
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
How to create a formula to apply conditional formatting in Excel in C#
2016-05-11 07:40:52 Written by KoohjiWe always use conditional formatting to highlight the cells with certain color from the whole data in the Excel worksheet. Spire.XLS also supports to create a formula to apply conditional formatting in Excel in C#. This article will show you how to apply a conditional formatting rule.
View the steps of Microsoft Excel set the conditional formatting.
Step 1: Choose the column B and then click "New Rule" under "Conditional Formatting"
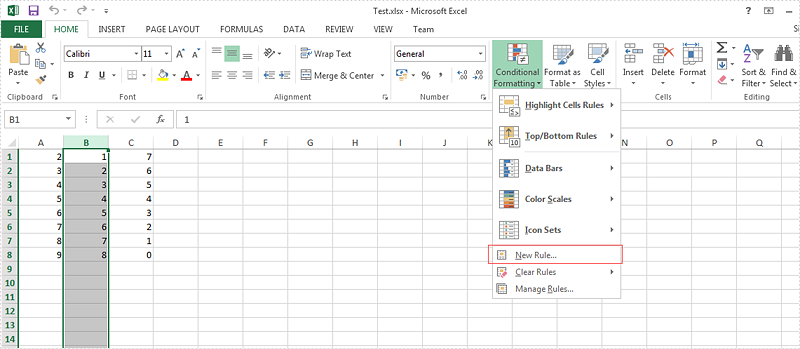
Step 2: Select the rule type, enter the rule by adding the formula and then add the highlight color for the format.
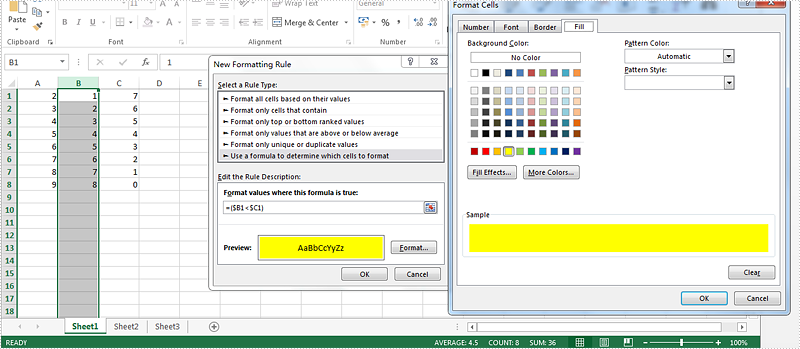
Here comes to the steps of how to set the conditional formatting rule by Spire.XLS in C#.
Step 1: Create a new excel workbook and load the document from file.
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
wb.LoadFromFile("Test.xlsx");
Step 2: Get the first worksheet and the second column from the workbook.
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0]; CellRange range = sheet.Columns[1];
Step 3: Set the conditional formatting formula and apply the rule to the chosen cell range.
XlsConditionalFormats xcfs = sheet.ConditionalFormats.Add(); xcfs.AddRange(range); IConditionalFormat conditional = xcfs.AddCondition(); conditional.FormatType = ConditionalFormatType.Formula; conditional.FirstFormula = "=($B1<$C1)"; conditional.BackKnownColor = ExcelColors.Yellow;
Step 4: Save the document to file.
wb.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
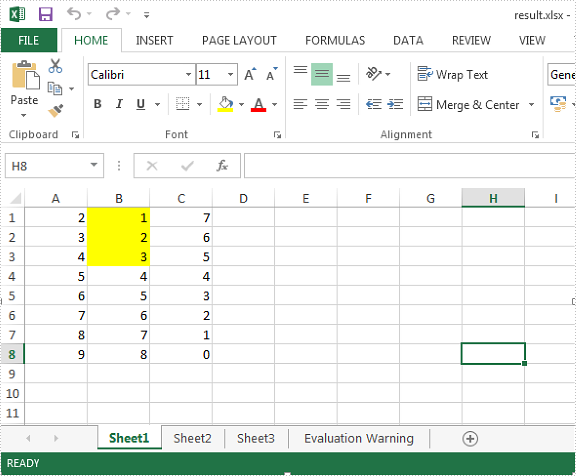
Effective screenshot:
Full codes:
using Spire.Xls;
namespace CreateFormula
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
wb.LoadFromFile("Test.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
CellRange range = sheet.Columns[1];
XlsConditionalFormats xcfs = sheet.ConditionalFormats.Add();
xcfs.AddRange(range);
IConditionalFormat conditional = xcfs.AddCondition();
conditional.FormatType = ConditionalFormatType.Formula;
conditional.FirstFormula = "=($B1<$C1)";
conditional.BackKnownColor = ExcelColors.Yellow;
wb.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Xls
Namespace CreateFormula
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
Dim wb As New Workbook()
wb.LoadFromFile("Test.xlsx")
Dim sheet As Worksheet = wb.Worksheets(0)
Dim range As CellRange = sheet.Columns(1)
Dim xcfs As XlsConditionalFormats = sheet.ConditionalFormats.Add()
xcfs.AddRange(range)
Dim conditional As IConditionalFormat = xcfs.AddCondition()
conditional.FormatType = ConditionalFormatType.Formula
conditional.FirstFormula = "=($B1<$C1)"
conditional.BackKnownColor = ExcelColors.Yellow
wb.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Spire.Xls enables developers to quickly find specific data, highlight the data as well as replace them with new data in excel files. We've already introduced how to find and highlight excel data, so this article is aimed to demonstrate how to replace selected data in excel on WPF applications using Spire.Xls for WPF.
Detail steps and code snippets:
Step 1: Create a WPF Application, add two buttons, three text boxes, two text blocks into the Main Window and align them like below.
Step 2: Double click the Browse button, add following codes to initialize a new OpenFileDialog object and set its properties to select excel file, and save its file name to the first text box.
OpenFileDialog openFileDialog1 = new OpenFileDialog();
openFileDialog1.InitialDirectory = @"E:\";
openFileDialog1.Title = "Select Excel Files";
openFileDialog1.DefaultExt = "xlsx";
openFileDialog1.Filter = "Excel files (*.xls;*.xlsx)|*.xls;*.xlsx|All files (*.*)|*.*";
openFileDialog1.FilterIndex = 1;
openFileDialog1.CheckFileExists = true;
openFileDialog1.CheckPathExists = true;
openFileDialog1.RestoreDirectory = true;
openFileDialog1.ReadOnlyChecked = true;
openFileDialog1.ShowReadOnly = true;
if (openFileDialog1.ShowDialog().Value)
{
textBox1.Text = openFileDialog1.FileName;
}
Step 3: Double click the Replace All button, add following codes to load the excel file, replace all of the text entered in the find box with new text entered in the replace box, then save the changes and launch the file.
//Load the sample excel file
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile(textBox1.Text);
//Get the first worksheet of the excel file
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Call Worksheet.FindAllString(string stringValue, bool formula, bool formulaValue) method to find all of the specific text from the first worksheet and save the results to a CellRange array
CellRange[] ranges = sheet.FindAllString(this.FindBox.Text, false, false);
//Loop through the array, replace the selected text with new text
foreach (CellRange range in ranges)
{
range.Text = this.ReplaceBox.Text;
}
//Save the changes and launch the file
workbook.SaveToFile("Replaced.xlsx");
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("Replaced.xlsx");
Result:
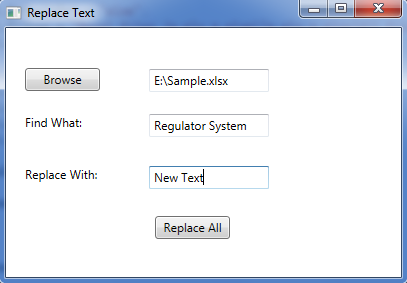
Run the project, you will get the following dialog box, Click Browse to choose excel file, then input the text that you want to find and the text used to replace, next click the Replace All button.
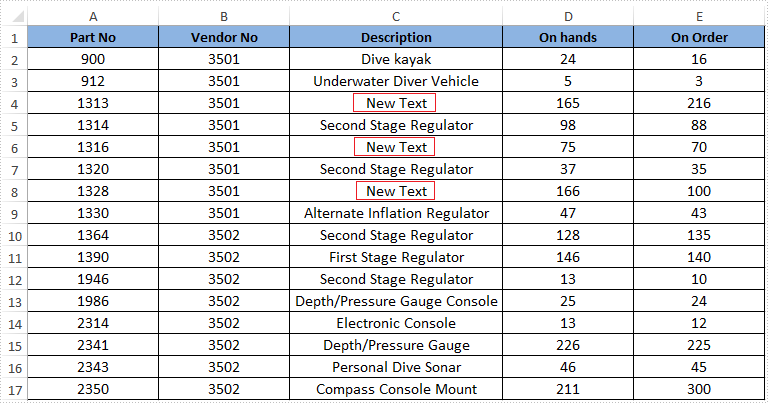
Effective screenshot of the result excel file:
Full codes:
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using Microsoft.Win32;
using Spire.Xls;
namespace Replace_Selected_Excel_Data_in_WPF
{
///
/// Interaction logic for MainWindow.xaml
///
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void BrowseBtn_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
OpenFileDialog openFileDialog1 = new OpenFileDialog();
openFileDialog1.InitialDirectory = @"E:\";
openFileDialog1.Title = "Select Excel Files";
openFileDialog1.DefaultExt = "xlsx";
openFileDialog1.Filter = "Excel files (*.xls;*.xlsx)|*.xls;*.xlsx|All files (*.*)|*.*";
openFileDialog1.FilterIndex = 1;
openFileDialog1.CheckFileExists = true;
openFileDialog1.CheckPathExists = true;
openFileDialog1.RestoreDirectory = true;
openFileDialog1.ReadOnlyChecked = true;
openFileDialog1.ShowReadOnly = true;
if (openFileDialog1.ShowDialog().Value)
{
textBox1.Text = openFileDialog1.FileName;
}
}
private void ReplaceBtn_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile(textBox1.Text);
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
CellRange[] ranges = sheet.FindAllString(this.FindBox.Text, false, false);
foreach (CellRange range in ranges)
{
range.Text = this.ReplaceBox.Text;
}
workbook.SaveToFile("Replaced.xlsx");
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("Replaced.xlsx");
}
}
}
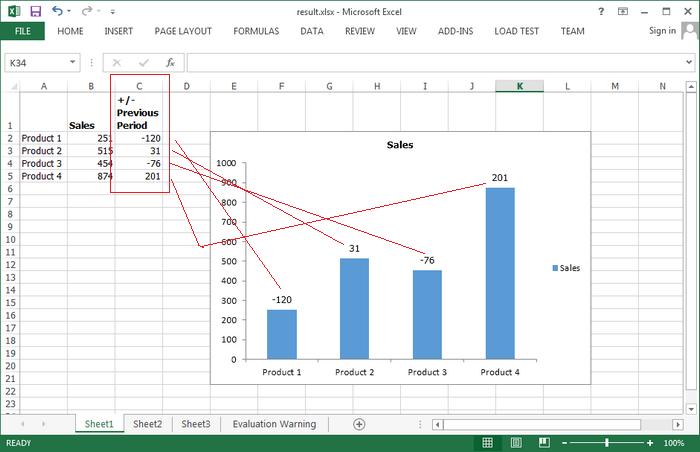
Excel version 2013 added a fantastic feature in Chart Data Label option that you can custom data labels from a column/row of data. The chart below uses labels from the data in cells C2: C5 next to the plotted values. This article will present how to add labels to data points using the values from cells in C#.
Code Snippets:
Step 1: Initialize a new instance of Workbook class and set the Excel version as 2013.
Workbook wb = new Workbook(); wb.Version = ExcelVersion.Version2013;
Step 2: Get the first sheet from workbook.
Worksheet ws = wb.Worksheets[0];
Step 3: Insert data.
ws.Range["A2"].Text = "Product 1"; ws.Range["A3"].Text = "Product 2"; ws.Range["A4"].Text = "Product 3"; ws.Range["A5"].Text = "Product 4"; ws.Range["B1"].Text = "Sales"; ws.Range["B1"].Style.Font.IsBold = true; ws.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 251; ws.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 515; ws.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 454; ws.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 874; ws.Range["C1"].Text = "+/-\nPrevious\nPeriod"; ws.Range["C1"].Style.Font.IsBold = true; ws.Range["C2"].NumberValue = -120; ws.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 31; ws.Range["C4"].NumberValue = -76; ws.Range["C5"].NumberValue = 201; ws.SetRowHeight(1, 40);
Step 4: Insert a Clustered Column Chart in Excel based on the data range from A1:B5.
Chart chart = ws.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered); chart.DataRange = ws.Range["A1:B5"]; chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false; chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = false;
Step 5: Set chart position.
chart.LeftColumn = 5; chart.TopRow = 2; chart.RightColumn = 13; chart.BottomRow = 22;
Step 6: Add labels to data points using the values from cell range C2:C5.
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.ValueFromCell = ws.Range["C2:C5"];
Step 7: Save and launch the file.
wb.SaveToFile("result.xlsx",ExcelVersion.Version2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.xlsx");
Full Code:
using Spire.Xls;
namespace CustomLabels
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
wb.Version = ExcelVersion.Version2013;
Worksheet ws = wb.Worksheets[0];
ws.Range["A2"].Text = "Product 1";
ws.Range["A3"].Text = "Product 2";
ws.Range["A4"].Text = "Product 3";
ws.Range["A5"].Text = "Product 4";
ws.Range["B1"].Text = "Sales";
ws.Range["B1"].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
ws.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 251;
ws.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 515;
ws.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 454;
ws.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 874;
ws.Range["C1"].Text = "+/-\nPrevious\nPeriod";
ws.Range["C1"].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
ws.Range["C2"].NumberValue = -120;
ws.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 31;
ws.Range["C4"].NumberValue = -76;
ws.Range["C5"].NumberValue = 201;
ws.SetRowHeight(1, 40);
Chart chart = ws.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered);
chart.DataRange = ws.Range["A1:B5"];
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = false;
chart.LeftColumn = 5;
chart.TopRow = 2;
chart.RightColumn = 13;
chart.BottomRow = 22;
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.ValueFromCell = ws.Range["C2:C5"];
wb.SaveToFile("result.xlsx",ExcelVersion.Version2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.xlsx");
}
}
}
