
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Searching for high or low values in large amounts of data can be cumbersome and error-prone. Fortunately, in Excel, you can apply conditional formatting to quickly highlight a specified number of top or bottom ranked values in a selected cell range. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically highlight top and bottom values in Excel using Spire.XLS for .NET.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Highlight Top and Bottom Values in Excel in C# and VB.NET
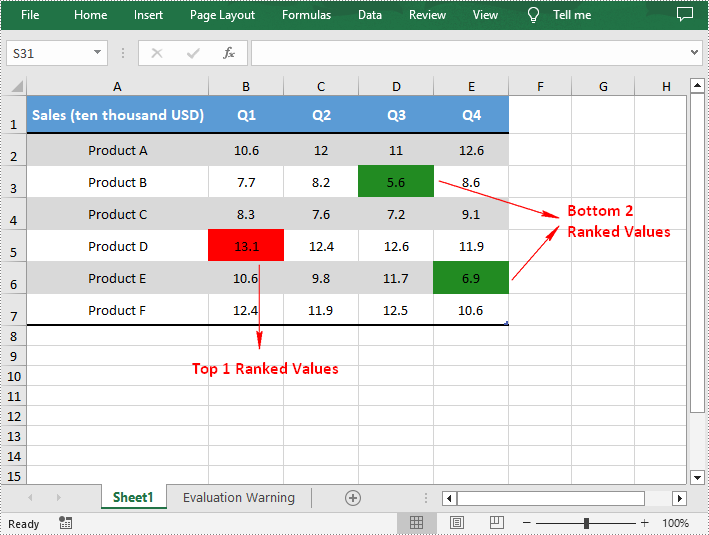
Spire.XLS for .NET provides the XlsConditionalFormats.AddTopBottomCondition(TopBottomType topBottomType, int rank) method to specify the top N or bottom N ranked values, and then you can highlight these values with a background color. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet by its index using Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Add a conditional formatting to the worksheet using Worksheet.ConditionalFormats.Add() method and return an object of XlsConditionalFormats class.
- Set the cell range where the conditional formatting will be applied using XlsConditionalFormats.AddRange() method.
- Add a top condition to specify the highest or top N ranked values using XlsConditionalFormats.AddTopBottomCondition(TopBottomType topBottomType, int rank) method. Then highlight the cells that meet the condition with a background color using IConditionalFormat.BackColor property.
- Add a bottom condition to specify the lowest or bottom N ranked values and highlight the cells that meet the condition with a background color.
- Save the result document using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
using Spire.Xls.Core;
using Spire.Xls.Core.Spreadsheet.Collections;
using System.Drawing;
namespace HighlightValues
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
{
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load a sample Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("sample.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Add a conditional format to the worksheet
XlsConditionalFormats format = sheet.ConditionalFormats.Add();
//Set the range where the conditional format will be applied
format.AddRange(sheet.Range["B2:F7"]);
//Apply conditional formatting to highlight the highest values
IConditionalFormat condition1 = format.AddTopBottomCondition(TopBottomType.Top, 1);
condition1.BackColor = Color.Red;
//Apply conditional formatting to highlight the bottom two values
IConditionalFormat condition2 = format.AddTopBottomCondition(TopBottomType.Bottom, 2);
condition2.BackColor = Color.ForestGreen;
//Save the result document
workbook.SaveToFile("TopBottomValues.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013);
}
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Create a Cross-Reference to Bookmark in Word in C#, VB.NET
2017-12-21 07:54:20 Written by AdministratorA cross-reference refers to related information elsewhere in the same document. You can create cross-references to any existing items such as headings, footnotes, bookmarks, captions, and numbered paragraphs. This article will show you how to create a cross-reference to bookmark using Spire.Doc with C# and VB.NET.
Step 1: Create a Document instance.
Document doc = new Document(); Section section = doc.AddSection();
Step 2: Insert a bookmark.
Paragraph paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendBookmarkStart("MyBookmark");
paragraph.AppendText("Text inside a bookmark");
paragraph.AppendBookmarkEnd("MyBookmark");
Step 3: Create a cross-reference field, and link it to the bookmark through bookmark name.
Field field = new Field(doc); field.Type = FieldType.FieldRef; field.Code = @"REF MyBookmark \p \h";
Step 4: Add a paragraph, and insert the field to the paragraph.
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("For more information, see ");
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(field);
Step 5: Insert a FieldSeparator object to the paragraph, which works as separator in a field.
FieldMark fieldSeparator= new FieldMark(doc, FieldMarkType.FieldSeparator); paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(fieldSeparator);
Step 6: Set the display text of the cross-reference field.
TextRange tr = new TextRange(doc); tr.Text = "above"; paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(tr);
Step 7: Insert a FieldEnd object to the paragraph, which is used to mark the end of a field.
FieldMark fieldEnd = new FieldMark(doc, FieldMarkType.FieldEnd); paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(fieldEnd);
Step 8: Save to file.
doc.SaveToFile("output.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013);
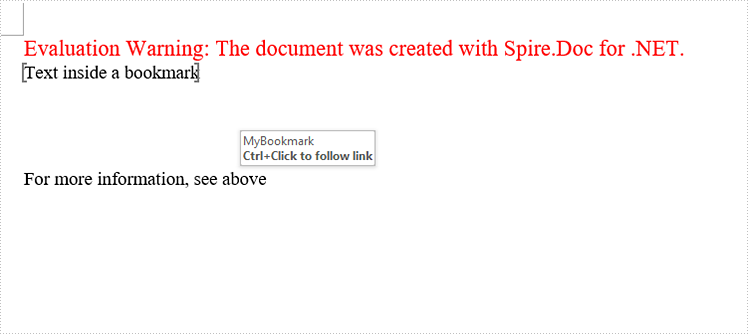
Output:
The cross-reference appears as a link that takes the reader to the referenced item.
Full Code:
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
namespace CreatCR
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Document doc = new Document();
Section section = doc.AddSection();
//create a bookmark
Paragraph paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendBookmarkStart("MyBookmark");
paragraph.AppendText("Text inside a bookmark");
paragraph.AppendBookmarkEnd("MyBookmark");
//insert line breaks
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak);
}
//create a cross-reference field, and link it to bookmark
Field field = new Field(doc);
field.Type = FieldType.FieldRef;
field.Code = @"REF MyBookmark \p \h";
//insert field to paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("For more information, see ");
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(field);
//insert FieldSeparator object
FieldMark fieldSeparator = new FieldMark(doc, FieldMarkType.FieldSeparator);
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(fieldSeparator);
//set display text of the field
TextRange tr = new TextRange(doc);
tr.Text = "above";
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(tr);
//insert FieldEnd object to mark the end of the field
FieldMark fieldEnd = new FieldMark(doc, FieldMarkType.FieldEnd);
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(fieldEnd);
//save file
doc.SaveToFile("output.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013);
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Doc
Imports Spire.Doc.Documents
Imports Spire.Doc.Fields
Namespace CreatCR
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
Dim doc As New Document()
Dim section As Section = doc.AddSection()
'create a bookmark
Dim paragraph As Paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendBookmarkStart("MyBookmark")
paragraph.AppendText("Text inside a bookmark")
paragraph.AppendBookmarkEnd("MyBookmark")
'insert line breaks
For i As Integer = 0 To 3
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak)
Next
'create a cross-reference field, and link it to bookmark
Dim field As New Field(doc)
field.Type = FieldType.FieldRef
field.Code = "REF MyBookmark \p \h"
'insert field to paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("For more information, see ")
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(field)
'insert FieldSeparator object
Dim fieldSeparator As New FieldMark(doc, FieldMarkType.FieldSeparator)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(fieldSeparator)
'set display text of the field
Dim tr As New TextRange(doc)
tr.Text = "above"
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(tr)
'insert FieldEnd object to mark the end of the field
Dim fieldEnd As New FieldMark(doc, FieldMarkType.FieldEnd)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(fieldEnd)
'save file
doc.SaveToFile("output.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Shapes in Excel serve as visual elements that can decorate or optimize worksheets, including objects such as text boxes and images. By inserting shapes, users are able to present data in a more intuitive manner and emphasize vital information, ultimately improving the readability of the spreadsheets. When it becomes necessary to deal with the contents within the shapes independently, you can programmatically extract them from shapes for further processing. In this article, we will show you how to extract text and images from excel shapes by using Spire.XLS for .NET.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for.NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLLs files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Extract Text from Excel Shapes
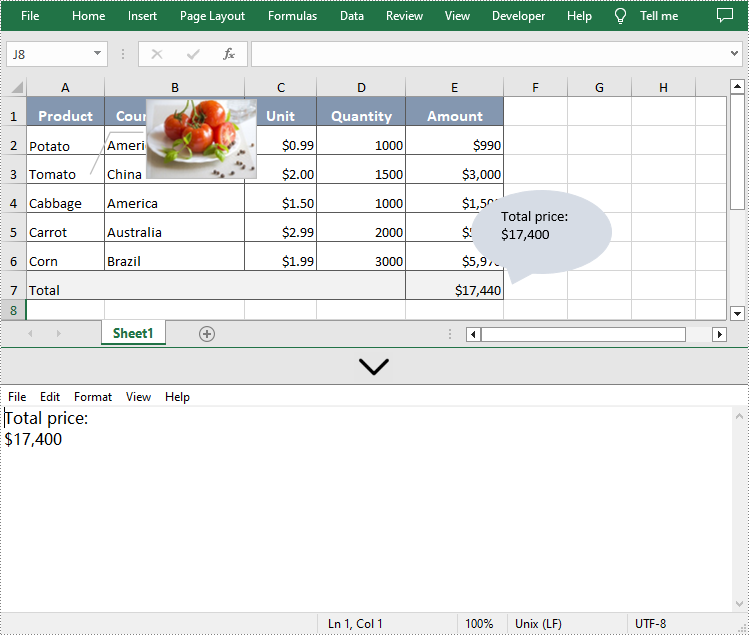
Spire.XLS for .NET allows users to extract text from shape object by using IPrstGeomShape.Text property and write it to a new .txt file. The following are detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first worksheet by Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Get the second shape by Worksheet.PrstGeomShapes[] property.
- Extract text content from the second shape and save it to the string variable.
- Create a StringBuilder object and append the extracted text to it.
- Write the text to a .txt file using File.WriteAllText() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using System.IO;
using System.Text;
using Spire.Xls;
using Spire.Xls.Core;
namespace Extracttext
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load the Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("sample.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Get the second shape and extract text from it
IPrstGeomShape shape1 = sheet.PrstGeomShapes[1];
string s = shape1.Text;
//Append the extracted text to StringBuilder object
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.AppendLine(s);
//Write the text to a .txt file
File.WriteAllText("ShapeText.txt", sb.ToString());
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
Extract Images from Excel Shapes
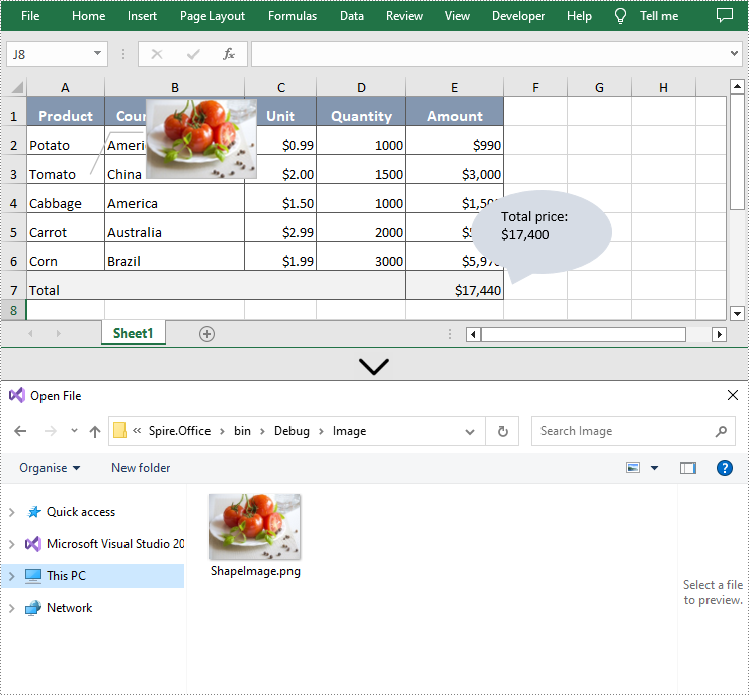
Additionally, Spire.XLS for .NET also supports extracting the image by using IPrstGeomShape.Fill.Picture property and save it to a local folder. The related steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first worksheet by Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Get the first shape by Worksheet.PrstGeomShapes[] property.
- Extract the image from the first shape by its Fill and Picture property.
- Save the extracted image to a folder by using Image.Save() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using System.Drawing;
using System.Drawing.Imaging;
using Spire.Xls;
using Spire.Xls.Core;
namespace Extractimage
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load the Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("sample.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Get the first shape and extract the image from it
IPrstGeomShape shape2 = sheet.PrstGeomShapes[0];
Image image = shape2.Fill.Picture;
//Save the extracted image to a folder
image.Save(@"Image\ShapeImage.png", ImageFormat.Png);
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
