
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Error bars in charts can help us to see margins of error and standard deviations at a glance. We can use error bars in area, bar, column, line, and XY charts. In XY charts i.e. scatter and bubble charts, we can show X (Horizontal) and Y (Vertical) error bars. However if the chart type is not XY, the error bars for X values are disabled.
This article demonstrates how to add and format error bars for non-XY and XY charts in a PowerPoint document using Spire.Presentation and C#.
Detail steps:
Step 1: Initialize an object of Presentation class and load the PowerPoint document.
Presentation ppt = new Presentation();
ppt.LoadFromFile("Input.pptx");
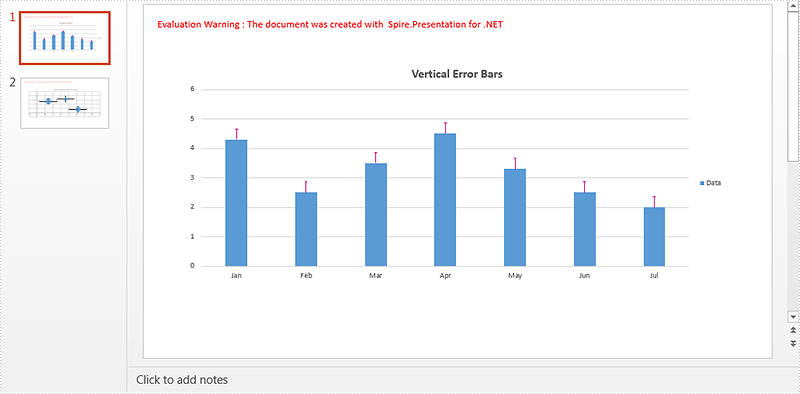
Step 2: Get the column chart on the first slide and set chart title.
IChart columnChart = ppt.Slides[0].Shapes[0] as IChart; columnChart.ChartTitle.TextProperties.Text = "Vertical Error Bars";
Step 3: Add Y (Vertical) error bars to the first chart series and format the error bars.
//Get Y error bars of the first chart series IErrorBarsFormat errorBarsYFormat1 = columnChart.Series[0].ErrorBarsYFormat; //Set end cap errorBarsYFormat1.ErrorBarNoEndCap = false; //Specify direction errorBarsYFormat1.ErrorBarSimType = ErrorBarSimpleType.Plus; //Specify error amount type errorBarsYFormat1.ErrorBarvType = ErrorValueType.StandardError; //Set value errorBarsYFormat1.ErrorBarVal = 0.3f; //Set line format errorBarsYFormat1.Line.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid; errorBarsYFormat1.Line.SolidFillColor.Color = Color.MediumVioletRed; errorBarsYFormat1.Line.Width = 1;
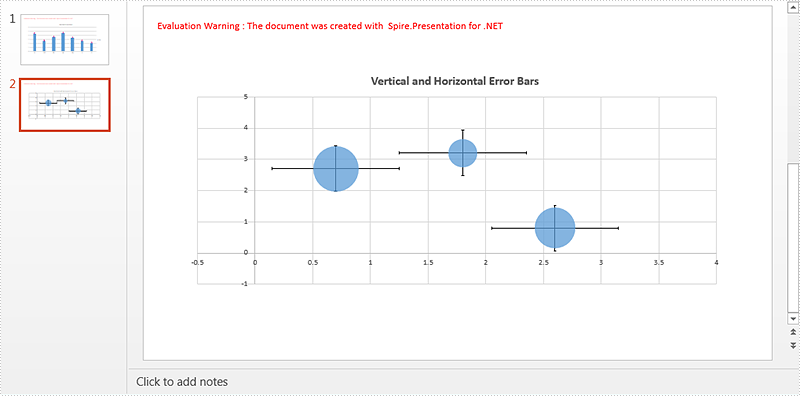
Step 4: Get the bubble chart on the second slide and set chart title.
IChart chart2 = ppt.Slides[1].Shapes[0] as IChart; chart2.ChartTitle.TextProperties.Text = "Vertical and Horizontal Error Bars";
Step 5: Add x (Horizontal) and Y (Vertical) error bars to the first chart series and format the error bars.
//Get X error bars of the first chart series
IErrorBarsFormat errorBarsXFormat = bubbleChart.Series[0].ErrorBarsXFormat;
//Set end cap
errorBarsXFormat.ErrorBarNoEndCap = false;
//Specify direction
errorBarsXFormat.ErrorBarSimType = ErrorBarSimpleType.Both;
//Specify error amount type
errorBarsXFormat.ErrorBarvType = ErrorValueType.StandardError;
//Set value
errorBarsXFormat.ErrorBarVal = 0.3f;
//Get Y error bars of the first chart series
IErrorBarsFormat errorBarsYFormat2 = bubbleChart.Series[0].ErrorBarsYFormat;
//Set end cap
errorBarsYFormat2.ErrorBarNoEndCap = false;
//Specify direction
errorBarsYFormat2.ErrorBarSimType = ErrorBarSimpleType.Both;
//Specify error amount type
errorBarsYFormat2.ErrorBarvType = ErrorValueType.StandardError;
//Set value
errorBarsYFormat2.ErrorBarVal = 0.3f;
Step 6: Save the document.
ppt.SaveToFile("ErrorBars.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013);
Screenshot:
Full code:
using System.Drawing;
using Spire.Presentation;
using Spire.Presentation.Charts;
using Spire.Presentation.Drawing;
namespace Add_error_bars_to_chart_in_PPT
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Load the PowerPoint document
Presentation ppt = new Presentation();
ppt.LoadFromFile("Input.pptx");
//Get the column chart on the first slide and set chart title
IChart columnChart = ppt.Slides[0].Shapes[0] as IChart;
columnChart.ChartTitle.TextProperties.Text = "Vertical Error Bars";
//Add Y (Vertical) Error Bars
//Get Y error bars of the first chart series
IErrorBarsFormat errorBarsYFormat1 = columnChart.Series[0].ErrorBarsYFormat;
//Set end cap
errorBarsYFormat1.ErrorBarNoEndCap = false;
//Specify direction
errorBarsYFormat1.ErrorBarSimType = ErrorBarSimpleType.Plus;
//Specify error amount type
errorBarsYFormat1.ErrorBarvType = ErrorValueType.StandardError;
//Set value
errorBarsYFormat1.ErrorBarVal = 0.3f;
//Set line format
errorBarsYFormat1.Line.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid;
errorBarsYFormat1.Line.SolidFillColor.Color = Color.MediumVioletRed;
errorBarsYFormat1.Line.Width = 1;
//Get the bubble chart on the second slide and set chart title
IChart bubbleChart = ppt.Slides[1].Shapes[0] as IChart;
bubbleChart.ChartTitle.TextProperties.Text = "Vertical and Horizontal Error Bars";
//Add X (Horizontal) and Y (Vertical) Error Bars
//Get X error bars of the first chart series
IErrorBarsFormat errorBarsXFormat = bubbleChart.Series[0].ErrorBarsXFormat;
//Set end cap
errorBarsXFormat.ErrorBarNoEndCap = false;
//Specify direction
errorBarsXFormat.ErrorBarSimType = ErrorBarSimpleType.Both;
//Specify error amount type
errorBarsXFormat.ErrorBarvType = ErrorValueType.StandardError;
//Set value
errorBarsXFormat.ErrorBarVal = 0.3f;
//Get Y error bars of the first chart series
IErrorBarsFormat errorBarsYFormat2 = bubbleChart.Series[0].ErrorBarsYFormat;
//Set end cap
errorBarsYFormat2.ErrorBarNoEndCap = false;
//Specify direction
errorBarsYFormat2.ErrorBarSimType = ErrorBarSimpleType.Both;
//Specify error amount type
errorBarsYFormat2.ErrorBarvType = ErrorValueType.StandardError;
//Set value
errorBarsYFormat2.ErrorBarVal = 0.3f;
//Save the document
ppt.SaveToFile("ErrorBars.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013);
}
}
}
How to set the indent style for the paragraph on presentation slide in C#
2018-01-30 07:45:45 Written by KoohjiSpire.Presentation supports to operate the paragraph styles from code. There are two kinds of special indentation styles for the paragraph, first line and hanging. This article will demonstrate how to set the indent style for the paragraph on presentation slide in C#.
Step 1: Create an instance of presentation and load the document from file.
Presentation presentation = new Presentation();
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx");
Step 2: Get the paragraphs from the first slide.
IAutoShape shape = (IAutoShape)presentation.Slides[0].Shapes[0]; ParagraphCollection paras = shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs;
Step 3: Set the indentation as first line for the first paragraph.
paras[0].Indent = 20; paras[0].SpaceAfter = 10;
Step 4: Set the indentation as Hanging for the third paragraph.
paras[2].Indent = -100; paras[2].LeftMargin = 30;
Step 5: Save the document to file.
presentation.SaveToFile("Result.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2010);
Effective screenshot of the presentation with indentation style:
Full codes:
using Spire.Presentation;
using Spire.Presentation.Collections;
namespace SetIndentStyle
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Presentation presentation = new Presentation();
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx");
IAutoShape shape = (IAutoShape)presentation.Slides[0].Shapes[0];
ParagraphCollection paras = shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs;
paras[0].Indent = 20;
paras[0].SpaceAfter = 10;
paras[2].Indent = -100;
paras[2].LeftMargin = 30;
presentation.SaveToFile("Result.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2010);
}
}
}
A file with the .ODT file extension is an OpenDocument Text document file. These files are most often created by the free OpenOffice Writer word processor program. ODT files are similar to the popular DOCX file format used with Microsoft Word. Both of the two file types can hold things like text, images, objects, and styles.
However, when you open an ODT document in Microsoft Word, the formatting of the ODT document may differ as a result of the two programs not sharing the same features. When converting ODT to DOCX or vice versa, the data and content will be converted successfully, but may not including the original formatting.
Following code snippets introduce how to convert ODT to DOC or DOCX and vice versa using Spire.Doc.
ODT to DOCX
To convert ODT to DOC, change the file extension and file format to .Doc in SaveToFile method.
using Spire.Doc;
namespace ODTtoDOCX
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Document doc = new Document();
doc.LoadFromFile("SampleODTFile.odt");
doc.SaveToFile("output.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Doc
Namespace ODTtoDOCX
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
Dim doc As New Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("SampleODTFile.odt")
doc.SaveToFile("output.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
DOCX to ODT
To convert Doc to ODT, load a .Doc file format document when loading the source file.
using Spire.Doc;
namespace DOCXtoODT
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Document doc = new Document();
doc.LoadFromFile("SampleODTFile.odt");
doc.SaveToFile("output.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Doc
Namespace DOCXtoODT
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
Dim doc As New Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("SampleODTFile.odt")
doc.SaveToFile("output.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
