
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Extract Background Images from PowerPoint Presentations using C# .NET
2025-05-16 09:01:16 Written by Administrator
PowerPoint presentations often contain background images that enhance the visual appeal of slides. Extracting these background images can be crucial for designers and content managers who wish to reuse, analyze, or archive slide visuals independently of the slide content.
This guide provides a clear, step-by-step approach to extracting background images from PowerPoint presentations in .NET using C# and the Spire.Presentation for .NET library.
Table of Contents
- Why Extract Background Images from PowerPoint
- Install .NET PowerPoint Library – Spire.Presentation for .NET
- Extract Background Images from PowerPoint in .NET using C#
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Why Extract Background Images from PowerPoint
Extracting background images from PowerPoint provides several key benefits:
- Reuse Designs: Repurpose background images in other presentations or design projects.
- Analyze Slides: Review and understand slide designs by examining background images separately.
- Archive Visuals: Store background images for documentation, backup, or future use.
Install .NET PowerPoint Library – Spire.Presentation for .NET
Spire.Presentation for .NET is a robust .NET PowerPoint library that enables developers to create, manipulate, and convert PowerPoint presentations without the need for Microsoft PowerPoint.
Key Features of Spire.Presentation for .NET
Here are some key features of Spire.Presentation for .NET:
- Create and edit PowerPoint presentations.
- Convert PowerPoint to other formats such as PDF, Images, HTML, Markdown, and XPS.
- Secure PowerPoint presentations
- Merge/split PowerPoint presentations.
- Slides management, including adding/removing slides, setting/extracting/removing backgrounds, and more.
- Image/shape/chart/smartart insertion and manipulation.
- Animate text/shapes.
Install Spire.Presentation for .NET
Before starting the background image extraction process, you will need to install Spire.Presentation for .NET into your C# project using one of the following methods:
Option1. Install via NuGet (Recommended)
Install-Package Spire.PresentationOption 2: Manually Add DLLs to Your Project
- Download the Spire.Presentation package and extract the files.
- In Visual Studio, right-click References > Add Reference > Browse, then select the appropriate Spire.Presentation.dll based on your target framework.
Extract Background Images from PowerPoint in .NET using C#
Background images in PowerPoint can be applied directly to individual slides or inherited from slide masters. This section demonstrates how to extract both types of background images using Spire.Presentation.
Extract Background Images from Individual Slides
To extract background images from individual slides in PowerPoint, follow these steps:
- Create a Presentation object and load the presentation.
- Loop through all slides in the presentation.
- Check if the slide’s background fill type is image fill (FillFormatType.Picture).
- If yes, retrieve and save the background image.
Sample Code
- C#
using Spire.Presentation;
using Spire.Presentation.Drawing;
using System.IO;
namespace ExtractSlideBackgroundImages
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Specify the input file path and output folder
string inputFile = @"example1.pptx";
string outputFolder = @"ExtractedBackgrounds\Slides";
// Load the PowerPoint presentation
Presentation presentation = new Presentation();
presentation.LoadFromFile(inputFile);
// Create the output folder
Directory.CreateDirectory(outputFolder);
// Loop through all slides
for (int i = 0; i < presentation.Slides.Count; i++)
{
// Check if the slide's background fill type is image fill
var fill = presentation.Slides[i].SlideBackground.Fill;
if (fill.FillType == FillFormatType.Picture)
{
// Extract and save the background image
var image = fill.PictureFill.Picture.EmbedImage;
if (image != null)
{
string outputPath = Path.Combine(outputFolder, $"SlideBackground_{i + 1}.png");
image.Image.Save(outputPath, ImageFormat.Png);
}
}
}
}
}
}Extract Background Images from Slide Masters
Slide masters define the design and layout of slides, including background images. To extract background images from slide masters:
- Create a Presentation object and load the presentation.
- Loop through all slide masters in the presentation.
- For each master, check if its background fill type is image fill.
- If yes, extract and save the background image.
Sample Code
- C#
using Spire.Presentation;
using Spire.Presentation.Drawing;
using System.Drawing.Imaging;
using System.IO;
namespace ExtractBackgroundImages
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Specify the input file path and output folder
string inputFile = @"example2.pptx";
string outputFolder = @"C:\ExtractedBackgrounds\Masters";
// Load the PowerPoint presentation
Presentation presentation = new Presentation();
presentation.LoadFromFile(inputFile);
// Create the output folder
Directory.CreateDirectory(outputFolder);
// Loop through all slide masters
for (int i = 0; i < presentation.Masters.Count; i++)
{
// Check if the slide master's background fill type is image fill
var fill = presentation.Masters[i].SlideBackground.Fill;
if (fill.FillType == FillFormatType.Picture)
{
// Extract and save the background image
var image = fill.PictureFill.Picture.EmbedImage;
if (image != null)
{
string outputPath = Path.Combine(outputFolder, $"MasterBackground_{i + 1}.png");
image.Image.Save(outputPath, ImageFormat.Png);
}
}
}
}
}
}Conclusion
Extracting background images from PowerPoint presentations is a crucial technique for developers and designers who want to access slide visuals independently of content. By leveraging the Spire.Presentation for .NET library with C#, you can programmatically extract background images from both individual slides and slide masters with ease.
FAQs
Q: What image formats are supported for extraction?
A: Extracted images can be saved in PNG, JPEG, BMP, or other formats supported by .NET.
Q: In addition to background images, can I extract other images from PowerPoint slides?
A: Yes, you can extract other images, such as those embedded within slide content or shapes, using Spire.Presentation.
Q: Does Spire.Presentation supports extracting text from PowerPoint presentations?
A: Yes, Spire.Presentation can also extract text from slides, including text in shapes, tables, and more.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Presentation for .NET without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.

In data processing and management scenarios, efficiently transforming raw text (TXT) files into structured Excel spreadsheets is a common requirement. For developers who are automating reports or processing log files, converting TXT to Excel using C# streamlines data organization and analysis. This guide explores how to achieve this using Spire.XLS for .NET, a powerful library designed to handle Excel XLS or XLSX files without requiring Microsoft Office.
- Why Convert TXT to Excel Programmatically?
- How to Convert Text Files to Excel in C# (Step-by-Step Guide)
- Pro Tips for TXT to Excel Conversion
Why Convert TXT to Excel Programmatically?
Text files are simple but lack the analytical power of Excel. Key advantages of converting TXT to XLS or XLSX format include:
- Automation: Process large or recurring files without manual intervention.
- Data Structuring: Organize raw text into rows, columns, and sheets.
- Advanced Features: Leverage Excel formulas, charts, and pivot tables.
- Integration: Embed conversion feature into .NET applications or APIs.
How to Convert Text Files to Excel in C# (Step-by-Step Guide)
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
Spire.XLS for .NET is a professional Excel document processing component, provides efficient and convenient APIs that allow developers to achieve TXT to Excel conversion through simple code.
Before getting started, you can choose one of these methods to install the library:
Method 1: NuGet Package Manager
- Open your project in Visual Studio.
- Right-click on the project in the Solution Explorer and select "Manage NuGet Packages."
- Search for "Spire.XLS" and click "Install".
Method 2: Package Manager Console
- Go to "Tools > NuGet Package Manager > Package Manager Console."
- Run the following command in the console:
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Method 3: Manual Installation with DLL Files
- Visit the Spire.XLS Download Page and get the latest version.
- Extract the files and then add the Spire.Xls.dll to your project.
Import a Text File into Excel Using C#
Follow the below steps to write the data in a txt file into an Excel worksheet:
- Read TXT File: use the File.ReadAllLines() method to read all lines in a text file and returns them as an array of strings.
- Parse each line:
- Use the string.Trim() method to remove the leading/trailing whitespaces.
- Use the string.Split() method to split the data based on specified delimiters.
- Add the split text data to a list.
- Create a Workbook instance and get a worksheet
- Write Data to specified cells:
- Iterate through the rows and columns in the list.
- Assign the data in the list to the corresponding Excel cells through the Worksheet.Range[].Value property.
- Save the Excel File.
Code Example:
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using System.IO;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class TxtToExcelConverter
{
static void Main()
{
// Open a text file and read all lines in it
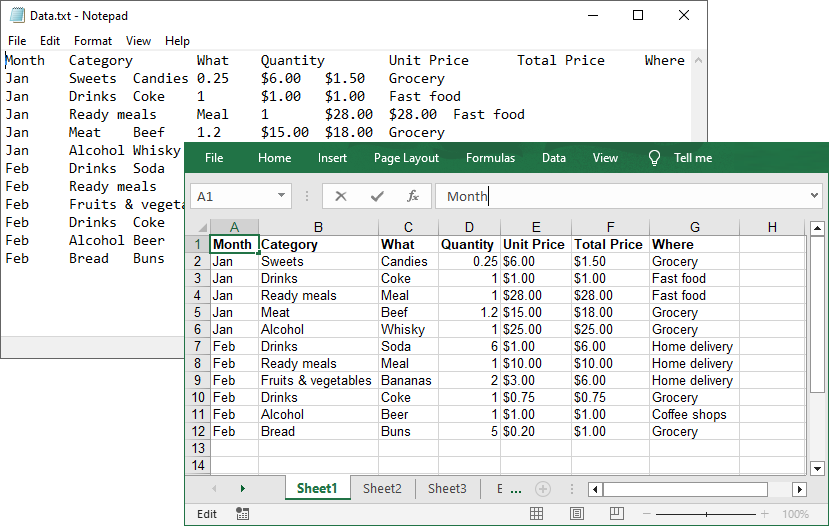
string[] lines = File.ReadAllLines("Data.txt");
// Create a list to store the data in text file
List data = new List();
// Split data into rows and columns and add to the list
foreach (string line in lines)
{
data.Add(line.Trim().Split('\t')); // Adjust delimiter as needed
}
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Iterate through the rows and columns in the data list
for (int row = 0; row < data.Count; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < data[row].Length; col++)
{
// Write the text data in specified cells
sheet.Range[row + 1, col + 1].Value = data[row][col];
// Set the header row to Bold
sheet.Range[1, col + 1].Style.Font.IsBold = true;
}
}
// Autofit columns
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns();
// Save the Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("TXTtoExcel.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
workbook.Dispose();
}
}Result:
Pro Tips for TXT to Excel Conversion
- Handling Different Delimiters:
If your TXT file uses a different delimiter (e.g., space, comma, semicolon), modify the parameter of the Split(params char[] separator) method.
- Format Cells:
After a text file being converted to an Excel file, you can take advantage of the Spire.XLS library’s rich features to format cells, such as setting the background colors, adding cell borders, applying number formats, etc.
Conclusion
By following this step-by-step guide, you can efficiently transform unstructured text data into organized Excel spreadsheets, which is ideal for data analysis, reporting, and management. Remember to optimize your implementation for your specific delimiters and leverage Spire.XLS's advanced features for complex conversion scenarios.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.XLS for .NET without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
In modern software development, generating dynamic Word documents from templates is a common requirement for applications that produce reports, contracts, invoices, or other business documents. Java developers seeking efficient solutions for document automation can leverage Spire.Doc for Java, a robust library for processing Word files without requiring Microsoft Office.
This guide explores how to use Spire.Doc for Java to create Word documents from templates. We will cover two key approaches: replacing text placeholders and modifying bookmark content.
- Java Libray for Creating Word Documents
- Generate a Word Document by Replacing Text Placeholders
- Generate a Word Document by Modifying Bookmark Content
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Java Library for Generating Word Documents
Spire.Doc for Java is a powerful library that enables developers to create, manipulate, and convert Word documents. It provides an intuitive API that allows for various operations, including the modification of text, images, and bookmarks in existing documents.
To get started, download the library from our official website and import it into your Java project. If you're using Maven, include the following dependency in your pom.xml file:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.doc</artifactId>
<version>14.1.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Generate a Word Document by Replacing Text Placeholders
This method uses a template document containing marked placeholders (e.g., #name#, #date#) that are dynamically replaced with real data. Spire.Doc's Document.replace() method handles text substitutions efficiently, while additional APIs enable advanced replacements like inserting images at specified locations.
Steps to generate Word documents from templates by replacing text placeholders:
- Initialize Document: A new Document object is created to work with the Word file.
- Load the template: The template document with placeholders is loaded.
- Create replacement mappings: A HashMap is created to store placeholder-replacement pairs.
- Perform text replacement: The replace() method finds and replaces all instances of each placeholder.
- Handle image insertion: The custom replaceTextWithImage() method replaces a text placeholder with an image.
- Save the result: The modified document is saved to a specified path.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.Document;
import com.spire.doc.FileFormat;
import com.spire.doc.documents.TextSelection;
import com.spire.doc.fields.DocPicture;
import com.spire.doc.fields.TextRange;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ReplaceTextPlaceholders {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Initialize a new Document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load the template Word file
document.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\template.docx");
// Map to hold text placeholders and their replacements
Map<String, String> replaceDict = new HashMap<>();
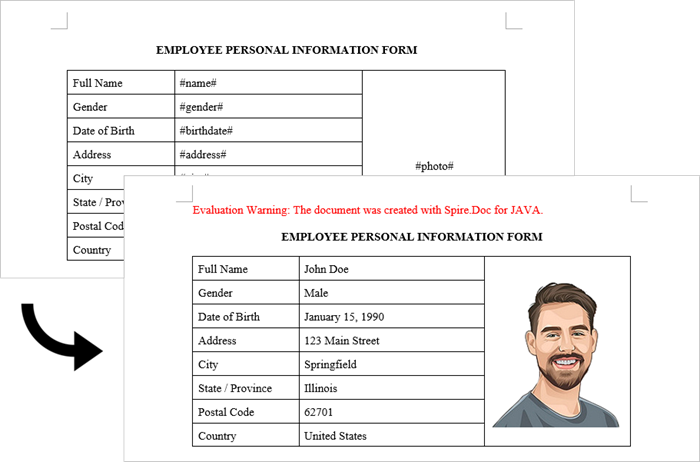
replaceDict.put("#name#", "John Doe");
replaceDict.put("#gender#", "Male");
replaceDict.put("#birthdate#", "January 15, 1990");
replaceDict.put("#address#", "123 Main Street");
replaceDict.put("#city#", "Springfield");
replaceDict.put("#state#", "Illinois");
replaceDict.put("#postal#", "62701");
replaceDict.put("#country#", "United States");
// Replace placeholders in the document with corresponding values
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : replaceDict.entrySet()) {
document.replace(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue(), true, true);
}
// Path to the image file
String imagePath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\portrait.png";
// Replace the placeholder “#photo#” with an image
replaceTextWithImage(document, "#photo#", imagePath);
// Save the modified document
document.saveToFile("output/ReplacePlaceholders.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Release resources
document.dispose();
}
// Method to replace a placeholder in the document with an image
static void replaceTextWithImage(Document document, String stringToReplace, String imagePath) {
// Load the image from the specified path
DocPicture pic = new DocPicture(document);
pic.loadImage(imagePath);
// Find the placeholder in the document
TextSelection selection = document.findString(stringToReplace, false, true);
// Get the range of the found text
TextRange range = selection.getAsOneRange();
int index = range.getOwnerParagraph().getChildObjects().indexOf(range);
// Insert the image and remove the placeholder text
range.getOwnerParagraph().getChildObjects().insert(index, pic);
range.getOwnerParagraph().getChildObjects().remove(range);
}
}Output:
Generate a Word Document by Modifying Bookmark Content
This approach uses Word bookmarks to identify locations in the document where content should be inserted or modified. The BookmarksNavigator class in Spire.Doc streamlines the process by enabling direct access to bookmarks, allowing targeted content replacement while automatically preserving the document's original structure and formatting.
Steps to generate Word documents from templates by modifying bookmark content:
- Initialize Document: A new Document object is initialized.
- Load the template: The template document with predefined bookmarks is loaded.
- Set up replacements: A HashMap is created to map bookmark names to their replacement values.
- Navigate to bookmarks: A BookmarksNavigator is instantiated to navigate through bookmarks in the document.
- Replace content: The replaceBookmarkContent() method updates the bookmark's content.
- Save the result: The modified document is saved to a specified path.
- Java
import com.spire.doc.*;
import com.spire.doc.documents.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ModifyBookmarkContent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Initialize a new Document object
Document document = new Document();
// Load the template Word file
document.loadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\template.docx");
// Define bookmark names and their replacement values
Map<String, String> replaceDict = new HashMap<>();
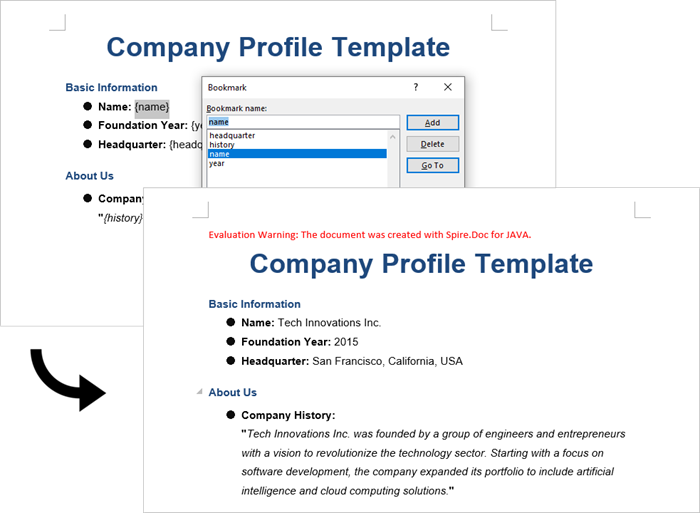
replaceDict.put("name", "Tech Innovations Inc.");
replaceDict.put("year", "2015");
replaceDict.put("headquarter", "San Francisco, California, USA");
replaceDict.put("history", "Tech Innovations Inc. was founded by a group of engineers and " +
"entrepreneurs with a vision to revolutionize the technology sector. Starting " +
"with a focus on software development, the company expanded its portfolio to " +
"include artificial intelligence and cloud computing solutions.");
// Create a BookmarksNavigator to manage bookmarks in the document
BookmarksNavigator bookmarkNavigator = new BookmarksNavigator(document);
// Iterate through the bookmarks
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : replaceDict.entrySet()) {
// Navigate to a specific bookmark
bookmarkNavigator.moveToBookmark(entry.getKey());
// Replace content
bookmarkNavigator.replaceBookmarkContent(entry.getValue(), true);
}
// Save the modified document
document.saveToFile("output/ReplaceBookmarkContent.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
// Release resources
document.dispose();
}
}Output:
Conclusion
Both methods provide effective ways to generate documents from templates, but they suit different scenarios:
Text Replacement Method is best when:
- You need simple text substitutions
- You need to insert images at specific locations
- You want to replace text anywhere in the document (not just specific locations)
Bookmark Method is preferable when:
- You're working with complex documents where precise location matters
- You need to replace larger sections of content or paragraphs
- You want to preserve bookmarks for future updates
Spire.Doc also offers Mail Merge capabilities, enabling high-volume document generation from templates. This feature excels at producing personalized documents like mass letters or reports by merging template fields with external data sources like databases.
FAQs
Q1: Can I convert the generated Word document to PDF?
A: Yes, Spire.Doc for Java supports converting documents to PDF and other formats. Simply use saveToFile() with FileFormat.PDF.
Q2: How can I handle complex formatting in generated documents?
A: Prepare your template with all required formatting in Word, then use placeholders or bookmarks in locations where dynamic content should appear. The formatting around these markers will be preserved.
Q3: What's the difference between mail merge and text replacement?
A: Mail merge is specifically designed for merging database-like data with documents and supports features like repeating sections for records. Text replacement is simpler but doesn't handle tabular data as elegantly.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Java without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
