
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Creating a fillable form in Word allows you to design a document that can be easily completed and customized by others. Whether you need to collect information, gather feedback, or create an interactive document, fillable forms provide a convenient way to capture data electronically. By adding various elements such as text fields, checkboxes, dropdown menus, and more, you can tailor the form to your specific requirements.
To create a fillable form in Word, you probably need to use the following tools.
- Content Controls: The areas where users input information in a form.
- Tables: Tables are used in forms to align text and form fields, and to create borders and boxes.
- Protection: Allows users to populate fields but not to make changes to the rest of the document.
In Word, content controls serve as containers for structured documents, allowing users to organize content within a document. Word 2013 provides ten types of content controls. This article introduces how to create a fillable form in Word that includes the following seven commonly-used content controls using Spire.Doc for Python.
| Content Control | Description |
| Plain Text | A text field limited to plain text, so no formatting can be included. |
| Rich Text | A text field that can contain formatted text or other items, such as tables, pictures, or other content controls. |
| Picture | Accepts a single picture. |
| Drop-Down List | A drop-down list displays a predefined list of items for the user to choose from. |
| Combo Box | A combo box enables users to select a predefined value in a list or type their own value in the text box of the control. |
| Check Box | A check box provides a graphical widget that allows the user to make a binary choice: yes (checked) or no (not checked). |
| Date Picker | Contains a calendar control from which the user can select a date. |
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Create a Fillable Form in Word in Python
Spire.Doc for Python offers the StructureDocumentTagInline class, which is utilized to generate structured document tags within a paragraph. By utilizing the SDTProperties property and SDTContent property of this class, one can define the properties and content of the current structured document tag. Below are the step-by-step instructions for creating a fill form in a Word document in Python.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Add a table using Section.AddTable() method.
- Add a paragraph to a specific table cell using TableCell.AddParagraph() method.
- Create an instance of StructureDocumentTagInline class, and add it to the paragraph as a child object using Paragraph.ChildObjects.Add() method.
- Specify the type, content and other attributes of the structured document tag through the SDTProperties property and the SDTContent property of the StructureDocumentTagInline object.
- Prevent users from editing content outside form fields using Document.Protect() method.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Add a table
table = section.AddTable(True)
table.ResetCells(7, 2)
table.SetColumnWidth(0, 120, CellWidthType.Point)
table.SetColumnWidth(1, 350, CellWidthType.Point)
# Add text to the cells of the first column
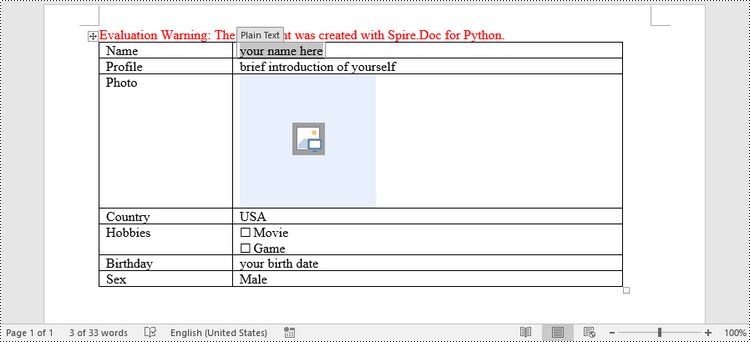
paragraph = table.Rows.get_Item(0).Cells.get_Item(0).AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Name")
paragraph = table.Rows[1].Cells[0].AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Profile")
paragraph = table.Rows[2].Cells[0].AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Photo")
paragraph = table.Rows[3].Cells[0].AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Country")
paragraph = table.Rows[4].Cells[0].AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Hobbies")
paragraph = table.Rows[5].Cells[0].AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Birthday")
paragraph = table.Rows[6].Cells[0].AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Sex")
# Add a plain text content control to the cell (0,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[0].Cells[1].AddParagraph()
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.Text
sdt.SDTProperties.Alias = "Plain Text"
sdt.SDTProperties.Tag = "Plain Text"
sdt.SDTProperties.IsShowingPlaceHolder = True
text = SdtText(True)
text.IsMultiline = False
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = text
textRange = TextRange(doc)
textRange.Text = "your name here"
sdt.SDTContent.ChildObjects.Add(textRange)
# Add a rich text content control to the cell (1,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[1].Cells[1].AddParagraph()
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.RichText
sdt.SDTProperties.Alias = "Rich Text"
sdt.SDTProperties.Tag = "Rich Text"
sdt.SDTProperties.IsShowingPlaceHolder = True
text = SdtText(True)
text.IsMultiline = False
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = text
textRange = TextRange(doc)
textRange.Text = "brief introduction of yourself"
sdt.SDTContent.ChildObjects.Add(textRange )
# Add a picture content control to the cell (2,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[2].Cells[1].AddParagraph()
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.Picture
sdt.SDTProperties.Alias = "Picture"
sdt.SDTProperties.Tag = "Picture"
sdtPicture = SdtPicture(True)
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = sdtPicture
pic = DocPicture(doc)
pic.LoadImage("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\placeHolder.png")
sdt.SDTContent.ChildObjects.Add(pic)
# Add a dropdown list content control to the cell (3,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[3].Cells[1].AddParagraph();
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.DropDownList
sdt.SDTProperties.Alias = "Dropdown List"
sdt.SDTProperties.Tag = "Dropdown List"
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
stdList = SdtDropDownList()
stdList.ListItems.Add(SdtListItem("USA", "1"))
stdList.ListItems.Add(SdtListItem("China", "2"))
stdList.ListItems.Add(SdtListItem("Briza", "3"))
stdList.ListItems.Add(SdtListItem("Austrilia", "4"))
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = stdList;
textRange = TextRange(doc)
textRange .Text = stdList.ListItems[0].DisplayText
sdt.SDTContent.ChildObjects.Add(textRange )
# Add two check box content controls to the cell (4,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[4].Cells[1].AddParagraph()
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.CheckBox
sdtCheckBox = SdtCheckBox()
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = sdtCheckBox
textRange = TextRange(doc)
sdt.ChildObjects.Add(textRange)
sdtCheckBox.Checked = False
paragraph.AppendText(" Movie")
paragraph = table.Rows[4].Cells[1].AddParagraph();
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.CheckBox
sdtCheckBox = SdtCheckBox()
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = sdtCheckBox
textRange = TextRange(doc)
sdt.ChildObjects.Add(textRange)
sdtCheckBox.Checked = False
paragraph.AppendText(" Game")
# Add a date picker content control to the cell (5,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[5].Cells[1].AddParagraph()
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.DatePicker
sdt.SDTProperties.Alias = "Date Picker"
sdt.SDTProperties.Tag = "Date Picker"
stdDate = SdtDate()
stdDate.CalendarType = CalendarType.Default
stdDate.DateFormat = "yyyy.MM.dd"
stdDate.FullDate = DateTime.get_Now()
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = stdDate
textRange = TextRange(doc)
textRange.Text = "your birth date"
sdt.SDTContent.ChildObjects.Add(textRange)
# Add a combo box content control to the cell (6,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[6].Cells[1].AddParagraph()
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.ComboBox
sdt.SDTProperties.Alias = "Combo Box"
sdt.SDTProperties.Tag = "Combo Box"
stdComboBox = SdtComboBox()
stdComboBox.ListItems.Add(SdtListItem("Male"))
stdComboBox.ListItems.Add(SdtListItem("Female"))
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = stdComboBox
textRange = TextRange(doc)
textRange.Text = stdComboBox.ListItems[0].DisplayText
sdt.SDTContent.ChildObjects.Add(textRange)
# Allow users to edit the form fields only
doc.Protect(ProtectionType.AllowOnlyFormFields, "permission-psd")
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/Form.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
PDF forms are commonly used to collect user information, and extracting form values programmatically allows for automated processing of submitted data, ensuring accurate data collection and analysis. After extraction, you can generate reports based on form field values or migrate them to other systems or databases. In this article, you will learn how to extract form field values from PDF with Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Extract Form Field Values from PDF with Python
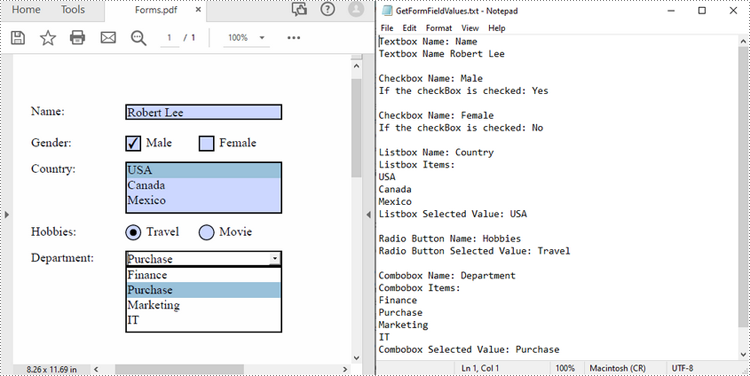
Spire.PDF for Python supports various types of PDF form fields, including:
- Text box field (represented by the PdfTextBoxFieldWidget class)
- Check box field (represented by the PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget class)
- Radio button field (represented by the PdfRadioButtonListFieldWidget class)
- List box field (represented by the PdfListBoxWidgetFieldWidget class)
- Combo box field (represented by the PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget class)
Before extracting data from the PDF forms, it is necessary to determine the specific type of each form field first, and then you can use the properties of the corresponding form field class to extract their values accurately. The following are the detailed steps.
- Initialize an instance of the PdfDocument class.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the form in the PDF document using PdfDocument.Form property.
- Create a list to store the extracted form field values.
- Iterate through all fields in the PDF form.
- Determine the types of the form fields, then get the names and values of the form fields using the corresponding properties.
- Write the results to a text file.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
inputFile = "Forms.pdf"
outputFile = "GetFormFieldValues.txt"
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get PDF forms
pdfform = pdf.Form
formWidget = PdfFormWidget(pdfform)
sb = []
# Iterate through all fields in the form
if formWidget.FieldsWidget.Count > 0:
for i in range(formWidget.FieldsWidget.Count):
field = formWidget.FieldsWidget.get_Item(i)
# Get the name and value of the textbox field
if isinstance(field, PdfTextBoxFieldWidget):
textBoxField = field if isinstance(field, PdfTextBoxFieldWidget) else None
name = textBoxField.Name
value = textBoxField.Text
sb.append("Textbox Name: " + name + "\r")
sb.append("Textbox Name " + value + "\r\n")
# Get the name of the listbox field
if isinstance(field, PdfListBoxWidgetFieldWidget):
listBoxField = field if isinstance(field, PdfListBoxWidgetFieldWidget) else None
name = listBoxField.Name
sb.append("Listbox Name: " + name + "\r")
# Get the items of the listbox field
sb.append("Listbox Items: \r")
items = listBoxField.Values
for i in range(items.Count):
item = items.get_Item(i)
sb.append(item.Value + "\r")
# Get the selected item of the listbox field
selectedValue = listBoxField.SelectedValue
sb.append("Listbox Selected Value: " + selectedValue + "\r\n")
# Get the name of the combo box field
if isinstance(field, PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget):
comBoxField = field if isinstance(field, PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget) else None
name = comBoxField.Name
sb.append("Combobox Name: " + name + "\r");
# Get the items of the combo box field
sb.append("Combobox Items: \r");
items = comBoxField.Values
for i in range(items.Count):
item = items.get_Item(i)
sb.append(item.Value + "\r")
# Get the selected item of the combo box field
selectedValue = comBoxField.SelectedValue
sb.append("Combobox Selected Value: " + selectedValue + "\r\n")
# Get the name and selected item of the radio button field
if isinstance(field, PdfRadioButtonListFieldWidget):
radioBtnField = field if isinstance(field, PdfRadioButtonListFieldWidget) else None
name = radioBtnField.Name
selectedValue = radioBtnField.SelectedValue
sb.append("Radio Button Name: " + name + "\r");
sb.append("Radio Button Selected Value: " + selectedValue + "\r\n")
# Get the name and status of the checkbox field
if isinstance(field, PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget):
checkBoxField = field if isinstance(field, PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget) else None
name = checkBoxField.Name
sb.append("Checkbox Name: " + name + "\r")
state = checkBoxField.Checked
stateValue = "Yes" if state else "No"
sb.append("If the checkBox is checked: " + stateValue + "\r\n")
# Write the results to a text file
f2=open(outputFile,'w', encoding='UTF-8')
for item in sb:
f2.write(item)
f2.close()
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Grouping rows and columns in Excel provides a more organized and structured view of data, making it easier to analyze and understand complex datasets. After grouping related rows or columns, you can collapse or expand them as needed to focus on specific subsets of information while hiding details. In this article, you will learn how to group or ungroup rows and columns , as well as how to collapse or expand groups in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Group Rows and Columns in Excel in Python
- Ungroup Rows and Columns in Excel in Python
- Expand or Collapse Groups in Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
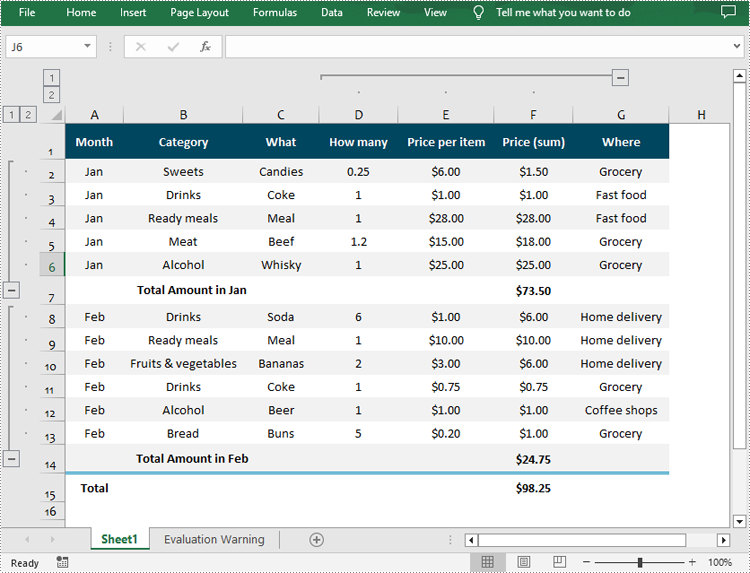
Group Rows and Columns in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the Worksheet.GroupByRows() and Worksheet.GroupByColumns() methods to group specific rows and columns in an Excel worksheet. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Group rows using Worksheet.GroupByRows() method.
- Group columns using Worksheet.GroupByColumns() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "Data.xlsx" outputFile = "GroupRowsAndColumns.xlsx" # Create a Workbook object workbook = Workbook() # Load a sample Excel file workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get the first worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] # Group rows sheet.GroupByRows(2, 6, False) sheet.GroupByRows(8, 13, False) # Group columns sheet.GroupByColumns(4, 6, False) # Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2016) workbook.Dispose()
Ungroup Rows and Columns in Excel in Python
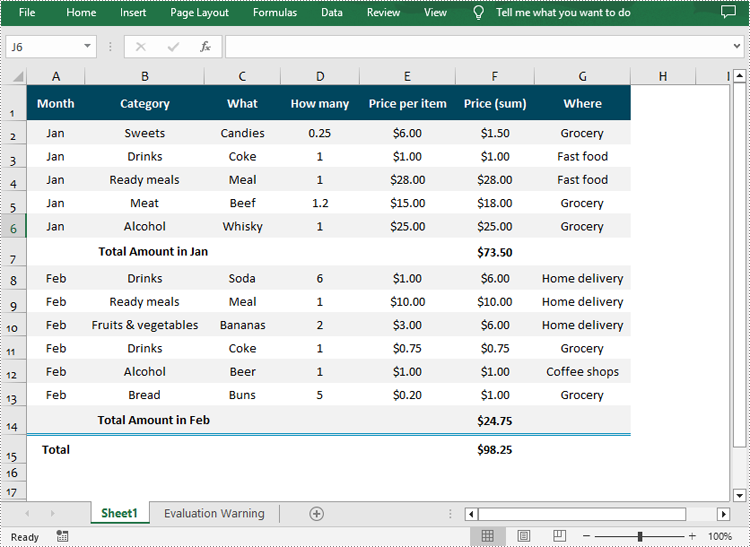
Ungrouping rows and columns in Excel refer to the process of reversing the grouping operation and restoring the individual rows or columns to their original state.
To ungroup rows and columns in an Excel worksheet, you can use the Worksheet.UngroupByRows() and Worksheet.UngroupByColumns() methods. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Ungroup rows using Worksheet.UngroupByRows() method.
- Ungroup columns using Worksheet.UngroupByColumns() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "GroupRowsAndColumns.xlsx" outputFile = "UnGroupRowsAndColumns.xlsx" # Create a Workbook object workbook = Workbook() # Load a sample Excel file workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get the first worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] # UnGroup rows sheet.UngroupByRows(2, 6) sheet.UngroupByRows(8, 13) # UnGroup columns sheet.UngroupByColumns(4, 6) # Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2016) workbook.Dispose()
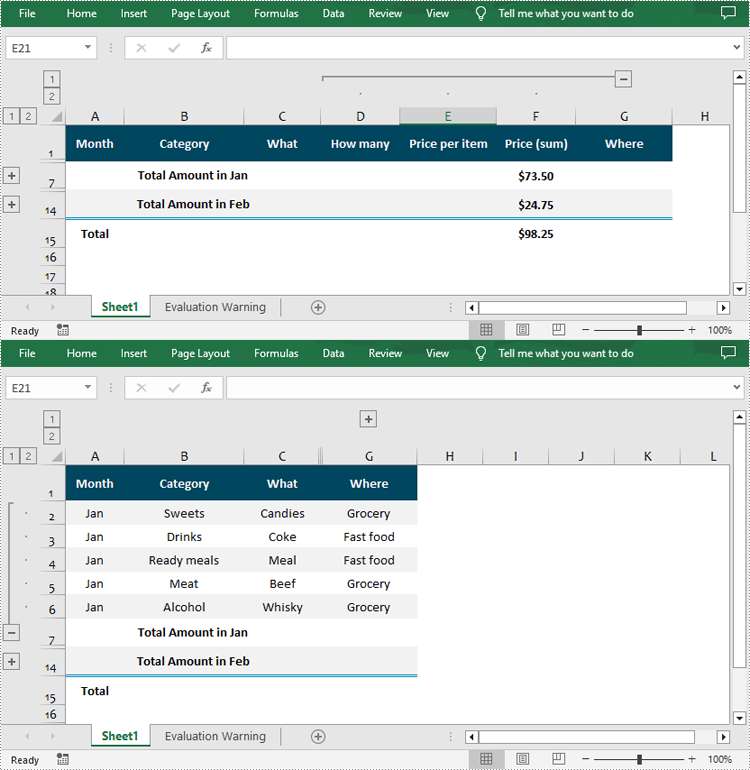
Expand or Collapse Groups in Excel in Python
Expanding or collapsing groups in Excel refers to the action of showing or hiding the detailed information within a grouped section. With Spire.XLS for Python, you can expand or collapse groups through the Worksheet.Range[].ExpandGroup() or Worksheet.Range[].CollapseGroup() methods. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Expand a specific group using the Worksheet.Range[].ExpandGroup() method.
- Collapse a specific group using the Worksheet.Range[].CollapseGroup() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "Grouped.xlsx" outputFile = "ExpandOrCollapseGroups.xlsx" # Create a Workbook object workbook = Workbook() # Load a sample Excel file workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get the first worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] # Expand a group sheet.Range["A2:G6"].ExpandGroup(GroupByType.ByRows) # Collapse a group sheet.Range["D1:F15"].CollapseGroup(GroupByType.ByColumns) # Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2016) workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
