
Python (355)
Convert HTML to Word DOC or DOCX in Python | Developer Tutorial
2023-11-17 00:56:39 Written by Koohji
Converting HTML files to Word documents in Python is an essential skill for developers building documentation systems, report generators, or applications that transform web-based content into offline editable formats. While HTML excels at displaying content on the web, Word documents provide a more versatile format for offline access, collaboration, and professional presentation.
This in-depth developer guide shows you how to automate the conversion from HTML files and HTML strings into Word DOCX/DOC documents in Python using Spire.Doc for Python—a powerful, standalone library that enables high-quality Word document generation and conversion without the need for Microsoft Word.
Table of Contents
- Why Convert HTML to Word Format
- Install HTML to Word Converter in Python
- Export HTML Files to Word Documents in Python
- Insert HTML Strings into Word Documents in Python
- Supported Output Formats
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Why Convert HTML to Word Format
HTML is ideal for online content delivery, but Word documents offer significant advantages for use cases that require formatting, annotation, printing, or offline access:
- Offline Access: View and edit documents without an internet connection.
- Advanced Editing: Enable features like tracked changes, comments, and section formatting.
- Professional Presentation: Suitable for formal reports, business contracts, user manuals, and documentation.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Open and edit using Microsoft Word, Google Docs, LibreOffice, and other word processors.
Install HTML to Word Converter in Python
Spire.Doc for Python is a feature-rich library designed to help developers create, read, convert, and manipulate Word documents directly within Python applications. It offers high-fidelity conversion of HTML content to Word format while preserving the original structure and styles.
Key Benefits
- Fully preserves original HTML structure, CSS styles, and layout
- Accepts both HTML files and HTML strings as input sources
- Supports conversion to .doc, .docx, and other formats
- 100% standalone; no Office automation needed
Installation
You can install the library from PyPI using the following pip command:
pip install spire.doc
Export HTML Files to Word Documents in Python
If you already have an HTML file—such as a saved webpage or generated HTML report—you can save it to a Word document with just a few lines of code.
Code Example
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Specify the input and output file paths
inputFile = "Input.html"
outputFile = "HtmlToWord.docx"
# Create an object of the Document class
document = Document()
# Load an HTML file
document.LoadFromFile(inputFile, FileFormat.Html, XHTMLValidationType.none)
# Save the HTML file to a .docx file
document.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()
Explanation:
This example demonstrates how to load an existing .html file and save it to a Word .docx document:
- Document(): creates a new Word document object.
- LoadFromFile(): loads the HTML file and parses it as an HTML document.
- XHTMLValidationType.none: disables strict validation of the HTML content.
- SaveToFile(): saves the result as a .docx file using the FileFormat.Docx2016 format.
To export as .doc, replace FileFormat.Docx2016 with FileFormat.Doc.
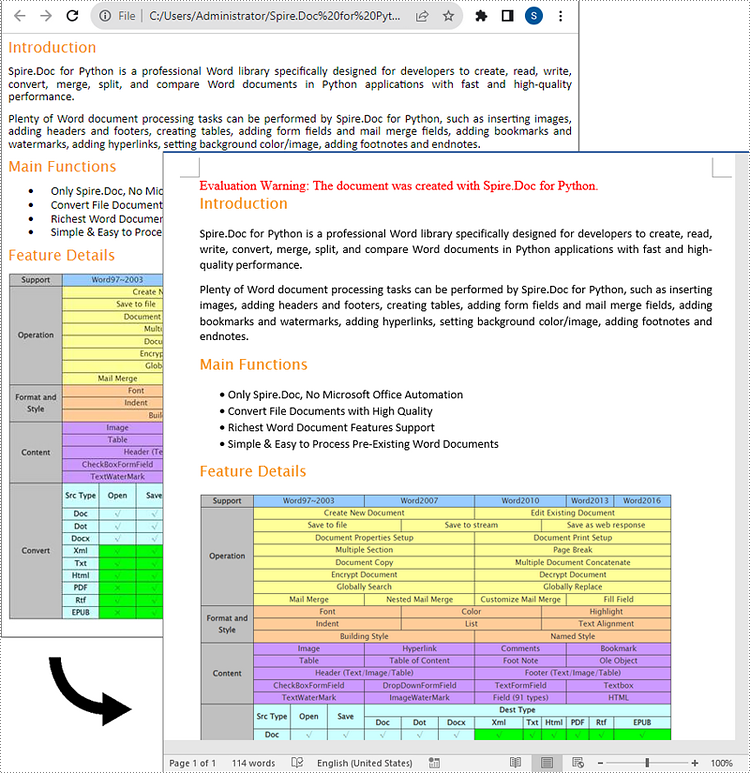
Output:
Here is the Word document generated from the HTML file:
Insert HTML Strings into Word Documents in Python
Sometimes, you may have HTML content as a string—perhaps scraped from the web or dynamically generated. Spire.Doc allows you to insert such HTML content into a Word document without saving it as a file first.
Code Example
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Specify the output file path
outputFile = "HtmlStringToWord.docx"
# Create an object of the Document class
document = Document()
# Add a section to the document
sec = document.AddSection()
# Add a paragraph to the section
paragraph = sec.AddParagraph()
# Specify the HTML string
htmlString = """
<html>
<head>
<title>HTML to Word Example</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
}
h1 {
color: #FF5733;
font-size: 24px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
p {
color: #333333;
font-size: 16px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
ul {
list-style-type: disc;
margin-left: 20px;
margin-bottom: 15px;
}
li {
font-size: 14px;
margin-bottom: 5px;
}
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
width: 100%;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
th, td {
border: 1px solid #CCCCCC;
padding: 8px;
text-align: left;
}
th {
background-color: #F2F2F2;
font-weight: bold;
}
td {
color: #0000FF;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a Heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph demonstrating the conversion of HTML to Word document.</p>
<p>Here's an example of an unordered list:</p>
<ul>
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
<li>Item 3</li>
</ul>
<p>And here's a table:</p>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Product</th>
<th>Quantity</th>
<th>Price</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Jacket</td>
<td>30</td>
<td>$150</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Sweater</td>
<td>25</td>
<td>$99</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
"""
# Append the HTML string to the paragraph
paragraph.AppendHTML(htmlString)
# Save the result document
document.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()
Explanation:
This code converts an HTML string directly into Word content:
- Document(): creates a new document.
- AddSection() and AddParagraph(): adds a section and paragraph to hold the content.
- AppendHTML(): parses and inserts the HTML string into the paragraph, preserving styles and structure.
- SaveToFile(): saves the document to a .docx file using the FileFormat.Docx2016 format.
This approach is ideal for use cases like email-to-Word, content pulled from CMS platforms, or HTML snippets generated dynamically at runtime.
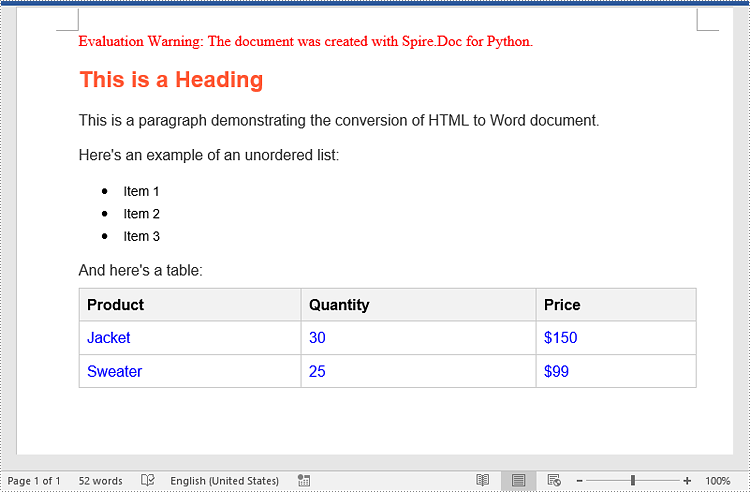
Output:
Here is the Word document generated from the HTML string:
Supported Output Formats
With Spire.Doc for Python, you’re not limited to Word output. You can also convert HTML to various formats, including:
- Image: .png, .jpg, .bmp
- Rich Text: .rtf
- Other: .xml, .xps, .epub, etc.
Conclusion
Spire.Doc for Python provides a powerful solution for developers looking to convert HTML to Word documents with precision and efficiency. Whether you’re working with HTML files or strings, the library simplifies the process while maintaining the integrity of your content.
Give Spire.Doc a try today and see how effortlessly you can add professional document generation to your Python projects!
FAQs
Q1: Can I convert HTML to Word without installing Microsoft Word?
A1: Yes. Spire.Doc is a standalone component and does not require Word or Office on the machine.
Q2: Are CSS styles and tables preserved?
A2: Yes. The library retains CSS styles, tables, images, lists, fonts, and layout formatting.
Q3: Can I batch-convert multiple HTML files to Word?
A3: Absolutely. You can loop through folders and apply the same conversion logic to each file.
Q4: What other formats can I export HTML to?
A4: HTML can be converted to .doc, .docx, .pdf, image formats, .rtf, .xml, and more.
Q5: Is there a trial license?
A5: Yes. you can request a 30-day trial license for full functionality.
A hyperlink is a clickable element, usually embedded in text or an image. It can direct users from their current location to a specific location on another web page or document. By adding hyperlinks in PowerPoint presentations, users can easily visit other related pages or slides while presenting slides. In this article, we will demonstrate how to add hyperlinks to PowerPoint presentations in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Add Hyperlink to Text on Slide in Python
Spire.Presentation for Python allows users to insert hyperlinks to text on slides easily by using TextRange.ClickAction.Address property. The following are detailed steps.
- Create a new PowerPoint presentation.
- Set the background for the first slide of the presentation by using Presentation.Slides[].Shapes.AppendEmbedImageByPath() method.
- Add a new shape to this slide using Presentation.Slides[].Shapes.AppendShape() method.
- Add some paragraphs to it by calling TextParagraph.TextRanges.Append() method.
- Create another TextRange instance to represent a text range and set link address for it by TextRange.ClickAction.Address property.
- Set the font for these paragraphs.
- Save the result file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
import math
outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/AddHyperlinkToText.pptx"
#Create a new PowerPoint presentation
presentation = Presentation()
#Set the background for the first slide
ImageFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/background.png"
rect = RectangleF.FromLTRB (0, 0, presentation.SlideSize.Size.Width, presentation.SlideSize.Size.Height)
presentation.Slides[0].Shapes.AppendEmbedImageByPath (ShapeType.Rectangle, ImageFile, rect)
#Add a new shape to the first slide
shape = presentation.Slides[0].Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, RectangleF.FromLTRB (80, 250, 650, 400))
shape.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.none
shape.ShapeStyle.LineColor.Color = Color.get_White()
#Add some paragraphs to the shape
para1 = TextParagraph()
tr = TextRange("Spire.Presentation for Python")
tr.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
tr.Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_Black()
para1.TextRanges.Append(tr)
para1.Alignment = TextAlignmentType.Left
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Append(para1)
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Append(TextParagraph())
para2 = TextParagraph()
tr1 = TextRange("This is a professional presentation processing API that is highly compatible with PowerPoint."
+"It supports developers to process PowerPoint presentations efficiently without installing Microsoft PowerPoint.")
tr1.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
tr1.Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_Black()
para2.TextRanges.Append(tr1)
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Append(para2)
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Append(TextParagraph())
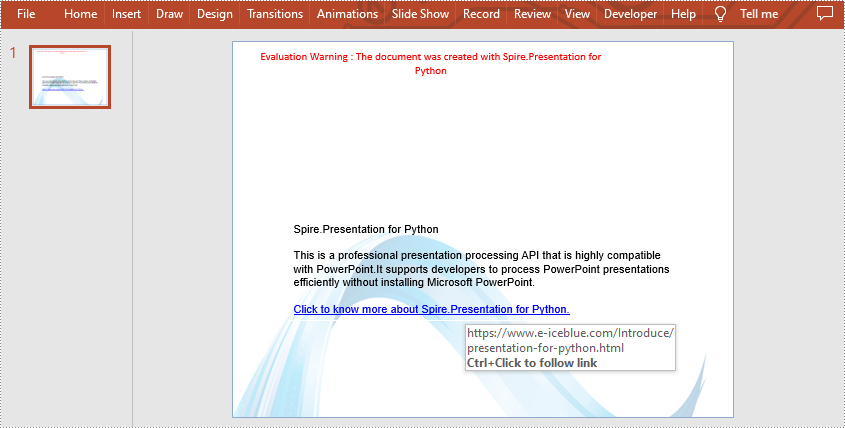
#Add text with a hyperlink
para3 = TextParagraph()
tr2 = TextRange("Click to know more about Spire.Presentation for Python.")
tr2.ClickAction.Address = "https://www.e-iceblue.com/Introduce/presentation-for-python.html"
para3.TextRanges.Append(tr2)
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Append(para3)
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Append(TextParagraph())
#Set the font for those paragraphs
for para in shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs:
if len(para.Text) != 0:
para.TextRanges[0].LatinFont = TextFont("Arial")
para.TextRanges[0].FontHeight = 16
#Save the result file
presentation.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Pptx2010)
presentation.Dispose()
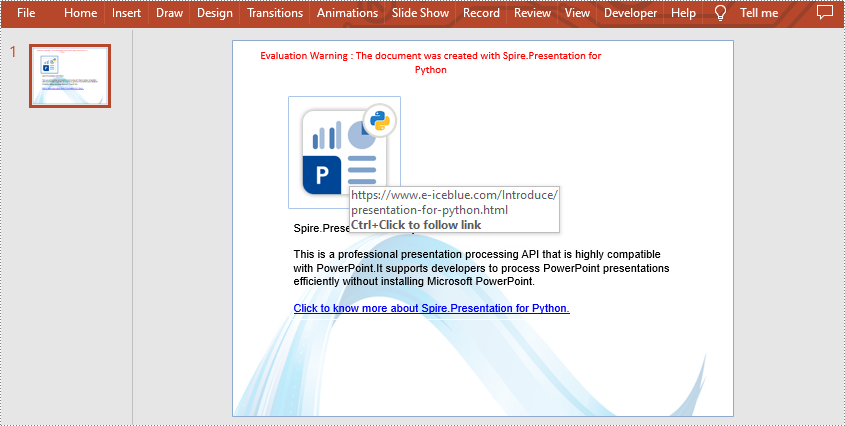
Add Hyperlink to Image on Slide in Python
Spire.Presentation for Python also supports adding a hyperlink to an image. You can create a hyperlink by ClickHyperlink class and then add it to the image using the IEmbedImage.Click property. The related steps are as follows.
- Create a new PowerPoint presentation.
- Load a PowerPoint file using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first slide by using Presentation.Slides[] property.
- Add an image to this slide using ISlide.Shapes.AppendEmbedImageByPath() method.
- Create a ClickHyperlink object and append the hyperlink to the added image using IEmbedImage.Click property.
- Save the result file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/AddHyperlinkToText.pptx"
outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/AddHyperlinkToImage.pptx"
#Create a new PowerPoint presentation
presentation = Presentation()
#Load a sample file from disk
presentation.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
#Get the first slide
slide = presentation.Slides[0]
#Add an image to this slide
rect = RectangleF.FromLTRB (80, 80, 240, 240)
image = slide.Shapes.AppendEmbedImageByPath (ShapeType.Rectangle, "image.png", rect)
#Add a hyperlink to the image
hyperlink = ClickHyperlink("https://www.e-iceblue.com/Introduce/presentation-for-python.html")
image.Click = hyperlink
#Save the result file
presentation.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Pptx2013)
presentation.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Conditional formatting is a powerful feature in Microsoft Excel that allows users to apply formatting rules to cells based on specific conditions or criteria. It provides a quick and efficient way to visually highlight and analyze data, making it easier to identify trends, patterns, and outliers. With conditional formatting, users can customize the appearance of cells, such as font color, cell background, and borders, to draw attention to specific data points or results. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically apply conditional formatting in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Alternate Row Colors in Excel Using Conditional Formatting in Python
- Highlight Top or Bottom Ranked Values in Excel in Python
- Highlight Values Below or Above Average in Excel in Python
- Highlight Values Between Two Numbers in Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Alternate Row Colors in Excel Using Conditional Formatting in Python
Apply alternating row colors enhances the readability and visual appeal of a spreadsheet. By using different background colors for adjacent rows, it makes it easier to distinguish and follow individual rows of data. The following are the steps to alternate row colors in Excel using conditional formatting with Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet from the workbook through Workbook.Worsheets[index] property.
- Add a conditional format to the worksheet using Worksheet.ConditionalFormats.Add() method and return an object of XlsConditionalFormats class.
- Specify the cell range where the conditional formatting will be applied using XlsConditionalFormats.AddRange() method.
- Add a condition using XlsConditionalFormats.AddCondition() method to change the color of even rows.
- Add another condition to change the color of odd rows.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load a file from disk
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/input.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add a conditional format to the worksheet
conditionalForamt = sheet.ConditionalFormats.Add()
# Specify the range where the conditional format will be applied
conditionalForamt .AddRange(sheet.Range[2, 1, sheet.LastRow, sheet.LastColumn])
# Specify the first condition and format the cells that match the condition
condition1 = conditionalForamt .AddCondition()
condition1.FirstFormula = "=MOD(ROW(),2)=0"
condition1.FormatType = ConditionalFormatType.Formula
condition1.BackColor = Color.get_White()
# Specify the second condition and format the cells that match the condition
condition2 = conditionalForamt.AddCondition()
condition2.FirstFormula = "=MOD(ROW(),2)=1"
condition2.FormatType = ConditionalFormatType.Formula
condition2.BackColor = Color.get_LightGray()
# Save to file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/AlternateRowColors.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()

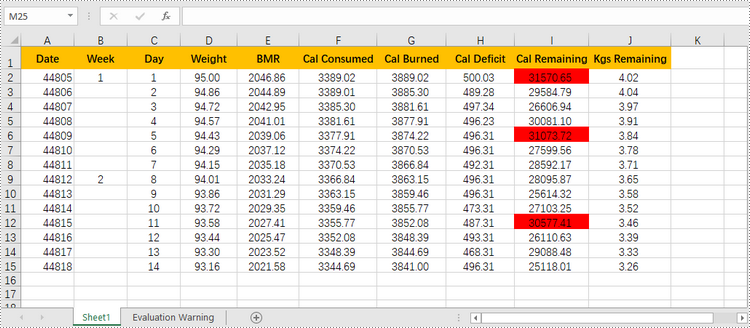
Highlight Top or Bottom Ranked Values in Excel
Highlighting top-ranked or bottom-ranked values in Excel can quickly identify the highest or the lowest values within a range or dataset, making it easier to analyze and interpret the data. The following are the steps to highlight top or bottom ranked values in Excel using conditional formatting with Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet from the workbook through Workbook.Worsheets[index] property.
- Add a conditional format to the worksheet using Worksheet.ConditionalFormats.Add() method and return an object of XlsConditionalFormats class.
- Specify the cell range where the conditional formatting will be applied using XlsConditionalFormats.AddRange() method.
- Add a condition using XlsConditionalFormats.AddCondition() method to change the color of the cells that have top ranked or bottom ranked values.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load a file from disk
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/input.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add a conditional format to the worksheet
conditionalForamt = sheet.ConditionalFormats.Add()
# Specify the range where the conditional format will be applied
conditionalForamt.AddRange(sheet.Range["I2:I15"])
# Add a condition to highlight the top 3 ranked values
condition1 = conditionalForamt.AddTopBottomCondition(TopBottomType.Top, 3)
condition1.BackColor = Color.get_Red()
# Add a condition to highlight the bottom 3 ranked values
# condition2 = conditionalForamt.AddTopBottomCondition(TopBottomType.Bottom, 3)
# condition2.BackColor = Color.get_Green()
# Save the workbook to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/TopOrBottomValues.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
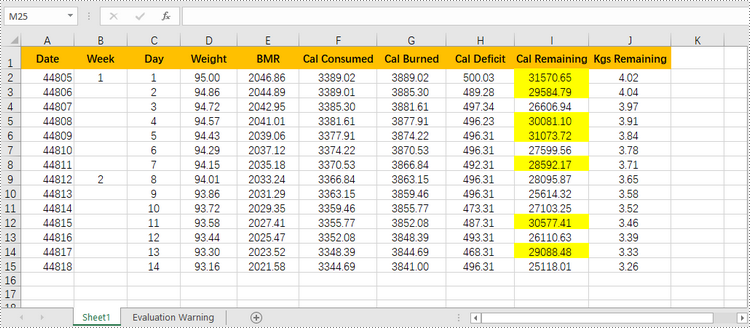
Highlight Values Below or Above Average in Excel
To quickly identify data points that are significantly higher or lower than the average, you can use conditional formatting as well. Here are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet from the workbook through Workbook.Worsheets[index] property.
- Add a conditional format to the worksheet using Worksheet.ConditionalFormats.Add() method and return an object of XlsConditionalFormats class.
- Specify the cell range where the conditional formatting will be applied using XlsConditionalFormats.AddRange() method.
- Add a condition using XlsConditionalFormats.AddCondition() method to change the color of the cells with values above or below the average.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load a file from disk
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/input.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add a conditional format to the worksheet
conditionalForamt = sheet.ConditionalFormats.Add()
# Specify the range where the conditional format will be applied
conditionalForamt.AddRange(sheet.Range["I2:I15"])
# Add a condition to highlight the values above average
condition1 = conditionalForamt.AddAverageCondition(AverageType.Above)
condition1.BackColor = Color.get_Yellow()
# Add a condition to highlight the values below average
# condition2 = conditionalForamt.AddAverageCondition(AverageType.Below)
# condition2.BackColor = Color.get_DarkGray()
# Save the workbook to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/AboveOrBelowAverage.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
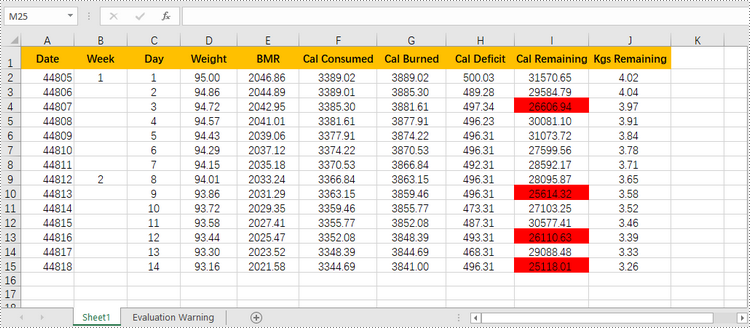
Highlight Values Between Two Numbers in Excel
Highlighting values between a specific range helps you quickly identify and focus on the relevant data points that fall within the range. The following are the steps to highlight values between two numbers using conditional formatting with Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet from the workbook through Workbook.Worsheets[index] property.
- Add a conditional format to the worksheet using Worksheet.ConditionalFormats.Add() method and return an object of XlsConditionalFormats class.
- Specify the cell range where the conditional formatting will be applied using XlsConditionalFormats.AddRange() method.
- Add a condition using XlsConditionalFormats.AddCondition() method to change the color of the cells with values between two specific numbers.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load a file from disk
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/input.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add a conditional format to the worksheet
conditionalForamt = sheet.ConditionalFormats.Add()
# Specify the range where the conditional format will be applied
conditionalForamt.AddRange(sheet.Range["I2:I15"])
# Create a condition and format the cells that meet the condition
condition = conditionalForamt.AddCondition()
condition.FormatType = ConditionalFormatType.CellValue
condition.Operator = ComparisonOperatorType.Between
condition.FirstFormula = "25000"
condition.SecondFormula = "27000"
condition.BackColor = Color.get_Red()
# Save the workbook to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/ValuesBetweenTwoNumbers.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Footnotes are a valuable tool in Microsoft Word that allows you to enhance the content of your documents by providing additional information, references, or citations at the bottom of a page. For example, you can use footnotes to provide in-depth explanations of complex concepts, cite sources to support your arguments, or offer tangential information that might be interesting to your readers. Whether you're working on an academic paper, a book, or any document that requires citations or explanations, footnotes offer a convenient way to maintain a clean and organized layout while presenting supplementary details. In this article, we will explain how to insert or remove footnotes in a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Insert a Footnote for a Specific Paragraph in Word in Python
- Insert a Footnote for a Specific Text in Word in Python
- Remove Footnotes in a Word Document in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Insert a Footnote for a Specific Paragraph in Word in Python
You can use the Paragraph.AppendFootnote(FootnoteType.Footnote) method provided by Spire.Doc for Python to easily add a footnote for a specific paragraph. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific section in the document using Document.Section[int] property and then get a specific paragraph of the section using Section.Paragraphs[int] property.
- Add a footnote at the end of the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendFootnote(FootnoteType.Footnote) method.
- Set the text content of the footnote, and then set the font and color for the footnote text and the footnote reference mark.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Load a sample Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Get a specific section
section = document.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get a specific paragraph
paragraph = section.Paragraphs.get_Item(3)
# Add a footnote at the end of the paragraph
footnote = paragraph.AppendFootnote(FootnoteType.Footnote)
# Set the text content of the footnote
text = footnote.TextBody.AddParagraph().AppendText("The industry code list is available online.")
# Set the text font and color
text.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
text.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
text.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_DarkBlue()
# Set the font and color of the footnote reference mark
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.FontName = "Calibri"
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.FontSize = 15
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.Bold = True
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_DarkCyan()
# Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("AddFootnoteForParagraph.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()

Insert a Footnote for a Specific Text in Word in Python
To add a footnote for a specific text, you need to find the text in the document, get the location of the text in its owner paragraph, and then insert the footnote after the text. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Find a specific text using Document.FindString() method.
- Get the found text as a single text range using TextSelection.GetAsOneRange() method.
- Get the paragraph where the text range is located using TextRange.OwnerParagraph property.
- Get the index position of the text range in the paragraph using Paragraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf() method.
- Add a footnote to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendFootnote(FootnoteType.Footnote) method, and then insert the footnote after the specific text using Paragraph.ChildObjects.Insert() method.
- Set the text content of the footnote, and then set the font and color for the footnote text and the footnote reference mark.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Load a sample Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Find a specific text
selection = document.FindString("major players", False, True)
# Get the found text as a single text range
textRange = selection.GetAsOneRange()
# Get the paragraph where the text range is located
paragraph = textRange.OwnerParagraph
# Get the index position of the text range in the paragraph
index = paragraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf(textRange)
# Add a footnote to the paragraph
footnote = paragraph.AppendFootnote(FootnoteType.Footnote)
# Insert the footnote after the text range
paragraph.ChildObjects.Insert(index + 1, footnote)
# Set the text content of the footnote
text = footnote.TextBody.AddParagraph().AppendText("Including suppliers, competitors, and customers")
# Set the text font and color
text.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
text.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
text.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_DarkBlue()
# Set the font and color of the footnote reference mark
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.FontName = "Calibri"
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.FontSize = 15
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.Bold = True
footnote.MarkerCharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_DarkGreen()
# Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("AddFootnoteForText.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()

Remove Footnotes in a Word Document in Python
When the footnotes of a Word document are no longer needed, you can remove them to make the document neater. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific section using Document.Sections[int] property.
- Loop through each paragraph in the section to find the footnotes.
- Remove the footnotes using Paragraph.ChildObjects.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Load a sample Word document
document.LoadFromFile("AddFootnoteForParagraph.docx")
# Get the first section of the document
section = document.Sections[0]
# Loop through the paragraphs in the section
for y in range(section.Paragraphs.Count):
para = section.Paragraphs.get_Item(y)
index = -1
i = 0
cnt = para.ChildObjects.Count
while i < cnt:
pBase = para.ChildObjects[i] if isinstance(para.ChildObjects[i], ParagraphBase) else None
if isinstance(pBase, Footnote):
index = i
break
i += 1
if index > -1:
# Remove the footnotes from the paragraph
para.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(index)
# Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("RemoveFootnotes.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
document.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
PDF properties refer to the information embedded within the document that provides detailed information about the documents, such as author, creation date, last modification date, etc. Users can check the properties of a PDF document in PDF viewers to quickly grasp the key information of the document. Apart from the built-in properties, PDF documents also offer the feature of customizing properties to help provide additional information about the document. Understanding how to specify and access this document information facilitates the creation of user-friendly documents and the processing of documents in large quantities. In this article, we will explore how to set and retrieve PDF properties through Python programs using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Set PDF Properties with Python
Spire.PDF for Python provides several properties under the PdfDocumentInformation class for setting built-in document properties, such as author, subject, keywords. Besides, it also provides the PdfDocumentInformation.SetCustomProperty() method to set custom properties. The following are the detailed steps to set PDF properties:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the properties of the document through PdfDocument.DocumentInformation property.
- Set the built-in properties through properties under PdfDocumentInformation class.
- Set custom properties using PdfDocumentInformation.SetCustomProperty() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get the properties of the document
properties = pdf.DocumentInformation
# Set built-in properties
properties.Author = "Tim Taylor"
properties.Creator = "Spire.PDF"
properties.Keywords = "cloud service; digital business"
properties.Subject = "The introduction of cloud service and its advantages"
properties.Title = "The Power of Cloud Services: Empowering Businesses in the Digital Age"
properties.Producer = "Spire.PDF for Python"
# Set custom properties
properties.SetCustomProperty("Company", "E-iceblue")
properties.SetCustomProperty("Tags", "Cloud; Business; Server")
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/SetPDFProperties.pdf")
pdf.Close()
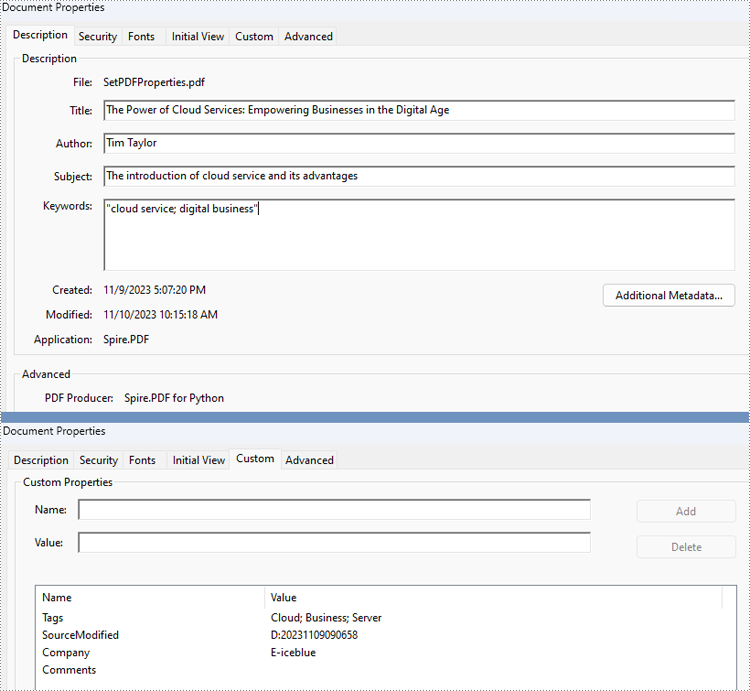
Retrieve PDF Properties with Python
Information in built-in PDF properties can be obtained using the properties under the PdfDocumentInformation class, while that in custom PDF properties can be obtained using PdfDocumentInformation.GetCustomProperty() method. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the properties of the document through PdfDocument.DocumentInformation property.
- Retrieve the built-in properties through properties under PdfDocumentInformation class and custom properties using PdfDocumentInformation.GetCustomProperty() method and print them.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("output\SetPDFProperties.pdf")
# Get the properties of the document
properties = pdf.DocumentInformation
# Create a StringBuilder object
information = ""
# Retrieve the built-in properties
information += "Author: " + properties.Author
information += "\nTitle: " + properties.Title
information += "\nSubject: " + properties.Subject
information += "\nKeywords: " + properties.Keywords
information += "\nCreator: " + properties.Creator
information += "\nProducer: " + properties.Producer
# Retrieve the custom properties
information += "\nCompany: " + properties.GetCustomProperty("Company")
information += "\nTags: " + properties.GetCustomProperty("Tags")
# Print the document properties
print(information)
pdf.Close()
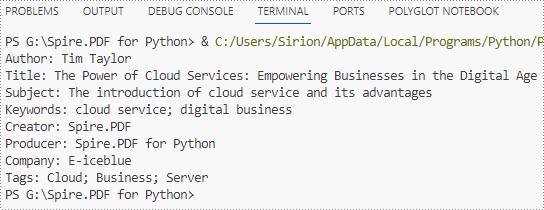
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
A table is a powerful tool in a Word document that allows you to organize and present information in a structured manner. It consists of rows and columns, forming a grid-like structure. Tables are commonly used for various purposes, such as creating schedules, comparing data, or displaying data in a neat and organized format. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically create tables in a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Create a Simple Table in Word in Python
- Create a Table from an HTML String in Python
- Merge and Split Cells in a Table in Python
- Fill a Table with Data in Word in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Prerequisite Knowledge
Spire.Doc for Python offers the Table class to represent a table in a Word document. You can create table objects either through the constructor or the Section.AddTable() method. After the table object is created, you can use the Table.AddRow() method to dynamically add rows to the table, or specify the number of rows and columns of the table, and then populate it with data in a single pass.
Also, Spire.Doc for Python supports creating tables from an HTML string. This method does not return an object of Table. Therefore, you cannot use the properties or methods under the Table class to deal with the table created from an HTML string. You need to set up the content and style of the table in the HTML string.
Create a Simple Table in Word in Python
This example demonstrates how to create a simple plain table using the Table class and how to add rows one by one. Here are the main steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section to it using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create a Table object.
- Add a row to it using Table.AddRow() method.
- Get a specific cell of the row through Row.Cells[index] property.
- Add text to the cell using TableCell.AddParagraph().AppendText() method.
- Add the table to the document using Section.AddTable() method.
- Save the document to a .docx file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Create a table
table = Table(doc, True)
# Set the width of table
table.PreferredWidth = PreferredWidth(WidthType.Percentage, int(100))
# Set the border of table
table.TableFormat.Borders.BorderType = BorderStyle.Single
table.TableFormat.Borders.Color = Color.get_Black()
# Add a row
row = table.AddRow(False, 3)
row.Height = 20.0
# Add data to the cells
cell = row.Cells[0]
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paragraph.AppendText("Row 1, Col 1")
cell = row.Cells[1]
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paragraph.AppendText("Row 1, Col 2")
cell = row.Cells[2]
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paragraph.AppendText("Row 1, Col 3")
# Add the second row
row = table.AddRow(False, 3)
row.Height = 20.0
cell = row.Cells[0]
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paragraph.AppendText("Row 2, Col 1")
cell = row.Cells[1]
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paragraph.AppendText("Row 2, Col 2")
cell = row.Cells[2]
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paragraph.AppendText("Row 2, Col 3")
# Add the table to the section
section.Tables.Add(table)
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/CreateTable.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
doc.Close()
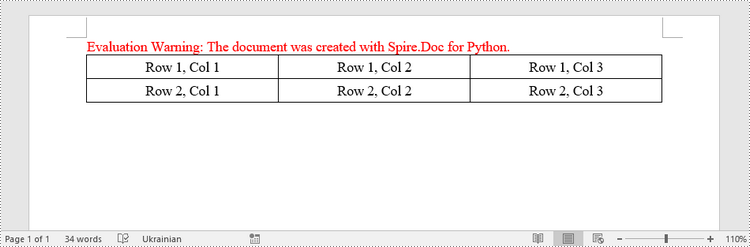
Create a Table from an HTML String in Python
To create a table from an HTML string, use the Paragraph.AppendHTML() method. The following are the steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section to it using Document.AddSection() method.
- Specify the HTML string for generating the table.
- Add a paragraph using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Add the HTML table to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendHTML() method.
- Save the document to a .docx file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Add a section
section = document.AddSection()
# Specify HTML string
HTML = "<table border='2px'>" + "<tr>" + "<td>Row 1, Cell 1</td>" + "<td>Row 1, Cell 2</td>" + \
"</tr>" + "<tr>" + "<td>Row 2, Cell 2</td>" + \
"<td>Row 2, Cell 2</td>" + "</tr>" + "</table>"
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
# Append HTML string to the paragraph
paragraph.AppendHTML(HTML)
# Save to Word document
document.SaveToFile("output/HtmlTable.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
document.Close()
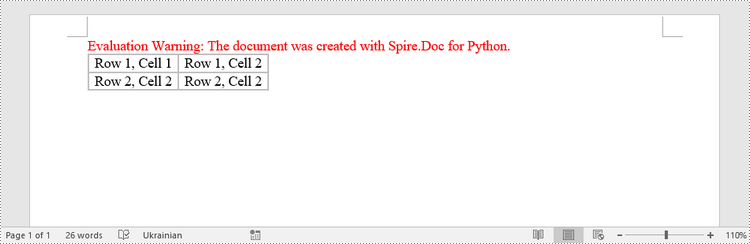
Merge and Split Cells in a Table in Python
When working with tables, the ability to merge or split cells provides a powerful way to customize and format data. This example shows you how to combine adjacent cells into a single cell and how to divide a single cell into multiple smaller cells using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Add a table using Section.AddTable() method.
- Set the column number and row number of the table using Table.ResetCells() method.
- Horizontally merge cells using Table.ApplyHorizontalMerge() method.
- Vertically merge cells using Table.ApplyVerticalMerge() method.
- Split a cell into multiple smaller cells using TableCell.SplitCell() method.
- Save the document to a .docx file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Add a section
section = document.AddSection()
# Create a table
table = section.AddTable(True)
# Set the row number and column number of table
table.ResetCells(4, 4)
# Set the width of table
table.PreferredWidth = PreferredWidth(WidthType.Percentage, int(100))
# Set row height
for i in range(0, table.Rows.Count):
table.Rows[i].Height = 20.0
# Horizontally merge cells
table.ApplyHorizontalMerge(0, 0, 3)
# Vertically merge cells
table.ApplyVerticalMerge(0, 2, 3)
# Get a cell
cell = table.Rows.get_Item(1).Cells.get_Item(3)
# Split the cell into 3 smaller cells
cell.SplitCell(3, 0)
# Fill specified cells with color
table.Rows[0].Cells[0].CellFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightBlue()
table.Rows[2].Cells[0].CellFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightBlue()
table.Rows[1].Cells[3].CellFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightGray()
table.Rows[1].Cells[4].CellFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightGray()
table.Rows[1].Cells[5].CellFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightGray()
# Save to Word document
document.SaveToFile("output/MergeAndSplit.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
document.Close()
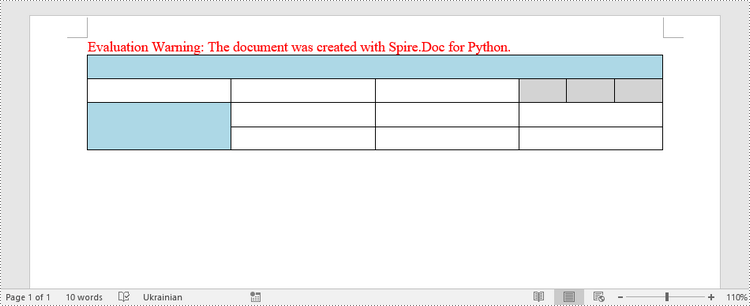
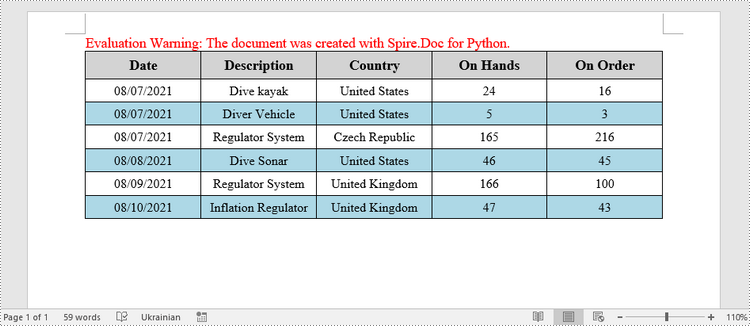
Fill a Table with Data in Word in Python
This example creates a 5x7 table, writes the data from lists into the cells, and applies different formatting to the header row and other rows. The following are the main steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Add a table using Section.AddTable() method.
- Specify the data for filling the table in two lists.
- Reset the row number and column number of the table depending on the height and width of the data using Table.ResetCells() method.
- Write data into the corresponding cells using TableCell.AddParagraph().AppendText() method.
- Apply different colors to different rows through TableCell.CellFormat.BackColor property.
- Save the document to a .docx file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
import math
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Create a table
table = section.AddTable(True)
# Specify table data
header_data = ["Date", "Description", "Country", "On Hands", "On Order"]
row_data = [ ["08/07/2021","Dive kayak","United States","24","16"],
["08/07/2021","Diver Vehicle","United States","5","3"],
["08/07/2021","Regulator System","Czech Republic","165","216"],
["08/08/2021","Dive Sonar","United States","46","45"],
["08/09/2021","Regulator System","United Kingdom","166","100"],
["08/10/2021","Inflation Regulator","United Kingdom","47","43"]]
# Set the row number and column number of table
table.ResetCells(len(row_data) + 1, len(header_data))
# Set the width of table
table.PreferredWidth = PreferredWidth(WidthType.Percentage, int(100))
# Get header row
headerRow = table.Rows[0]
headerRow.IsHeader = True
headerRow.Height = 23
headerRow.RowFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightGray()
# Fill the header row with data and set the text formatting
i = 0
while i < len(header_data):
headerRow.Cells[i].CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = headerRow.Cells[i].AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
txtRange = paragraph.AppendText(header_data[i])
txtRange.CharacterFormat.Bold = True
txtRange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
i += 1
# Fill the rest rows with data and set the text formatting
r = 0
while r < len(row_data):
dataRow = table.Rows[r + 1]
dataRow.Height = 20
dataRow.HeightType = TableRowHeightType.Exactly
c = 0
while c < len(row_data[r]):
dataRow.Cells[c].CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = dataRow.Cells[c].AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
txtRange = paragraph.AppendText(row_data[r][c])
txtRange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 11
c += 1
r += 1
# Alternate row color
for j in range(1, table.Rows.Count):
if math.fmod(j, 2) == 0:
row2 = table.Rows[j]
for f in range(row2.Cells.Count):
row2.Cells[f].CellFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightBlue()
# Set the border of table
table.TableFormat.Borders.BorderType = BorderStyle.Single
table.TableFormat.Borders.LineWidth = 1.0
table.TableFormat.Borders.Color = Color.get_Black()
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/Table.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Images play a crucial role in effectively communicating complex ideas or concepts. When there are low-quality or outdated images in a Word document, it is necessary to replace the images to enhance the overall visual appeal and professionalism of your document. In this article, you will learn how to replace images in a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
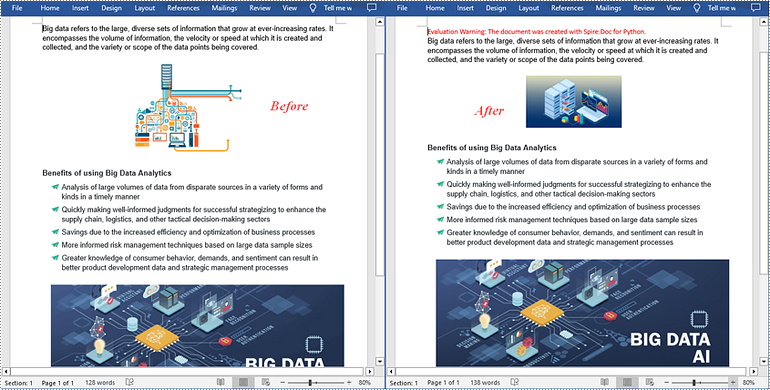
Replace Image with New Image in Word in Python
Spire.Doc for Python supports not only inserting images in Word, but also replacing existing images. The following are the detailed steps to get a specific image in Word and then replace it with a new image.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a list to store the images.
- Iterate through all sections in the document.
- Iterate through all paragraphs in each section.
- Iterate through all child objects in each paragraph.
- Find the images and add them to the list.
- Get a specific image from the list and replace it with another image using DocPicture.LoadImage() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Data.docx")
# Create a list to store the images
pictures = []
# Iterate through all sections in the document
for i in range(doc.Sections.Count):
sec = doc.Sections.get_Item(i)
# Iterate through all paragraphs in each section
for j in range(sec.Paragraphs.Count):
para = sec.Paragraphs.get_Item(j)
# Iterate through all child objects in each paragraph
for k in range(para.ChildObjects.Count):
docObj = para.ChildObjects.get_Item(k)
# Find the images and add them to the list
if docObj.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Picture:
pictures.append(docObj)
# Replace the first picture in the list with a new image
picture = pictures[0] if isinstance(pictures[0], DocPicture) else None
picture.LoadImage("data.jpg")
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("ReplaceImage.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
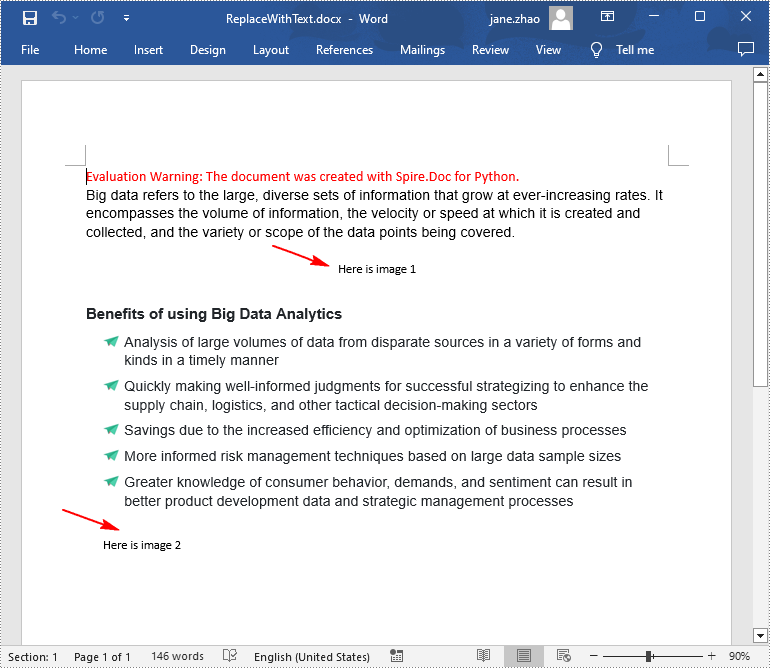
Replace Image with Text in Word in Python
Spire.Doc for Python doesn't provide a direct method to replace image with text, but you can achieve this task by inserting text at the image location and then removing the image from the document.
The following are the steps to replace all images in a Word document with text:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through all sections in the document.
- Iterate through all paragraphs in each section.
- Create a list to store the images.
- Iterate through all child objects in each paragraph.
- Find the images and add them to the list.
- Iterate through the images in the list.
- Get the index of the image in the paragraph using Paragraph.ChildObjects.Indexof() method.
- Initialize an instance of TextRange class and set text for the text range through TextRange.Text property.
- Insert the text range at the image location using Paragraph.ChildObjects.Insert() method.
- Remove the image from the paragraph using Paragraph.ChildObjects.Remove() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Data.docx")
j = 1
# Iterate through all sections in the document
for k in range(doc.Sections.Count):
sec = doc.Sections.get_Item(k)
# Iterate through all sections in the document
for m in range(sec.Paragraphs.Count):
para = sec.Paragraphs.get_Item(m)
# Create a list to store the images
pictures = []
# Find the images and add them to the list
for x in range(para.ChildObjects.Count):
docObj = para.ChildObjects.get_Item(x)
if docObj.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Picture:
pictures.append(docObj)
# Iterate through all images in the list and replace them with text "Here is image {image index}"
for pic in pictures:
index = para.ChildObjects.IndexOf(pic)
textRange = TextRange(doc)
textRange.Text = "Here is image {0}".format(j)
para.ChildObjects.Insert(index, textRange)
para.ChildObjects.Remove(pic)
j += 1
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("ReplaceWithText.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
When working with Word documents, sometimes you may need to adjust the content or layout of the document by deleting certain paragraphs. For example, when you have copied a very long paragraph from the Internet, you can delete redundant paragraphs as needed and keep only the useful ones. Or you can create a new document by deleting irrelevant paragraphs in an existing document. In this case, performing this process programmatically is a better option than tedious manual deletion, which can help you batch process a large number of documents in a short period of time. In this article, we will show you how to remove a specific paragraph or all paragraphs from Word documents in python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Delete a Specific Paragraph from Word Documents
With Spire.Doc for Python library, you are allowed to remove specific paragraphs from Word documents. You just need to get the desired section, and then call the Section.Paragraphs.RemoveAt() method to remove the paragraphs you want. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of Document class.
- Load a Word document from disk using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first section of this file using Document.Sections[] property.
- Remove the first paragraph from this section using Section.Paragraphs.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the result file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Sample.docx"
outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/RemoveParagraphs.docx"
#Create an object of Document class
document = Document()
#Load a sample file from disk
document.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
#Get the first section of this file
section=document.Sections[0]
#Remove the first paragraph from this section
section.Paragraphs.RemoveAt(0)
#Save the result file
document.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx2013)
document.Close()

Delete All Paragraphs from Word Documents
In addition, if you want to clear all paragraphs of the Word document at once, please loop through all sections first and call the Section.Paragraphs.Clear() method to do that. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of Document class.
- Load a Word document from disk using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Loop through all sections first and remove all paragraphs in each section by using Section.Paragraphs.Clear() method.
- Save the result file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Sample.docx"
outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/RemoveAllParagraphs.docx"
#Create an object of Document class
document = Document()
#Load a sample file from disk
document.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
#Remove paragraphs from the body of every section in the document
for i in range(document.Sections.Count):
section = document.Sections.get_Item(i)
section.Paragraphs.Clear()
#Save the result file
document.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx2013)
document.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
PowerPoint presentations often contain sensitive information, such as financial data, trade secrets, or personal details. When sharing these files via email or cloud storage, it is important to prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing or viewing them. To protect the content of your PowerPoint presentation, there are various security measures you can employ. For instance, you can implement password protection, or make the presentation as final or read-only. In certain situations, you may find the need to unprotect a password-protected or encrypted PowerPoint presentation. This may be necessary when you need to share the file with the public or when the password is no longer needed. In this article, we will explain how to protect or unprotect a PowerPoint presentation in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Protect a PowerPoint Presentation with a Password
- Mark a PowerPoint Presentation as Final
- Make a PowerPoint Presentation Read-Only
- Remove Password Protection from a PowerPoint Presentation
- Remove Mark as Final Option from a PowerPoint Presentation
- Remove Read-Only Option from a PowerPoint Presentation
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
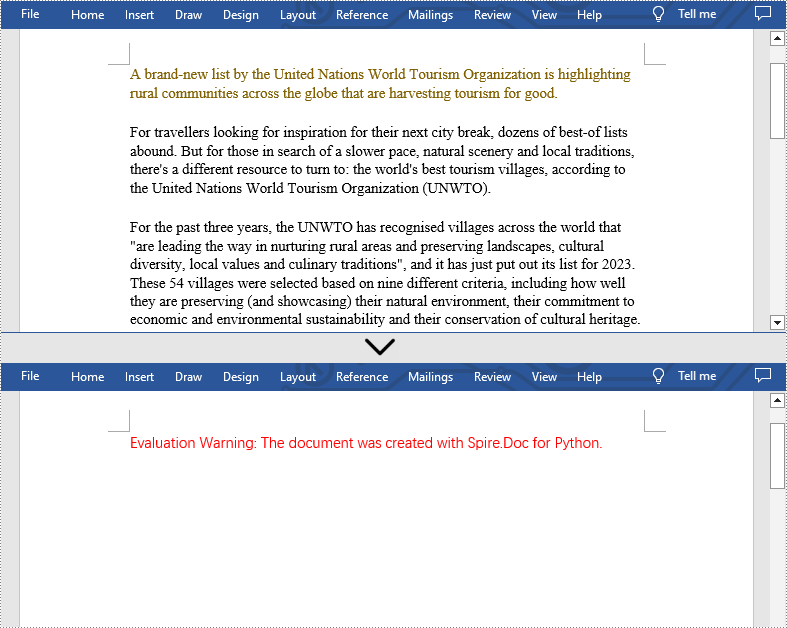
Protect a PowerPoint Presentation with a Password
You can protect a PowerPoint presentation with a password to ensure that only the people who have the right password can view and edit it.
The following steps demonstrate how to protect a PowerPoint presentation with a password:
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Encrypt the presentation with a password using Presentation.Encrypt() method.
- Save the resulting presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Encrypy the presentation with a password
presentation.Encrypt("your password")
# Save the resulting presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("Encrypted.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
presentation.Dispose()
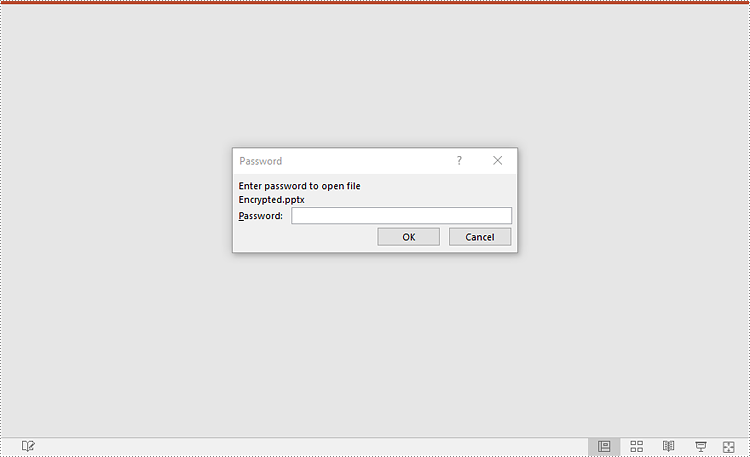
Mark a PowerPoint Presentation as Final
You can mark a PowerPoint presentation as final to inform readers that the document is final and no further editing is expected.
The following steps demonstrate how to mark a PowerPoint presentation as final:
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Mark the presentation as final using presentation.DocumentProperty.MarkAsFinal property.
- Save the resulting presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Mark the presentation as final
presentation.DocumentProperty.MarkAsFinal = True
# Save the resulting presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("MarkAsFinal.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
presentation.Dispose()
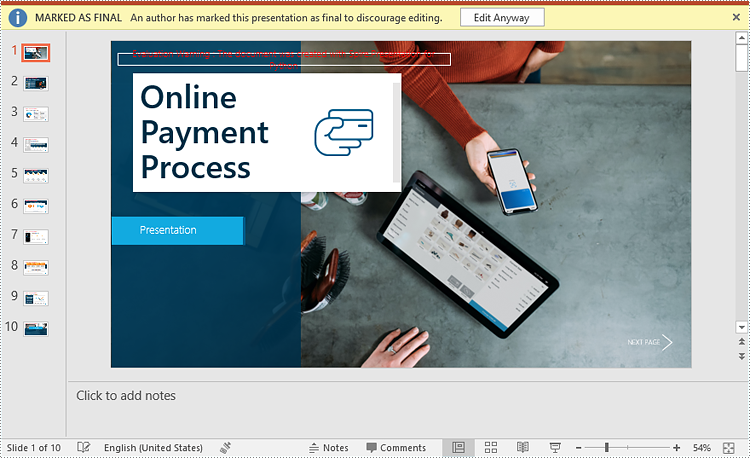
Make a PowerPoint Presentation Read-Only
You can make a PowerPoint presentation read-only to allow others to view it while preventing them from making any changes to the content.
The following steps demonstrate how to make a PowerPoint presentation read-only:
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Make the presentation read-only using Presentation.Protect() method.
- Save the resulting presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Make the presentation read-only by protecting it with a password
presentation.Protect("your password")
# Save the resulting presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("ReadOnly.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
presentation.Dispose()
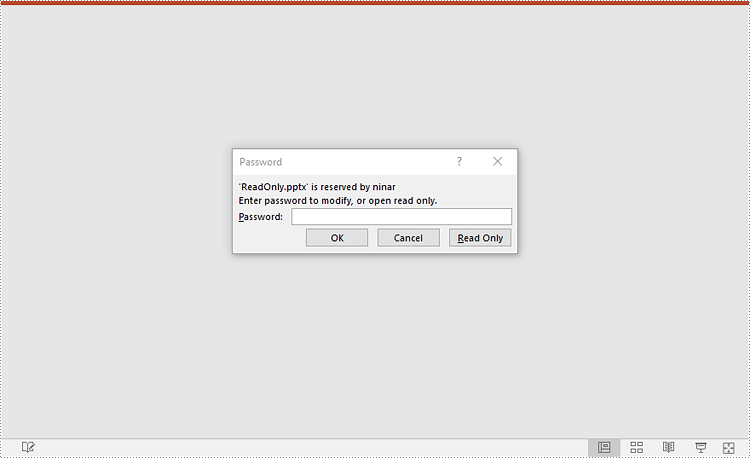
Remove Password Protection from a PowerPoint Presentation
You can remove password protection from a PowerPoint presentation by loading the presentation with the correct password and then removing the password protection from it.
The following steps demonstrate how to remove password protection from a PowerPoint presentation:
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a password-protected PowerPoint presentation with its password using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove password protection from the presentation using Presentation.RemoveEncryption() method.
- Save the resulting presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load an encrypted PowerPoint presentation with its password
presentation.LoadFromFile("Encrypted.pptx", "your password")
# Remove password encryption from the presentation
presentation.RemoveEncryption()
# Save the resulting presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("Decrypted.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
presentation.Dispose()
Remove Mark as Final Option from a PowerPoint Presentation
The mark as final feature makes a PowerPoint presentation read-only to prevent further changes, if you decide to make changes to the presentation later, you can remove the mark as final option from it.
The following steps demonstrate how to remove the mark as final option from a PowerPoint presentation:
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation that has been marked as final using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove the mark as final option from the presentation using presentation.DocumentProperty.MarkAsFinal property.
- Save the resulting presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation that has been marked as final
presentation.LoadFromFile("MarkAsFinal.pptx")
# Remove the mark as final option from the presentation
presentation.DocumentProperty.MarkAsFinal = False
# Save the resulting presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("RemoveMarkAsFinal.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
presentation.Dispose()

Remove Read-Only Option from a PowerPoint Presentation
Removing the read-only option from a PowerPoint presentation allows you to regain full editing capabilities, enabling you to modify, add, or delete content within the presentation as needed.
The following steps demonstrate how to remove the read-only option from a PowerPoint presentation:
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation that has been made as read-only using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove the read-only option from the presentation using Presentation.RemoveProtect() method.
- Save the resulting presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation that has been made as read-only
presentation.LoadFromFile("ReadOnly.pptx")
# Remove the read-only option from the presentation
presentation.RemoveProtect()
# Save the resulting presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("RemoveReadOnly.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
presentation.Dispose()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Data validation in Excel is a powerful feature that allows you to control the type and range of data that can be entered into a cell or a range of cells. The main goal of data validation is to prevent errors and inconsistencies in data, which can lead to inaccurate analysis, reporting, and decision-making. Data validation helps ensure data accuracy by setting specific criteria for data entry. In this article, you will learn how to add or remove data validation in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Add Various Types of Data Validation to Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the DataValidation class to handle data validation in a specific cell or range. Through the properties under the DataValidation object, you can specify validation type, formula, compare operator, etc. The following are the steps to add data validation to an Excel cell using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific cell through Worksheet.Range property.
- Set the data validation type, formula, compare operator and other related attributes through the properties under CellRarange.DataValidation object.
- Save the workbook to another Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Insert text in cells
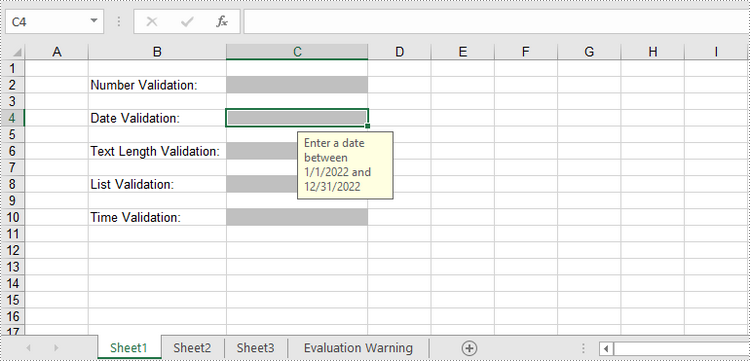
sheet.Range["B2"].Text = "Number Validation:"
sheet.Range["B4"].Text = "Date Validation:"
sheet.Range["B6"].Text = "Text Length Validation:"
sheet.Range["B8"].Text = "List Validation:"
sheet.Range["B10"].Text = "Time Validation:"
# Add number validation to C2
rangeNumber = sheet.Range["C2"]
rangeNumber.DataValidation.AllowType = CellDataType.Integer
rangeNumber.DataValidation.CompareOperator = ValidationComparisonOperator.Between
rangeNumber.DataValidation.Formula1 = "1"
rangeNumber.DataValidation.Formula2 = "10"
rangeNumber.DataValidation.InputMessage = "Enter a number between 1 and 10"
rangeNumber.Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.Gray25Percent
# Add date validation to C4
rangeDate = sheet.Range["C4"]
rangeDate.DataValidation.AllowType = CellDataType.Date
rangeDate.DataValidation.CompareOperator = ValidationComparisonOperator.Between
rangeDate.DataValidation.Formula1 = "01/01/2022"
rangeDate.DataValidation.Formula2 = "31/12/2022"
rangeDate.DataValidation.InputMessage = "Enter a date between 01/01/2022 and 31/12/2022"
rangeDate.Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.Gray25Percent
# Add text length validation to C6
rangeTextLength = sheet.Range["C6"]
rangeTextLength.DataValidation.AllowType = CellDataType.TextLength
rangeTextLength.DataValidation.CompareOperator = ValidationComparisonOperator.LessOrEqual
rangeTextLength.DataValidation.Formula1 = "5"
rangeTextLength.DataValidation.InputMessage = "Enter text lesser than 5 characters"
rangeTextLength.Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.Gray25Percent
# Apply list validation to C8
rangeList = sheet.Range["C8"]
rangeList.DataValidation.Values = ["United States", "Canada", "United Kingdom", "Germany"]
rangeList.DataValidation.IsSuppressDropDownArrow = False
rangeList.DataValidation.InputMessage = "Choose an item from the list"
rangeList.Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.Gray25Percent
# Apply time validation to C10
rangeTime = sheet.Range["C10"]
rangeTime.DataValidation.AllowType = CellDataType.Time
rangeTime.DataValidation.CompareOperator = ValidationComparisonOperator.Between
rangeTime.DataValidation.Formula1 = "9:00"
rangeTime.DataValidation.Formula2 = "12:00"
rangeTime.DataValidation.InputMessage = "Enter a time between 9:00 and 12:00"
rangeTime.Style.KnownColor = ExcelColors.Gray25Percent
# Auto fit width of column 2
sheet.AutoFitColumn(2)
# Set the width of column 3
sheet.Columns[2].ColumnWidth = 20
# Save to file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/DataValidation.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
Remove Data Validation from Excel in Python
To remove the data validation from an Excel worksheet, use the Worksheet.DVTable.Remove(list rectangles) method. The parameter list specifies the cells to remove validation. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load the Excel file containing data validation using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the specified worksheet though Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Create a list of rectangles, which is used to specify the cells where the validation will be removed.
- Remove the data validation from the selected cells using Worksheet.DVTable.Remove() method.
- Save the workbook to another Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load a sample Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\DataValidation.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Create a list of rectangles to specify the cells or cell ranges where the data validation will be removed
rects= []
rects.append(Rectangle.FromLTRB(0,0,2,9))
# Remove the data validation from the selected cells
worksheet.DVTable.Remove(rects)
# Save the workbook to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/RemoveDataValidation.xlsx")
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
