
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Python: Add Tables to Excel Documents or Delete Tables from Excel Documents
2024-01-18 01:07:41 Written by KoohjiTables in Excel are powerful tools for organizing, storing, analyzing, and visualizing data. They are widely used in various industries and fields, including finance, business, science, education, and more. The table functionality in Excel makes data processing easier and provides users with flexibility and efficiency to make decisions and solve problems. This article will explain how to use Spire.XLS for Python to add or delete tables in Excel documents using Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Add Tables to an Excel Document in Python
Spire.XLS for Python creates table objects for the specified data source using the Worksheet.ListObjects.Create(tableName, range) method. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Use the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method to load an Excel document.
- Use the Workbook.Worksheets[] property to retrieve the desired worksheet.
- Create a table object using the Worksheet.ListObjects.Create() method.
- Set the table style using the Worksheet.ListObjects[].BuiltInTableStyle property.
- Use the Workbook.SaveToFile() method to save the resulting file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an .xlsx document
workbook.LoadFromFile("Data/sample1.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Create a table named "table" in the worksheet, with range [1,1,13,5]
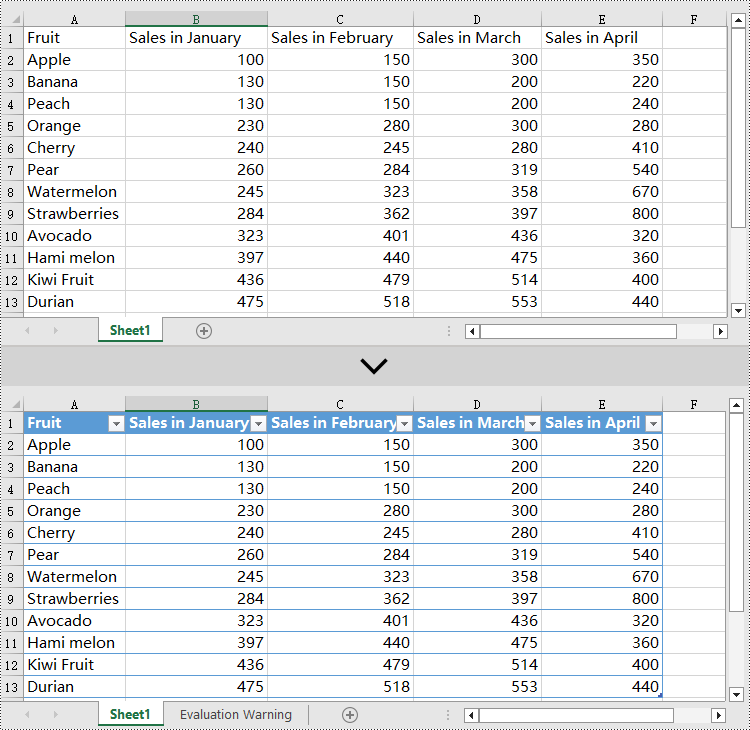
sheet.ListObjects.Create("table", sheet.Range[1,1,13,5])
# Set the built-in table style of the first table to TableStyleLight9
sheet.ListObjects[0].BuiltInTableStyle = TableBuiltInStyles.TableStyleLight9
# Save the workbook to a file
workbook.SaveToFile("AddTable.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Release resources and clean up the workbook object
workbook.Dispose()
Delete Tables from an Excel Document in Python
Excel table objects are located in the Worksheet.ListObjects collection. To delete a table object, you need to iterate through the collection, find the table object based on its name, and remove it from the collection. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Use the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method to load an Excel document.
- Use the Workbook.Worksheets[] property to retrieve the desired worksheet.
- Iterate through the Worksheet.ListObjects collection in the worksheet to obtain the name of each ListObject object for finding the table object to delete.
- Use the Worksheet.ListObjects.RemoveAt() method to remove the table object.
- Use the Workbook.SaveToFile() method to save the resulting file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an .xlsx document
workbook.LoadFromFile("Data/Sample2.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Iterate through all the tables in the worksheet
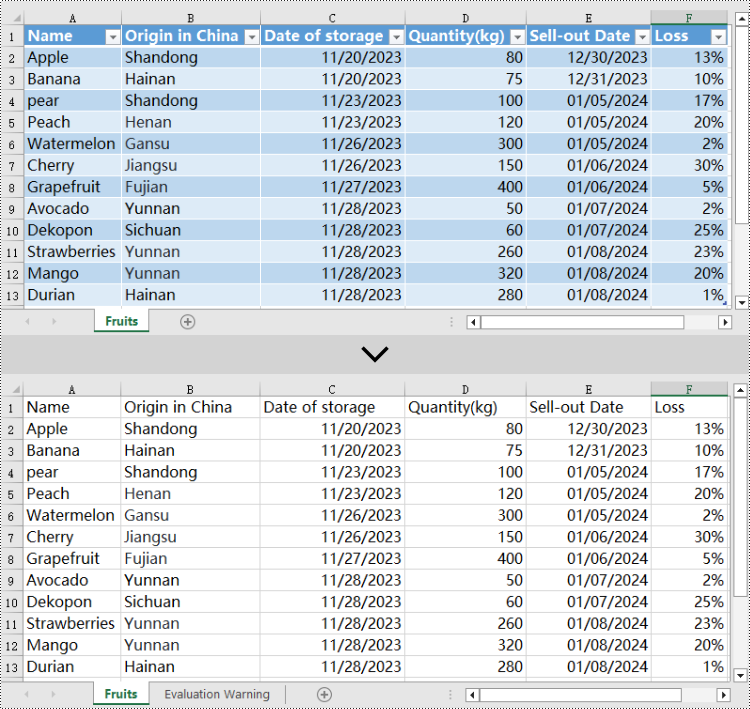
for i in range(len(sheet.ListObjects)):
# Check if the table's name is "FruitTable"
if sheet.ListObjects[i].Name == "FruitTable":
# If a matching table is found, remove it
sheet.ListObjects.RemoveAt(i)
# Save the workbook to a file
workbook.SaveToFile("DeleteTable.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Release resources and clean up the workbook object
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
By incorporating supplemental resources directly into the PDF, it consolidates all relevant information in a single file, making it easier to organize, share, and archive. This feature enables users to seamlessly share supporting documents, images, or multimedia elements, eliminating the need for separate file transfers or external links. It streamlines communication, improves efficiency, and ensures that recipients have convenient access to all the necessary resources within the PDF itself. In this article, you will learn how to attach files to a PDF document in Python with the help of Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Background Knowledge
There are generally two types of attachments in PDF, namely document level attachment and annotation attachment. Both are supported by Spire.PDF for Python. The table below lists the differences between them.
| Attachment type | Represented by | Definition |
| Document level attachment | PdfAttachment class | A file attached to a PDF at the document level won't appear on a page, but can be viewed in the "Attachments" panel of a PDF reader. |
| Annotation attachment | PdfAnnotationAttachment class | A file attached as an annotation can be found on a page or in the "Attachment" panel. An Annotation attachment is shown as a paper clip icon on the page; reviewers can double-click the icon to open the file. |
Attach Files to a PDF Document in Python
To attach files to PDFs at the document level, you first need to create a PdfAttachment object based on an external file, and then you can add it to a PDF document using the PdfDocument.Attachments.Add() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a PdfAttachment object based on an external file.
- Add the attachment to the document using PdfDocument.Attachments.Add() method.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a sample PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.pdf")
# Create PdfAttachment objects based on external files
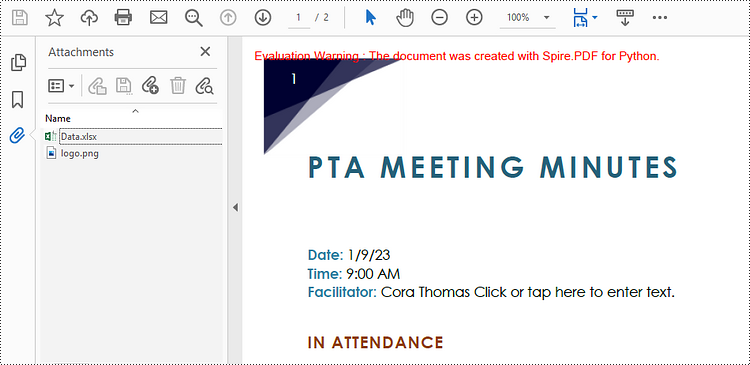
attachment_one = PdfAttachment("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Data.xlsx")
attachment_two = PdfAttachment("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\logo.png")
# Add the attachments to PDF
doc.Attachments.Add(attachment_one)
doc.Attachments.Add(attachment_two)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/Attachment.pdf")
Attach Files as Annotations in PDF in Python
An annotation attachment is represented by the PdfAttachmentAnnotation class. Create an instance of this class, specify its attributes such as bounds, flag and text, and then add it to a specified page using the PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.Add() method.
Below are the steps to attach files as annotations in PDF using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific page to add annotation through PdfDocument.Pages[] property.
- Create a PdfAttachmentAnnotation object based on an external file.
- Add the annotation attachment to the page using PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.Add() method.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a sample PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.pdf")
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(1)
# Draw a string on PDF
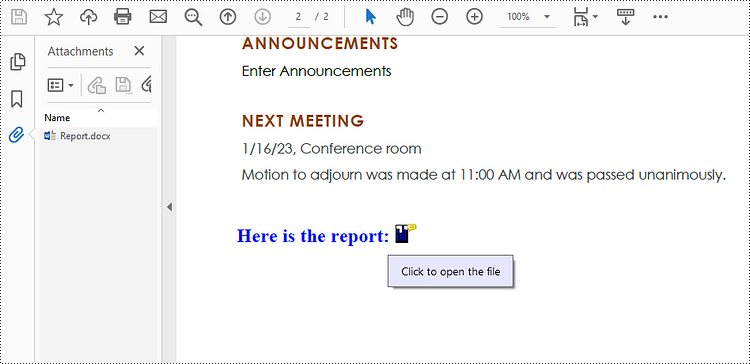
str = ""Here is the report:""
font = PdfTrueTypeFont(""Times New Roman"", 16.0, PdfFontStyle.Bold, True)
x = 50.0
y = doc.Pages.get_Item(0).ActualSize.Height - 300.0
page.Canvas.DrawString(str, font, PdfBrushes.get_Blue(), x, y)
# Create a PdfAttachmentAnnotation object based on an external file
data = Stream("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Data.xlsx")
size = font.MeasureString(str);
bounds = RectangleF((x + size.Width + 5.0), y, 10.0, 15.0)
annotation = PdfAttachmentAnnotation(bounds, "Report.docx", data);
# Set color, flag, icon and text of the annotation
annotation.Color = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue())
annotation.Flags = PdfAnnotationFlags.Default
annotation.Icon = PdfAttachmentIcon.Graph
annotation.Text = "Click to open the file"
# Add the attachment annotation to PDF
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(annotation)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/AnnotationAttachment.pdf")
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Content controls play an important role in Excel, providing powerful functionality for data input, display, and user interaction. These controls include text boxes, radio buttons, checkboxes, drop-down lists, and more. They offer users more efficient, intuitive, and flexible ways of handling data, making Excel a powerful tool for data management and analysis. This article will introduce how to use Spire.XLS for Python to add content controls to Excel documents or edit content controls in Excel documents using Python.
- Add Content Controls to an Excel document in Python
- Edit Content Controls in an Excel document in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Add Content Controls to an Excel document in Python
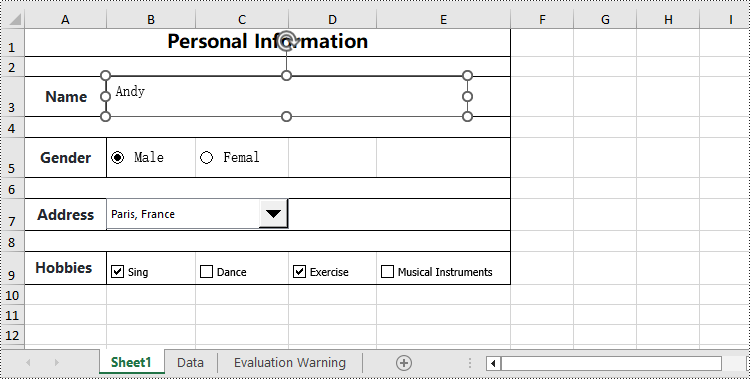
Spire.XLS for Python allows you to add content controls supported by Excel, such as text boxes, radio buttons, drop-down lists (also known as combo boxes), checkboxes, and more. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Use the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method to load an Excel data document.
- Use the Workbook.Worksheets[] property to retrieve the desired worksheet.
- Add a text box using the Worksheet.TextBoxes.AddTextBox() method.
- Add a radio button using the Worksheet.RadioButtons.Add() method.
- Add a combo box using the Worksheet.ComboBoxes.AddComboBox() method.
- Add a checkbox using the Worksheet.CheckBoxes.AddCheckBox() method.
- Use the Workbook.SaveToFile() method to save the resulting file.
- Python
from spire.xls.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Create a new Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an existing Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Data/Sample01.xlsx")
# Select the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set the height of the text box (unit: points)
height = 40
# Add a text box to the worksheet
textbox = worksheet.TextBoxes.AddTextBox(3, 2, height, 400)
textbox.Line.ForeKnownColor = ExcelColors.Black
textbox.Text = "Andy"
# Add radio buttons to the worksheet
radioButton1 = worksheet.RadioButtons.Add(5, 2, height, 60)
radioButton1.Text = "Male"
radioButton1.CheckState=CheckState.Checked
radioButton2 = worksheet.RadioButtons.Add(5, 3, height, 60)
radioButton2.Text = "Female"
# Assign a data range from another worksheet to a combo box
dataSheet = workbook.Worksheets[1]
comboBoxShape = worksheet.ComboBoxes.AddComboBox(7, 2, 30, 200)
comboBoxShape.ListFillRange = dataSheet.Range["A1:A7"]
comboBoxShape.SelectedIndex=1
# Add check boxes to the worksheet
checkBox = worksheet.CheckBoxes.AddCheckBox(9, 2, height, 60)
checkBox.CheckState = CheckState.Checked
checkBox.Text = "Sing"
checkBox = worksheet.CheckBoxes.AddCheckBox(9, 3, height, 60)
checkBox.CheckState = CheckState.Unchecked
checkBox.Text = "Dance"
checkBox = worksheet.CheckBoxes.AddCheckBox(9, 4, height, 60)
checkBox.CheckState = CheckState.Checked
checkBox.Text = "Exercise"
checkBox = worksheet.CheckBoxes.AddCheckBox(9, 5, height, 100)
checkBox.CheckState = CheckState.Unchecked
checkBox.Text = "Musical Instruments"
# Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("AddContentControls.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Clean up and release the workbook object
workbook.Dispose()
Edit Content Controls in an Excel document in Python
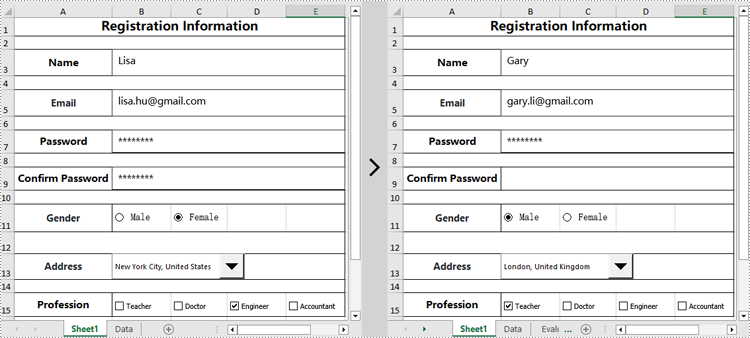
Spire.XLS for Python can also modify the properties of existing content controls in an Excel document, such as changing the text of a text box, resetting the selected item of a drop-down list, hiding a specific content control, and more. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Use the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method to load an Excel document.
- Use the Workbook.Worksheets[] property to retrieve the desired worksheet.
- Modify the display content of a text box using the Worksheet.TextBoxes[].Text property.
- Set whether to display a specific text box using the Worksheet.TextBoxes[].Visible property.
- Set whether a radio button is checked using the Worksheet.RadioButtons[].CheckState property.
- Set the selected item of a combo box using the Worksheet.ComboBoxes[].SelectedIndex property.
- Set whether a checkbox is checked using the Worksheet.CheckBoxes[].CheckState property.
- Use the Workbook.SaveToFile() method to save the resulting file.
- Python
from spire.xls.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load Excel data from file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Data/Sample02.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set the text content of the first textbox to "Gary"
worksheet.TextBoxes[0].Text = "Gary"
# Set the text content of the second textbox to "gary.li@gmail.com"
worksheet.TextBoxes[1].Text = "gary.li@gmail.com"
# Hide the fourth textbox
worksheet.TextBoxes[3].Visible = False
# Check the first radio button
worksheet.RadioButtons[0].CheckState = CheckState.Checked
# Set the selected index of the first combobox to 0 (the first option)
worksheet.ComboBoxes[0].SelectedIndex = 0
# Check the first checkbox
worksheet.CheckBoxes[0].CheckState = CheckState.Checked
# Uncheck the third checkbox
worksheet.CheckBoxes[2].CheckState = CheckState.Unchecked
# Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("EditContentControls.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Clean up and release the workbook object
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
