
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Transferring content between Microsoft Word documents is a frequent task for many users. Whether you need to consolidate information spread across multiple files or quickly reuse existing text and other elements, the ability to effectively copy and paste between documents can save you time and effort.
In this article, you will learn how to copy content from one Word document to another using Java and Spire.Doc for Java.
- Copy Specified Paragraphs from One Word Document to Another
- Copy a Section from One Word Document to Another
- Copy the Entire Document and Append it to Another
- Create a Copy of a Word Document
Install Spire.Doc for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Doc.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>14.1.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Copy Specified Paragraphs from One Word Document to Another in Java
Spire.Doc for Java provides a flexible way to copy content between Microsoft Word documents. This is achieved by cloning individual paragraphs and then adding those cloned paragraphs to a different document.
To copy specific paragraphs from one Word document to another, you can follow these steps:
- Load the source document into a Document object.
- Load the target document into a separate Document object.
- Identify the paragraphs you want to copy from the source document.
- Create copies of those selected paragraphs using Paragraph.deepClone() method
- Add the cloned paragraphs to the target document using ParagraphCollection.add() method.
- Save the updated target document to a new Word file.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
import com.spire.doc.Section;
import com.spire.doc.documents.Paragraph;
public class CopyParagraphs {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Document object
Document sourceDoc = new Document();
// Load the source file
sourceDoc.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\source.docx");
// Get a specific section
Section section = sourceDoc.getSections().get(0);
// Get the specified paragraphs from the source file
Paragraph p1 = section.getParagraphs().get(2);
Paragraph p2 = section.getParagraphs().get(3);
// Create another Document object
Document targetDoc = new Document();
// Load the target file
targetDoc.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\target.docx");
// Get the last section
Section lastSection = targetDoc.getLastSection();
// Add the paragraphs from the source file to the target file
lastSection.getParagraphs().add((Paragraph)p1.deepClone());
lastSection.getParagraphs().add((Paragraph)p2.deepClone());
// Save the target file to a different Word file
targetDoc.saveToFile("CopyParagraphs.docx", FileFormat.Docx_2019);
// Dispose resources
sourceDoc.dispose();
targetDoc.dispose();
}
}
Copy a Section from One Word Document to Another in Java
When copying content between Microsoft Word documents, it's important to consider that a section can contain not only paragraphs, but also other elements like tables. To successfully transfer an entire section from one document to another, you need to iterate through all the child objects within the section and add them individually to a specific section in the target document.
The steps to copy a section between different Word documents are as follows:
- Create Document objects to load the source file and the target file, respectively.
- Get the specified section from the source document.
- Iterate through the child objects within the section.
- Clone a specific child object using DocumentObject.deepClone() method.
- Add the cloned child objects to a designated section in the target document using DocumentObjectCollection.add() method.
- Save the updated target document to a new file.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.DocumentObject;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
import com.spire.doc.Section;
public class CopySection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Document object
Document sourceDoc = new Document();
// Load the source file
sourceDoc.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\source.docx");
// Get the specified section from the source file
Section section = sourceDoc.getSections().get(0);
// Create another Document object
Document targetDoc = new Document();
// Load the target file
targetDoc.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\target.docx");
// Get the last section of the target file
Section lastSection = targetDoc.getLastSection();
// Iterate through the child objects in the selected section
for (int i = 0; i < section.getBody().getChildObjects().getCount(); i++) {
// Get a specific child object
DocumentObject childObject = section.getBody().getChildObjects().get(i);
// Add the child object to the last section of the target file
lastSection.getBody().getChildObjects().add(childObject.deepClone());
}
// Save the target file to a different Word file
targetDoc.saveToFile("CopySection.docx", FileFormat.Docx_2019);
// Dispose resources
sourceDoc.dispose();
targetDoc.dispose();
}
}

Copy the Entire Document and Append it to Another in Java
Copying the full contents from one Microsoft Word document into another can be achieved using the Document.insertTextFromFile() method. This method enables you to seamlessly append the contents of a source document to a target document.
The steps to copy an entire document and append it to another are as follows:
- Create a Document object to represent the target file.
- Load the target file from the given file path.
- Insert the content of a different Word document into the target file using Document.insertTextFromFile() method.
- Save the updated target file to a new Word document.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
public class CopyEntireDocument {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Specify the path of the source document
String sourceFile = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\source.docx";
// Create a Document object
Document targetDoc = new Document();
// Load the target file
targetDoc.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\target.docx");
// Insert content of the source file to the target file
targetDoc.insertTextFromFile(sourceFile, FileFormat.Docx);
// Save the target file to a different Word file
targetDoc.saveToFile("CopyEntireDocument.docx", FileFormat.Docx_2019);
// Dispose resources
targetDoc.dispose();
}
}
Create a Copy of a Word Document in Java
Spire.Doc for Java provides a straightforward way to create a duplicate of a Microsoft Word document by using the Document.deepClone() method.
To make a copy of a Word document, follow these steps:
- Create a Document object to relisent the source document.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Create a copy of the document using Document.deepClone() method.
- Save the cloned document to a new Word file.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
public class DuplicateDocument {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new document object
Document sourceDoc = new Document();
// Load a Word file
sourceDoc.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\target.docx");
// Clone the document
Document newDoc = sourceDoc.deepClone();
// Save the cloned document as a docx file
newDoc.saveToFile("Copy.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Dispose resources
sourceDoc.dispose();
newDoc.dispose();
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Detect Page Orientation or Rotation Angle in PDF
2024-08-27 01:00:23 Written by AdministratorProper presentation of a PDF document is critical for maintaining its accuracy and professionalism. By checking the orientation and rotation of each PDF page, you can confirm that all elements, including diagrams and images, are displayed correctly as intended on the viewing device or platform, thus avoiding confusion or misinterpretation of content. In this article, you will learn how to detect the orientation and rotation angle of a PDF page in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python. It can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
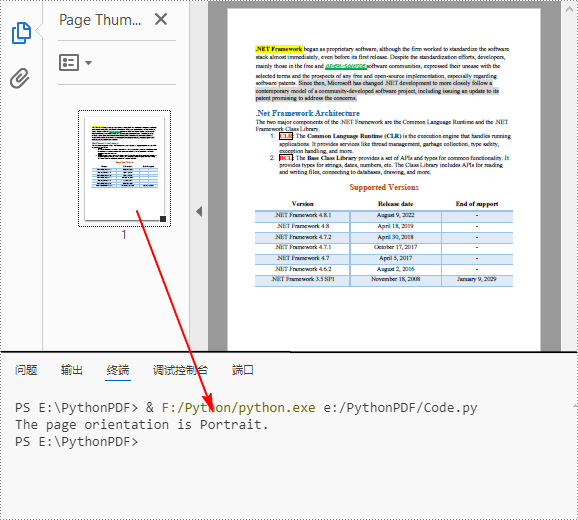
Detect PDF Page Orientation in Python
Page orientation is determined by the relationship between page width and height. Using Spire.PDF for Python, you can compare these two values to detect whether a page is landscape (width greater than height) or portrait (width less than height). The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified page using PdfDocument.Pages[] property.
- Get the width and height of the PDF page using PdfPageBase.Size.Width and PdfPageBase.Size.Height properties.
- Compare the values of page width and height to detect the page orientation.
- Print out the result.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file from disk
pdf.LoadFromFile("SamplePDF.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Get the width and height of the page
Width = page.Size.Width
Height = page.Size.Height
# Compare the values of page width and height
if Width > Height:
print("The page orientation is Landscape.")
else:
print("The page orientation is Portrait.")
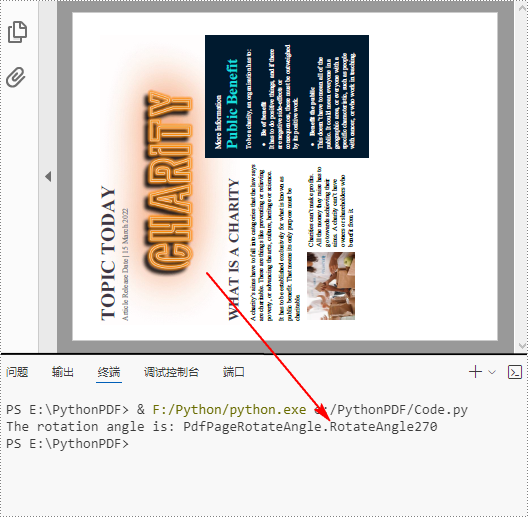
Detect PDF Page Rotation Angle in Python
PDF pages can be rotated by a certain angle. To detect the rotation angle of a PDF page, you can use the PdfPageBase.Rotation property. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified page using PdfDocument.Pages[] property.
- Get the rotation angle of the page using PdfPageBase.Rotation property, and then convert it to text string.
- Print out the result.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file from disk
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Get the rotation angle of the current page
rotationAngle = page.Rotation
rotation = str(rotationAngle)
# Print out the result
print("The rotation angle is: " + rotation)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
In some cases, checking the size, orientation, and rotation of PDF pages can be part of the quality control process. For example, before publishing or distributing a document, you might need to verify this information to ensure that all pages in the document are correctly presented. In this article, you will learn how to get PDF page size, orientation and rotation angle in C# using Spire.PDF for .NET.
Install Spire.PDF for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.PDF for.NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.PDF
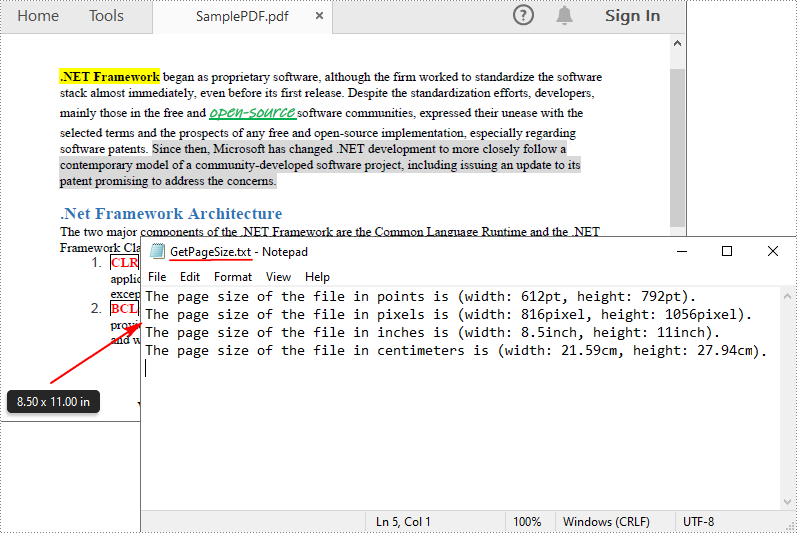
Get PDF Page Size in C#
Spire.PDF for .NET offers the PdfPageBase.Size.Width and PdfPageBase.Size.Height properties to get the width and height of a PDF page in points. If you want to convert the default unit of measure to other units, you can use the PdfUnitConvertor class. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified page using PdfDocument.Pages[] property.
- Get the width and height of the PDF page using PdfPageBase.Size.Width and PdfPageBase.Size.Height properties.
- Create a PdfUnitConvertor instance, and then convert the size units from points to other units of measure using PdfUnitConvertor.ConvertUnits() method.
- Add the page size information to a StringBuilder instance, and then save the result to a TXT file.
- C#
using System.Text;
using Spire.Pdf;
using Spire.Pdf.Graphics;
namespace GetPDFPageSize
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a PdfDocument object
PdfDocument pdf = new PdfDocument();
//Load a PDF file from disk
pdf.LoadFromFile("SamplePDF.pdf");
//Get the first page
PdfPageBase page = pdf.Pages[0];
//Get the width and height of the page in "point"
float pointWidth = page.Size.Width;
float pointHeight = page.Size.Height;
//Create PdfUnitConvertor to convert the unit
PdfUnitConvertor unitCvtr = new PdfUnitConvertor();
//Convert size units from points to pixels
float pixelWidth = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(pointWidth, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point, PdfGraphicsUnit.Pixel);
float pixelHeight = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(pointHeight, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point, PdfGraphicsUnit.Pixel);
//Convert size units from points to inches
float inchWidth = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(pointWidth, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point, PdfGraphicsUnit.Inch);
float inchHeight = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(pointHeight, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point, PdfGraphicsUnit.Inch);
//Convert size units from points to centimeters
float centimeterWidth = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(pointWidth, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point, PdfGraphicsUnit.Centimeter);
float centimeterHeight = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(pointHeight, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point, PdfGraphicsUnit.Centimeter);
//Create a StringBuilder instance
StringBuilder content = new StringBuilder();
//Add the page size information to the StringBuilder instance
content.AppendLine("The page size of the file in points is (width: " + pointWidth + "pt, height: " + pointHeight + "pt).");
content.AppendLine("The page size of the file in pixels is (width: " + pixelWidth + "pixel, height: " + pixelHeight + "pixel).");
content.AppendLine("The page size of the file in inches is (width: " + inchWidth + "inch, height: " + inchHeight + "inch).");
content.AppendLine("The page size of the file in centimeters is (width: " + centimeterWidth + "cm, height: " + centimeterHeight + "cm).");
//Save to a txt file
File.WriteAllText("GetPageSize.txt", content.ToString());
}
}
}
Detect PDF Page Orientation in C#
To detect the orientation of a PDF page, you can compare the width and height of the page. If the page width is greater than the height, then the page orientation is landscape, otherwise it is portrait. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified page using PdfDocument.Pages[] property.
- Get the width and height of the PDF page using PdfPageBase.Size.Width and PdfPageBase.Size.Height properties.
- Compare the values of page width and height to detect the page orientation.
- Output the result using Console.WriteLine() method.
- C#
using Spire.Pdf;
namespace GetPDFPageOrientation
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a PdfDocument object
PdfDocument pdf = new PdfDocument();
//Load a PDF file from disk
pdf.LoadFromFile("SamplePDF.pdf");
//Get the first page
PdfPageBase page = pdf.Pages[0];
//Get the width and height of the page
float width = page.Size.Width;
float height = page.Size.Height;
//Compare the values of page width and height
if (width > height)
{
Console.WriteLine("The page orientation is Landscape.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("The page orientation is Portrait.");
}
}
}
}
Detect PDF Page Rotation Angle in C#
The rotation angle of a PDF page can be obtained through the PdfPageBase.Rotation property. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified page using PdfDocument.Pages[] property.
- Get the rotation angle of the page using PdfPageBase.Rotation property, and then convert it to text string.
- Output the result using Console.WriteLine() method.
- C#
using Spire.Pdf;
namespace GetPDFPageRotationAngle
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a PdfDocument object
PdfDocument pdf = new PdfDocument();
//Load a PDF file from disk
pdf.LoadFromFile("E:\\PythonPDF\\Sample.pdf");
//Get the first page
PdfPageBase page = pdf.Pages[0];
//Get the rotation angle of the current page
PdfPageRotateAngle rotationAngle = page.Rotation;
string rotation = rotationAngle.ToString();
//Output the page rotation angle information
Console.WriteLine("The rotation angle of the current page is: " + rotation);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
