Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Text alignment and orientation are essential formatting features in Excel that allow you to position and orient text within cells according to your specific needs. By adjusting text alignment and orientation, you can enhance the readability and aesthetics of your spreadsheet. In this article, we will explain how to set text alignment and orientation in Excel in C# and VB.NET using Spire.XLS for .NET.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for.NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Set Text Alignment and Orientation in Excel in C# and VB.NET
You can set the horizontal or vertical alignment of text in individual cells or a range of cells using the CellRange.Style.HorizontalAlignment or CellRange.Style.VerticalAlignment properties. In addition, you are also able to change the orientation of text by assigning a rotation value to the corresponding cell or cells using the CellRange.Style.Rotation property. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[int index] property.
- Access specific cells in the worksheet using Worksheet.Range[string name] property and then set the horizontal alignment of text in them using CellRange.Style.HorizontalAlignment property.
- Access specific cells in the worksheet using Worksheet.Range[string name] property and then set the vertical alignment of text in them using CellRange.Style.VerticalAlignment property.
- Access specific cells in the worksheet using Worksheet.Range[string name] property and then change their text orientation using CellRange.Style.Rotation property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
namespace TextAlignmentAndRotation
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile(@"Sample.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Set the horizontal alignment for text in a specific cell to Left
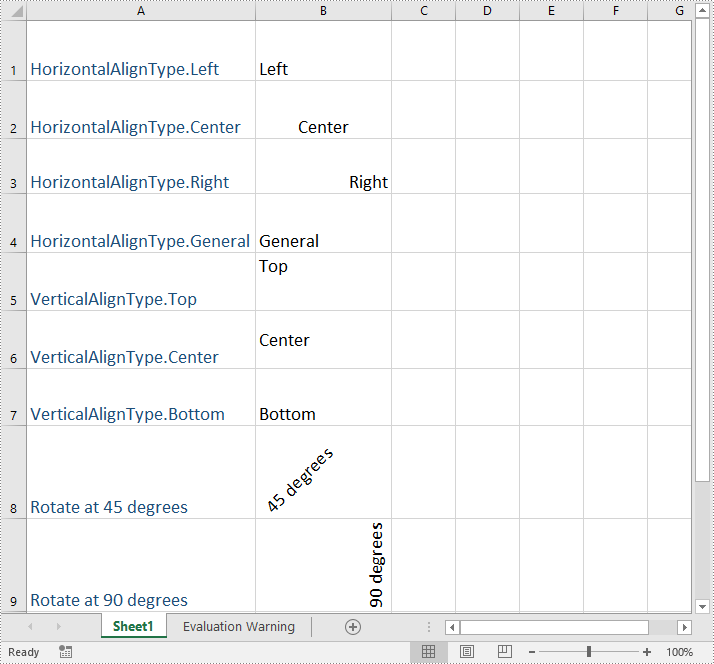
sheet.Range["B1"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left;
//Set the horizontal alignment for text in a specific cell to Center
sheet.Range["B2"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center;
//Set the horizontal alignment for text in a specific cell to Right
sheet.Range["B3"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Right;
//Set the horizontal alignment for text in a specific cell to General
sheet.Range["B4"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.General;
//Set the vertical alignment for text in a specific cell to Top
sheet.Range["B5"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Top;
//Set the vertical alignment for text in a specific cell to Center
sheet.Range["B6"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center;
//Set the vertical alignment for text in a specific cell to Bottom
sheet.Range["B7"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Bottom;
//Change the text orientation in specific cells by assigning a rotation value
sheet.Range["B8"].Style.Rotation = 45;
sheet.Range["B9"].Style.Rotation = 90;
//Set the row height for specific cells
sheet.Range["B8:C9"].RowHeight = 70;
//Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("TextAlignmentAndOrientation.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.Dispose();
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Shading is a powerful feature in MS Word that adds a background color to specified text or paragraphs in a document. This not only enhances the visual appeal of the document, but also helps to differentiate between different sections and makes the content more readable. In this article, you will learn how to apply shading to a paragraph or text in Word in C# using Spire.Doc for .NET.
Install Spire.Doc for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Doc for.NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
Apply Paragraph Shading in Word in C#
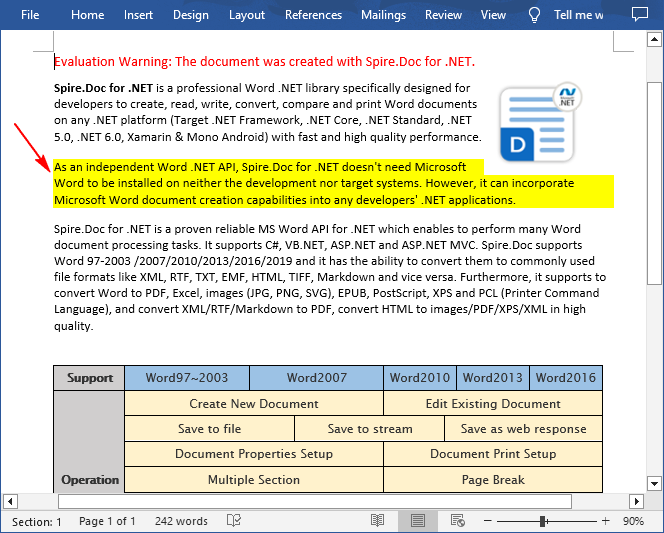
Spire.Doc for .NET provides developers with the Paragraph.Format.BackColor property to apply a background color to a specified paragraph in Word. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Get a specified paragraph using Section.Paragraphs[] property.
- Set a background color for the paragraph using Paragraph.Format.BackColor property.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using System.Drawing;
namespace WordParagrahShade
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Document instance
Document document = new Document();
// Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Get the first section
Section section = document.Sections[0];
// Get the second paragraph
Paragraph paragaph = section.Paragraphs[1];
// Set a background color for the paragraph
paragaph.Format.BackColor = Color.Yellow;
// Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("ParagraphBackground.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
}
}
}
Apply Shading to Specified Text in Word in C#
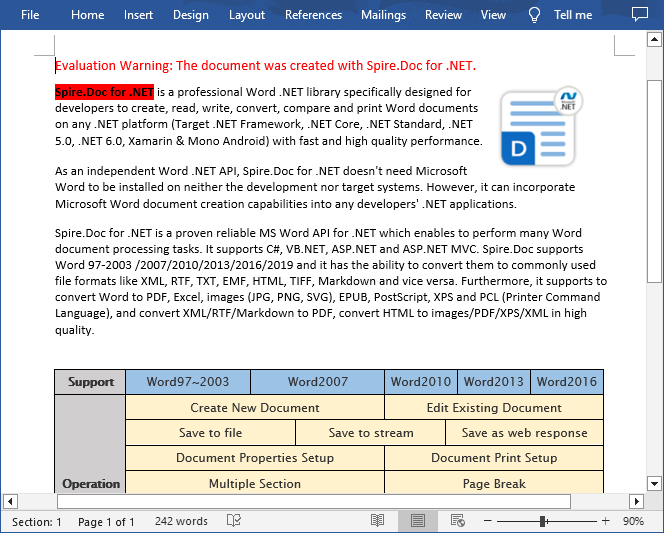
If you only need to apply shading to specified text, you can first find the specific text through the Paragraph.Find() method, get its text range and then set a background color for the text range through the TextRange.CharacterFormat.TextBackgroundColor property. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Get a specified paragraph using Section.Paragraphs[] property.
- Find a specified text in the paragraph Paragraph.Find() method.
- Get the text range of the found text using TextSelection.GetAsOneRange() method.
- Set a background color for the text range using TextRange.CharacterFormat.TextBackgroundColor property.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
using System.Drawing;
namespace ShadeText
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Document instance
Document document = new Document();
// Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx");
// Get the first section
Section section = document.Sections[0];
// Get the first paragraph
Paragraph paragaph = section.Paragraphs[0];
// Find a specified text in the paragraph
TextSelection selection = paragaph.Find("Spire.Doc for .NET", true, false);
// Get the text range of the found text
TextRange range = selection.GetAsOneRange();
// Set a background color for the text range
range.CharacterFormat.TextBackgroundColor = Color.Red;
// Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("TextBackground.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Group the Excel cells is to tie a range of cells together so that they can be collapsed or expanded. But usually, we also need to ungroup the Excel cells. Consequently, the articles aims at introducing how to ungroup Excel cells in C#, through a professional Excel .NET Component Spire.Xls.
Just as its name implies, ungroup Excel cells is to ungroup a range of cells that were previously grouped. Before ungroup Excel cells, we should complete the preparatory work:
- Download the Spire.XLS and install it on your machine.
- Add the Spire.XLS.dll files as reference.
- Open bin folder and select the three dll files under .NET 4.0.
- Right click property and select properties in its menu.
- Set the target framework as .NET 4.
- Add Spire.XLS as namespace.
Then here comes to the explanation of the code:
Step 1: Create an instance of Spire.XLS.Workbook.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
Step 2: Load the file base on a specified file path.
workbook.LoadFromFile(@"group.xlsx");
Step 3: Get the first worksheet.
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
Step 4: Ungroup the first 5 row cells.
sheet.UngroupByRows(1, 5);
Step 5: Save as the generated file.
workbook.SaveToFile(@"result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
Full code:
using Spire.Xls;
namespace UngroupCell
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile(@"group.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
sheet.UngroupByRows(1, 5);
workbook.SaveToFile(@"..\..\result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
}
}
}
Please preview the original group effect screenshot:
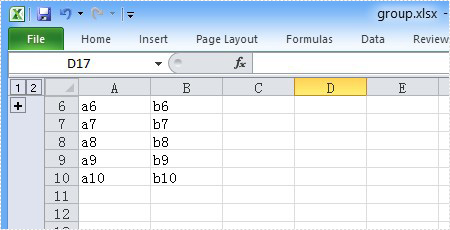
And the generated ungroup effect screenshot: