
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Handling PDF documents using bytes and bytearray provides an efficient and flexible approach within applications. By processing PDFs directly as byte streams, developers can manage documents in memory or transfer them over networks without the need for temporary file storage, optimizing space and improving overall application performance. This method also facilitates seamless integration with web services and APIs. Additionally, using bytearray allows developers to make precise byte-level modifications to PDF documents.
This article will demonstrate how to save PDFs as bytes and bytearray and load PDFs from bytes and bytearray using Spire.PDF for Python, offering practical examples for Python developers.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Create a PDF Document and Save It to Bytes and Bytearray
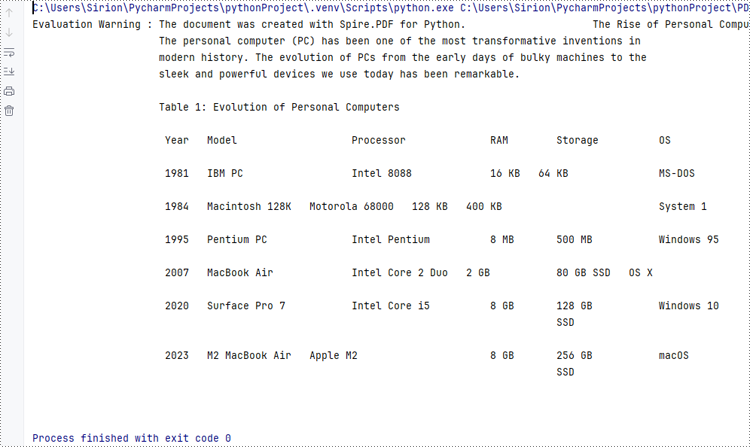
Developers can create PDF documents using the classes and methods provided by Spire.PDF for Python, save them to a Stream object, and then convert it to an immutable bytes object or a mutable bytearray object. The Stream object can also be used to perform byte-level operations.
The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class to create a PDF document.
- Add a page to the document and draw text on the page.
- Save the document to a Stream object using PdfDocument.SaveToStream() method.
- Convert the Stream object to a bytes object using Stream.ToArray() method.
- The bytes object can be directly converted to a bytearray object.
- Afterward, the byte streams can be used for further operations, such as writing them to a file using the BinaryIO.write() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
# Create an instance of PdfDocument class
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Set the page size and margins of the document
pageSettings = pdf.PageSettings
pageSettings.Size = PdfPageSize.A4()
pageSettings.Margins.Top = 50
pageSettings.Margins.Bottom = 50
pageSettings.Margins.Left = 40
pageSettings.Margins.Right = 40
# Add a new page to the document
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Create fonts and brushes for the document content
titleFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("HarmonyOS Sans SC", 16.0, PdfFontStyle.Bold, True)
titleBrush = PdfBrushes.get_Brown()
contentFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("HarmonyOS Sans SC", 13.0, PdfFontStyle.Regular, True)
contentBrush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
# Draw the title on the page
titleText = "Brief Introduction to Cloud Services"
titleSize = titleFont.MeasureString(titleText)
page.Canvas.DrawString(titleText, titleFont, titleBrush, PointF(0.0, 30.0))
# Draw the body text on the page
contentText = ("Cloud computing is a service model where computing resources are provided over the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis. "
"It is a type of infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), platform-as-a-service (PaaS), and software-as-a-service (SaaS) model. "
"Cloud computing is typically offered througha subscription-based model, where users pay for access to the cloud resources on a monthly, yearly, or other basis.")
# Set the string format of the body text
contentFormat = PdfStringFormat()
contentFormat.Alignment = PdfTextAlignment.Justify
contentFormat.LineSpacing = 20.0
# Create a TextWidget object with the body text and apply the string format
textWidget = PdfTextWidget(contentText, contentFont, contentBrush)
textWidget.StringFormat = contentFormat
# Create a TextLayout object and set the layout options
textLayout = PdfTextLayout()
textLayout.Layout = PdfLayoutType.Paginate
textLayout.Break = PdfLayoutBreakType.FitPage
# Draw the TextWidget on the page
rect = RectangleF(PointF(0.0, titleSize.Height + 50.0), page.Canvas.ClientSize)
textWidget.Draw(page, rect, textLayout)
# Save the PDF document to a Stream object
pdfStream = Stream()
pdf.SaveToStream(pdfStream)
# Convert the Stream object to a bytes object
pdfBytes = pdfStream.ToArray()
# Convert the Stream object to a bytearray object
pdfBytearray = bytearray(pdfStream.ToArray())
# Write the byte stream to a file
with open("output/PDFBytearray.pdf", "wb") as f:
f.write(pdfBytearray)

Load a PDF Document from Byte Streams
Developers can use a bytes object of a PDF file to create a stream and load it using the PdfDocument.LoadFromStream() method. Once the PDF document is loaded, various operations such as reading, modifying, and converting the PDF can be performed. The following is an example of the steps:
- Create a bytes object with a PDF file.
- Create a Stream object using the bytes object.
- Load the Stream object as a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromStream() method.
- Extract the text from the first page of the document and print the text.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a byte array from a PDF file
with open("Sample.pdf", "rb") as f:
byteData = f.read()
# Create a Stream object from the byte array
stream = Stream(byteData)
# Load the Stream object as a PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument(stream)
# Get the text from the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
textExtractor = PdfTextExtractor(page)
extractOptions = PdfTextExtractOptions()
extractOptions.IsExtractAllText = True
text = textExtractor.ExtractText(extractOptions)
# Print the text
print(text)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Adding page numbers to a PDF enhances its organization and readability, making it easier for readers to navigate the document. Whether for reports, manuals, or e-books, page numbers provide a professional touch and help maintain the flow of information. This process involves determining the placement, alignment, and style of the numbers within the footer or header.
In this article, you will learn how to add page numbers to the PDF footer using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Add Left-Aligned Page Numbers to PDF Footer
- Add Center-Aligned Page Numbers to PDF Footer
- Add Right-Aligned Page Numbers to PDF Footer
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
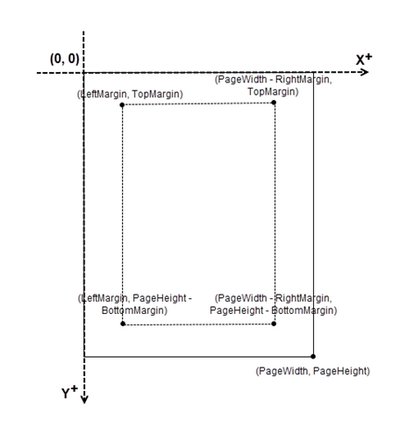
Coordinate System in PDF
When using Spire.PDF for Python to modify a PDF document, the coordinate system's origin is at the top-left corner of the page. The x-axis extends to the right, while the y-axis extends downward.
Page numbers are usually positioned in the header or footer. Thus, it's important to consider the page size and margins when determining the placement of the page numbers.
Classes and Methods for Creating Page Numbers
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfPageNumberField and PdfPageCountField classes to retrieve the current page number and total page count. These can be merged into a single PdfCompositeField that formats the output as "Page X of Y", where X represents the current page number and Y indicates the total number of pages.
To position the PdfCompositeField on the page, use the Location property, and render it with the Draw() method.
Add Left-Aligned Page Numbers to PDF Footer
To add left-aligned page numbers in the footer, you need to consider the left and bottom page margins as well as the page height. For example, you can use coordinates such as (LeftMargin, PageHeight – BottomMargin + SmallNumber). This ensures that the page numbers align with the left side of the text while keeping a comfortable distance from both the content and the edges of the page.
The steps to add left-aligned page numbers to PDF footer are as follows:
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file from a specified path.
- Create a PdfPageNumberField object and a PdfPageCountField object.
- Create a PdfCompositeField object to combine page count field and page number field in a single string.
- Set the position of the composite field through PdfCompositeField.Location property to ensure the page number aligns with the left side of the text.
- Iterate through the pages in the document, and draw the composite field on each page at the specified location.
- Save the document to a different PDF file.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Privacy Policy.pdf")
# Create font, brush and pen
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Times New Roman", 12.0, PdfFontStyle.Regular, True)
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
pen = PdfPen(brush, 1.0)
# Create a PdfPageNumberField object and a PdfPageCountField object
pageNumberField = PdfPageNumberField()
pageCountField = PdfPageCountField()
# Create a PdfCompositeField object to combine page count field and page number field in a single string
compositeField = PdfCompositeField(font, brush, "Page {0} of {1}", [pageNumberField, pageCountField])
# Get the page size
pageSize = doc.Pages.get_Item(0).Size
# Specify the blank areas around the page
leftMargin = 54.0
rightMargin = 54.0
bottomMargin = 72.0
# Set the location of the composite field
compositeField.Location = PointF(leftMargin, pageSize.Height - bottomMargin + 18.0)
# Iterate through the pages in the document
for i in range(doc.Pages.Count):
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Draw a line at the specified position
page.Canvas.DrawLine(pen, leftMargin, pageSize.Height - bottomMargin + 15.0, pageSize.Width - rightMargin, pageSize.Height - bottomMargin + 15.0)
# Draw the composite field on the page
compositeField.Draw(page.Canvas, 0.0, 0.0)
# Save to a different PDF file
doc.SaveToFile("Output/LeftAlignedPageNumbers.pdf")
# Dispose resources
doc.Dispose()
Add Center-Aligned Page Numbers to PDF Footer
To position the page number in the center of the footer, you first need to measure the width of the page number itself. Once you have this measurement, you can calculate the appropriate X coordinate by using the formula (PageWidth - PageNumberWidth) / 2. This ensures the page number is horizontally centered within the footer.
The steps to add center-aligned page numbers to PDF footer are as follows:
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file from a specified path.
- Create a PdfPageNumberField object and a PdfPageCountField object.
- Create a PdfCompositeField object to combine page count field and page number field in a single string.
- Set the position of the composite field through PdfCompositeField.Location property to ensure the page number is perfectly centered in the footer.
- Iterate through the pages in the document, and draw the composite field on each page at the specified location.
- Save the document to a different PDF file.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Privacy Policy.pdf")
# Create font, brush and pen
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Times New Roman", 12.0, PdfFontStyle.Regular, True)
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
pen = PdfPen(brush, 1.0)
# Specify the blank margins around the page
leftMargin = 54.0
rightMargin = 54.0
bottomMargin = 72.0
# Create a PdfPageNumberField object and a PdfPageCountField object
pageNumberField = PdfPageNumberField()
pageCountField = PdfPageCountField()
# Create a PdfCompositeField object to combine page count field and page number field in a single field
compositeField = PdfCompositeField(font, brush, "Page {0} of {1}", [pageNumberField, pageCountField])
# Iterate through the pages in the document
for i in range(doc.Pages.Count):
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Get the page size
pageSize = doc.Pages.get_Item(i).Size
# Draw a line at the specified position
page.Canvas.DrawLine(pen, leftMargin, pageSize.Height - bottomMargin + 15.0, pageSize.Width - rightMargin, pageSize.Height - bottomMargin + 15.0)
# Measure the size the "Page X of Y"
pageNumberSize = font.MeasureString("Page {} of {}".format(i + 1, doc.Pages.Count))
# Set the location of the composite field
compositeField.Location = PointF((pageSize.Width - pageNumberSize.Width)/2, pageSize.Height - bottomMargin + 18.0)
# Draw the composite field on the page
compositeField.Draw(page.Canvas, 0.0, 0.0)
# Save to a different PDF file
doc.SaveToFile("Output/CenterAlignedPageNumbers.pdf")
# Dispose resources
doc.Dispose()
Add Right-Aligned Page Numbers to PDF Footer
To add a right-aligned page number in the footer, measure the width of the page number. Then, calculate the X coordinate using the formula PageWidth - PageNumberWidth - RightMargin. This ensures that the page number aligns with the right side of the text.
The following are the steps to add right-aligned page numbers to PDF footer:
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file from a specified path.
- Create a PdfPageNumberField object and a PdfPageCountField object.
- Create a PdfCompositeField object to combine page count field and page number field in a single string.
- Set the position of the composite field through PdfCompositeField.Location property to ensure the page number aligns with the right side of the text.
- Iterate through the pages in the document, and draw the composite field on each page at the specified location.
- Save the document to a different PDF file.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Privacy Policy.pdf")
# Create font, brush and pen
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Times New Roman", 12.0, PdfFontStyle.Regular, True)
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
pen = PdfPen(brush, 1.0)
# Specify the blank margins around the page
leftMargin = 54.0
rightMargin = 54.0
bottomMargin = 72.0
# Create a PdfPageNumberField object and a PdfPageCountField object
pageNumberField = PdfPageNumberField()
pageCountField = PdfPageCountField()
# Create a PdfCompositeField object to combine page count field and page number field in a single string
compositeField = PdfCompositeField(font, brush, "Page {0} of {1}", [pageNumberField, pageCountField])
# Iterate through the pages in the document
for i in range(doc.Pages.Count):
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Get the page size
pageSize = doc.Pages.get_Item(i).Size
# Draw a line at the specified position
page.Canvas.DrawLine(pen, leftMargin, pageSize.Height - bottomMargin + 15.0, pageSize.Width - rightMargin, pageSize.Height - bottomMargin + 15.0)
# Measure the size the "Page X of Y"
pageNumberSize = font.MeasureString("Page {} of {}".format(i + 1, doc.Pages.Count))
# Set the location of the composite field
compositeField.Location = PointF(pageSize.Width - pageNumberSize.Width - rightMargin, pageSize.Height - bottomMargin + 18.0)
# Draw the composite field on the page
compositeField.Draw(page.Canvas, 0.0, 0.0)
# Save to a different PDF file
doc.SaveToFile("Output/RightAlignedPageNumbers.pdf")
# Dispose resources
doc.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Apply Shadow, Transparent, and 3D Effects to Text in PowerPoint
2024-09-04 00:49:50 Written by KoohjiEnhancing the visual appeal of your PowerPoint presentations is crucial for capturing your audience's attention. One effective way to achieve this is by applying advanced text effects such as shadows, transparency, and 3D effects. These techniques can add depth, dimension, and a modern look to your text, making your slides more engaging and professional. In this article, we'll demonstrate how to apply shadow, transparent and 3D effects to text in PowerPoint in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Apply Shadow Effect to Text in PowerPoint in Python
- Apply Transparent Effect to Text in PowerPoint in Python
- Apply 3D Effect to Text in PowerPoint in Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python. It can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Apply Shadow Effect to Text in PowerPoint in Python
Spire.Presentation for Python offers the InnerShadowEffect and OuterShadowEffect classes for creating inner and outer shadow effects. These shadow effects can then be applied to the text within shapes by using the IAutoShape.TextFrame.TextRange.EffectDag.InnerShadowEffect and IAutoShape.TextFrame.TextRange.EffectDag.OuterShadowEffect properties. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Get a specific slide in the presentation using the Presentation.Slides[index] property.
- Add a shape to the slide using the ISilde.Shapes.AppendShape() method.
- Add text to the shape using the IAutoShape.AppendTextFrame() method.
- Create an inner or outer shadow effect using the InnerShadowEffect or OuterShadowEffect class.
- Set the blur radius, direction, distance and color, for the inner or outer shadow effect using the properties offered by the InnerShadowEffect or OuterShadowEffect class.
- Apply the inner or outer shadow effect to the text within the shape using the IAutoShape.TextFrame.TextRange.EffectDag.InnerShadowEffect or IAutoShape.TextFrame.TextRange.EffectDag.OuterShadowEffect property.
- Save the resulting presentation using the Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
ppt = Presentation()
# Get the first slide
slide = ppt.Slides[0]
# Add the first rectangular shape to the slide
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, RectangleF.FromLTRB(120, 60, 500, 200))
shape.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.none
# Add text to the shape
shape.AppendTextFrame("Text With Outer Shadow Effect")
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs[0].TextRanges[0].LatinFont = TextFont("Arial")
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs[0].TextRanges[0].FontHeight = 21
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs[0].TextRanges[0].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs[0].TextRanges[0].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_Black()
# Create an outer shadow effect
outerShadow = OuterShadowEffect()
# Set the blur radius, direction, distance and color for the outer shadow effect
outerShadow.BlurRadius = 0
outerShadow.Direction = 50
outerShadow.Distance = 10
outerShadow.ColorFormat.Color = Color.get_LightBlue()
# Apply the outer shadow effect to the text in the first rectangular shape
shape.TextFrame.TextRange.EffectDag.OuterShadowEffect = outerShadow
# Add the second rectangular shape to the slide
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, RectangleF.FromLTRB(120, 300, 500, 440))
shape.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.none
# Add text to the shape
shape.AppendTextFrame("Text With Inner Shadow Effect")
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs[0].TextRanges[0].LatinFont = TextFont("Arial")
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs[0].TextRanges[0].FontHeight = 21
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs[0].TextRanges[0].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs[0].TextRanges[0].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_Black()
# Create an inner shadow effect
innerShadow = InnerShadowEffect()
# Set the blur radius, direction, distance and color for the inner shadow effect
innerShadow.BlurRadius = 0
innerShadow.Direction = 50
innerShadow.Distance = 10
innerShadow.ColorFormat.Color = Color.get_LightBlue()
# Apply the inner shadow effect to the text in the second rectangular shape
shape.TextFrame.TextRange.EffectDag.InnerShadowEffect = innerShadow
# Save the resulting presentation
ppt.SaveToFile("SetShadowEffect.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
ppt.Dispose()

Apply Transparent Effect to Text in PowerPoint in Python
Spire.Presentation for Python does not offer a direct method to apply transparency effect to text, but you can control the transparency by adjusting the alpha value of the text color. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Get a specific slide in the presentation using the Presentation.Slides[index] property.
- Add a shape to the slide using the ISilde.Shapes.AppendShape() method.
- Retrieve the paragraph collection from the text frame within the shape using the IAutoShape.TextFrame.Paragraphs property, then remove any default paragraphs from the collection using the ParagraphList.Clear() method.
- Add new paragraphs to the collection using the ParagraphList.Append() method, and insert text into each paragraph using the TextParagraph.TextRanges.Append() method.
- Set the fill type of the text to solid using the TextRange.Fill.FillType property.
- Adjust the transparency of the text by setting the color with varying alpha values using the Color.FromArgb(alpha:int, red:int, green:int, blue:int) method, where the alpha value controls the transparency level—the lower the alpha, the more transparent the text.
- Save the resulting presentation using the Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
ppt = Presentation()
# Get the first slide
slide = ppt.Slides[0]
# Add a rectangular shape to the slide
textboxShape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, RectangleF.FromLTRB(100, 100, 400, 220))
# Make the border of the shape transparent
textboxShape.ShapeStyle.LineColor.Color = Color.get_Transparent()
# Set the shape's fill to none
textboxShape.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.none
# Retrieve the paragraph collection from the text frame within the shape
paras = textboxShape.TextFrame.Paragraphs
# Remove any default paragraphs
paras.Clear()
# Add three new paragraphs to the text frame, each with a different transparency level for the text
alpha = 55 # Initial alpha value for text transparency
for i in range(3):
# Create and add a new paragraph
paras.Append(TextParagraph())
# Add text to the paragraph
paras[i].TextRanges.Append(TextRange("Text with Different Transparency"))
# Set the text fill type to solid
paras[i].TextRanges[0].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
# Set the text color with varying transparency, controlled by the alpha value
paras[i].TextRanges[0].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.FromArgb(
alpha,
Color.get_Blue().R,
Color.get_Blue().G,
Color.get_Blue().B
)
# Increase alpha value to reduce transparency for the next paragraph
alpha += 100
# Save the resulting presentation
ppt.SaveToFile("SetTransparency.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
ppt.Dispose()

Apply 3D Effect to Text in PowerPoint in Python
The FormatThreeD class in Spire.Presentation for Python is used for creating a 3D effect. You can access the FormatThreeD object using the IAutoShape.TextFrame.TextThreeD property, then use the properties of the FormatThreeD class to configure the settings for the 3D effect. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Get a specific slide in the presentation using the Presentation.Slides[index] property.
- Add a shape to the slide using the ISilde.Shapes.AppendShape() method.
- Add text to the shape using the IAutoshape.AppendTextFrame() method.
- Access the FormatThreeD object using the IAutoShape.TextFrame.TextThreeD property.
- Set the material type, top bevel type, contour color and width, and lighting type for the 3D effect through the properties of the FormatThreeD class.
- Save the resulting presentation using the Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
ppt = Presentation()
# Get the first slide
slide = ppt.Slides[0]
# Add a rectangular shape to the slide
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, RectangleF.FromLTRB(30, 40, 680, 240))
# Make the border of the shape transparent
shape.ShapeStyle.LineColor.Color = Color.get_Transparent()
# Set the shape's fill to none
shape.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.none
# Add text to the shape
shape.AppendTextFrame("Text with 3D Effect")
# Set text color
textRange = shape.TextFrame.TextRange
textRange.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
textRange.Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_LightBlue()
# Set font
textRange.FontHeight = 40
textRange.LatinFont = TextFont("Arial")
# Access the FormatThreeD object
threeD = shape.TextFrame.TextThreeD
# Set the material type for the 3D effect
threeD.ShapeThreeD.PresetMaterial = PresetMaterialType.Metal
# Set the top bevel type for the 3D effect
threeD.ShapeThreeD.TopBevel.PresetType = BevelPresetType.Circle
# Set the contour color and width for the 3D effect
threeD.ShapeThreeD.ContourColor.Color = Color.get_Green()
threeD.ShapeThreeD.ContourWidth = 3
# Set the lighting type for the 3D effect
threeD.LightRig.PresetType = PresetLightRigType.Sunrise
# Save the resulting presentation
ppt.SaveToFile("Set3DEffect.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
ppt.Dispose()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
