
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Shapes are a powerful tool in Excel that enables you to transform raw data into visually appealing and informative representations. By inserting and customizing shapes, you can create clear, engaging, and visually impactful spreadsheets that effectively communicate your data and captivate your audience. In this article, we will demonstrate how to insert and remove shapes in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Insert Shapes in Excel in Python
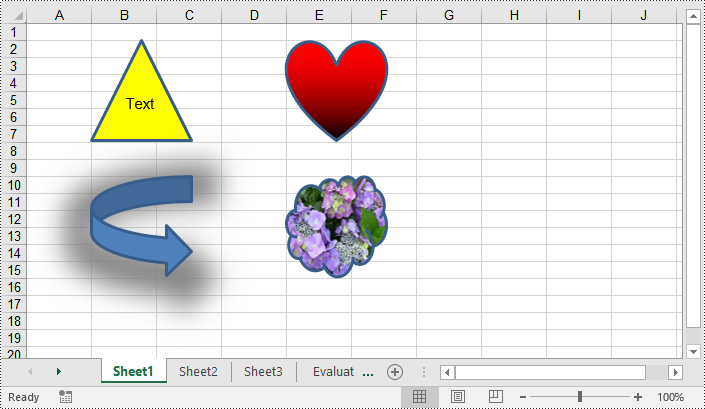
You can add numerous types of shapes, such as lines, rectangles, triangles, and stars, to an Excel worksheet by using the Worksheet.PrstGeomShapes.AddPrstGeomShape() method provided by Spire.XLS for Python. Once added, you can customize the shapes, such as adding text to the shapes, filling the shapes with solid or gradient colors or images, and setting shadow styles for the shapes. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Get the first worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Add a shape to the worksheet using Worksheet.PrstGeomShapes.AddPrstGeomShape() method.
- Add text to the shape using IPrstGeomShape.Text property.
- Fill the shape with a color using IPrstGeomShape.Fill.ForeColor property.
- Set the fill type of the shape as solid using IPrstGeomShape.Fill.FillType property.
- Repeat the above steps to add more shapes to the worksheet.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add a triangle shape to the worksheet
triangle = sheet.PrstGeomShapes.AddPrstGeomShape(2, 2, 100, 100, PrstGeomShapeType.Triangle)
# Add text to the shape
triangle.Text = "Text"
# Fill the triangle with a solid color
triangle.Fill.ForeColor = Color.get_Yellow()
triangle.Fill.FillType = ShapeFillType.SolidColor
# Add a heart shape to the worksheet
heart = sheet.PrstGeomShapes.AddPrstGeomShape(2, 5, 100, 100, PrstGeomShapeType.Heart)
# Fill the heart with a gradient color
heart.Fill.ForeColor = Color.get_Red()
heart.Fill.FillType = ShapeFillType.Gradient
# Add an arrow shape with the default color to the worksheet
arrow = sheet.PrstGeomShapes.AddPrstGeomShape(10, 2, 100, 100, PrstGeomShapeType.CurvedRightArrow)
# Set shadow style for the arrow
arrow.Shadow.Angle = 90
arrow.Shadow.Distance = 10
arrow.Shadow.Size = 150
arrow.Shadow.Color = Color.get_Gray()
arrow.Shadow.Blur = 30
arrow.Shadow.Transparency = 1
arrow.Shadow.HasCustomStyle = True
# Add a cloud shape to the worksheet
cloud = sheet.PrstGeomShapes.AddPrstGeomShape(10, 5, 100, 100, PrstGeomShapeType.Cloud)
# Fill the cloud with a custom picture
cloud.Fill.CustomPicture(Image.FromFile("Hydrangea.jpg"), "Hydrangea.jpg")
cloud.Fill.FillType = ShapeFillType.Picture
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("InsertShapes.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Remove Shapes from Excel in Python
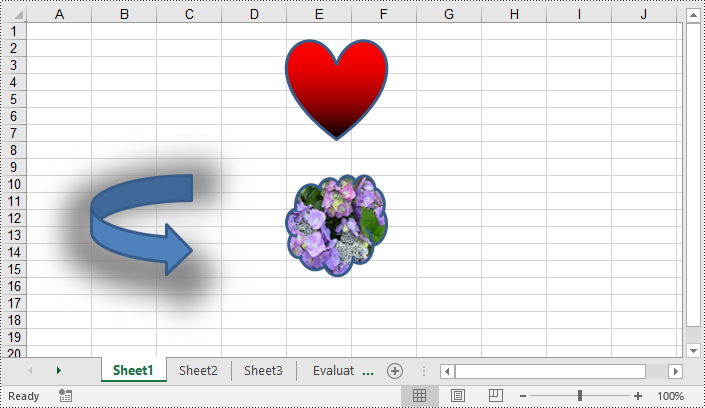
Shapes can improve the visual appearance of your workbook, but they can also increase the file size of it. Removing unnecessary shapes helps reduce the file size, making it more manageable and easier to share or store. Spire.XLS for Python enables you to remove specific shapes from a worksheet effortlessly by using the Worksheet.PrstGeomShapes[index].Remove() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove a specific shape from the Worksheet using Worksheet.PrstGeomShapes[index].Remove() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("InsertShapes.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Remove the first shape from the worksheet
sheet.PrstGeomShapes[0].Remove()
#Save to file.
workbook.SaveToFile("RemoveShapes.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Table borders in PowerPoint refer to the visible lines or outlines that surround the cells within a table. These borders provide a visual separation between cells and help define the boundaries of the table. By setting or modifying table borders, you can customize the appearance of tables in your PowerPoint presentations. In this article, we will guide you on how to set and remove table borders in PowerPoint in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Set Table Borders in PowerPoint in Python
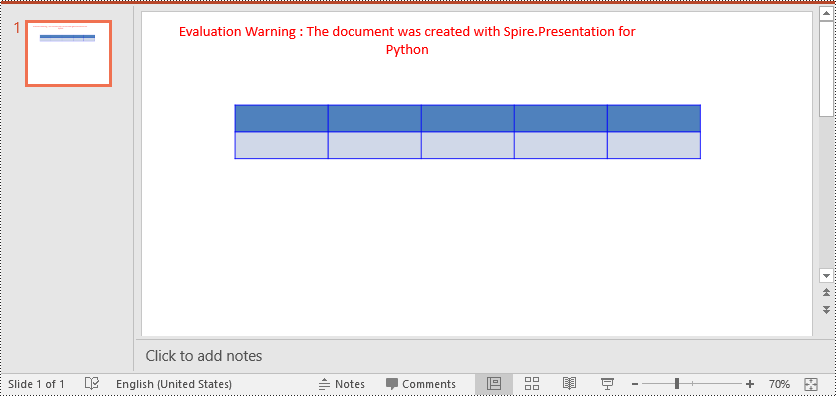
Spire.Presentation for Python provides the ITable.SetTableBorder() method, which allows you to set borders for a table in PowerPoint. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Get the first slide of the presentation using Presentation.Slides[] property.
- Add a table to the slide using ISlide.Shapes.AppendTable() method.
- Add borders to the table and set the border type, width, and color using ITable.SetTableBorder() method.
- Save the result presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Get the first slide of the presentation
slide = presentation.Slides[0]
# Specify the number and size of rows and columns in table
widths = [100, 100, 100, 100, 100]
heights = [20, 20]
# Add a table to the first slide
table = slide.Shapes.AppendTable(100, 100, widths, heights)
# Add borders to the table and set the border type, width, and color
table.SetTableBorder(TableBorderType.All, 1, Color.get_Blue())
# Save the result presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("SetBorders.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
presentation.Dispose()
Remove Table Borders in PowerPoint in Python
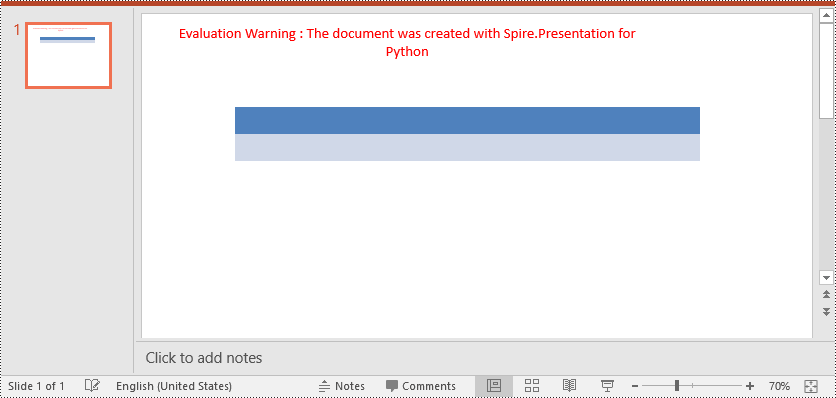
To remove borders from a table, you need to iterate through the cells in the table and then remove the borders from each cell. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific slide of the presentation using Presentation.Slides[] property.
- Get the table on the slide.
- Iterate through the rows in the table and the cells in each row.
- Remove the borders from each cell by setting the fill type of the top, bottom, left and right borders of the cell as none.
- Save the result presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a PowerPoint presentation
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("SetBorders.pptx")
# Get the first slide
slide = presentation.Slides[0]
# Get the table on the slide
table = slide.Shapes[0] if isinstance(slide.Shapes[0], ITable) else None
table = (ITable)(table)
# Iterate through the rows and cells in the table
for row in table.TableRows:
for cell in row:
# Remove borders from each cell by setting the fill type of the top, bottom, left and right borders of the cell as none
cell.BorderTop.FillType = FillFormatType.none
cell.BorderBottom.FillType = FillFormatType.none
cell.BorderLeft.FillType = FillFormatType.none
cell.BorderRight.FillType = FillFormatType.none
# Save the result presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("RemoveBorders.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
presentation.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Adding the ability to edit permission area in a Word document can help users specify certain sections for others to edit while protecting the rest of the document from accidental modifications. This is particularly useful for scenarios like collaborative documents, document reviews, and comments. On the other hand, removing editable area functionality allows the document to be restored to a read-only state when specific sections do not need to be edited, ensuring the integrity and security of the document content. This article will explain how to use Spire.Doc for .NET to add or remove editable area in a Word document within a C# project.
Install Spire.Doc for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Doc for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
Add Editable Area in a Word Document in C#
The steps to add editable area in a Word document involve inserting PermissionStart and PermissionEnd objects in the document and setting the document to read-only protection mode to ensure that the content within the specified areas can be edited while the rest remains read-only. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Access a section of the document through the Document.Sections[index] property.
- Create a PermissionStart object using PermissionStart permissionStart = new PermissionStart(document, id) to mark the beginning of the editable area .
- Create a PermissionEnd object using PermissionEnd permissionEnd = new PermissionEnd(document, id) to mark the end of the editable area .
- Access a paragraph using the Section.Paragraphs[index] property.
- Insert the permission start object at the beginning of the paragraph using the Paragraph.ChildObjects.Insert(0, permissionStart) method.
- Add the permission end object at the end of the paragraph using the Paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(permissionEnd) method.
- Set the document to read-only protection mode and restrict editing permissions using the Document.Protect(ProtectionType.AllowOnlyReading, password) method.
- Save the resulting document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
namespace SpireDocDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load the document from the specified path
document.LoadFromFile("Sample1.docx");
// Get the first section of the document
Section section = document.Sections[0];
// Create a permission start object
PermissionStart permissionStart = new PermissionStart(document, "restricted1");
// Create a permission end object
PermissionEnd permissionEnd = new PermissionEnd(document, "restricted1");
// Get the second paragraph in the section
Paragraph paragraph = section.Paragraphs[1];
// Insert the permission start object at the beginning of the paragraph
paragraph.ChildObjects.Insert(0, permissionStart);
// Add the permission end object at the end of the paragraph
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(permissionEnd);
// Set the document to be read-only protected
document.Protect(ProtectionType.AllowOnlyReading, "123456");
// Save the modified document to the specified path
document.SaveToFile("AddedEditingPermissionsArea.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Close the document and release the resources occupied by the document object
document.Close();
document.Dispose();
}
}
}
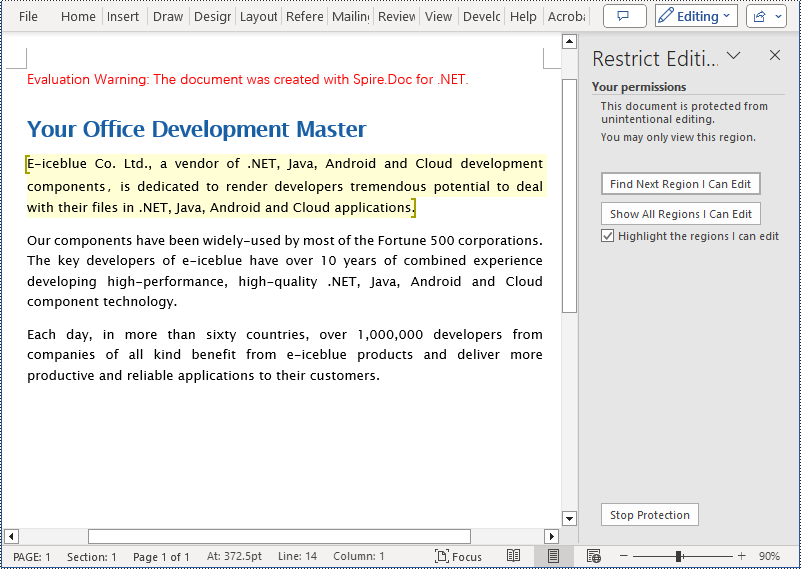
Remove Editable Area in a Word Document in C#
The key steps to remove editable area in a Word document involve iterating through each paragraph of the document and removing the PermissionStart and PermissionEnd objects. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through each paragraph in each section of the document, check for the presence of PermissionStart or PermissionEnd objects, and remove them.
- Save the resulting document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
namespace SpireDocDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load the document from the specified path
document.LoadFromFile("Sample2.docx");
// Iterate through the sections of the document
for (int a = 0; a < document.Sections.Count; a++)
{
// Get the body of the current section
Body body = document.Sections[a].Body;
// Iterate through the child objects of the body
for (int i = 0; i < body.ChildObjects.Count; i++)
{
// Check if the child object is a paragraph
if (body.ChildObjects[i] is Paragraph)
{
// Get the current paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = (Paragraph)body.ChildObjects[i];
// Iterate backwards from the last child object of the paragraph
for (int j = paragraph.ChildObjects.Count - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
// Get the current child object
DocumentObject documentObject = paragraph.ChildObjects[j];
// Remove the current child object if it is a permission start object
if (documentObject.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.PermissionStart)
{
paragraph.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(j);
}
// Remove the current child object if it is a permission end object
else if (documentObject.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.PermissionEnd)
{
paragraph.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(j);
}
}
}
}
}
// Save the modified document to the specified path
document.SaveToFile("RemovedEditingPermissionsArea.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Close the document and release the resources occupied by the document object
document.Close();
document.Dispose();
}
}
}
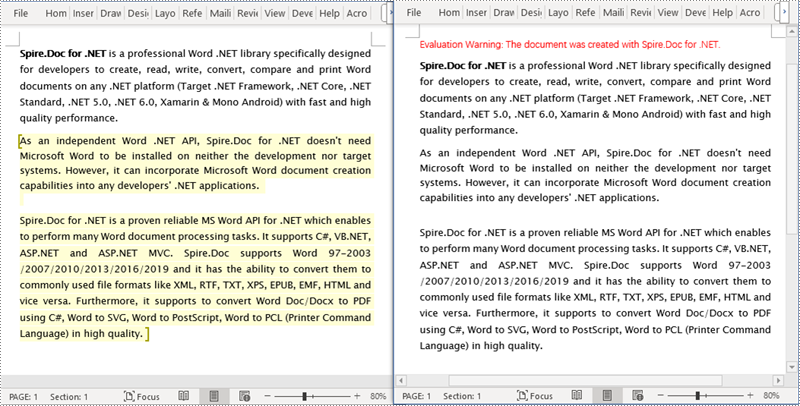
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
