
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Images in Excel can enhance data visualization and help convey information effectively. Apart from inserting/deleting images in Excel with Spire.XLS for Python, you can also use the library to replace existing images with new ones, or extract images for reuse or backup. This article will demonstrate how to replace or extract images in Excel in Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Replace Images in Excel with Python
To replace a picture in Excel, you can load a new picture and then set it as the value of the ExcelPicture.Picture property. The following are the detailed steps to replace an Excel image with another one.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Get a specified picture from the worksheet using Worksheet.Pictures[] property.
- Load an image and then replace the original picture with it using ExcelPicture.Picture property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile ("ExcelImg.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the first picture from the worksheet
excelPicture = sheet.Pictures[0]
# Replace the picture with another one
excelPicture.Picture = Image.FromFile("logo.png")
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("ReplaceImage.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)

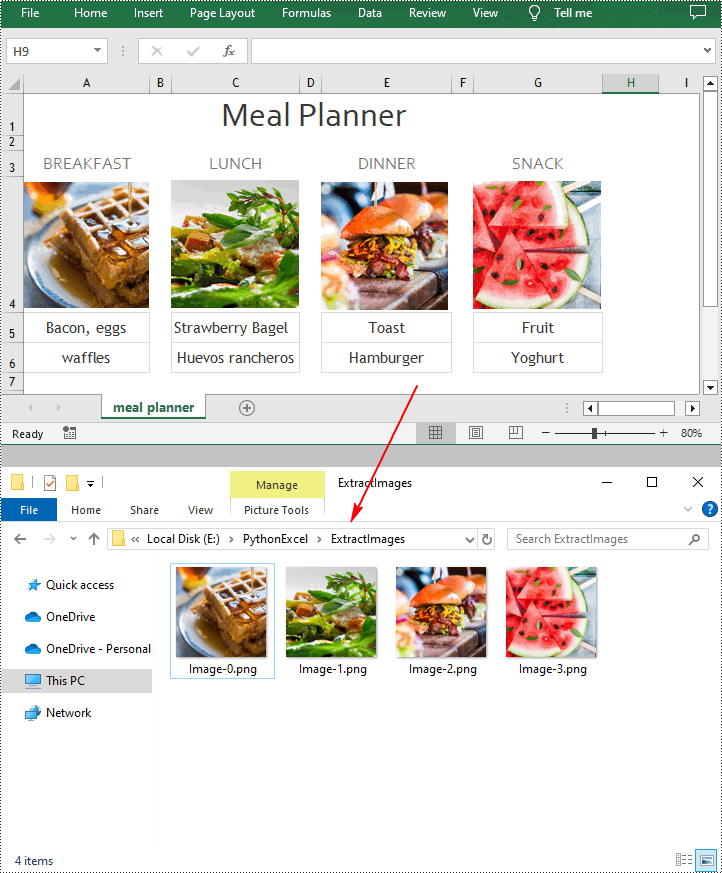
Extract Images from Excel with Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the ExcelPicture.Picture.Save() method to save the images in Excel to a specified file path. The following are the detailed steps to extract all images in an Excel worksheet at once.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Loop through to get all pictures in the worksheet using Worksheet.Pictures property.
- Extract pictures and save them to a specified file path using ExcelPicture.Picture.Save() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Test.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get all images in the worksheet
for i in range(sheet.Pictures.Count - 1, -1, -1):
pic = sheet.Pictures[i]
# Save each image as a PNG file
pic.Picture.Save("ExtractImages\\Image-{0:d}.png".format(i), ImageFormat.get_Png())
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
In the era of big data, facing the challenge of processing massive amounts of information stored in Excel documents, artificial intelligence (AI) technology provides a new solution for efficiently and accurately extracting key content and generating summaries.
This article focuses on the application of AI to automatically identify and extract core data from Excel documents, enabling the automated generation of concise and highlighted document summaries. This technology not only enhances data processing efficiency but also empowers decision-makers to gain deeper insights and utilize the data effectively. In the following sections, we will gradually explore how to apply AI technology to precisely extract summaries from Excel documents.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
The Excel AI integrated into Spire.XLS for .NET package, hence to begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Request a License Key of AI Product
A license key is required to run Spire.XLS AI, please contact our sales department (sales@e-iceblue.com) to request one.
Use AI to get Document Summaries
Spire.XLS AI provides the ExcelAI class, which encapsulates the ability to perform intelligent analysis and search on Excel data. In fact, ExcelAI goes beyond merely supporting intelligent analysis of Excel data, it also extends its capabilities to encompass a variety of file formats such as txt, csv, pdf, and md, thereby enabling cross-format intelligent processing and insights. Within this class, three key methods are included:
- UploadWorkbook(Workbook wb): This method is used to upload a Workbook object processed by Spire.XLS to the AI server, facilitating the integration of Excel content with the AI system's data.
- UploadFile(string fileName, Stream stream): This method is used to upload txt files or files in other formats to the AI server.
- DocumentSearch(string question, string file_server_path, bool enableHistory = false): This method allows posing specific questions to the AI system against a designated Excel document, generating intelligent responses based on its contents. The optional parameter enableHistory is set to false by default, if set to true, it enables the search history feature, allowing subsequent operations to track or leverage previous query results.
1. The following code demonstrates how to retrieve a summary of content from an Excel document:
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using Spire.Xls.AI;
using System.IO;
using System.Text;
// Define the file path of the Excel document
string inputfile = "input.xlsx";
// Create a new instance of the Workbook
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Load the Excel file
wb.LoadFromFile(inputfile);
// Create a new instance of the ExcelAI
ExcelAI excelAI = new ExcelAI();
// Upload the workbook and obtain the file path where it's stored in the AI system
string fpath = excelAI.UploadWorkbook(wb);
// Set the question to be asked to the AI system. In this case, asking it to generate a concise summary from the Excel
string question = "Please generate a concise summary from the document";
// Get the answer generated by the AI based on the question
string answer = excelAI.DocumentSearch(question, fpath, true);
// Create a StringBuilder object to append the answer
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.AppendLine(answer);
// Write the answer to the txt file
File.WriteAllText("SummaryFromExcel.txt", builder.ToString());
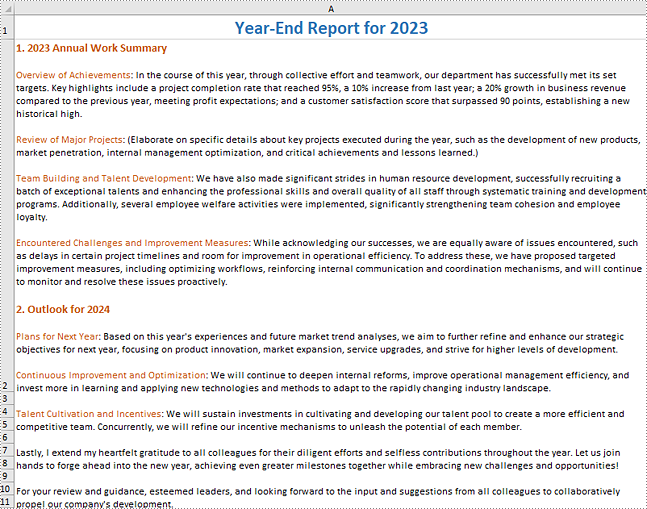
Input Excel Content:
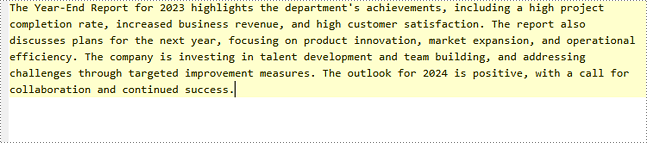
Generated TXT Content:
2. The following code demonstrates how to retrieve a summary of content from a TXT:
- C#
using Spire.Xls.AI;
using System.IO;
using System.Text;
// Define the file path of the txt
string inputfile = "input.txt";
// Create a new instance of the ExcelAI
ExcelAI excelAI = new ExcelAI();
// Open and read the content of the text file as a stream
using (Stream stream = File.Open(inputfile, FileMode.Open))
{
// Upload the text file to the AI system
string fpath = excelAI.UploadFile(inputfile, stream);
// Set the question to be asked to the AI system. In this case, asking it to generate a concise summary from the txt
string question = "Please generate a concise summary from the document";
// Get the answer generated by the AI based on the question
string answer = excelAI.DocumentSearch(question, fpath, true);
// Create a StringBuilder object to append the answer
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.AppendLine(answer);
// Write the answer to the txt file
File.WriteAllText("SummaryFromTxt.txt", builder.ToString());
}
Input TXT Content:

Generated TXT Content:

A column chart in PowerPoint is a graphical representation of data that uses bars or columns to show comparisons between categories. It is commonly used to display financial data, statistics, and other quantitative information. Each column represents a category, and the height of the column corresponds to the value associated with that category. Column charts are easy to create and customize within PowerPoint, allowing users to quickly visualize their data.
In this article, you will learn how to programmatically create column charts in a PowerPoint document using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Create a Clustered Column Chart in PowerPoint in Python
- Create a Stacked Column Chart in PowerPoint in Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Create a Clustered Column Chart in PowerPoint in Python
A clustered column chart is a type of bar graph where the bars (or columns) are grouped together in clusters or segments, with each cluster representing a category and the height of the columns within the cluster reflecting the value of a data point for that category.
To add a clustered column chart in PowerPoint using Spire.Prensetion for Python, you can use the ISlide.Shapes.AppendChartInit(type: ChartType, rectangle RectangleF, init bool) method and specify the chart type as ColumnClustered. This method returns an object of IChart class, which you can use to set the chart data, title, series labels, category labels, series values and other attributes.
The following are the steps to create a clustered column chart in PowerPoint in Python.
- Create a Presentation object.
- Get the first slide using Prenstion.Slides[] property.
- Add a clustered column chart to the side using ISlide.Shapes.AppendChartInit(type: ChartType, rectangle RectangleF, init bool).
- Add text and numbers to the chart sheet as chart data using IChart.ChartData property.
- Set series labels, category labels, series values and other attributes using the properties of the IChart class.
- Save the document to a PowerPoint file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Set slide size type
presentation.SlideSize.Type = SlideSizeType.Screen16x9
# Get the first slide
slide = presentation.Slides[0]
# Add clustered column chart
rect = RectangleF.FromLTRB(40, 80, 700, 450)
chart = slide.Shapes.AppendChartInit(ChartType.ColumnClustered, rect, False)
# Set chart title
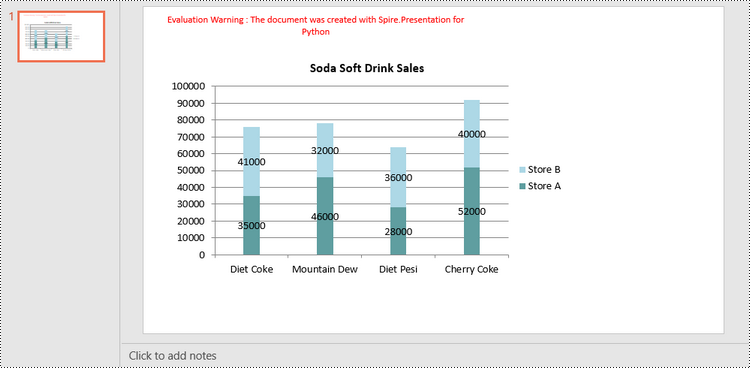
chart.ChartTitle.TextProperties.Text = "Soda Soft Drink Sales"
chart.ChartTitle.TextProperties.IsCentered = True
chart.ChartTitle.Height = 25
chart.HasTitle = True
# Insert text to chart as series labels
chart.ChartData[0,0].Text = "Product"
chart.ChartData[0,1].Text = "Store A"
chart.ChartData[0,2].Text = "Store B"
# Insert text to chart as category labels
chart.ChartData[1,0].Text = "Diet Coke"
chart.ChartData[2,0].Text = "Mountain Dew"
chart.ChartData[3,0].Text = "Diet Pesi"
chart.ChartData[4,0].Text = "Cherry Coke"
# Insert numbers to chart as values of series
Series1 = [35000, 46000, 28000, 52000]
Series2 = [41000, 32000, 36000, 40000]
i = 0
while i < len(Series1):
chart.ChartData[i + 1,1].NumberValue = Series1[i]
chart.ChartData[i + 1,2].NumberValue = Series2[i]
i += 1
# Set series labels
chart.Series.SeriesLabel = chart.ChartData["B1","C1"]
# Set category labels
chart.Categories.CategoryLabels = chart.ChartData["A2","A5"]
# Set values for series
chart.Series[0].Values = chart.ChartData["B2","B5"]
chart.Series[1].Values = chart.ChartData["C2","C5"]
# Set gap width
chart.GapWidth = 350
# Set overlap
chart.OverLap = -50
# Set fill color of each series
chart.Series[0].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
chart.Series[0].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_CadetBlue()
chart.Series[1].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
chart.Series[1].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_LightBlue()
# Add data labels
for i in range(len(Series1)):
chart.Series[0].DataLabels.Add()
chart.Series[1].DataLabels.Add()
# Save the document
presentation.SaveToFile("output/ClusteredColumnChart.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2019)
presentation.Dispose()

Create a Stacked Column Chart in PowerPoint in Python
A stacked column chart is a variation of the standard column chart where each column represents a category, and the height of the column corresponds to the total value of the category.
To add a stacked column chart in PowerPoint using Spire.Prensetion for Python, you use the ISlide.Shapes.AppendChartInit(type: ChartType, rectangle RectangleF, init bool) method and specify the chart type as ColumnStacked. Then, you can use to set the chart data, title, series labels, category labels, series values and other attributes using the properties of the IChart class.
The following are the steps to create a stacked column chart in PowerPoint in Python.
- Create a Presentation object.
- Get the first slide using Prenstion.Slides[] property.
- Add a stacked column chart to the side using ISlide.Shapes.AppendChartInit(type: ChartType, rectangle RectangleF, init bool).
- Add text and numbers to the chart sheet as chart data using IChart.ChartData property.
- Set series labels, category labels, series values and other attributes using the properties of the IChart class.
- Save the document to a PowerPoint file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Set slide size type
presentation.SlideSize.Type = SlideSizeType.Screen16x9
# Get the first slide
slide = presentation.Slides[0]
# Add a stacked column chart
rect = RectangleF.FromLTRB(40, 80, 700, 450)
chart = slide.Shapes.AppendChartInit(ChartType.ColumnStacked, rect, False)
# Set chart title
chart.ChartTitle.TextProperties.Text = "Soda Soft Drink Sales"
chart.ChartTitle.TextProperties.IsCentered = True
chart.ChartTitle.Height = 25
chart.HasTitle = True
# Insert text to chart as series labels
chart.ChartData[0,0].Text = "Product"
chart.ChartData[0,1].Text = "Store A"
chart.ChartData[0,2].Text = "Store B"
# Insert text to chart as category labels
chart.ChartData[1,0].Text = "Diet Coke"
chart.ChartData[2,0].Text = "Mountain Dew"
chart.ChartData[3,0].Text = "Diet Pesi"
chart.ChartData[4,0].Text = "Cherry Coke"
# Insert numbers to chart as values of series
Series1 = [35000, 46000, 28000, 52000]
Series2 = [41000, 32000, 36000, 40000]
i = 0
while i < len(Series1):
chart.ChartData[i + 1,1].NumberValue = Series1[i]
chart.ChartData[i + 1,2].NumberValue = Series2[i]
i += 1
# Set series labels
chart.Series.SeriesLabel = chart.ChartData["B1","C1"]
# Set category labels
chart.Categories.CategoryLabels = chart.ChartData["A2","A5"]
# Set values for series
chart.Series[0].Values = chart.ChartData["B2","B5"]
chart.Series[1].Values = chart.ChartData["C2","C5"]
# Set gap width
chart.GapWidth = 350
# Set fill color of each series
chart.Series[0].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
chart.Series[0].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_CadetBlue()
chart.Series[1].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
chart.Series[1].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_LightBlue()
# Add data labels
for i in range(len(Series1)):
chart.Series[0].DataLabels.Add()
chart.Series[1].DataLabels.Add()
# Save the document
presentation.SaveToFile("output/StackedColumnChart.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2019)
presentation.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
