
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
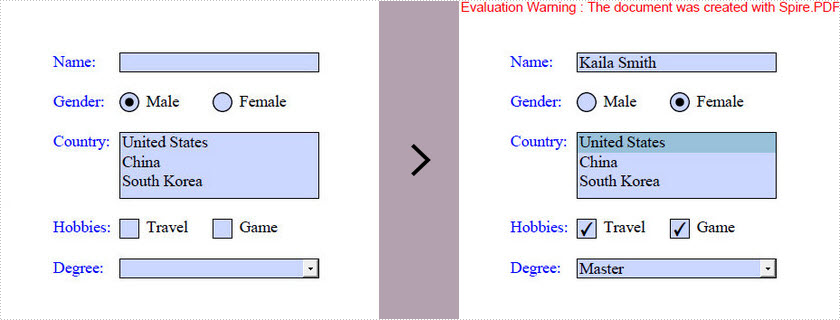
The tutorial shows you how to access the form fields in a PDF document and how to fill each form field with value by using Spire.PDF for Java.
Entire Code:
import com.spire.pdf.FileFormat;
import com.spire.pdf.PdfDocument;
import com.spire.pdf.fields.PdfField;
import com.spire.pdf.widget.*;
public class FillFormField{
public static void main(String[] args){
//create a PdfDocument object
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
//load a sample PDF containing forms
doc.loadFromFile("G:\\java-workspace\\Spire.Pdf\\Forms.pdf");
//get the form fields from the document
PdfFormWidget form = (PdfFormWidget) doc.getForm();
//get the form widget collection
PdfFormFieldWidgetCollection formWidgetCollection = form.getFieldsWidget();
//loop through the widget collection and fill each field with value
for (int i = 0; i < formWidgetCollection.getCount(); i++) {
PdfField field = formWidgetCollection.get(i);
if (field instanceof PdfTextBoxFieldWidget) {
PdfTextBoxFieldWidget textBoxField = (PdfTextBoxFieldWidget) field;
textBoxField.setText("Kaila Smith");
}
if (field instanceof PdfRadioButtonListFieldWidget) {
PdfRadioButtonListFieldWidget radioButtonListField = (PdfRadioButtonListFieldWidget) field;
radioButtonListField.setSelectedIndex(1);
}
if (field instanceof PdfListBoxWidgetFieldWidget) {
PdfListBoxWidgetFieldWidget listBox = (PdfListBoxWidgetFieldWidget) field;
listBox.setSelectedIndex(0);
}
if (field instanceof PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget) {
PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget checkBoxField = (PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget) field;
switch(checkBoxField.getName()){
case "checkbox1":
checkBoxField.setChecked(true);
break;
case "checkbox2":
checkBoxField.setChecked(true);
break;
}
}
if (field instanceof PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget) {
PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget comboBoxField = (PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget) field;
comboBoxField.setSelectedIndex(1);
}
}
//Save the file
doc.saveToFile("FillFormFields.pdf", FileFormat.PDF);
}
}
Output:
Converting PDF files to images is essential for various document processing tasks, including generating thumbnails, archiving, and image manipulation. These conversions allow applications to present PDF content in more accessible formats, enhancing user experience and functionality. Java libraries such as Spire.PDF for Java enable efficient conversions to formats like PNG , JPEG , GIF , BMP , TIFF , and SVG , each serving specific purposes based on their characteristics.
This guide will walk you through the conversion process using Spire.PDF for Java, providing optimized code examples for each format. Additionally, it will explain the key differences among these formats to help you select the most suitable option for your needs.
- Java PDF-to-Image Conversion Library
- Image Format Comparison
- Convert PDF to PNG, JPEG, GIF, and BMP
- Convert PDF to TIFF in Java
- Convert PDF to SVG in Java
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Java PDF-to-Image Conversion Library
Spire.PDF for Java is a robust, feature-rich library for PDF manipulation. It offers several advantages for image conversion:
- High-quality rendering that preserves document formatting and layout
- Batch processing capabilities for handling multiple documents
- Flexible output options including resolution and format control
- Lightweight implementation with minimal memory footprint
The library supports conversion to all major image formats while maintaining excellent text clarity and graphic fidelity, making it suitable for both simple conversions and complex document processing pipelines.
Installation
To get started, download Spire.PDF for Java from our website and add it as a dependency in your project. For Maven users, include the following in your pom.xml:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.pdf</artifactId>
<version>11.6.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Image Format Comparison
Different image formats serve distinct purposes. Below is a comparison of commonly used formats:
| Format | Compression | Transparency | Best For | File Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PNG | Lossless | Yes | High-quality graphics, logos | Medium |
| JPEG | Lossy | No | Photographs, web images | Small |
| GIF | Lossless | Yes (limited) | Simple animations, low-color graphics | Small |
| BMP | None | No | Uncompressed images, Windows apps | Large |
| TIFF | Lossless | Yes | High-quality scans, printing | Very Large |
| SVG | Vector-based | Yes (scalable) | Logos, icons, web graphics | Small |
PNG is ideal for images requiring transparency and lossless quality, while JPEG is better for photographs due to its smaller file size. GIF supports simple animations, and BMP is rarely used due to its large size. TIFF is preferred for professional printing, and SVG is perfect for scalable vector graphics.
Convert PDF to PNG, JPEG, GIF, and BMP
Converting PDF files into various image formats like PNG, JPEG, GIF, and BMP allows developers to cater to diverse application needs. Each format serves different purposes; for example, PNG is ideal for high-quality graphics with transparency, while JPEG is better suited for photographs with smooth gradients.
By leveraging Spire.PDF's capabilities, developers can easily generate the required image formats for their projects, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance.
Basic Conversion Example
Let's start with the fundamental conversion process. The following code demonstrates how to convert each page of a PDF into individual PNG images:
import com.spire.pdf.PdfDocument;
import com.spire.pdf.graphics.PdfImageType;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ConvertPdfToImage {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// Create a PdfDocument instance
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
// Load a PDF file
doc.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.pdf");
// Iterate through the pages
for (int i = 0; i < doc.getPages().getCount(); i++) {
// Convert the current page to BufferedImage
BufferedImage image = doc.saveAsImage(i, PdfImageType.Bitmap);
// Save the image data as a png file
File file = new File("output/" + String.format(("ToImage-img-%d.png"), i));
ImageIO.write(image, "PNG", file);
}
// Clear up resources
doc.close();
}
}
Explanation:
- The PdfDocument class loads the input PDF file.
- saveAsImage() converts each page into a BufferedImage .
- ImageIO.write() saves the image in PNG format.
Tip : To convert to JPEG, GIF, or BMP, simply replace " PNG " with " JPEG ", " GIF ", or " BMP " in the ImageIO.write() method.
Output:
PNG with Transparent Background
Converting a PDF page to PNG with a transparent background involves adjusting the conversion options using the setPdfToImageOptionsmethod. This adjustment provides greater flexibility in generating the images, allowing for customized output that meets specific requirements.
Here’s how to achieve this:
doc.getConvertOptions().setPdfToImageOptions(0);
for (int i = 0; i < doc.getPages().getCount(); i++) {
BufferedImage image = doc.saveAsImage(i, PdfImageType.Bitmap);
File file = new File("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Images\\" + String.format(("ToImage-img-%d.png"), i));
ImageIO.write(image, "PNG", file);
}
Explanation:
- setPdfToImageOptions(0) ensures transparency is preserved.
- The rest of the process remains the same as the basic conversion.
Custom DPI Settings
The saveAsImage method also provides an overload that allows developers to specify the DPI (dots per inch) for the output images. This feature is crucial for ensuring that the images are rendered at the desired resolution, particularly when high-quality images are required.
Here’s an example of converting a PDF to images with a specified DPI:
for (int i = 0; i < doc.getPages().getCount(); i++) {
BufferedImage image = doc.saveAsImage(i, PdfImageType.Bitmap,300, 300);
File file = new File("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Images\\" + String.format(("ToImage-img-%d.png"), i));
ImageIO.write(image, "PNG", file);
}
Explanation:
- The saveAsImage() method accepts dpiX and dpiY parameters for resolution control.
- Higher DPI values (e.g., 300) produce sharper images but increase file size.
DPI Selection Tip:
- 72-100 DPI : Suitable for screen display
- 150-200 DPI : Good for basic printing
- 300+ DPI : Professional printing quality
- 600+ DPI : High-resolution archival
Convert PDF to TIFF in Java
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) is another popular image format, especially in the publishing and printing industries. Spire.PDF makes it easy to convert PDF pages to TIFF format using the saveToTiff method.
Here’s a simple example demonstrating how to convert a PDF to a multi-page TIFF:
import com.spire.pdf.PdfDocument;
public class ConvertPdfToTiff {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a PdfDocument object
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
// Load a PDF file
doc.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.pdf");
// Convert a page range to tiff
doc.saveToTiff("output/PageToTiff.tiff",0,2,300,300);
// Clear up resources
doc.dispose();
}
}
Explanation:
- saveToTiff() converts a specified page range (here, pages 0 to 2).
- The last two parameters set the DPI for the output image.
Output:
Convert PDF to SVG in Java
SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) is a vector image format that is widely used for its scalability and compatibility with web technologies. Converting PDF to SVG can be beneficial for web applications that require responsive images.
To convert a PDF document to SVG using Spire.PDF, the following code can be implemented:
import com.spire.pdf.FileFormat;
import com.spire.pdf.PdfDocument;
public class ConvertPdfToSvg {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Initialize a PdfDocument object
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
// Load the PDF document from the specified path
doc.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.pdf");
// Optionally, convert to a single SVG (uncomment to enable)
// doc.getConvertOptions().setOutputToOneSvg(true);
// Save the document as SVG files (one SVG per page by default)
doc.saveToFile("Output/PDFToSVG.svg", FileFormat.SVG);
// Clear up resources
doc.dispose();
}
}
Explanation:
- saveToFile() with FileFormat.SVG exports the PDF as an SVG file.
- Optionally, setOutputToOneSvg(true) merges all pages into a single SVG.
Output:
Conclusion
Spire.PDF for Java simplifies PDF-to-image conversion with support for popular formats like PNG, JPEG, TIFF, SVG, and more . Key features such as transparency control, custom DPI settings, and multi-page TIFF/SVG output enable tailored solutions for generating thumbnails, high-quality prints, or web-optimized graphics. The library ensures high fidelity and performance , making it ideal for batch processing or dynamic rendering. Easily integrate the provided code snippets and APIs to enhance document handling in your Java applications, whether for reporting, archiving, or interactive content.
FAQs
Q1. Can I specify the DPI when converting to TIFF or SVG?
When converting to TIFF, you can specify the DPI to ensure high-quality output. However, SVG is a vector format and does not require DPI settings, as it scales based on the display size.
Q2. Can I convert specific pages of a PDF to images?
Yes, both the saveAsImage and saveToTiff methods allow you to indicate which pages to include in the conversion.
Q3. What is the difference between lossless and lossy image formats?
Lossless formats (like PNG and TIFF) retain all image quality during compression, while lossy formats (like JPEG) reduce file size by discarding some image information, which may affect quality.
Q4. How does converting to SVG differ from raster formats?
Converting to SVG generates vector images that scale without losing quality, while raster formats like PNG and JPEG are pixel-based and can lose quality when resized.
Q5. What other file formats can Spire.PDF convert PDFs to?
Spire.PDF is a powerful Java PDF library that supports converting PDF files to multiple formats, such as:
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.PDF for Java without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
PDF to Text in Java: Extract Text from PDFs (Text-Based & Scanned)
2022-12-02 07:57:00 Written by Koohji
Extracting text from PDF files is a common task for Java developers working on document processing, data extraction, search indexing, and automation. PDFs often contain text in two formats: digital text embedded in the file or scanned images of text. Extracting content from these requires different approaches.
This article explains how to extract text from both text-based PDFs and scanned (image-based) PDFs using Java, complete with detailed code examples and explanations. Whether you need to process reports, invoices, or scanned documents, this guide will help you get started quickly and efficiently.
Table of Contents
- Why Extract Text from PDFs in Java?
- Difference Between Text-Based and Scanned PDFs
- How to Extract Text from Text-Based PDFs in Java
- How to Extract Text from Scanned PDFs Using Java & OCR
- Common Challenges and Best Practices for PDF Text Extraction
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Why Extract Text from PDFs in Java?
PDF files are designed for consistent visual formatting across platforms. However, extracting the underlying text lets developers:
- Enable full-text search
- Automate form and invoice processing
- Feed text into AI models
- Convert content for analysis or reporting
- Repurpose documents into other formats (HTML, Markdown, CSV)
Difference Between Text-Based and Scanned PDFs
Before extracting text, it’s important to understand the PDF type because the extraction approach differs:
Text-Based PDFs
- Contain embedded, selectable text stored in the document structure
- Text can be extracted directly by parsing the PDF’s text objects
- Typically created by exporting from word processors, reports, or digital sources
Scanned PDFs
- Are images of pages, often created by scanning paper documents
- Do not contain embedded text—only images of text
- Require Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to convert images into machine-readable text
Knowing your PDF type determines the extraction method and tools you need.
How to Extract Text from Text-Based PDFs in Java
Text-based PDFs allow direct extraction of text content. With libraries like Spire.PDF for Java, you can extract text from an entire PDF, specific pages, or designated rectangular areas. This is useful for a variety of tasks, such as content indexing, document analysis, and data processing.
Key Features
- Extract text from full documents or individual pages
- Target specific rectangular regions within a page
- Preserve original layout
- Support for multi-language text extraction
Maven Dependency
To begin, add the following Maven dependency for Spire.PDF to your pom.xml:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.pdf</artifactId>
<version>11.7.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
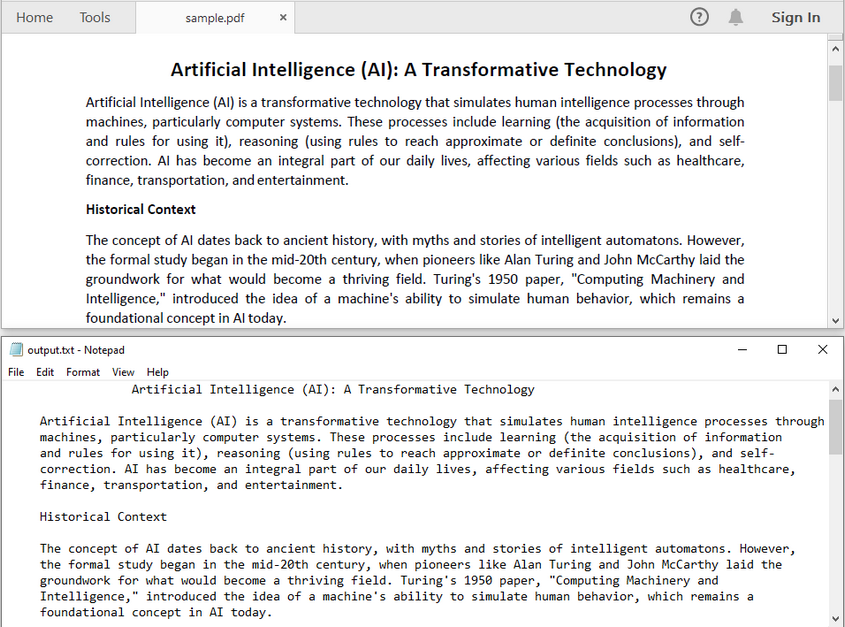
Extract All Text from a PDF
If you want to convert an entire PDF to plain text, you can iterate through all the pages and use the extract method provided by the PdfTextExtractor class to retrieve text from each page in sequence. This method returns a string containing the textual content of the page and preserves the original layout, including spacing, line breaks, and paragraph structure as much as possible.
import com.spire.pdf.PdfDocument;
import com.spire.pdf.PdfPageBase;
import com.spire.pdf.texts.PdfTextExtractOptions;
import com.spire.pdf.texts.PdfTextExtractor;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ExtractAllTextFromPDF {
public static void main(String[] args){
// Create a PdfDocument instance and load the PDF file
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
doc.loadFromFile("sample.pdf");
// Create a StringBuilder to store extracted text from all pages
StringBuilder fullText = new StringBuilder();
// Loop through each page in the PDF
for (int i = 0; i < doc.getPages().getCount(); i++) {
// Get the current page
PdfPageBase page = doc.getPages().get(i);
// Create a text extractor for the page
PdfTextExtractor extractor = new PdfTextExtractor(page);
// Extract text using default options
String text = extractor.extract(new PdfTextExtractOptions());
// Append extracted text and add spacing between pages
fullText.append(text).append("\n\n\n\n");
}
// Write the extracted text to a .txt file
try (BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("output.txt"))) {
writer.write(fullText.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
// Print any file I/O errors
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Close the PDF document to free resources
doc.close();
}
}
Note: You need to modify the PDF file path as needed.
Extract Text from a Page
When working with multi-page PDFs, you may only need to extract content from a specific page—for example, a summary, cover sheet, or signature page. In such cases, you can access the target page by its index and use the extract method from the PdfTextExtractor class to retrieve text from that individual page.
import com.spire.pdf.PdfDocument;
import com.spire.pdf.PdfPageBase;
import com.spire.pdf.texts.PdfTextExtractOptions;
import com.spire.pdf.texts.PdfTextExtractor;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ExtractTextFromSelectedPage {
public static void main(String[] args){
// Create a PdfDocument instance and load the PDF file
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
doc.loadFromFile("sample.pdf");
// Define the target page index (e.g., 0 for the first page)
int pageIndex = 0;
// Check if the specified page exists in the document
if (pageIndex >= 0 && pageIndex < doc.getPages().getCount()) {
// Get the specified page
PdfPageBase page = doc.getPages().get(pageIndex);
// Create a text extractor for the page
PdfTextExtractor extractor = new PdfTextExtractor(page);
// Extract text from the page
String text = extractor.extract(new PdfTextExtractOptions());
// Write the extracted text to a .txt file
try (BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("output.txt"))) {
writer.write(text);
} catch (IOException e) {
// Print any file I/O errors
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
System.out.println("Invalid page index.");
}
// Close the PDF document to free resources
doc.close();
}
}
Note: You need to change the page index according to your needs.
Extract Text from a Page Area (Rectangular Region)
To extract text from a specific area of a PDF page, first define the rectangular region using a Rectangle2D object, then use the setExtractArea method of the PdfTextExtractOptions class to limit extraction to that area. This helps isolate relevant content and exclude unrelated text outside the defined region.
import com.spire.pdf.PdfDocument;
import com.spire.pdf.PdfPageBase;
import com.spire.pdf.texts.PdfTextExtractOptions;
import com.spire.pdf.texts.PdfTextExtractor;
import java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ExtractTextFromSelectedPage {
public static void main(String[] args){
// Create a PdfDocument instance and load the PDF file
PdfDocument doc = new PdfDocument();
doc.loadFromFile("sample.pdf");
// Define the target page index (0-based, 0 means first page)
int pageIndex = 0;
// Check if the specified page exists in the document
if (pageIndex >= 0 && pageIndex < doc.getPages().getCount()) {
// Get the specified page
PdfPageBase page = doc.getPages().get(pageIndex);
// Define the rectangular region (x, y, width, height)
// Coordinates are relative to the PDF page coordinate system in the top-left corner
Rectangle2D region = new Rectangle2D.Float(100, 150, 300, 100);
// Initialize a text extractor for the page
PdfTextExtractor extractor = new PdfTextExtractor(page);
// Create extraction options and set the region to extract text from
PdfTextExtractOptions options = new PdfTextExtractOptions();
options.setExtractArea(region);
// Extract text from the defined rectangular area
String text = extractor.extract(options);
// Write the extracted text to a text file
try (BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("output.txt"))) {
writer.write(text);
} catch (IOException e) {
// Print any errors during file writing
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
// Inform if the specified page index is invalid
System.out.println("Invalid page index.");
}
// Close the PDF document to free resources
doc.close();
}
}
Tip: Coordinates are relative to the PDF page, with the origin (0,0) at the top-left corner. The X-axis increases to the right, and the Y-axis increases downward. Learn more about PDF coordinate positioning in our guide: Generate PDF Files in Java (Developer Tutorial).
How to Extract Text from Scanned PDFs Using Java & OCR
Scanned PDFs do not contain embedded, selectable text; instead, they store images of the document pages. To extract text from such PDFs, you need to:
- Convert each PDF page into an image using a PDF processing library (e.g., Spire.PDF).
- Use an OCR (Optical Character Recognition) engine (e.g., Spire.OCR) to recognize and convert text from these images into machine-readable format.
Maven Dependencies
Add the following repositories and dependencies to your pom.xml to include the required libraries in your Java project:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.pdf</artifactId>
<version>11.7.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.ocr</artifactId>
<version>1.9.22</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Download OCR Model
Spire.OCR for Java requires downloading a language model compatible with your operating system:
After downloading, extract the package to a directory accessible by your application. You'll reference its path in your code.
Java Code Example for OCR Text Extraction from Scanned PDF
The code below demonstrates how to extract text from scanned PDFs that contain only images. Each page is first converted into an image using saveAsImage(). Then, the OCR engine (OcrScanner) reads the image and extracts the text. The recognized text from all pages is saved to a .txt file.
import com.spire.ocr.ConfigureOptions;
import com.spire.ocr.OCRImageFormat;
import com.spire.ocr.OcrException;
import com.spire.ocr.OcrScanner;
import com.spire.pdf.PdfDocument;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.*;
public class ExtractTextFromScannedPDF {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, OcrException {
// Load a scanned PDF
PdfDocument pdf = new PdfDocument();
pdf.loadFromFile("sample.pdf");
// Create a StringBuilder to store all extracted text
StringBuilder allText = new StringBuilder();
// Loop through each page
for (int i = 0; i < pdf.getPages().getCount(); i++) {
// Convert current page to image
BufferedImage image = pdf.saveAsImage(i);
// Convert image to input stream
ByteArrayOutputStream os = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ImageIO.write(image, "PNG", os);
InputStream imageStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(os.toByteArray());
// Configure OCR options
OcrScanner scanner = new OcrScanner();
ConfigureOptions options = new ConfigureOptions();
// Set the language for OCR engine
// Supported languages include: English, Chinese, Chinesetraditional, French, German, Japanese, and Korean.
options.setLanguage("English");
// Se the path to OCR model folder
options.setModelPath("E:\\win-x64");
scanner.ConfigureDependencies(options);
// Perform OCR and collect text
scanner.Scan(imageStream, OCRImageFormat.Png);
String text = scanner.getText().toString();
allText.append(text).append(System.lineSeparator()).append(System.lineSeparator());
}
// Save all extracted text to a .txt file
try (FileWriter writer = new FileWriter("OCR_ExtractedText.txt")) {
writer.write(allText.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Failed to save extracted text.");
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Close the PDF document to free resources
pdf.close();
}
}
Note: The model path should point to the folder that contains the OCR model and language data. Make sure the folder is accessible in your environment.
Common Challenges and Best Practices for PDF Text Extraction
When extracting text from PDFs, developers often face several common challenges; the following table outlines these issues along with practical tips to help overcome them effectively.
| Challenge | Description | Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Formatting Loss | Extracted text might lose original layout | Use libraries supporting layout retention |
| OCR Accuracy | Low-quality scans reduce recognition accuracy | Use high-resolution images and appropriate models |
| Multilingual Support | Scanned PDFs might contain languages other than English | Use corresponding OCR language models |
Conclusion
Converting PDF files to text in Java enables efficient document processing, search, and automation. Spire.PDF for Java simplifies text extraction from digital PDFs, while Spire.OCR for Java provides a reliable solution for handling scanned and image-based PDFs. By combining these tools, developers can build robust, end-to-end PDF text extraction systems tailored to any business need.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can I extract text from scanned PDFs in Java?
A1: Yes. You’ll need to convert each page to an image and then use OCR (Optical Character Recognition) to recognize and extract the text from the image.
Q2: How can I tell if a PDF is scanned or text-based?
A2: Open the PDF and try selecting the text with your mouse. If you can select and copy text, it’s text-based. If not, it's likely a scanned image.
Q3: Can I extract text from a password-protected PDF in Java?
A3: Yes. If the password is known, the PDF can be decrypted before extracting text using a supported library like Spire.PDF.
Q4: Can I extract tables or structured data from PDFs using Java?
A4: Yes. Some Java PDF libraries support extracting tables or structured content by detecting text alignment, cell boundaries, or using region-based extraction. For more accurate results, tools that offer table recognition features - such as Spire.PDF for Java - can help simplify the process.
