
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Excel’s AutoFilter feature is a powerful tool that allows you to quickly filter worksheet data based on specific criteria. When applying auto filter to a range of cells, you can display only those rows that meet certain conditions and hide the rest of the data.
However, while filters simplify workflows, knowing how to remove auto filters in Excel is equally critical to maintaining accurate, accessible, and error-free datasets. In this article, you will learn how to add or remove AutoFilters in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python library.
- Installation Guide for Spire.XLS for Python
- How to Use Excel Auto Filters in Python
- How to Remove Auto Filters in Excel
- Conclusion
Installation Guide for Spire.XLS for Python
Spire.XLS for Python is a robust library that enables developers to automate AutoFilter operations in Excel, including adding or removing auto filters.
To install the Python library, open your terminal or command prompt and run the following:
pip install Spire.XLSThe pip tool will search for the latest version of the Spire.XLS library on the Python Package Index (PyPI) and then download and install it along with any necessary dependencies.
How to Use Excel Auto Filters in Python
Add AutoFilter in Excel in Python
Excel AutoFilter can be applied to entire columns or specified cell ranges. The following are the core properties used:
- Worksheet.AutoFilters property: Gets a collection of auto filters in the worksheet, and return an AutoFiltersCollection object.
- AutoFiltersCollection.Range property: Specify the cell range to be filtered.
Code Example:
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
inputFile = "Data.xlsx"
outputFile = "ExcelAutoFilter.xlsx"
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Create an AutoFilter in the sheet and specify the range to be filtered
sheet.AutoFilters.Range = sheet.Range["A1:C1"]
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()Result: Dropdown arrows appear in the header row for filtering.
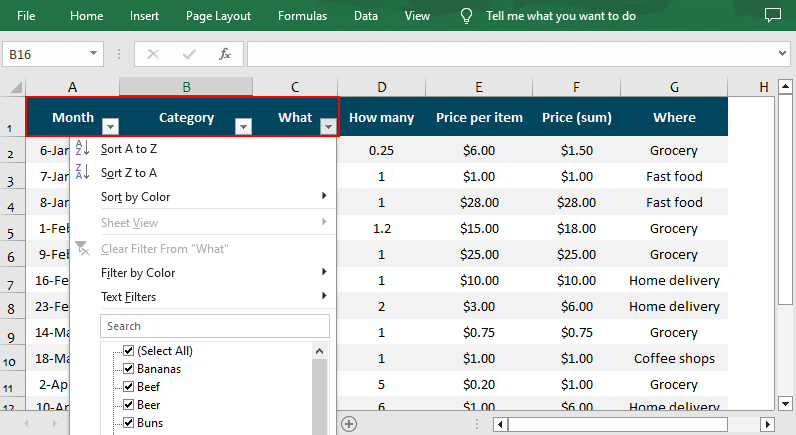
Different Excel Filter Types in Spire.XLS
The AutoFiltersCollection class of the Spire.XLS for Python library offers various methods for you to filter data in Excel in different ways. Check below for the details:
| Filters | Details |
| Filter text data | Use the AddFilter() to filter cells that contain specified text content. |
| Filter dates | Use the AddDateFilter() method to filter dates associated with the specified year/month/date, etc. |
| Filter blank / non-blank cells |
|
| Filter by color |
|
| Custom filter | Use the CustomFilter() method to filter by the custom criteria. |
Apply Custom Auto Filter in Excel in Python
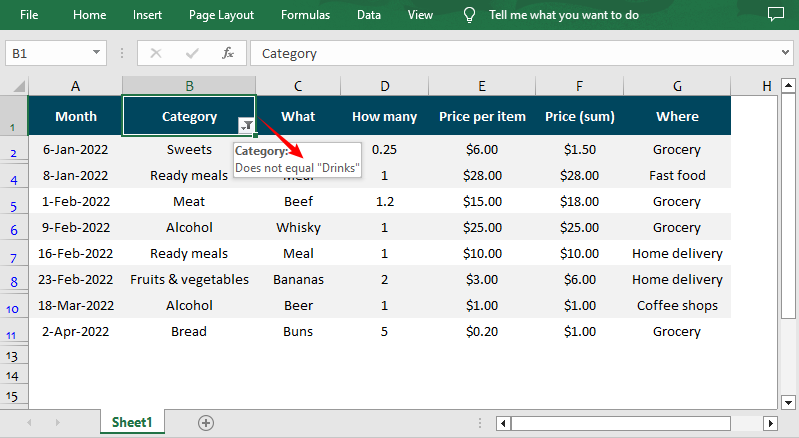
After adding one of the above filters, you can use the AutoFiltersCollection.Filter() method to apply the filter within the given range. The following is a code example of applying a custom AutoFilter to filter data that is not equal to the specified text string.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
inputFile = "Data.xlsx"
outputFile = "CustomFilter.xlsx"
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
#Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
#Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Create an auto filter in the sheet and specify the range to be filtered
sheet.AutoFilters.Range = sheet.Range["B1:B12"]
# Get the column to be filtered
filtercolumn = sheet.AutoFilters[0]
# Add a custom filter to filter data that does not contain the string "Drinks"
strCrt = String("Drinks")
sheet.AutoFilters.CustomFilter(filtercolumn , FilterOperatorType.NotEqual, strCrt)
# Apply the filter
sheet.AutoFilters.Filter()
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()Result: Only cells that are not equal to the string “Drinks” are visible.
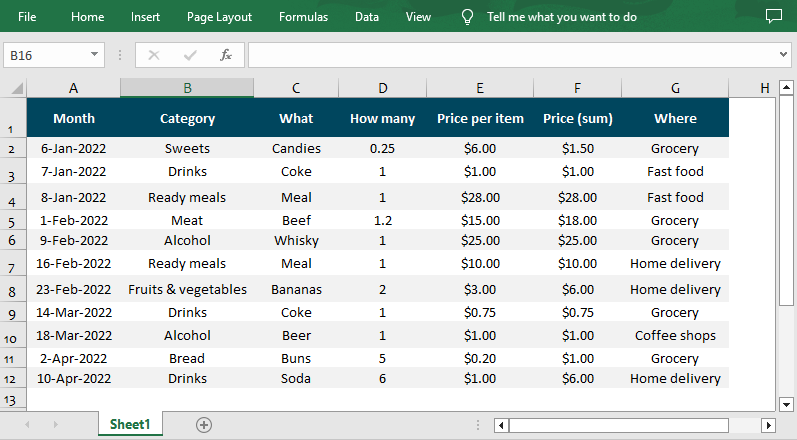
How to Remove Auto Filters in Excel in Python
AutoFilters are great for focusing on specific data, but leaving them active can lead to critical issues. Removing auto filters ensures:
- Full data disclosure: All rows/columns are visible.
- Consistent formatting: Eliminates dropdown arrows for a cleaner look.
- Avoid confusion: Prevents recipients from misinterpreting filtered data as the complete dataset.
Spire.XLS for Python provides the AutoFiltersCollection.Clear() method to remove or delete all AutoFilters from an Excel worksheet. Here’s the complete code example:
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
inputFile = "CustomFilter.xlsx"
outputFile = "RemoveAutoFilter.xlsx"
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Delete AutoFilter from the sheet
sheet.AutoFilters.Clear()
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()Result: All rows are visible, and AutoFilter dropdowns are removed.
Conclusion
With Spire.XLS for Python, adding or removing auto filters in Excel becomes a seamless, automated process. This guide covered installation, basic and custom filters, and code examples to help you streamline data tasks. For more advanced features, explore the Python Excel library’s full documentation.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.XLS for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Protecting valuable and sensitive information from unauthorized access is a crucial task for individuals and organizations alike. When it comes to sharing and storing confidential Word documents, such as financial records, legal documents, or personal records, encrypting the documents provides extra protection for their security and confidentiality. Moreover, using Python, users can easily encrypt large numbers of Word documents. This article shows how to use Spire.Doc for Python to encrypt Word documents in Python programs.
- Encrypt a Word Document with a Password
- Change the Password of a Word Document
- Remove the Encryption from a Word Document
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Encrypt a Word Document with a Password
Using the Document.Encrypt(password: str) method provided by Spire.Doc for Python, developers can set an open password for a Word document, ensuring that only authorized people can open and view the document. The detailed steps for encrypting a Word document with a password are as follows:
- Create an instance of Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Encrypt the document using Document.Encrypt() method.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an instance of Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Encrypt the document
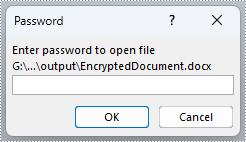
doc.Encrypt("password")
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/EncryptedDocument.docx")
doc.Close()
Change the Encryption from a Word Document
By passing the password as the parameter, developers can load an encrypted document using Document.LoadFromFile(fileName: str, fileFormat: FileFormat, password: str) method. After loading the encrypted document, the Document.Encrypt() method can be used to set a new password. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an instance of Document class.
- Load an encrypted Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Change the password of the document using Document.Encrypt() method.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an instance of Document class
doc = Document()
# Load an encrypted Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("output/EncryptedDocument.docx", FileFormat.Docx, "password")
# Change the password
doc.Encrypt("password1")
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/ChangeDocument.docx")
doc.Close()
Remove the Password from a Word Document
After loading an encrypted Word document, developers can also use Document.RemoveEncryption() method to remove the encryption from the document directly, thus making the document available to all users. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an instance of Document class.
- Load an encrypted Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove the password using Document.RemoveEncryption() method.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an instance of Document class
doc = Document()
# Load an encrypted Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("output/EncryptedDocument.docx", FileFormat.Auto, "password")
# Remove the password
doc.RemoveEncryption()
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/RemovePassword.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Flattening forms in PDF means transforming the interactive form fields (such as text boxes, checkboxes, and drop-down menus) into static content. Once a form is flattened, it cannot be edited or filled out anymore. When you need to maintain a permanent and unalterable record of a completed form, flattening is essential. This ensures that the data entered into the form fields cannot be modified or tampered with, providing a reliable reference for future use. In this article, we will demonstrate how to flatten forms in PDF in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
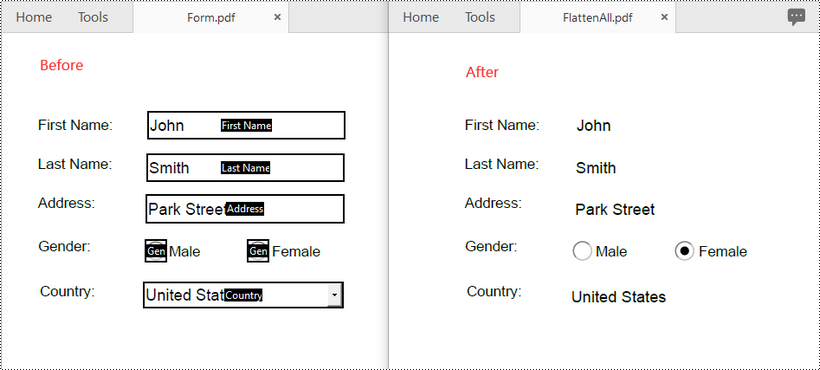
Flatten All Forms in a PDF in Python
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfDocument.Form.IsFlatten property, which enables you to flatten all forms in a PDF file. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Flatten all forms in the PDF file by setting the PdfDocument.Form.IsFlatten property to True.
- Save the result file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import * from spire.pdf import * # Specify the input and output PDF file paths input_file = "Form.pdf" output_file = "FlattenAll.pdf" # Create an object of the PdfDocument class doc = PdfDocument() # Load a PDF file doc.LoadFromFile(input_file) # Flatten all forms in the PDF file doc.Form.IsFlatten = True # Save the result file doc.SaveToFile(output_file) doc.Close()
Flatten a Specific Form in a PDF in Python
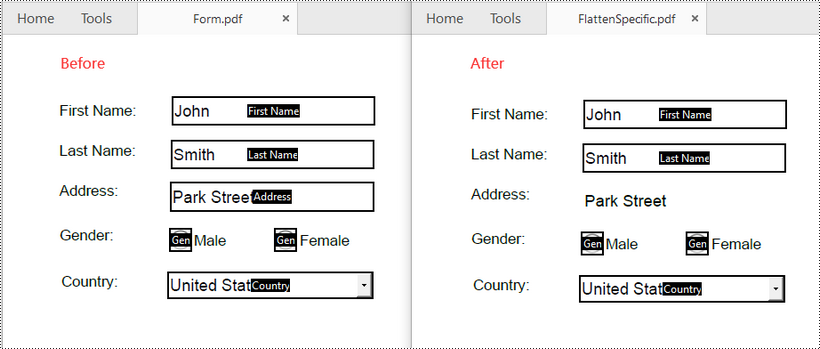
To flatten a specific form in a PDF file, you can use the PdfField.Flatten property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load a PDF file using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the forms of the PDF file using PdfDocument.Form property.
- Get a specific form by its index or name using PdfFormWidget.FieldsWidget.get_Item() method.
- Flatten the form by setting the PdfField.Flatten property to True.
- Save the result file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Specify the input and output PDF file paths
input_file = "Form.pdf"
output_file = "FlattenSpecific.pdf"
# Create an object of the PdfDocument class
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile(input_file)
# Get the forms of the PDF file
loadedForm = doc.Form
# Get a specific form by its index or name
formWidget = PdfFormWidget(loadedForm)
form = formWidget.FieldsWidget.get_Item(2)
# form = formWidget.FieldsWidget.get_Item("Address")
# Flatten the specific form
form.Flatten = True
# Save the result file
doc.SaveToFile(output_file)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
