
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
If you have additional pieces of information to include in your spreadsheet, inserting rows or columns can provide room for these new fields. In addition,
adding blank rows or columns between data sets can also help to effectively separate different categories of information, making them easier to read and analyze. This article will demonstrate how to insert rows and columns in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Insert a Row and a Column in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the Worksheet.InsertRow(rowIndex: int) and Worksheet.InsertColumn(columnIndex: int) methods for inserting a blank row and a blank column in an Excel worksheet. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Insert a row into the worksheet using Worksheet.InsertRow(rowIndex: int) method.
- Insert a column into the worksheet using Worksheet.InsertColumn(columnIndex: int) method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "input.xlsx" outputFile = "InsertRowAndColumn.xlsx" # Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() # Load an Excel document workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get a specified worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] # Insert a blank row as the 5th row in the worksheet worksheet.InsertRow(5) # Insert a blank column as the 4th column in the worksheet worksheet.InsertColumn(4) # Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2016) workbook.Dispose()
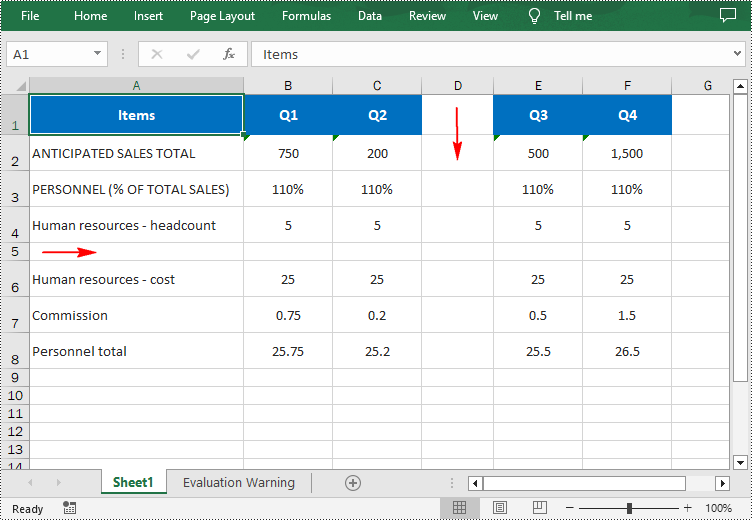
Insert Multiple Rows and Columns in Excel in Python
To insert multiple rows and columns into a worksheet, you can use the Worksheet.InsertRow(rowIndex: int, rowCount: int) and Worksheet.InsertColumn(columnIndex: int, columnCount: int) methods. The following are detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Insert multiple rows into the worksheet using Worksheet.InsertRow(rowIndex: int, rowCount: int) method.
- Insert multiple columns into the worksheet using Worksheet.InsertColumn(columnIndex: int, columnCount: int) method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "input.xlsx" outputFile = "InsertRowsAndColumns.xlsx" # Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() # Load an Excel document workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get a specified worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] # Insert three blank rows into the worksheet worksheet.InsertRow(5, 3) #Insert two blank columns into the worksheet worksheet.InsertColumn(4, 2) # Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2016) workbook.Dispose()
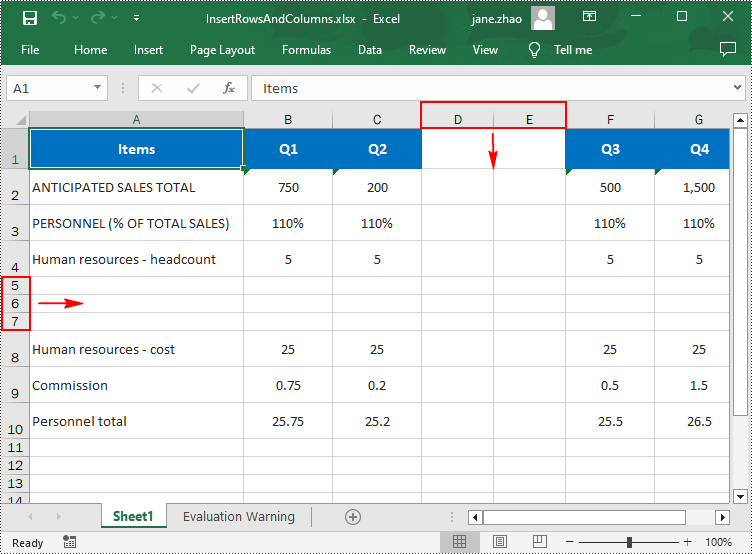
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Incorporating audio and videos in slides has become a common practice for creating interactive and dynamic PowerPoint presentations, which helps the presenter in sharing information, engaging the audience, and delivering impactful messages. However, as content requirements change, there arises a need to replace or update these multimedia elements. This article will show how to use Spire.Presentation for Python to replace audio and videos in PowerPoint presentations for content updating needs such as updating outdated videos, enhancing audio quality, or simply swapping in new content.
- Replace a Video in a PowerPoint Presentation with Python
- Replace an Audio in a PowerPoint Presentation with Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Replace a Video in a PowerPoint Presentation with Python
With Spire.Presentation for Python, developers can find the video shapes in slides and replace the video data through IVideo.EmbeddedVideoData property. It is important to note that, after replacing the video, the preview of the video should also be updated with the IVideo.PictureFill.Picture property. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Presentation class and load a PowerPoint presentation file using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the collection of the videos embedded in the presentation through Presentation.Videos property.
- Get the slide that contains the video to be replaced through Presentation.Slides[] property.
- Iterate through the shapes in the slide and determine if a shape is an instance of IVideo class. If it is, append the new video to the video collection using VideoCollection.AppendByStream() method and replace the original video with the new video through IVideo.EmbeddedVideoData property.
- Embed a new image to the presentation using Presentation.Images.AppendStream() method and set it as the preview of the video through IVideo.PictureFill.Picture.EmbedImage property. You can also set an online image as the preview through IVideo.PictureFill.Picture.Url property.
- Save the presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
from spire.presentation.common import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
pres = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
pres.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Get the second slide
slide = pres.Slides[1]
# Get the videos in the presentation
videos = pres.Videos
# Iterate through the shapes on the slide
for shape in slide.Shapes:
# Check if the shape is a video
if isinstance(shape, IVideo):
video = shape if isinstance(shape, IVideo) else None
# Append a new video to the video collection
videoData = videos.AppendByStream(Stream("Ocean2.mp4"))
# Replace the video in the shape with the new video
video.EmbeddedVideoData = videoData
# Embed a picture in the presentation
imageData = pres.Images.AppendStream(Stream("Ocean2.png"))
# Set the new picture as the preview of the video
video.PictureFill.Picture.EmbedImage = imageData
# Save the presentation
pres.SaveToFile("output/ReplaceVideo.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
pres.Dispose()
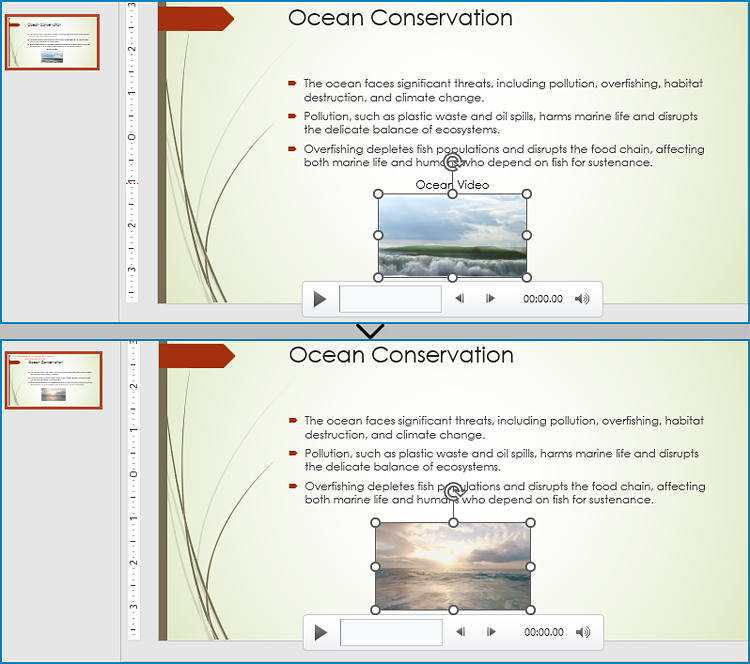
Replace an Audio in a PowerPoint Presentation with Python
Similarly, developers can also use Spire.Presentation for Python to find specific audio in a presentation slide and replace the audio data. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Presentation class and load a PowerPoint presentation file using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the collection of the audio embedded in the presentation through Presentation.WavAudios property.
- Get the slide that contains audio to be replaced through Presentation.Slides[] property.
- Iterate through each shape in the slide and check if a shape is an instance of IAudio class. If it is, append the new audio to the audio collection using WavAudioCollection.Append() method and replace the original audio with the new audio through IAudio.Data property.
- Save the presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
from spire.presentation.common import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
pres = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation file
pres.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Get the audio collection from the presentation
audios = pres.WavAudios
# Get the slide that contains the audio
slide = pres.Slides[0]
# Iterate through each shape in the slide
for shape in slide.Shapes:
# Check if the shape is an audio shape
if isinstance(shape, IAudio):
audio = shape if isinstance(shape, IAudio) else None
# Load an audio file
stream = Stream("Wave.wav")
# Replace the audio in the shape
audioData = audios.Append(stream)
audio.Data = audioData
# Save the presentation
pres.SaveToFile("output/ReplaceAudio.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
pres.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Directly extracting text has emerged as a crucial method for obtaining textual information from information-dense PowerPoint presentations. By utilizing Python programs, users can conveniently and quickly access the content within slides, enabling efficient collection of information and further data processing. This article shows how to use Spire.Presentation for Python to extract text from PowerPoint presentations, including text in slides, speaker notes, and comments.
- Extract Text from Presentation Slides with Python
- Extract Text from Speaker Notes with Python
- Extract Text from Presentation Comments with Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Extract Text from Presentation Slides with Python
The text within PowerPoint presentation slides is placed within shapes. Therefore, developers can extract the text from the presentation by accessing all the shapes within each slide and extracting the text contained within them. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Presentation class and load PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through the slides in the presentation and then iterate through the shapes in each slide.
- Check if a shape is an IAutoShape instance. If it is, get the paragraphs in the shape through IAutoShape.TextFrame.Paragraphs property and then get the text in the paragraphs through Paragraph.Text property.
- Write the slide text to a text file.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
from spire.presentation.common import *
# Create an object of Presentation class
pres = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
pres.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
text = []
# Loop through each slide
for slide in pres.Slides:
# Loop through each shape
for shape in slide.Shapes:
# Check if the shape is an IAutoShape instance
if isinstance(shape, IAutoShape):
# Extract the text from the shape
for paragraph in (shape if isinstance(shape, IAutoShape) else None).TextFrame.Paragraphs:
text.append(paragraph.Text)
# Write the text to a text file
f = open("output/SlideText.txt","w", encoding = 'utf-8')
for s in text:
f.write(s + "\n")
f.close()
pres.Dispose()
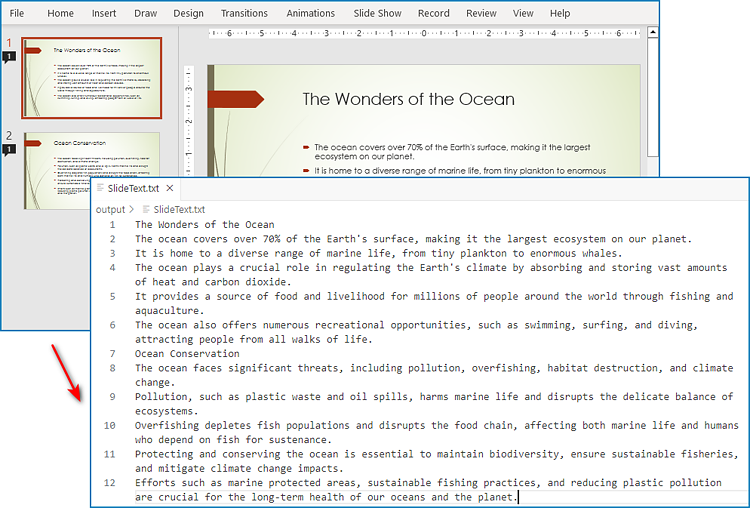
Extract Text from Speaker Notes with Python
Speaker notes are additional information that provides guidance to the presenter and are not visible to the audience. The text in speaker notes of each slide is stored in the notes slide and developers can extract the text through NotesSlide.NotesTextFrame.Text property. The detailed steps for extracting text in speaker notes are as follows:
- Create an object of Presentation class and load PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through each slide.
- Get the note slide through ISlide.NotesSlide property and retrieve the text through NotesSlide.NotesTextFrame.Text property.
- Write the speaker note text to a text file.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
from spire.presentation.common import *
# Create an object of Presentation class
pres = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
pres.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
list = []
# Iterate through each slide
for slide in pres.Slides:
# Get the notes slide
notesSlide = slide.NotesSlide
# Get the notes
notes = notesSlide.NotesTextFrame.Text
list.append(notes)
# Write the notes to a text file
f = open("output/SpeakerNoteText.txt", "w", encoding="utf-8")
for note in list:
f.write(note)
f.write("\n")
f.close()
pres.Dispose()

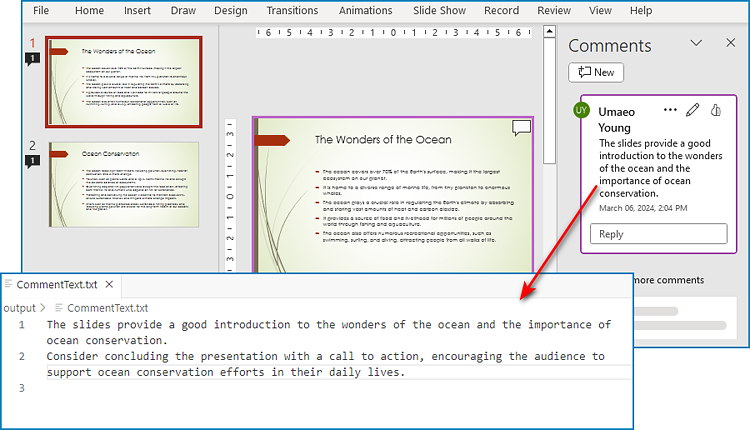
Extract Text from Presentation Comments with Python
With Spire.Presentation for Python, developers can also extract the text from comments in PowerPoint presentations by getting comments from slides with ISlide.Comments property and retrieving text from comments with Comment.Text property. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Presentation class and load PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through each slide and get the comment from each slide through ISlide.Comments property.
- Iterate through each comment and retrieve the text from each comment through Comment.Text property.
- Write the comment text to a text file.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
from spire.presentation.common import *
# Create an object of Presentation class
pres = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
pres.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
list = []
# Iterate through all slides
for slide in pres.Slides:
# Get all comments from the slide
comments = slide.Comments
# Iterate through the comments
for comment in comments:
# Get the comment text
commentText = comment.Text
list.append(commentText)
# Write the comments to a text file
f = open("output/CommentText.txt", "w", encoding="utf-8")
for i in range(len(list)):
f.write(list[i] + "\n")
f.close()
pres.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
