
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Introduction
Digital signatures help verify the authenticity and integrity of PDF documents. However, if a signing certificate expires or is revoked, the signature alone may no longer be considered valid. To solve this, a timestamp can be added to the digital signature, proving that the document was signed at a specific point in time-validated by a trusted Time Stamp Authority (TSA).
In this tutorial, we will introduce how to use the Spire.PDF for Python library to digitally sign a PDF document with a timestamp in Python.
Prerequisites
To follow this tutorial, ensure you have the following:
- Spire.PDF for Python library
- A valid digital certificate (.pfx file)
- A sample PDF file
- An image to display as the signature appearance (optional)
- A reliable Time Stamp Authority (TSA) URL
pip install Spire.PDF
How to Digitally Sign a PDF with a Timestamp in Python
In Spire.PDF for Python, the Security_PdfSignature class is used to create a digital signature, and the ConfigureTimestamp(tsaUrl) method in this class is used to embed a timestamp into the signature. The tsaUrl parameter specifies the address of the TSA server.
Steps to Add a Timestamped Digital Signature
Follow these steps to add a timestamped digital signature to a PDF in Python using Spire.PDF for Python:
- Create a PdfDocument instance and use the LoadFromFile() method to load the PDF you want to sign.
- Create a Security_PdfSignature object, specifying the target page, certificate file path, certificate password, and signature name.
- Configure the signature's appearance, including its position, size, display labels, and signature image.
- Embed a timestamp by calling the ConfigureTimestamp(tsaUrl) method with a valid Time Stamp Authority (TSA) URL.
- Save the signed PDF using the SaveToFile() method.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import * inputFile = "Sample.pdf" inputFile_pfx = "gary.pfx" inputImage = "E-iceblueLogo.png" outputFile = "SignWithTimestamp.pdf" # Create a PdfDocument instance and load the PDF file to be signed doc = PdfDocument() doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Create a digital signature object by specifying the document, target page, certificate file path, certificate password, and signature name signature = Security_PdfSignature(doc, doc.Pages.get_Item(0), inputFile_pfx, "e-iceblue", "signature") # Define the position and size of the signature on the page (unit: point) signature.Bounds = RectangleF(PointF(90.0, 600.0), SizeF(180.0, 90.0)) # Set the labels and content for the signature details signature.NameLabel = "Digitally signed by: " signature.Name = "Gary" signature.LocationInfoLabel = "Location: " signature.LocationInfo = "CN" signature.ReasonLabel = "Reason: " signature.Reason = "Ensure authenticity" signature.ContactInfoLabel = "Contact Number: " signature.ContactInfo = "028-81705109" # Set document permissions: allow form filling, forbid further changes signature.DocumentPermissions = PdfCertificationFlags.AllowFormFill.value | PdfCertificationFlags.ForbidChanges.value # Set the graphic mode to include both image and signature details, # and set the signature image signature.GraphicsMode = Security_GraphicMode.SignImageAndSignDetail signature.SignImageSource = PdfImage.FromFile(inputImage) # Embed a timestamp into the signature using a Time Stamp Authority (TSA) server url = "http://tsa.cesnet.cz:3161/tsa" signature.ConfigureTimestamp(url) # Save the signed PDF and close the document doc.SaveToFile(outputFile) doc.Close()
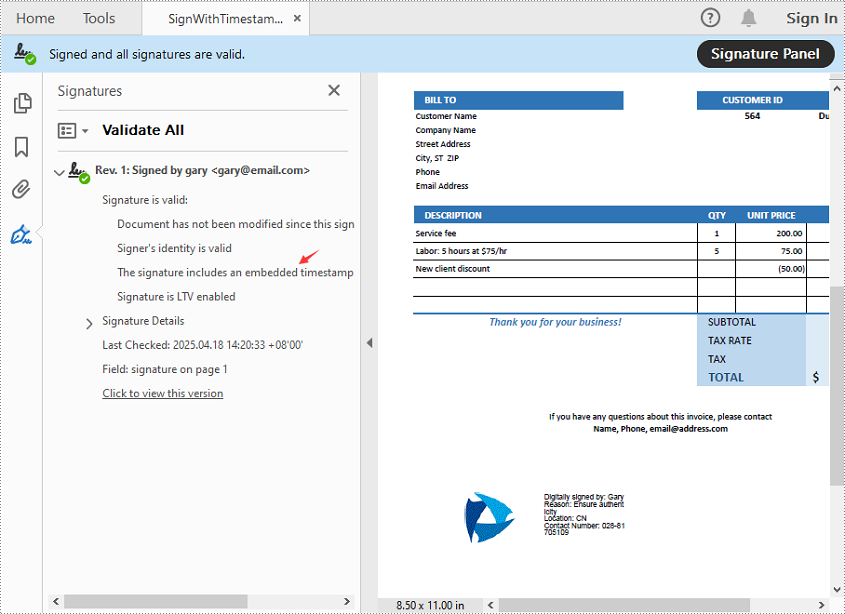
View the Timestamp in PDF
When you open the signed PDF in a viewer like Adobe Acrobat, you can click the Signature Panel to view both the digital signature and the timestamp, which confirm the document’s validity and the signing time:
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.PDF for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Conclusion
Timestamping enhances the reliability of digital signatures by proving when a PDF was signed-even after the certificate has expired. With Spire.PDF for Python, implementing a timestamped digital signature is a straightforward process. Whether you're handling contracts, invoices, or confidential records, this approach ensures long-term document validity and compliance.
PostScript, developed by Adobe, is a page description language known for its high-quality graphics and text rendering capabilities. By converting PDF to PostScript, you can have a precise control over complex graphics, fonts and colors when printing brochures, magazines, advertisements, or other materials.
PCL, on the other hand, is a printer control language developed by Hewlett-Packard. It is designed to be efficient and easy for the printers to interpret. Converting PDF to PCL ensures compatibility with a large number of printers and also optimizes the printing speed for text-heavy documents such as academic reports, letters, or contracts.
This article will demonstrate how to convert PDF to PS or PDF to PCL in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python. It can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Convert PDF to PostScript in Python
Converting PDF to PS can improve the quality of the printed output. Spire.PDF for .NET allows you to load a PDF file and then converting it to PS format using PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename: string, FileFormat.POSTSCRIPT) method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the PDF file to PostScript format using PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename: string, FileFormat.POSTSCRIPT) method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import * from spire.pdf import * # Specify the input and output file paths inputFile = "input1.pdf" outputFile = "PdfToPostScript.ps" # Create a PdfDocument instance pdf = PdfDocument() # Load a PDF document pdf.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Convert the PDF to a PostScript file pdf.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.POSTSCRIPT) pdf.Close()

Convert PDF to PCL in Python
Converting PDF to PCL can ensure faster printing speed. By using the PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename: string, FileFormat.PCL) method, you can save a loaded PDF file as a PCL file. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the PDF file to PCL format using PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename: string, FileFormat.PCL) method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import * from spire.pdf import * # Specify the input and output file paths inputFile = "input1.pdf" outputFile = "ToPCL\\PdfToPcl.pcl" # Create a PdfDocument instance pdf = PdfDocument() # Load a PDF document pdf.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Convert the PDF to a PCL file pdf.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.PCL) pdf.Close()

Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.PDF for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
In Microsoft Excel, each worksheet acts as a unique space for organizing distinct sets of data, projects, or analyses. Efficient management of these worksheets is crucial for quick navigation and effective data handling. By renaming worksheets, users can create intuitive labels that clearly indicate the content of each sheet, making it easier to locate specific information. Furthermore, customizing tab colors enhances visual organization, allowing users to differentiate between various sections or categories at a glance.
In this article, we will demonstrate how to change worksheet names and set tab colors in Excel using Python and the Spire.XLS for Python library.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Change Worksheet Names in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the Worksheet.Name property to rename a worksheet in an Excel file. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load a sample Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the desired worksheet using the Worbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Rename the worksheet using the Worksheet.Name property.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * # Specify the input and output file paths inputFile = "Sample1.xlsx" outputFile = "RenameWorksheets.xlsx" # Create an object of the Workbook class workbook = Workbook() # Load a sample Excel file workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Rename the first worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] sheet.Name = "Probate Inventory" # Rename the second worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[1] sheet.Name = "Probate Assets" # Rename the third worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[2] sheet.Name = "Probate Liabilities" # Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()
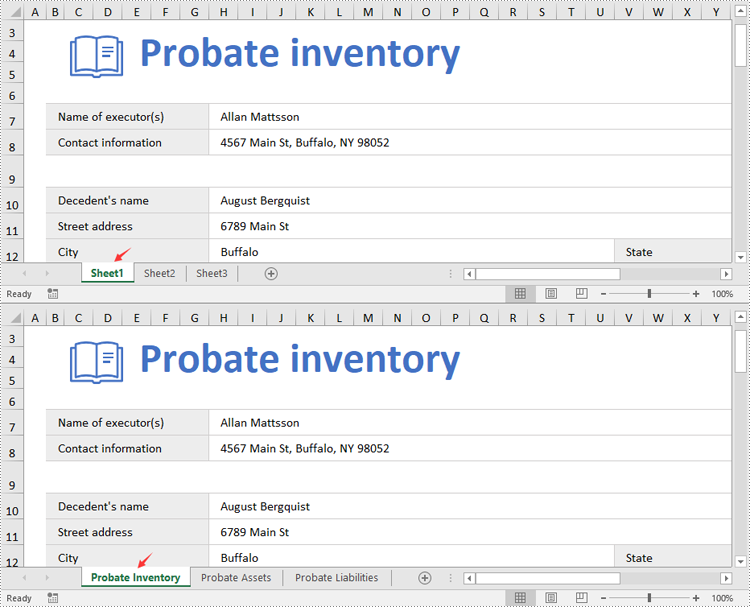
Set Worksheet Tab Colors in Excel in Python
The Worksheet.TabColor property allows setting a tab color for a worksheet in an Excel file. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load a sample Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the desired worksheet using the Worbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Rename the worksheet using the Worksheet.TabColor property.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * # Specify the input and output file paths inputFile = "Sample2.xlsx" outputFile = "SetTabColor.xlsx" # Create an object of the Workbook class workbook = Workbook() # Load a sample Excel file workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Set the tab color for the first worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] worksheet.TabColor = Color.get_Red() # Set the tab color for the second worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[1] worksheet.TabColor = Color.get_Green() # Set the tab color for the third worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[2] worksheet.TabColor = Color.get_LightBlue() # Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()

Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.XLS for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
