C#/VB.NET: Apply Fonts to Excel Cells
When you’re creating or reviewing a worksheet, you may want to format text in some specific cells using font styles in order to make them stand out. For example, you can change the font type, font color, font size and make text bold. This article will show you how to apply fonts to individual cells or cell ranges by using Spire.XLS for .NET.
- Apply Different Fonts to Different Cells
- Appy Multiple Fonts in a Single Cell
- Apply a Font to a Cell Range
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for.NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Apply Different Fonts to Different Cells
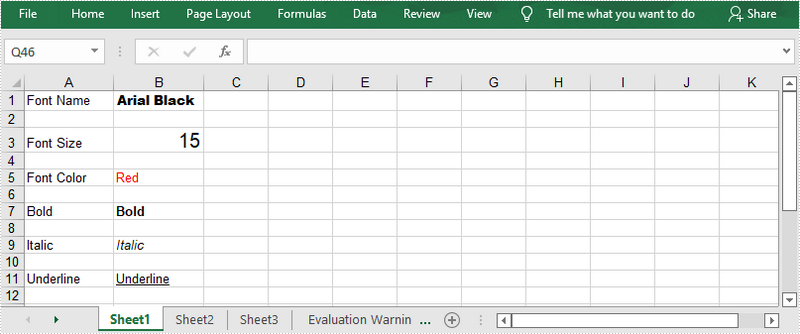
Spire.XLS provides the CellRange.Style.Font property which you can use to set or change the font name, color, size and style in a cell easily. The following are the steps to apply a font style to a specific cell using Spire.XLS for .NET.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get the first worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific cell using Worksheet.Range[int Row, int Column] property.
- Set the value of the cell using CellRange.Value property.
- Set the font name, color, size and style of the cell value through the properties under the CellRange.Value.Font object.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Drawing;
namespace ApplySingleFontInCellRange
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Set font name
int row = 1;
sheet.Range[row, 1].Value = "Font Name";
sheet.Range[row, 2].Value = "Arial Black";
sheet.Range[row, 2].Style.Font.FontName = "Arial Black";
//Set font size
sheet.Range[row += 2, 1].Value = "Font Size";
sheet.Range[row, 2].Value = "15";
sheet.Range[row, 2].Style.Font.Size = 15;
//Set font color
sheet.Range[row += 2, 1].Value = "Font Color";
sheet.Range[row, 2].Value = "Red";
sheet.Range[row, 2].Style.Font.Color = Color.Red;
//Make text bold
sheet.Range[row += 2, 1].Value = "Bold";
sheet.Range[row, 2].Value = "Bold";
sheet.Range[row, 2].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
//Make text italic
sheet.Range[row += 2, 1].Value = "Italic";
sheet.Range[row, 2].Value = "Italic";
sheet.Range[row, 2].Style.Font.IsItalic = true;
//Underline text
sheet.Range[row += 2, 1].Value = "Underline";
sheet.Range[row, 2].Value = "Underline";
sheet.Range[row, 2].Style.Font.Underline = FontUnderlineType.Single;
//Strikethrough text
sheet.Range[row += 2, 1].Value = "Strikethrough ";
sheet.Range[row, 2].Value = "Strikethrough ";
sheet.Range[row, 2].Style.Font.IsStrikethrough = true;
//Auto fit column width
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns();
//Save the workbook to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("ApplySingleFontInCell.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
}
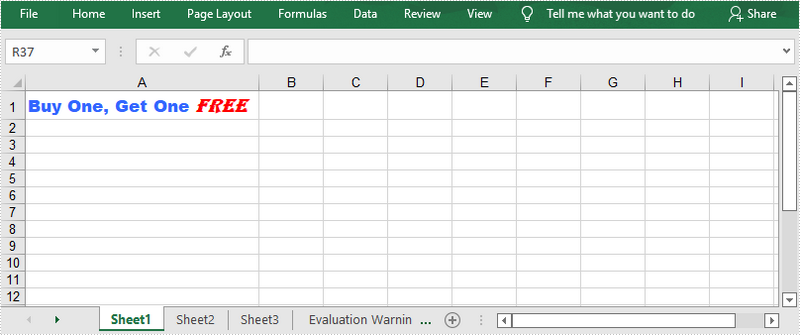
Appy Multiple Fonts in a Single Cell
Mixing fonts in a single cell can help you emphasize some specific characters within the cell. The following are the steps to apply multiple fonts in a cell using Spire.XLS for .NET.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get the first worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Create two ExcelFont objects using Workbook.CreateFont() method.
- Get a specific cell using Worksheet.Range[int Row, int Column] property, and set the rich text content of the cell using CellRange.RichText.Text property.
- Apply the two ExcelFont objects to the rich text using RichText.SetFont() method.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
namespace ApplyMultipleFontsInACell
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Create a font
ExcelFont font1 = workbook.CreateFont();
font1.FontName = "Arial Black";
font1.KnownColor = ExcelColors.LightBlue;
font1.IsBold = true;
font1.Size = 13;
//Create another font
ExcelFont font2 = workbook.CreateFont();
font2.KnownColor = ExcelColors.Red;
font2.IsBold = true;
font2.IsItalic = true;
font2.FontName = "Algerian";
font2.Size = 15;
//Returns a RichText object from a specified cell
RichText richText = sheet.Range["A1"].RichText;
//Set the text of RichText object
richText.Text = "Buy One, Get One Free";
//Apply the first font to specified range of characters
richText.SetFont(0, 16, font1);
//Apply the second font to specified range of characters
richText.SetFont(17, 21, font2);
//Set column width
sheet.Columns[0].ColumnWidth = 33;
//Save the workbook to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("ApplyMultipleFonts.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
}
Apply a Font to a Cell Range
Spire.XLS provides the CellStyle class to manage the cell formatting such as fill color, text alignment and font style. You can create a cell style and apply it to a cell range or the whole worksheet using CellRange.ApplyStyle() method and Worksheet.ApplyStyle() method, respectively. The following are the steps to apply a font to a cell range using Spire.XLS for .NET.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Create a CellStyle object using Workbook.Styles.Add() method, and set the font style through the CellStyle.Font property.
- Apply the cell style to a cell range using CellRange.ApplyStyle() method.
- Save the workbook to another Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Drawing;
namespace ApplyFontToCellRange
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load a sample Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile(@"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\sample.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Create a CellStyle object
CellStyle fontStyle = workbook.Styles.Add("headerFontStyle");
//Set the font color, size and style
fontStyle.Font.Color = Color.White;
fontStyle.Font.IsBold = true;
fontStyle.Font.Size = 12;
fontStyle.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center;
//Create a CellStyleFlag object, setting the FontColor, FontBold, FontSize and HorizontalAlignment properties to true
CellStyleFlag flag = new CellStyleFlag();
flag.FontColor = true;
flag.FontBold = true;
flag.FontSize = true;
flag.HorizontalAlignment = true;
//Apply the cell style to header row
sheet.Range[1, 1, 1, 8].ApplyStyle(fontStyle, flag);
//Apply the cell style to the whole worksheet
//sheet.ApplyStyle(fontStyle);
//Save the workbook to another Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("ApplyFontToCellRange.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
C#/VB.NET: Set Background Color and Pattern for Excel Cells
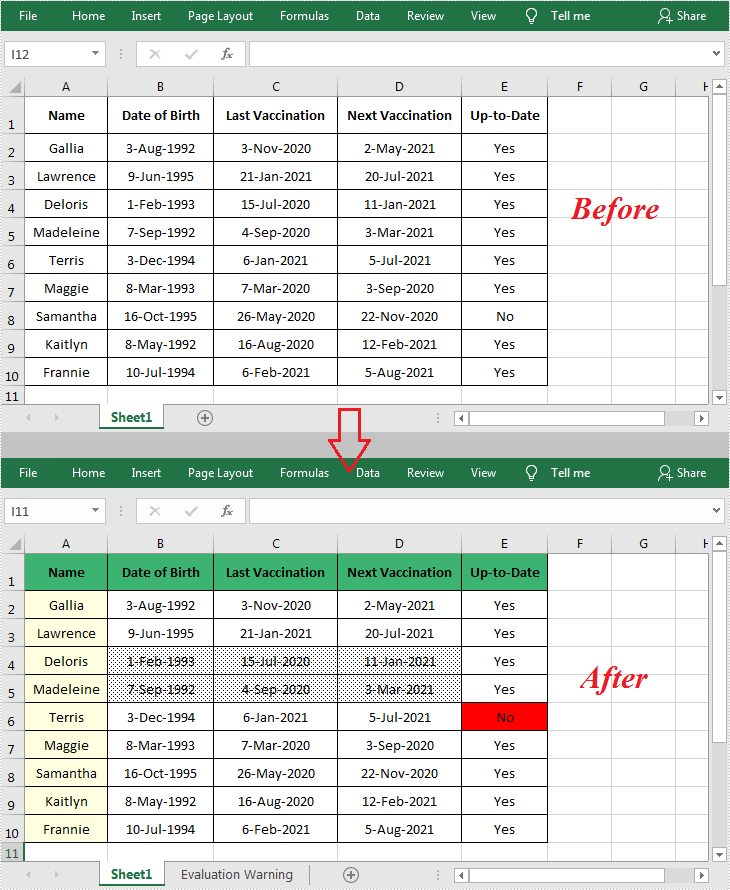
By default, the cells in an Excel document are formatted with a background color of transparent. When you need to emphasize some important data in particular cells, Microsoft Excel provides the "Fill Color" formatting option to change the background color or pattern style of the cells. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically set background color and pattern style for a specified cell or cell range in Excel using Spire.XLS for .NET.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Set Background Color and Pattern for Excel Cells
The detailed steps are as follows.
- Instantiate a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Get a specified cell range using Worksheet.Range[] property.
- Get the style of the specified cell range using CellRange.Style property.
- Set the background color for the specified cell range using CellStyle.Color property.
- Set the fill pattern style for the specified cell range using CellStyle.FillPattern property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using System.Drawing;
using Spire.Xls;
namespace CellBackground
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Instantiate a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load a sample Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile(@"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\data.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Set background color for Range ["A1:E1"] and ["A2:A10"]
worksheet.Range["A1:E1"].Style.Color = Color.MediumSeaGreen;
worksheet.Range["A2:A10"].Style.Color = Color.LightYellow;
//Set background color for cell E6
worksheet.Range["E6"].Style.Color = Color.Red;
//Set pattern style for Range ["B4:D5"]
worksheet.Range["B4:D5"].Style.FillPattern = ExcelPatternType.Percent125Gray;
//Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("CellBackground.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
C#/VB.NET: Add Hyperlinks to Excel
A hyperlink in Excel is a clickable text or an image that navigates to a specific location, such as a webpage, an existing file, an email address, or another cell in the current workbook. This article will demonstrate how to add hyperlinks to Excel in C# and VB.NET using Spire.XLS for .NET library.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Add Text Hyperlinks to Excel in C# and VB.NET
The following are the steps to add a text hyperlink to Excel:
- Create an instance of Workbook class.
- Get the desired worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Access the specific cell that you want to add hyperlink to using Worksheet.Range[cellName] property.
- Add a hyperlink to the cell using Worksheet.HyperLinks.Add() method.
- Set the type, display text and address for the hyperlink using XlsHyperLink.Type, XlsHyperLink.TextToDisplay and XlsHyperLink.Address properties.
- Autofit column width using XlsWorksheet.AutoFitColumn() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
namespace AddTextHyperlinks
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Add a text hyperlink that leads to a webpage
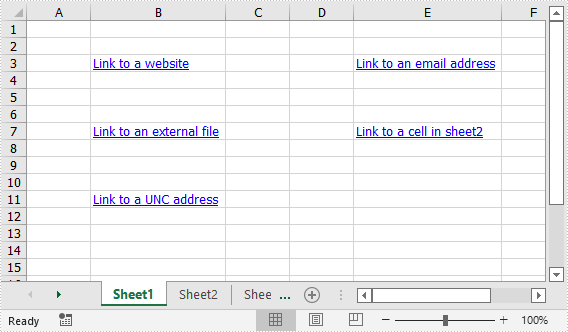
CellRange cell1 = sheet.Range["B3"];
HyperLink urlLink = sheet.HyperLinks.Add(cell1);
urlLink.Type = HyperLinkType.Url;
urlLink.TextToDisplay = "Link to a website";
urlLink.Address = "https://www.google.com/";
//Add a text hyperlink that leads to an email address
CellRange cell2 = sheet.Range["E3"];
HyperLink mailLink = sheet.HyperLinks.Add(cell2);
mailLink.Type = HyperLinkType.Url;
mailLink.TextToDisplay = "Link to an email address";
mailLink.Address = "mailto:abc@outlook.com";
//Add a text hyperlink that leads to an external file
CellRange cell3 = sheet.Range["B7"];
HyperLink fileLink = sheet.HyperLinks.Add(cell3);
fileLink.Type = HyperLinkType.File;
fileLink.TextToDisplay = "Link to an external file";
fileLink.Address = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Report.xlsx";
//Add a text hyperlink that leads to a cell in another sheet
CellRange cell4 = sheet.Range["E7"];
HyperLink linkToSheet = sheet.HyperLinks.Add(cell4);
linkToSheet.Type = HyperLinkType.Workbook;
linkToSheet.TextToDisplay = "Link to a cell in sheet2";
linkToSheet.Address = "Sheet2!B5";
//Add a text hyperlink that leads to a UNC address
CellRange cell5 = sheet.Range["B11"];
HyperLink uncLink = sheet.HyperLinks.Add(cell5);
uncLink.Type = HyperLinkType.Unc;
uncLink.TextToDisplay = "Link to a UNC address";
uncLink.Address = "\\\\192.168.0.121";
//Autofit column width
sheet.AutoFitColumn(2);
sheet.AutoFitColumn(5);
//Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("AddTextHyperlinks.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
}
}
}
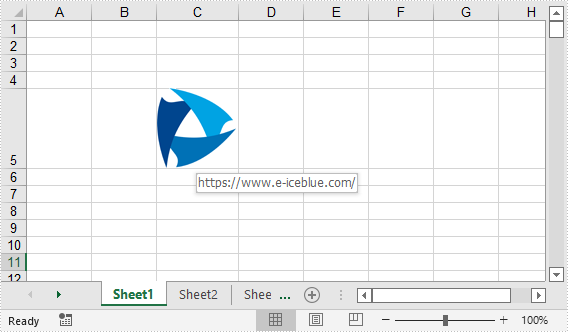
Add Image Hyperlinks to Excel in C# and VB.NET
The following are the steps to add an image hyperlink to Excel:
- Create an instance of Workbook class.
- Get the desired worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Insert an image into the worksheet using Worksheet.Pictures.Add() method and set column width and row height.
- Add a hyperlink to the image using XlsBitmapShape.SetHyperLink() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
namespace AddImageHyperlinks
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Insert an image into the worksheet
ExcelPicture picture = sheet.Pictures.Add(5, 3, "Logo.png");
sheet.Columns[2].ColumnWidth = 11;
sheet.Rows[4].RowHeight = 60;
//Add a hyperlink to the image
picture.SetHyperLink("https://www.e-iceblue.com", true);
//Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("AddImageHyperlink.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Spire.XLS for .NET Program Guide Content
Spire.XLS for .NET is a professional Excel .NET API that can be used to create, read, write, convert and print Excel files in any type of .NET (C#, VB.NET, ASP.NET, .NET Core, .NET 5.0, .NET 6.0, MonoAndroid and Xamarin.iOS) application. Spire.XLS for .NET offers object model Excel API for speeding up Excel programming in .NET platform - create new Excel documents from template, edit existing Excel documents and convert Excel files.
Spire.XLS for .NET enjoys good reputation in both enterprise and individual customers. These customer types include Banks, Data processing houses, Educational institutions, Government organizations, Insurance firms, Legal institutions, Postal/cargo services and etc.
Extract Images from Word Documents Using C#
Extracting images from a Word document programmatically can be useful for automating document processing tasks. In this article, we’ll demonstrate how to extract images from a Word file using C# and the Spire.Doc for .NET library. Spire.Doc is a powerful .NET library that enables developers to manipulate Word documents efficiently.
- Getting Started: Installing Spire.Doc
- Steps for Extracting Images from Word
- Using the Code
- Additional Tips & Best Practices
- Conclusion
Getting Started: Installing Spire.Doc
Before you can start extracting images, you need to install Spire.Doc for .NET. Here's how:
- Using NuGet Package Manager:
- Open your Visual Studio project.
- Right-click on the project in the Solution Explorer and select "Manage NuGet Packages."
- Search for "Spire.Doc" and install the latest version.
- Manual Installation:
- Download the Spire.Doc package from the official website.
- Extract the files and reference the DLLs in your project.
Once installed, you're ready to begin.
Steps for Extracting Images from Word
- Import Spire.Doc module.
- Load the Word document.
- Iterate through sections, paragraphs, and child objects.
- Identify images and saving them to a specified location.
Using the Code
The following C# code demonstrates how to extract images from a Word document:
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
namespace ExtractImages
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Initialize a Document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load the Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx");
// Counter for image files
int index = 0;
// Loop through each section in the document
foreach (Section section in document.Sections)
{
// Loop through paragraphs in the section
foreach (Paragraph paragraph in section.Paragraphs)
{
// Loop through objects in the paragraph
foreach (DocumentObject docObject in paragraph.ChildObjects)
{
// Check if the object is an image
if (docObject.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Picture)
{
// Save the image as a PNG file
DocPicture picture = docObject as DocPicture;
picture.Image.Save(string.Format("output/image_{0}.png", index), System.Drawing.Imaging.ImageFormat.Png);
index++;
}
}
}
}
// Dispose resources
document.Dispose();
}
}
}
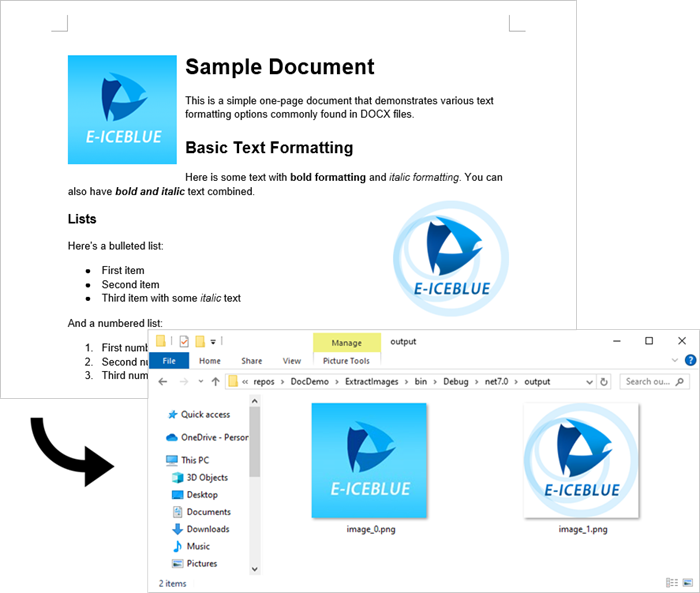
The extracted images will be saved in the "output" folder with filenames like image_0.png, image_1.png, etc.
Additional Tips & Best Practices
- Handling Different Image Formats:
- Convert images to preferred formats (JPEG, BMP) by changing ImageFormat.Png
- Consider using ImageFormat.Jpeg for smaller file sizes
- Error Handling:
- C#
try { // extraction code } catch (Exception ex) { Console.WriteLine($"Error: {ex.Message}"); } - Performance Optimization:
- For large documents, consider using parallel processing
- Implement progress reporting for user feedback
- Advanced Extraction Scenarios:
- Extract images from headers/footers by checking Section.HeadersFooters
Conclusion
Using Spire.Doc in C# simplifies the process of extracting images from Word documents. This approach is efficient and can be integrated into larger document-processing workflows.
Beyond images, Spire.Doc also supports extracting various other elements from Word documents, including:
- Text
- Metadata
- Tables
- Comments
- Textboxes
- Hyperlinks
- OLE Objects
Whether you're building a document management system or automating report generation, Spire.Doc provides a reliable way to handle Word documents programmatically.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for .NET without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
How to Traverse a Document Tree
Document Tree Traversal
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
using Spire.Doc.Interface;
using Spire.Doc.Collections;
namespace ExtractText
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Open a word document.
Document document = new Document("Sample.doc");
IList<IDocumentObject> nodes = GetAllObjects(document);
foreach (IDocumentObject node in nodes)
{
//Judge the object type.
if (node.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.TextRange)
{
TextRange textNode = node as TextRange;
Console.WriteLine(textNode.Text);
}
}
}
private static IList<IDocumentObject> GetAllObjects(Document document)
{
//Create a list.
List<IDocumentObject> nodes = new List<IDocumentObject>();
//Create a new queue.
Queue<ICompositeObject> containers = new Queue<ICompositeObject>();
//Put the document objects in the queue.
containers.Enqueue(document);
while (containers.Count > 0)
{
ICompositeObject container = containers.Dequeue();
DocumentObjectCollection docObjects = container.ChildObjects;
foreach (DocumentObject docObject in docObjects)
{
nodes.Add(docObject);
//Judge the docObject.
if (docObject is ICompositeObject)
{
containers.Enqueue(docObject as ICompositeObject);
}
}
}
return nodes;
}
}
}
Imports System
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports Spire.Doc
Imports Spire.Doc.Documents
Imports Spire.Doc.Fields
Imports Spire.Doc.Interface
Imports Spire.Doc.Collections
Module Module1
Sub Main()
'Open a word document.
Dim document As New Document("Sample.doc")
Dim nodes As IList(Of IDocumentObject)() = GetAllObjects(document)
Dim containers As New Queue(Of ICompositeObject)()
For Each node As IDocumentObject In nodes
'Judge the object type.
If (node.DocumentObjectType = DocumentObjectType.TextRange) Then
Dim textNode As TextRange = node
Console.WriteLine(textNode.Text)
End If
Next
End Sub
Function GetAllObjects(ByVal document As Document) As IList(Of IDocumentObject)
'Create a list.
Dim nodes As New List(Of IDocumentObject)()
'Create a new queue.
Dim containers As New Queue(Of ICompositeObject)()
'Put the document objects in the queue.
containers.Enqueue(document)
While (containers.Count > 0)
Dim container As ICompositeObject = containers.Dequeue()
Dim docObjects As DocumentObjectCollection = container.ChildObjects
For Each docObject As DocumentObject In docObjects
nodes.Add(docObject)
'Judge the docObject.
If TypeOf docObject Is ICompositeObject Then
containers.Enqueue(TryCast(docObject, ICompositeObject))
End If
Next
End While
Return nodes
End Function
End Module
C#: Add or Remove Bookmarks in Word Documents
Bookmarks in Microsoft Word are useful for quickly navigating to specific sections of a document. They allow you to create and name "markers" within your document that you can easily jump to. This can be particularly helpful when working with long or complex documents.
In this article, you will learn how to add and remove bookmarks in a Word document using C# and the Spire.Doc for .NET library.
- Add a Bookmark to a Paragraph in C#
- Add a Bookmark to Specific Text within a Paragraph in C#
- Remove Bookmarks from a Word Document in C#
Install Spire.Doc for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Doc for.NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
Add a Bookmark to a Paragraph in C#
Using Spire.Doc, you can create a bookmark for a paragraph by inserting a BookmarkStart object at the beginning of the paragraph and a BookmarkEnd object at the end of the paragraph. The space between the bookmark start and end points becomes a defined bookmark that can be referenced and accessed as needed.
The detailed steps to add a bookmark to a paragraph are as follows.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document.
- Get a specific paragraph from a specified section.
- Create a BookmarkStart object using Paragraph.AppendBookmarkStart() method.
- Insert the BookmarkStart at the beginning of the selected paragraph.
- Append a BookmarkEnd object to the end of the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendBookmarkEnd() method.
- Save the document to a different Word file.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
namespace AddBookmarkToParagraph
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load a Word file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx");
// Get a specified paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = doc.Sections[0].Paragraphs[2];
// Create a bookmark start
BookmarkStart start = paragraph.AppendBookmarkStart("myBookmark");
// Insert it at the beginning of the paragraph
paragraph.Items.Insert(0, start);
// Append a bookmark end at the end of the paragraph
paragraph.AppendBookmarkEnd("myBookmark");
// Save the file
doc.SaveToFile("AddBookmarkToParagraph.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019);
// Dispose resources
doc.Dispose();
}
}
}
Add a Bookmark to Specific Text within a Paragraph in C#
To add a bookmark to specific text, you need first to find the text and its position within the paragraph. Then, insert a BookmarkStart object before the text and a BookmarkEnd object after the text.
The following are the steps to add a bookmark to specific text within a paragraph using Spire.Doc.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document.
- Find the desired text from the document, and get its position in its owner paragraph.
- Create a BookmarkStart object using Paragraph.AppendBookmarkStart() method.
- Insert the BookmarkStart before the selected text.
- Create a BookmarkEnd object using Paragraph.AppendBookmarkEnd() method.
- Insert the BookmarkEnd object behind the selected text.
- Save the document to a different Word file.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
namespace AddBookmarkToText
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load a Word file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx");
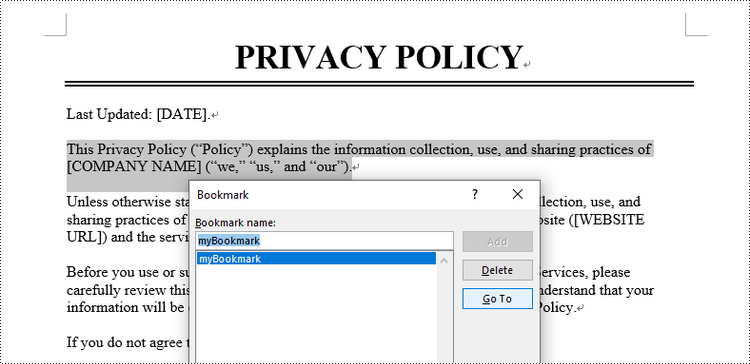
// Specify the string to find
string stringToFind = "Privacy Policy";
// Find the selected text from the document
TextSelection[] finds = doc.FindAllString(stringToFind, false, true);
TextSelection specificText = finds[1];
// Find the paragraph where the text is located
Paragraph para = specificText.GetAsOneRange().OwnerParagraph;
// Get the index of the text in the paragraph
int index = para.ChildObjects.IndexOf(specificText.GetAsOneRange());
// Create a bookmark start
BookmarkStart start = para.AppendBookmarkStart("myBookmark");
// Insert the bookmark start at the index position
para.ChildObjects.Insert(index, start);
// Create a bookmark end
BookmarkEnd end = para.AppendBookmarkEnd("myBookmark");
// Insert the bookmark end at the end of the selected text
para.ChildObjects.Insert(index + 2, end);
// Save the document to another file
doc.SaveToFile("AddBookmarkToText.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019);
// Dispose resources
doc.Dispose();
}
}
}
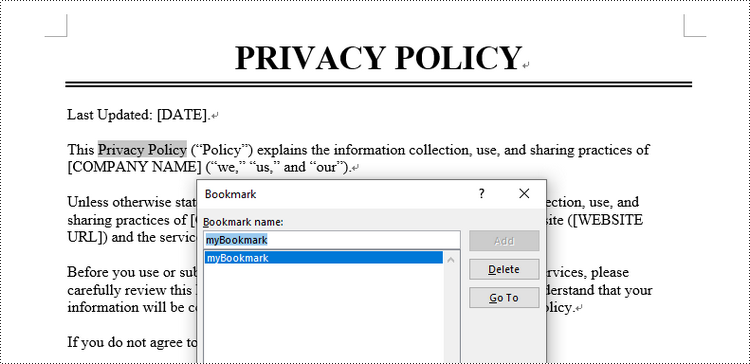
Remove Bookmarks from a Word Document in C#
To remove a specific bookmark or all bookmarks from a Word document, you can use the Bookmarks.Remove() method or the Bookmarks.Clear() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document.
- Get a specific bookmark from the document by its index using Document.Bookmarks[index] property.
- Remove the bookmark using Bookmarks.Remove() method.
- To remove all bookmarks at once, use Document.Bookmarks.Clear() method.
- Save the document to a different Word file.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
namespace RemoveBookmarks
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load a Word file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Bookmarks.docx");
// Get a specific bookmark by its index
Bookmark bookmark = doc.Bookmarks[0];
// Remove the bookmark
doc.Bookmarks.Remove(bookmark);
// Remove all bookmarks at once
// doc.Bookmarks.Clear();
// Save the document.
doc.SaveToFile("RemoveBookmark.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019);
// Dispose resources
doc.Dispose();
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
C#/VB.NET: Add Header and Footer in Word Documents
In Word documents, you can add time, date, title, reference information, page number, content description and image /logo in header or footer to enrich the document. This article shows how to add headers and footers in C# and VB.NET applications using Spire.Doc for .NET.
Install Spire.Doc for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Doc for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLLs files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
- Package Manager
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
Add Header and Footer
The table gives a list of main classes, properties and methods used in the operation.
| Name | Description |
| Document Class | Represents a Word document model. |
| Document. LoadFromFile() Method | Load a Word document. |
| Section Class | Represents a section in a Word document. |
| Document.Sections Property | Gets document sections. |
| HeaderFooter Class | Represents a header and footer model for Word. |
| Section.HeadersFooters.Header Property | Gets headers/footers of current section. |
| Paragraph Class | Represents a paragraph in a document. |
| HeaderFooter. AddParagraph() Method | Adds paragraph at end of section. |
| TextRange Class | Represents a text range. |
| Paragraph.AppendText() Method | Appends text to the end of paragraph. |
| Document. SaveToFile() Method | Saves the document to file in Microsoft Word or another file format. |
The following are the steps about adding header and footer.
- Create an instance of Document class.
- Load the sample document using Document.LoadFromFile(string fileName) method.
- Get the specified section of Word Document using Document.Sections Property
- Add Header
- Get header using HeadersFooters.Header property.
- Add paragraph using HeaderFooter. AddParagraph() method and set paragraph alignment.
- Append text using Paragraph.AppendText(string text) method and set font name, size, color ,etc.
- Add Footer
- Get footer using HeadersFooters.Footer proterty.
- Add paragraph and text in footer.
- Save Word document using Document. SaveToFile(string filename, FileFormat fileFormat) method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using System.Drawing;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
namespace AddHeaderAndFooter
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create an instance of Document class
Document document = new Document();
//Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("input.docx");
//Get the first section of Word Document
Section section = document.Sections[0];
//Get header via HeadersFooters.Header property
HeaderFooter header = section.HeadersFooters.Header;
//Add a paragraph and set paragraph alignment style
Paragraph headerPara = header.AddParagraph();
headerPara.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Left;
//Append text and set font name, size, color,etc.
TextRange textrange = headerPara.AppendText("E-iceblue Co. Ltd." + "\n Your Office Development Master");
textrange.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial";
textrange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 13;
textrange.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.DodgerBlue;
textrange.CharacterFormat.Bold = true;
//Get footer, add paragraph and append text
HeaderFooter footer = section.HeadersFooters.Footer;
Paragraph footerPara = footer.AddParagraph();
footerPara.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center;
textrange = footerPara.AppendText("Copyright © 2021 All Rights Reserved.");
textrange.CharacterFormat.Bold = false;
textrange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 11;
//Save to file
document.SaveToFile("output.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Doc
Imports Spire.Doc.Documents
Imports System.Drawing
Imports Spire.Doc.Fields
Namespace AddHeaderAndFooter
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
'Create an instance of Document class
Dim document As New Document()
'Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("input.docx")
'Get the first section of Word Document
Dim section As Section = document.Sections(0)
'Get header via HeadersFooters.Header property
Dim header As HeaderFooter = section.HeadersFooters.Header
'Add a paragraph and set paragraph alignment style
Dim headerPara As Paragraph = header.AddParagraph()
headerPara.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Left
'Append text and set font name, size, color ,etc.
Dim textrange As TextRange = headerPara.AppendText("E-iceblue Co. Ltd." + vbLf & " Your Office Development Master")
textrange.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
textrange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 13
textrange.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.DodgerBlue
textrange.CharacterFormat.Bold = True
'Get footer, add paragraph and append text
Dim footer As HeaderFooter = section.HeadersFooters.Footer
Dim footerPara As Paragraph = footer.AddParagraph()
footerPara.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
textrange = footerPara.AppendText("Copyright © 2021 All Rights Reserved.")
textrange.CharacterFormat.Bold = False
textrange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 11
'Save to file
document.SaveToFile("output.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
How to Insert Images to Word Documents in C#

Adding images to Word documents programmatically is a common requirement in document automation. Whether you're generating reports, creating invoices, or building dynamic documents, inserting and customizing images can enhance your document's visual appeal.
In this article, we'll explore how to insert images into Word documents using Spire.Doc for .NET, covering local files, byte arrays, and advanced image customization.
- .NET Library for Adding Images to Word
- Insert an Imge from Local to Word
- Insert an Image from a Byte Array to Word
- Further Customize the Image
- Conclusion
.NET Library for Adding Images to Word
Spire.Doc for .NET is a powerful library that enables developers to create, edit, and manipulate Word documents without Microsoft Office dependencies. It provides straightforward methods to insert and format images in Word files.
Key Features:
- Insert images from local storage or byte arrays.
- Adjust image size, rotation, and positioning.
- Control text wrapping around images.
- Support for various image formats (PNG, JPG, BMP, etc.).
To get started, downoad Spire.Doc from our offical website and reference the DLLs in your project. Or, you can install it via NuGet through the following command:
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
Insert an Imge from Local to Word
The simplest method for inserting images into a Word document is to load them directly from your file system. Using Spire.Doc's AppendPicture() method, you can easily specify the file path of the image. This method automatically detects the image format and embeds it into the document.
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
namespace InsertImageFromLocal
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Document object
Document document = new Document();
// Add a section
Section section = document.AddSection();
// Add a paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
// Append a picture from the local disk
paragraph.AppendPicture("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\MyPic.png");
// Save the document
document.SaveToFile("output.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Dispose resources
document.Dispose();
}
}
}

Insert an Image from a Byte Array to Word
In dynamic applications, integrating images from web sources or databases is often essential for enhancing user experience and content relevance.This method downloads images as byte arrays and injecte into the document using a MemoryStream .
By utilizing this technique, developers can dynamically populate documents with up-to-date content, such as logos or product images, directly from online resources or databases.
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
namespace InsertImageFromByteArray
{
class Program
{
static async System.Threading.Tasks.Task Main(string[] args)
{
// URL of the image
string imageUrl = "https://example.com/image.png";
// Download the image
byte[] imageBytes;
using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient())
{
imageBytes = await client.GetByteArrayAsync(imageUrl);
}
// Create a Document object
Document document = new Document();
// Add a section
Section section = document.AddSection();
// Add a paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
// Append a picture from the byte array
using (MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream(imageBytes))
{
paragraph.AppendPicture(stream);
}
// Save the document
document.SaveToFile("output.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Dispose resources
document.Dispose();
}
}
}
Further Customize the Image
Professional documents often demand precise image formatting. Spire.Doc offers extensive controls through the DocPicture class, enabling users to manipulate images effectively.
Key features include resizing to fit layouts, rotating for optimal orientation, and text wrapping options that allow text to flow seamlessly around images. Additionally, users can specify spacing and alignment to position images accurately relative to surrounding content.
// Append an image from disk
DocPicture picture = paragraph.AppendPicture("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\MyPic.png");
// Resize the image to 70%
picture.SetScale(70f);
// Rotate the image 10 degrees counterclockwise
picture.Rotation = -10;
// Specify top and bottom distance to 3 units
picture.DistanceTop = picture.DistanceBottom = 3;
// Set the text wrapping style around the image
picture.TextWrappingStyle = TextWrappingStyle.TopAndBottom;
// Center align the paragraph containing the image
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center;
Conclusion
Using Spire.Doc for .NET simplifies the process of inserting and customizing images in Word documents. Whether pulling images from local storage or online sources, the library provides flexible options to enhance document presentation.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for .NET without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
C#: Edit Word Documents
Editing a Word document is necessary when you want to improve readability, correct errors, refine formatting, maintain consistency, adapt content, facilitate collaboration, and optimize the document for any other purposes. Programmatically editing a Word document using C# can be a powerful approach to automate document processing and manipulation tasks.
In this article, you will learn how to edit a Word document using C# and the Spire.Doc for .NET library.
- Modify Text in a Word Document
- Change Formatting of Text in a Word Document
- Add New Elements to a Word Document
- Remove Paragraphs from a Word Document
Install Spire.Doc for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Doc for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
Modify Text in a Word Document in C#
Spire.Doc allows you to programmatically access specific sections and paragraphs in Word documents. To retrieve a particular section, use the Document.Sections[index] property. Then, to get a particular paragraph within that section, leverage the Section.Paragraphs[index] property. Finally, you can update the text content of the paragraph using the Paragraph.Text property.
The steps to modify text in a Word document using C# are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Get a specific section through Document.Sections[index] property.
- Get a specific paragraph through Section.Paragraphs[index] property.
- Reset the text of the paragraph through Paragraph.Text property.
- Save the updated document to a different Word file.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
namespace ModifyText
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load an existing Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx");
// Get a specific section
Section section = document.Sections[0];
// Get a specific paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = section.Paragraphs[0];
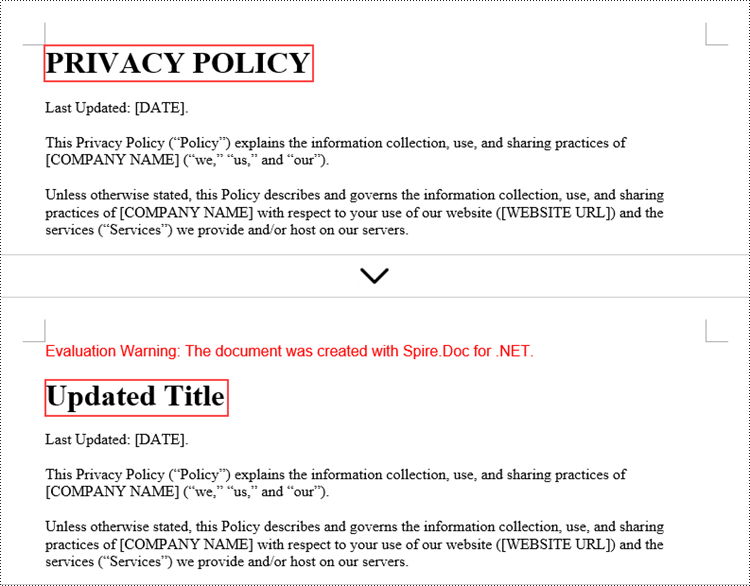
// Modify the text of the paragraph
paragraph.Text = "Updated Title";
// Save the document to a different Word file
document.SaveToFile("ModifyText.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Dispose resource
document.Dispose();
}
}
}
Change Formatting of Text in a Word Document in C#
To change the text formatting within a paragraph, first obtain the paragraph object, then iterate through its child objects to locate the individual text ranges. For each text range, you can reset the formatting using the CharacterFormat property of the TextRange.
The steps to change text formatting in a Word document are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Get a specific section through Document.Sections[index] property.
- Get a specific paragraph through Section.Paragraphs[index] property.
- Iterate through the child objects in the paragraph.
- Determine if a child object is a text range.
- Get a specific text range.
- Reset the text formatting through TextRange.CharacterFormat property.
- Save the updated document to a different Word file.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
using System.Drawing;
namespace ChangeTextFont
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load an existing Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx");
// Get a specific section
Section section = document.Sections[0];
// Get a specific paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = section.Paragraphs[2];
// Iterate through the child objects in the paragraph
for (int i = 0; i < paragraph.ChildObjects.Count; i++)
{
// Determine if a child object is text range
if (paragraph.ChildObjects[i] is TextRange)
{
// Get a specific text range
TextRange textRange = (TextRange)paragraph.ChildObjects[i];
// Reset font name for it
textRange.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Corbel Light";
// Reset font size for it
textRange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 11;
// Reset text color for it
textRange.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.Blue;
// Apply italic to the text range
textRange.CharacterFormat.Italic = true;
}
}
// Save the document to a different Word file
document.SaveToFile("ChangeFont.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Dispose resource
document.Dispose();
}
}
}

Add New Elements to a Word Document in C#
In addition to modifying the existing content in a Word document, you can also insert various types of new elements, such as text, images, tables, lists, and charts. As most elements are paragraph-based, you have the flexibility to add a new paragraph at the end of the document or insert it mid-document. You can then populate this new paragraph with the desired content, whether that's plain text, images, or other elements.
Below are the steps to add new elements (text and images) to a Word document using C#:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Get a specific section through Document.Sections[index] property.
- Add a paragraph to the section using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Add text to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendText() method.
- Add an image to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendPicture() method.
- Save the updated document to a different Word file.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
namespace AddNewElementsToWord
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load an existing Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx");
// Get the last section
Section lastSection = document.LastSection;
// Add a paragraph to the section
Paragraph paragraph = lastSection.AddParagraph();
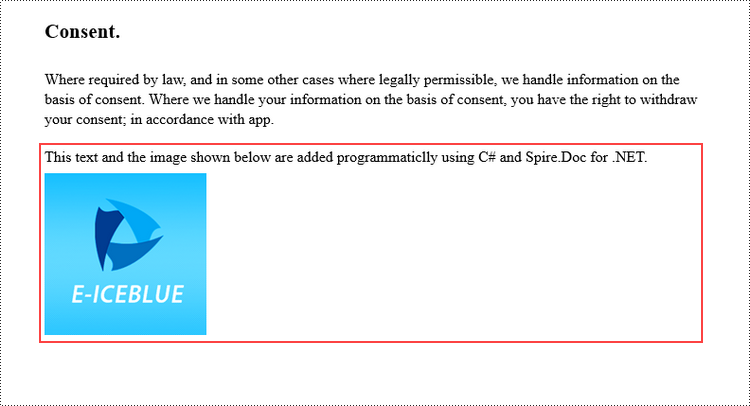
// Add text to the paragraph
paragraph.AppendText("This text and the image shown below are added programmatically using C# and Spire.Doc for .NET.");
// Add an image to the paragraph
paragraph.AppendPicture("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\logo.png");
// Create a paragraph style
ParagraphStyle style = new ParagraphStyle(document);
style.Name = "FontStyle";
style.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Times New Roman";
style.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12;
document.Styles.Add(style);
// Apply the style to the paragraph
paragraph.ApplyStyle(style.Name);
// Save the document to a different Word file
document.SaveToFile("AddNewElements.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Dispose resource
document.Dispose();
}
}
}
Remove Paragraphs from a Word Document in C#
With the Spire.Doc library, you can perform a variety of document operations, including updating existing content, adding new elements, as well as removing elements from a Word document. For example, to remove a paragraph from the document, you can use the Section.Paragraphs.RemoveAt() method.
The following are the steps to remove paragraphs from a Word document using C#:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file from the given file path.
- Get a specific section through Document.Sections[index] property.
- Remove a specific paragraph from the section using Section.Paragraphs.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the updated document to a different Word file.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
namespace RemoveParagraphs
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load an existing Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx");
// Get a specific section
Section section = document.Sections[0];
// Remove a specific paragraph
section.Paragraphs.RemoveAt(0);
// Save the document to a different Word file
document.SaveToFile("RemoveParagraph.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Dispose resource
document.Dispose();
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.


