
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Converting a PDF to grayscale reduces file size by removing unnecessary color data, turning the content into shades of gray. This is especially useful for documents where color isn’t critical, such as text-heavy reports or forms, resulting in more efficient storage and faster transmission. On the other hand, linearization optimizes the PDF’s internal structure for web use. It enables users to start viewing the first page while the rest of the file is still loading, providing a faster and smoother experience, particularly for online viewing. In this article, we will demonstrate how to convert PDF files to grayscale or linearized PDFs in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Convert PDF to Grayscale in Python
Converting a PDF document to grayscale can be achieved by using the PdfGrayConverter.ToGrayPdf() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Load a PDF document using the PdfGrayConverter class.
- Convert the PDF document to grayscale using the PdfGrayConverter.ToGrayPdf() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import * from spire.pdf import * # Specify the input and output PDF file paths inputFile = "Sample.pdf" outputFile = "Output/ConvertToGrayscale.pdf" # Load a PDF document using the PdfGrayConverter class converter = PdfGrayConverter(inputFile) # Convert the PDF document to grayscale converter.ToGrayPdf(outputFile)
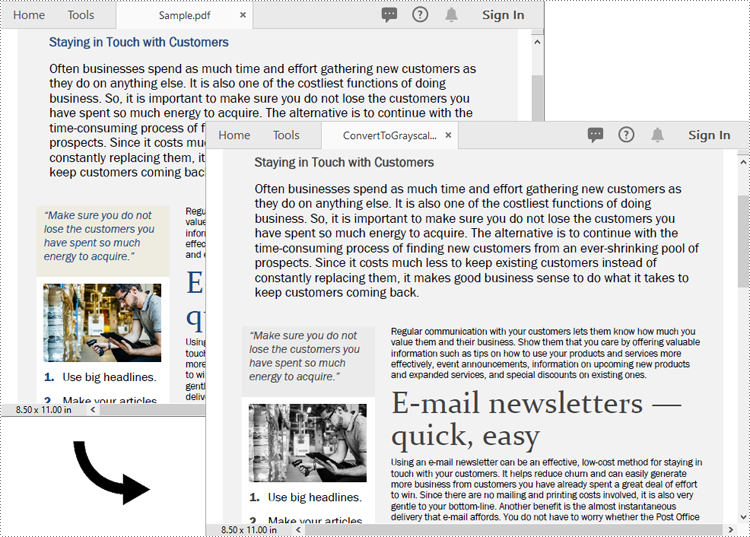
Convert PDF to Linearized in Python
To convert a PDF to linearized, you can use the PdfToLinearizedPdfConverter.ToLinearizedPdf() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Load a PDF document using the PdfToLinearizedPdfConverter class.
- Convert the PDF document to linearized using the PdfToLinearizedPdfConverter.ToLinearizedPdf() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import * from spire.pdf import * # Specify the input and output PDF file paths inputFile = "Sample.pdf" outputFile = "Output/ConvertToLinearizedPdf.pdf" # Load a PDF document using the PdfToLinearizedPdfConverter class converter = PdfToLinearizedPdfConverter(inputFile) # Convert the PDF document to a linearized PDF converter.ToLinearizedPdf(outputFile)
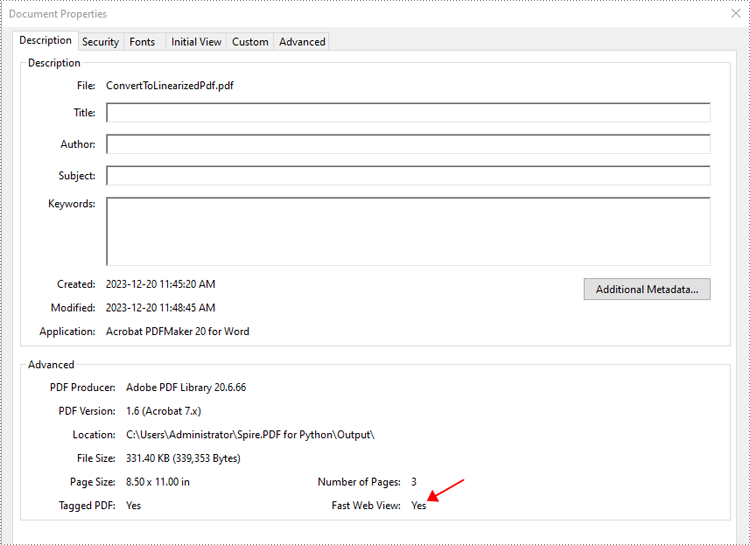
Open the result file in Adobe Acrobat and check the document properties. You will see that the value for "Fast Web View" is set to "Yes", indicating that the file has been linearized.
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
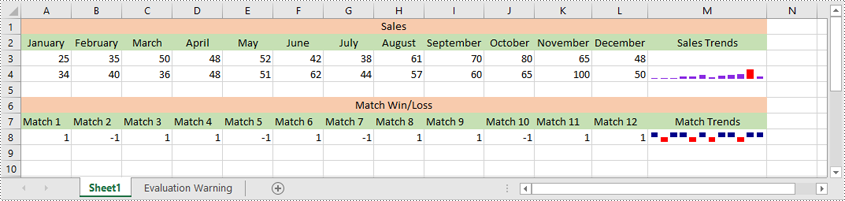
Sparklines in Excel are small, lightweight charts that fit inside individual cells of a worksheet. They are particularly useful for showing variations in data across rows or columns, allowing users to quickly identify trends without taking up much space. In this article, we'll demonstrate how to insert, modify, and delete sparklines in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Insert a Sparkline in Excel in Python
- Modify a Sparkline in Excel in Python
- Delete Sparklines from Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Insert a Sparkline in Excel in Python
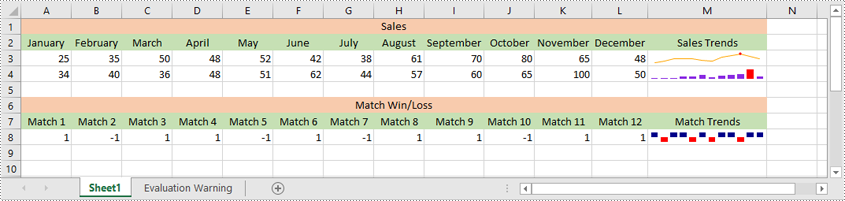
Excel offers 3 main types of sparklines:
- Line Sparkline: Shows data trends as a line, similar to a miniature line graph.
- Column Sparkline: Displays data as vertical bars, emphasizing individual data points.
- Win/Loss Sparkline: Illustrates positive and negative values, useful for tracking binary outcomes like wins or losses.
Spire.XLS for Python supports inserting all of the above types of sparklines. Below are the detailed steps for inserting a sparkline in Excel using Spire.XLS for Python:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Add a sparkline group to the worksheet using Worksheet.SparklineGroups.AddGroup() method.
- Specify the sparkline type, color, and data point color for the sparkline group.
- Add a sparkline collection to the group using SparklineGroup.Add() method, and then add a sparkline to the collection using SparklineCollection.Add() method.
- Save the resulting file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet in the workbook
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add a sparkline group to the worksheet
sparkline_group1 = sheet.SparklineGroups.AddGroup()
# Set the sparkline type to line
sparkline_group1.SparklineType = SparklineType.Line
# Set the sparkline color
sparkline_group1.SparklineColor = Color.get_Orange()
# Set the highest data point color
sparkline_group1.HighPointColor = Color.get_Red()
# Add a sparkline collection
sparklines1 = sparkline_group1.Add()
# Add a sparkline to the collection, define the data range for the sparkline and the target cell for displaying the sparkline
sparklines1.Add(sheet.Range["A3:L3"], sheet.Range["M3"])
# Add a sparkline group to the worksheet
sparkline_group2 = sheet.SparklineGroups.AddGroup()
# Set the sparkline type to column
sparkline_group2.SparklineType = SparklineType.Column
# Set the sparkline color
sparkline_group2.SparklineColor = Color.get_BlueViolet()
# Set the highest data point color
sparkline_group2.HighPointColor = Color.get_Red()
# Add a sparkline collection
sparklines2 = sparkline_group2.Add()
# Add a sparkline to the collection, define the data range for the sparkline and the target cell for displaying the sparkline
sparklines2.Add(sheet.Range["A4:L4"], sheet.Range["M4"])
# Add a sparkline group to the worksheet
sparkline_group3 = sheet.SparklineGroups.AddGroup()
# Set the sparkline type to stacked (win/loss)
sparkline_group3.SparklineType = SparklineType.Stacked
# Set the sparkline color
sparkline_group3.SparklineColor = Color.get_DarkBlue()
# Set the negative data point color
sparkline_group3.NegativePointColor = Color.get_Red()
# Add a sparkline collection
sparklines3 = sparkline_group3.Add()
# Add a sparkline to the collection, define the data range for the sparkline and the target cell for displaying the sparkline
sparklines3.Add(sheet.Range["A8:L8"], sheet.Range["M8"])
# Save the resulting workbook to file
workbook.SaveToFile("AddSparklines.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Modify a Sparkline in Excel in Python
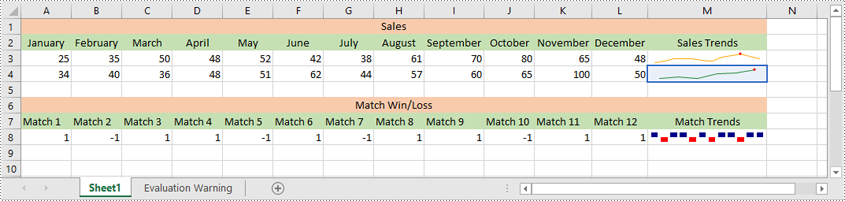
After inserting a sparkline, you can modify its type, color, and data source to make it more effective at displaying the information you need.
The following steps explain how to modify a sparkline in Excel using Spire.XLS for Python:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific sparkline group in the worksheet using Worksheet.SparklineGroups[index] property.
- Change the sparkline type and color for the sparkline group using SparklineGroup.SparklineType and SparklineGroup.SparklineColor properties.
- Get a specific sparkline in the group and change its data source using ISparklines.RefreshRanges() method.
- Save the resulting file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file that contains sparklines
workbook.LoadFromFile("AddSparklines.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet in the workbook
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the second sparkline group
sparklineGroup = sheet.SparklineGroups[1]
# Change the sparkline type
sparklineGroup.SparklineType = SparklineType.Line
# Change the sparkline color
sparklineGroup.SparklineColor = Color.get_ForestGreen()
# Change the data range of the sparkline
sparklines = sparklineGroup[0]
sparklines.RefreshRanges(sheet.Range["A4:F4"], sheet.Range["M4"])
# Save the resulting workbook to file
workbook.SaveToFile("ModifySparklines.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Delete Sparklines from Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python allows you to remove specific sparklines from a sparkline group and to remove the entire sparkline group from an Excel worksheet.
The following steps explain how to remove an entire sparkline group or specific sparklines from a sparkline group using Spire.XLS for Python:
- Create an object of the Workbook class
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific sparkline group in the worksheet using Worksheet.SparklineGroups[index] property.
- Delete the entire sparkline group using Worksheet.SparklineGroups.Clear() method. Or delete a specific sparkline using ISparklines.Remove() method.
- Save the resulting file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file that contains sparklines
workbook.LoadFromFile("AddSparklines.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet in the workbook
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the first sparkline group in the worksheet
sparklineGroup = sheet.SparklineGroups[0]
# Remove the first sparkline group from the worksheet
sheet.SparklineGroups.Clear(sparklineGroup)
# # Remove the first sparkline
# sparklines = sparklineGroup[0]
# sparklines.Remove(sparklines[0])
# Save the resulting workbook to file
workbook.SaveToFile("RemoveSparklines.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
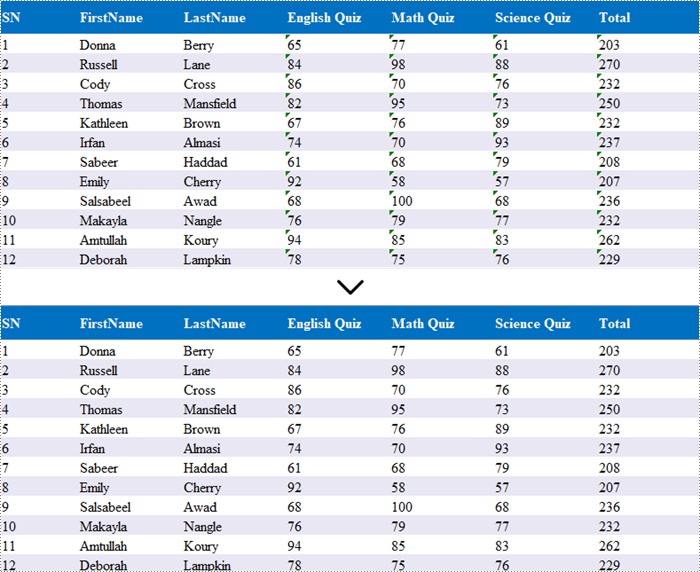
Transforming text to numbers and vice versa in Excel is essential for effective data management. By converting text to numbers, you enhance the accuracy of calculations and data processing, which is vital for activities such as financial reporting and statistical analysis. Conversely, changing numbers to text can improve formatting, making outputs clearer and more readable, ultimately presenting data in a more user-friendly way.
In this article, you will learn how to convert text to numbers and numbers to text in Excel using Spire.XLS for .NET.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Convert Text to Numbers in C#
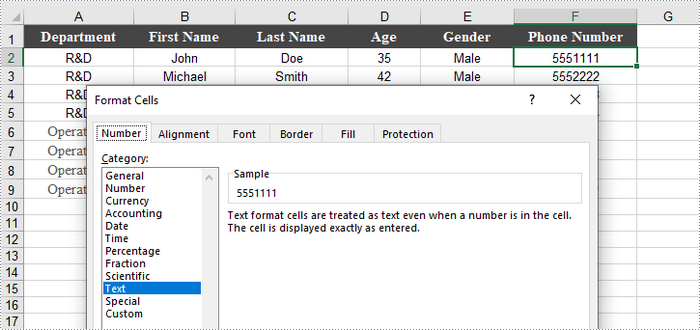
When you import data from an external source into Excel, you might notice a small green triangle in the upper-left corner of certain cells. This triangle serves as an error indicator, signaling that the number is formatted as text. When numbers are stored as text, it can lead to unexpected outcomes, such as formulas not calculating correctly and displaying as text instead of yielding results.
To convert text-formatted numbers back to numeric format, you can use the CellRange.ConvertToNumber() method. The CellRange object can refer to either a single cell or a range of cells.
Here are the steps to convert text to numbers in Excel:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Access a specific worksheet with Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Retrieve a cell or range of cells using Worksheet.Range property.
- Convert the text in the cell(s) to numbers using CellRange.ConvertToNumber() method.
- Save the document as a new Excel file.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
namespace ConvertTextToNumbers
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get a specific worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Get a cell range
CellRange range = worksheet.Range["D2:G13"];
// Convert text to number
range.ConvertToNumber();
// Save the workbook to a different Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("TextToNumbers.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
// Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
Convert Numbers to Text in C#
When working with numerical data in Excel, you may find occasions where converting numbers to text is necessary. This is especially crucial for data that requires specific formatting, such as IDs or phone numbers, where leading zeros must be preserved.
To convert a number in a cell to text, you can set the CellRange.NumberFormat property to @. The CellRange object can represent either a single cell or a range of cells.
Here are the steps to convert numbers to text in Excel:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Access a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Retrieve a specific cell or range of cells using Worksheet.Range property.
- Convert the numbers in the cell(s) to text by setting CellRange.NumberFormat to @.
- Save the document as a new Excel file.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
namespace ConvertNumbersToText
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Employee.xlsx");
// Get a specific worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Get a cell range
CellRange cellRange = worksheet.Range["F2:F9"];
// Convert numbers in the cell range to text
cellRange.NumberFormat = "@";
// Save the workbook to a different Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("NumbersToText.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
// Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
