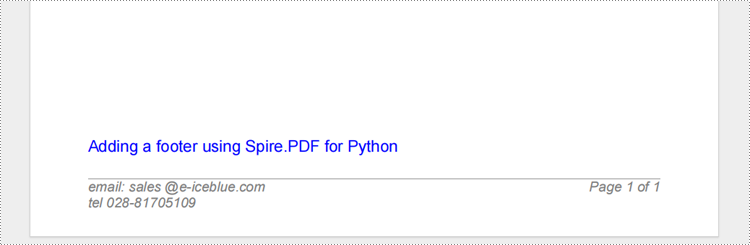
Adding A Footer When Creating A New PDF Document with Python
The following is about how to add text, lines, and page content to the footer by Spire.PDF for Python when creating a new PDF:
Part 1: Customize CreateFooterTemplate() to design footer template elements
- Create a PdfPageTemplateElement object.
- Define PdfTrueTypeFont, PdfBrushes, PdfPen, and PdfTextAlignment to set font, brush, pen, and the text alignment format for drawing the content of footers.
- Draw lines and text in the footer template element using PdfPageTemplateElement Graphics.DrawString() and PdfPageTemplateElement Graphics.DrawLine() methods.
- Create PdfPageNumberField () and PdfPageCountField() objects.
- Create a PdfCompositeField() object to set the composite format and convert it to a PdfGraphicsWidget type. Use PdfGraphicsWidget.Draw() method to draw the page number field content.
Part 2: Create PDF document objects and call the custom method above to add the footer
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Set page size using PdfDocoment.PageSettings.Size. Reset the top, bottom, left, and right margins to 0 by PageSettings.Margins.
- Create a new PdfMargins object to set the sizes of the header, footer, and left and right templates.
- Call the custom method CreateFooterTemplate() to add a Footer.
- Add pages using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Define PdfTrueTypeFont and PdfBrushes to set font and brushes for drawing the main content.
- Draw content in the specified area on the newly created page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Save the resulting file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Define CreateFooterTemplate()
def CreateFooterTemplate(doc, pageSize, margins):
# Create a footer template with specified sizes
footerSpace = PdfPageTemplateElement(pageSize.Width, margins.Bottom)
footerSpace.Foreground = True
doc.Template.Bottom = footerSpace
# Initialize the x and y coordinate points
x = margins.Left
y = 0.0
# Set font, brush, pen, and ext alignment format
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 12.0, PdfFontStyle.Italic, True)
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Gray()
pen = PdfPen(PdfBrushes.get_Gray(), 1.0)
leftAlign = PdfTextAlignment.Left
# Draw footer lines at the specified place
footerSpace.Graphics.DrawLine(pen, x, y, pageSize.Width - x, y)
# Draw footer text at the specified position
footerSpace.Graphics.DrawString("email: sales @e-iceblue.com\ntel:028-81705109 ", font, brush, x, y, PdfStringFormat(leftAlign))
# Create fields for page number and total page count
number = PdfPageNumberField()
count = PdfPageCountField()
listAutomaticField = [number, count]
# Create a composite field and set string formatting for drawing
compositeField = PdfCompositeField(font, PdfBrushes.get_Gray(), "Page {0} of {1}", listAutomaticField)
compositeField.StringFormat = PdfStringFormat(PdfTextAlignment.Right, PdfVerticalAlignment.Top)
size = font.MeasureString(compositeField.Text)
compositeField.Bounds = RectangleF(pageSize.Width -x-size.Width, y, size.Width, size.Height)
newTemplate = compositeField
templateGraphicsWidget = PdfGraphicsWidget(newTemplate.Ptr)
templateGraphicsWidget.Draw(footerSpace.Graphics)
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Set page sizes and the margin
pageSize =PdfPageSize.A4()
doc.PageSettings.Size = pageSize
doc.PageSettings.Margins = PdfMargins(0.0)
# Create a new PdfMargins object for setting sizes of the header, footer, and left and right templates
margins = PdfMargins(50.0, 50.0, 50.0, 50.0)
doc.Template.Left = PdfPageTemplateElement(margins.Left, pageSize.Height-margins.Top-margins.Bottom)
doc.Template.Right = PdfPageTemplateElement(margins.Right, pageSize.Height-margins.Top-margins.Bottom)
doc.Template.Top = PdfPageTemplateElement(pageSize.Width, margins.Top)
# Call CreateFooterTemplate() to add a footer
CreateFooterTemplate(doc, pageSize, margins)
# Add pages according to the settings above
page = doc.Pages.Add()
# Create font and brush for page content
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 14.0, PdfFontStyle.Regular, True)
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Blue()
# Draw text on the page
text = "Adding a footer using Spire.PDF for Python"
page.Canvas.DrawString(text, font, brush, 0.0, pageSize.Height-margins.Bottom-margins.Top-font.Height-20)
# Save the document as PDF
doc.SaveToFile("output/result.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
# Dispose document object
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
