
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
How to Extract Text from Image Using Python (OCR Code Examples)
2025-06-11 01:58:59 Written by Administrator
Extracting text from images using Python is a widely used technique in OCR-driven workflows such as document digitization, form recognition, and invoice processing. Many important documents still exist only as scanned images or photos, making it essential to convert visual information into machine-readable text.
With the help of powerful Python libraries, you can easily perform text extraction from image files with Python — even for multilingual documents or layout-sensitive content. In this article, you’ll learn how to use Python to extract text from an image, through practical OCR examples, useful tips, and proven methods to improve recognition accuracy.
The guide is structured as follows:
- Powerful Python Library to Extract Text from Image
- Step-by-Step: Python Code to Extract Text from Image
- Real-World Use Cases for Text Extraction from Images
- Supported Languages and Image Formats
- How to Improve OCR Accuracy (Best Practices)
- FAQ
Powerful Python Library to Extract Text from Image
Spire.OCR for Python is a powerful OCR library for Python, especially suited for applications requiring structured layout extraction and multilingual support. This Python OCR engine supports:
- Text recognition with layout and position information
- Multilingual support (English, Chinese, French, etc.)
- Supports multiple image formats including JPG, PNG, BMP, GIF, and TIFF
Setup: Install Dependencies and OCR Models
Before extracting text from images using Python, you need to install the spire.ocr library and download the OCR model files compatible with your operating system.
1. Install the Spire.OCR Python Package
Use pip to install the Spire.OCR for Python package:
pip install spire.ocr
2. Download the OCR Model Package
Download the OCR model files based on your OS:
- Windows: win-x64.zip
- Linux: linux.zip
- macOS: mac.zip
- linux_aarch: linux_aarch.zip
After downloading, extract the files and set the model path in your Python script when configuring the OCR engine.
Step-by-Step: Python Code to Extract Text from Image
In this section, we’ll walk through different ways to extract text from images using Python — starting with a simple plain-text extraction, and then moving to more advanced structured recognition.
Basic OCR Text Extraction (Image to Plain Text)
Here’s how to extract plain text from an image using Python:
from spire.ocr import *
# Create OCR scanner instance
scanner = OcrScanner()
# Configure OCR model path and language
configureOptions = ConfigureOptions()
configureOptions.ModelPath = r'D:\OCR\win-x64'
configureOptions.Language = 'English'
scanner.ConfigureDependencies(configureOptions)
# Perform OCR on the image
scanner.Scan(r'Sample.png')
# Save extracted text to file
text = scanner.Text.ToString()
with open('output.txt', 'a', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write(text + '\n')
Optional: Clean and Preprocess Extracted Text (Post-OCR)
After OCR, the output may contain empty lines or noise. This snippet shows how to clean the text:
# Clean extracted text: remove empty or short lines
clean_lines = [line.strip() for line in text.split('\n') if len(line.strip()) > 2]
cleaned_text = '\n'.join(clean_lines)
# Save to a clean version
with open('output_clean.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write(cleaned_text)
Use Case: Useful for post-processing OCR output before feeding into NLP tasks or database storage.
Here’s an example of plain-text OCR output using Spire.OCR:
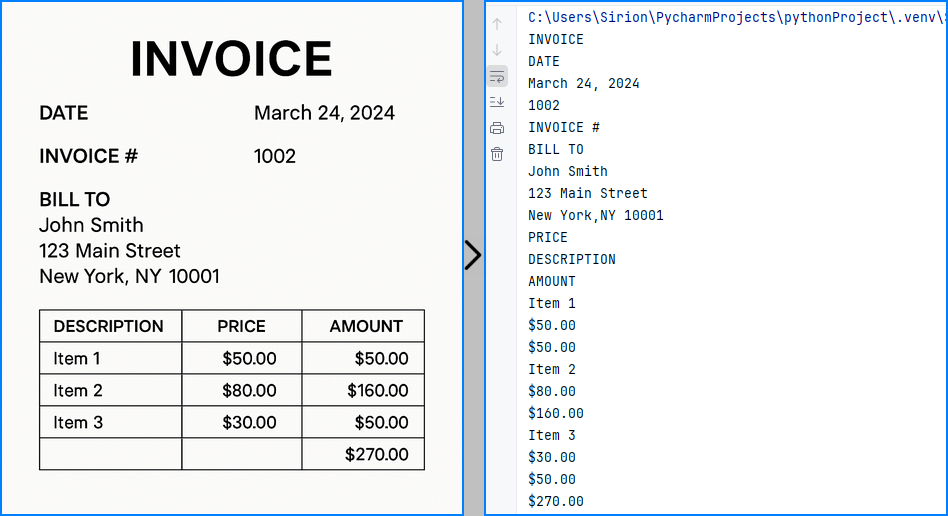
Extract Text from Image with Coordinates
In forms or invoices, you may need both text content and layout. The code below outputs each block’s bounding box info:
from spire.ocr import *
scanner = OcrScanner()
configureOptions = ConfigureOptions()
configureOptions.ModelPath = r'D:\OCR\win-x64'
configureOptions.Language = 'English'
scanner.ConfigureDependencies(configureOptions)
scanner.Scan(r'sample.png')
text = scanner.Text
# Extract block-level text with position
block_text = ""
for block in text.Blocks:
rectangle = block.Box
block_info = f'{block.Text} -> x: {rectangle.X}, y: {rectangle.Y}, w: {rectangle.Width}, h: {rectangle.Height}'
block_text += block_info + '\n'
with open('output.txt', 'a', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write(block_text + '\n')
Extract Text from Multiple Images in a Folder
You can also batch process a folder of images:
import os
from spire.ocr import *
def extract_text_from_folder(folder_path, model_path):
scanner = OcrScanner()
config = ConfigureOptions()
config.ModelPath = model_path
config.Language = 'English'
scanner.ConfigureDependencies(config)
for filename in os.listdir(folder_path):
if filename.lower().endswith(('.png', '.jpg', '.jpeg')):
image_path = os.path.join(folder_path, filename)
scanner.Scan(image_path)
text = scanner.Text.ToString()
# Save each result as a separate file
output_file = os.path.splitext(filename)[0] + '_output.txt'
with open(output_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(text)
# Example usage
extract_text_from_folder(r'D:\images', r'D:\OCR\win-x64')
The recognized text blocks with position information are shown below:

Real-World Use Cases for Text Extraction from Images
Python-based OCR can be applied in:
- ✅ Invoice and receipt scanning
- ✅ Identity document OCR (passport, license)
- ✅ Business card digitization
- ✅ Form and survey data extraction
- ✅ Multilingual document indexing
Tip: For text extraction from PDF documents instead of images, you might also want to explore this tutorial on extracting text from PDF using Python.
Supported Languages and Image Formats
Spire.OCR supports multiple languages and a wide range of image formats for broader application scenarios.
Supported Languages:
- English
- Simplified / Traditional Chinese
- French
- German
- Japanese
- Korean
You can set the language using configureOptions.Language.
Supported Image Formats:
- JPG / JPEG
- PNG
- BMP
- GIF
- TIFF
How to Improve OCR Accuracy (Best Practices)
For better OCR text extraction from images using Python, follow these tips:
- Use high-resolution images (≥300 DPI)
- Preprocess with grayscale, thresholding, or denoising
- Avoid skewed or noisy scans
- Match the OCR language with the image content
FAQ
How to extract text from an image in Python code?
To extract text from an image using Python, you can use an OCR library like Spire.OCR for Python. With just a few lines of Python code, you can recognize text in scanned documents or photos and convert it into editable, searchable content.
What is the best Python library to extract text from image?
Spire.OCR for Python is a powerful Python OCR library that offers high-accuracy recognition, multilingual support, and layout-aware output. It also works seamlessly with Spire.Office components, allowing full automation — such as saving extracted text to Excel, Word, or searchable PDFs. You can also explore open-source tools to build your Python text extraction from image projects, depending on your specific needs and preferences.
How to extract data (including position) from image in Python?
When performing text extraction from image using Python, Spire.OCR provides not just the recognized text, but also bounding box coordinates for each block — ideal for processing structured content like tables, forms, or receipts.
How to extract text using Python from scanned PDF files?
To perform text extraction from scanned PDF files using Python, you can first convert each PDF page into an image, then apply OCR using Spire.OCR for Python. For this, we recommend using Spire.PDF for Python — it allows you to save PDF pages as images or directly extract embedded images from scanned PDFs, making it easy to integrate with your OCR pipeline.
Conclusion: Efficient Text Extraction from Images with Python
Thanks to powerful libraries like Spire.OCR, text extraction from images in Python is both fast and reliable. Whether you're processing receipts or building an intelligent OCR pipeline, this approach gives you precise control over both content and layout.
If you want to remove usage limitations of Spire.OCR for Python, you can apply for a free temporary license.
How to Read PDF Files in Python – Text, Tables, Images, and More
2025-06-06 08:07:20 Written by zaki zou
Reading PDF files using Python is essential for tasks like document automation, content analysis, and data scraping. Whether you're working with contracts, reports, invoices, or scientific papers, being able to programmatically access PDF content saves time and enables powerful workflows.
To reliably read PDF content in Python — including text, tables, images, and metadata — you need a reliable Python PDF reader. In this guide, we’ll show you how to read PDFs in Python using Spire.PDF for Python, a professional and easy-to-use library that supports full-featured PDF reading without relying on any third-party tools.
Here's what's covered:
- Preparing Your Environment
- Load a PDF File in Python
- Read Text from PDF Pages in Python
- Read Table Data from PDFs in Python
- Read Images from PDFs in Python
- Read PDF Metadata (Title, Author, etc.)
- Common Questions on Reading PDFs
Environment Setup for Reading PDFs in Python
Spire.PDF for Python is a powerful Python PDF reader that allows users to read PDF content with simple Python code, including text, tables, images, and metadata. It offers a developer-friendly interface and supports a wide range of PDF reading operations:
- Read PDF files from disk or memory
- Access text, tables, metadata, and images
- No need for third-party tools
- High accuracy for structured data reading
- Free version available
It’s suitable for developers who want to read and process PDFs with minimal setup.
You can install Spire.PDF for Python via pip:
pip install spire.pdf
Or the free version Free Spire.PDF for Python for small tasks:
pip install spire.pdf.free
Load a PDF File in Python
Before accessing content, the first step is to load the PDF into memory. Spire.PDF lets you read PDF files from a path on disk or directly from in-memory byte streams — ideal for reading from web uploads or APIs.
Read PDF from File Path
To begin reading a PDF in Python, load the file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile(). This creates a document object you can use to access content.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
Read PDF from Bytes (In-Memory)
To read a PDF file from memory without saving it to disk, you can first load its byte content and then initialize a PdfDocument using a Stream object. This method is especially useful when handling PDF files received from web uploads, APIs, or temporary in-memory data.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, Stream
# Read the PDF file to a byte array
with open("sample.pdf", "rb") as f:
byte_data = f.read()
# Create a stream using the byte array
pdfStream = Stream(byte_data)
# Create a PdfDocument using the stream
pdf = PdfDocument(pdfStream)
To go further, check out this guide: Loading and Saving PDFs via Byte Streams in Python
Read Text from PDF Pages in Python
Reading text from a PDF file is one of the most common use cases in document automation. With Spire.PDF, you can easily retrieve all visible text from the entire PDF or from individual pages using simple methods.
Read All Text from PDF
To extract all text from a PDF, loop through each page and call PdfTextExtractor.ExtractText() to collect visible text content.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTextExtractor, PdfTextExtractOptions
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
all_text = ""
# Loop through each page
for pageIndex in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(pageIndex)
# Create a PdfTextExtract instance
text_extractor = PdfTextExtractor(page)
# Configure extracting options
options = PdfTextExtractOptions()
options.IsExtractAllText = True
options.IsSimpleExtraction = True
# Extract text from the current page
all_text += text_extractor.ExtractText(options)
print(all_text)
Sample text content retrieved:

Read Text from Specific Area of a Page
You can also read text from a defined region of a page using a bounding box. This is useful when only a portion of the layout contains relevant information.
from spire.pdf import RectangleF, PdfDocument, PdfTextExtractor, PdfTextExtractOptions
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create a PdfTextExtractor instance
textExtractor = PdfTextExtractor(page)
# Set the area to extract text by configuring the PdfTextExtractOptions
options = PdfTextExtractOptions()
area = RectangleF.FromLTRB(0, 200, page.Size.Width, 270) # x, y, width, height
options.ExtractArea = area
options.IsSimpleExtraction = True
# Extract text from the area
text = textExtractor.ExtractText(options)
print(text)
The text read from the PDF page area:
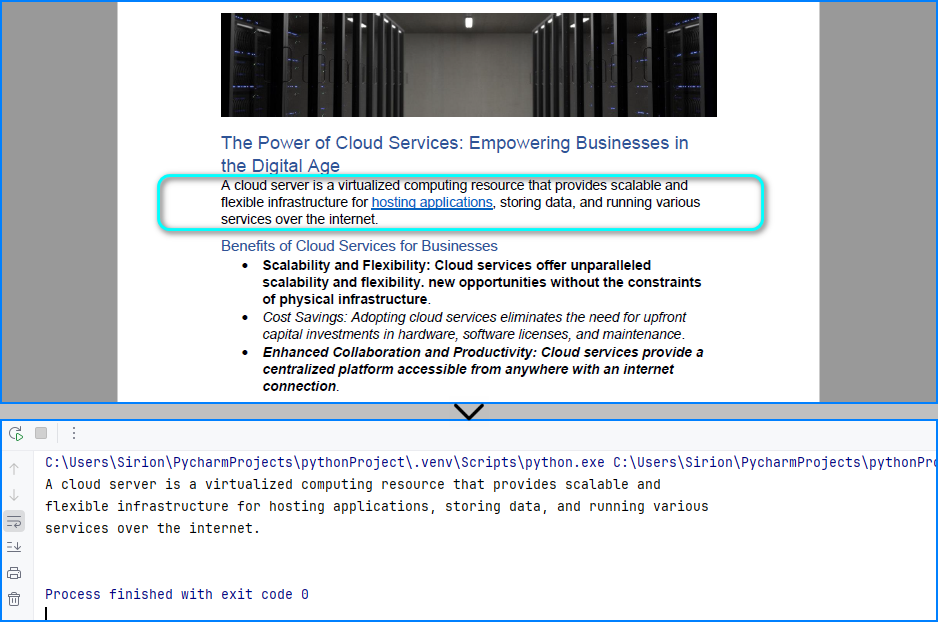
Read Table Data from PDFs in Python
PDF tables are often used in reports, invoices, and statements. With Spire.PDF, you can read PDF tables in Python by extracting structured tabular content using its layout-aware table extractor, making it ideal for financial and business documents. Use PdfTableExtractor.ExtractTable() to detect tables page by page and output each row and cell as structured text.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTableExtractor
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
# Create a PdfTableExtractor instance
table_extractor = PdfTableExtractor(pdf)
# Extract the table from the first page
tables = table_extractor.ExtractTable(0)
for table in tables:
# Get the number of rows and columns
row_count = table.GetRowCount()
column_count = table.GetColumnCount()
# Iterate all rows
for i in range(row_count):
table_row = []
# Iterate all columns
for j in range(column_count):
# Get the cell
cell_text = table.GetText(i, j)
table_row.append(cell_text)
print(table_row)
Table content extracted using the code above:
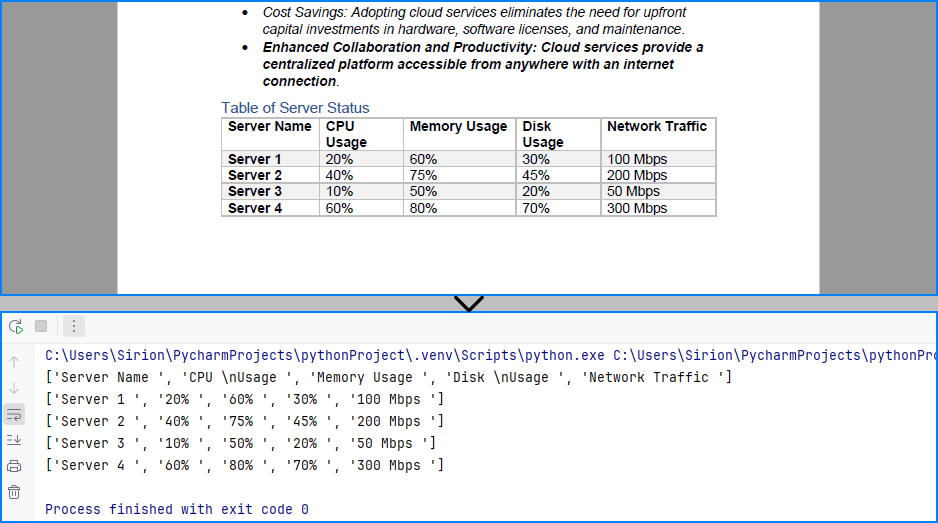
Want to extract text from scanned PDFs using OCR? Read this guide on OCR with Python
Read Images from PDF in Python
PDF files often contain logos, scanned pages, or embedded images. Spire.PDF allows you to read and export these images, which is helpful for working with digitized documents or preserving visual content. Use PdfImageHelper.GetImagesInfo() on each page to retrieve and save all embedded images.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfImageHelper
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create a PdfImageHelper object
image_helper = PdfImageHelper()
# Get the image information from the page
images_info = image_helper.GetImagesInfo(page)
# Save the images from the page as image files
for i in range(len(images_info)):
images_info[i].Image.Save("output/Images/image" + str(i) + ".png")
The image read from the PDF file:
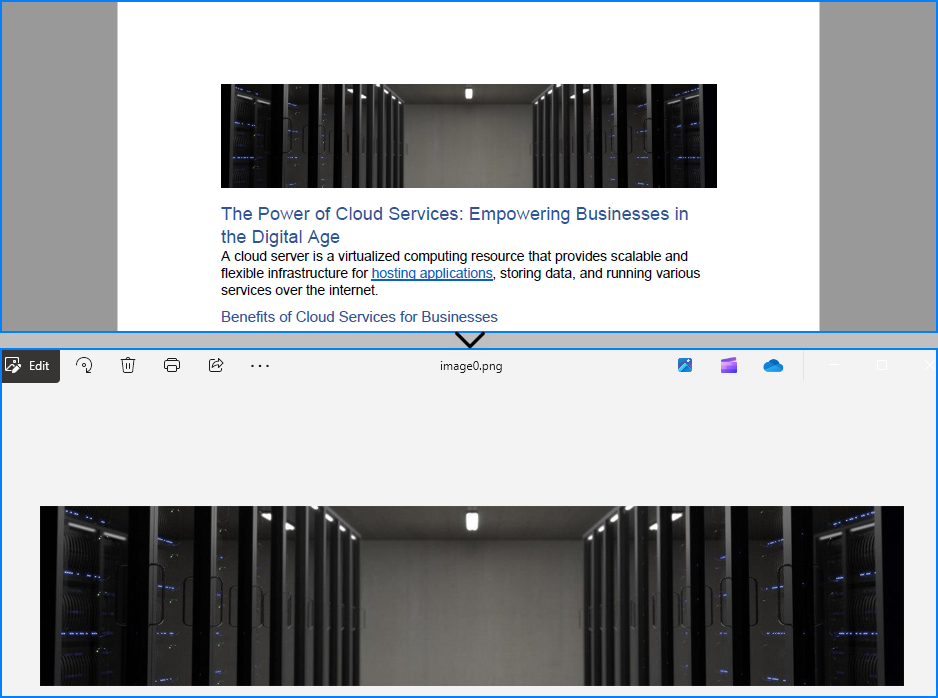
Read PDF Metadata (Title, Author, etc.)
Sometimes you may want to access document metadata like author, subject, and title. This can be helpful for indexing or organizing files. Use the ocumentInformation property to read metadata fields.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
# Get the document properties
properties = pdf.DocumentInformation
print("Title: " + properties.Title)
print("Author: " + properties.Author)
print("Subject: " + properties.Subject)
print("Keywords: " + properties.Keywords)
The metadata read from the PDF document:

Common Questions on Reading PDFs
Can Python parse a PDF file?
Yes. Libraries like Spire.PDF for Python allow you to read PDF text, extract tables, and access embedded images or metadata. It supports methods like PdfTextExtractor.ExtractText() and PdfTableExtractor.ExtractTable() for structured content parsing.
How do I read a PDF in Jupyter?
Spire.PDF works seamlessly in Jupyter Notebooks. Just install it via pip and use its API to read PDF files, extract text, or parse tables and images directly in your notebook environment.
How to read text from a PDF file?
Use the PdfTextExtractor.ExtractText() method on each page after loading the PDF with Spire.PDF. This lets you read PDF file to text in Python and retrieve visible content for processing or analysis.
Can I read a PDF file without saving it to disk?
Yes. You can use LoadFromStream() to read PDF content as bytes and load it directly from memory. This is useful for processing PDFs received from web APIs or file uploads.
Conclusion
With Spire.PDF for Python, you can easily read a PDF in Python — including reading PDF text, tables, images, and metadata — and even read a PDF file to text for further processing or automation. This makes it an ideal solution for document automation, data ingestion, and content parsing in Python.
Need to process large PDF files or unlock all features? Request a free license and take full advantage of Spire.PDF for Python today!
How to Convert CSV to Excel (XLSX) in Python – Single & Batch Guide
2025-06-06 08:04:25 Written by zaki zouWhile working with CSV files is common in data processing, Excel (XLSX) often provides more advantages when it comes to data sharing, visualization, and large-scale analysis. In this guide, you’ll learn how to convert CSV to Excel in Python, including both single file and batch conversion methods. Whether you're automating reports or preparing data for further analysis, this guide will help you handle the conversion efficiently.

- Why Convert CSV to Excel
- Install Required Python Libraries
- Convert Single CSV to Excel
- Batch Convert CSV to XLSX
- FAQs
Why Convert CSV to Excel?
While CSV files are widely used for data storage and exchange due to their simplicity, they come with several limitations—especially when it comes to formatting, presentation, and usability. Converting CSV to Excel can bring several advantages:
Benefits of Converting CSV to Excel
- Better formatting support: Excel allows rich formatting options like fonts, colors, borders, and cell merging, making your data easier to read and present.
- Multiple worksheets: Unlike CSV files that support only a single sheet, Excel files can store multiple worksheets in one file, which is better for large datasets.
- Built-in formulas and charts: You can apply Excel formulas, pivot tables, and charts to analyze and visualize your data.
- Improved compatibility for business users: Excel is the preferred tool for many non-technical users, making it easier to share and collaborate on data.
Limitations of CSV Files
- No styling or formatting (plain text only)
- Single-sheet structure only
- Encoding issues (e.g., with non-English characters)
- Not ideal for large datasets or advanced reporting If your workflow involves reporting, data analysis, or sharing data with others, converting CSV to Excel is often a more practical and flexible choice.
Install Required Python Libraries
This guide demonstrates how to effortlessly convert CSV to Excel using Spire.XLS for Python. Spire.XLS is a powerful and professional Python Excel library that allows you to read, edit, and convert Excel files (both .xlsx and .xls) without relying on Microsoft Excel. Installing this CSV to Excel converter on your device is simple — just run the following command:
pip install Spire.XLS
Alternatively, you can download the Spire.XLS package manually for custom installation.
How to Convert CSV to Excel in Python: Single File
Now let’s get to the main part — how to convert a single CSV file to Excel using Python. With the help of Spire.XLS, this task becomes incredibly simple. All it takes is three easy steps: create a new workbook, load the CSV file, and save it as an Excel (.xlsx) file. Below is a detailed walkthrough along with a complete code example — let’s take a look!
Steps to convert a single CSV to Excel in Python:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample CSV file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the CSV file as Excel through Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
Below is the Python code to convert a CSV file to Excel. It also ignores parsing errors and automatically adjusts the column widths for better readability.
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Load a csv file
workbook.LoadFromFile("/sample csv.csv", ",", 1, 1)
# Set ignore error options
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
sheet.Range["D2:E19"].IgnoreErrorOptions = IgnoreErrorType.NumberAsText
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns()
# Save the document and launch it
workbook.SaveToFile("/CSVToExcel1.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
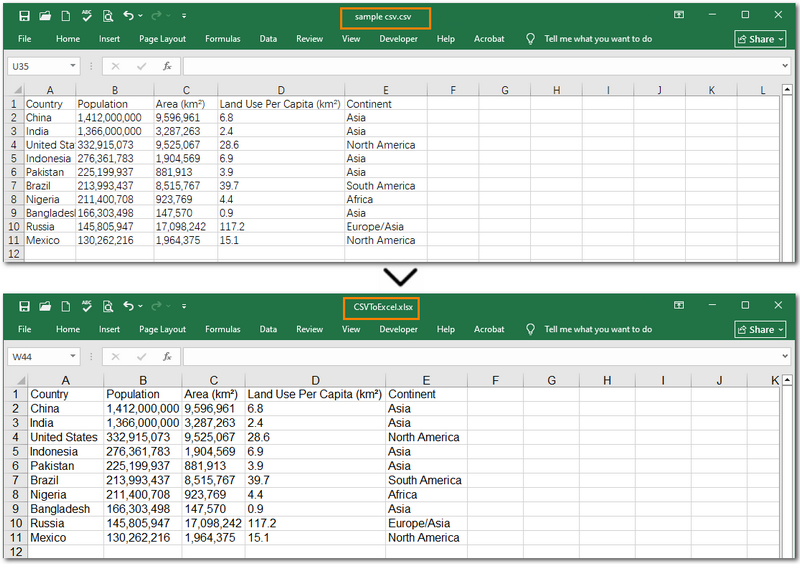
Warm Note: If you're only working with small files or doing some light testing, you can also use the free Spire.XLS. It's a great option for getting started quickly.
How to Batch Convert CSV to XLSX in Python
Another common scenario is when you need to convert multiple CSV files to Excel. Instead of manually replacing the file path and name for each one, there's a much more efficient approach. Simply place all the CSV files in the same folder, then use Python to loop through each file and convert them to Excel using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method. Let’s walk through the detailed steps below!
Steps to batch convert CSVs to Excel files in Python:
- Specify the file paths of input and output folders.
- Loop through all CSV files in the input folder.
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Load each CSV file from the input folder with Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the current CSV as an Excel file through Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
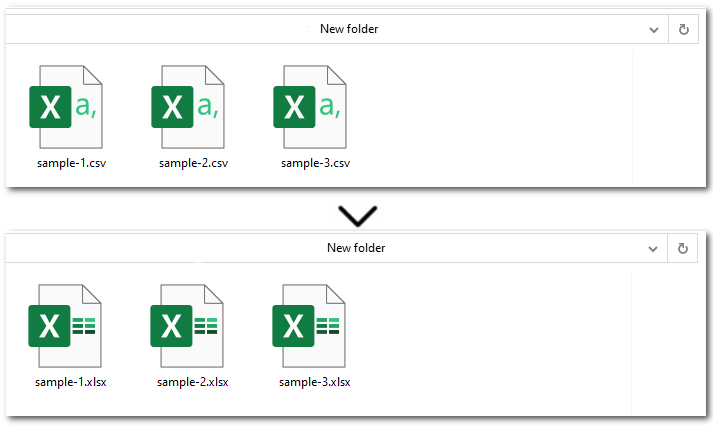
Here's the Python code to batch convert CSV to Excel (.XLSX):
import os
from spire.xls import *
input_folder = r"E:input\New folder"
output_folder = r"output\New folder"
# Loop through each CSV file
for csv_file in os.listdir(input_folder):
if csv_file.endswith(".csv"):
input_path = os.path.join(input_folder, csv_file)
output_name = os.path.splitext(csv_file)[0] + ".xlsx"
output_path = os.path.join(output_folder, output_name)
# Create a Workbook instance and load CSV files
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile(input_path, ",", 1, 1)
# Save each CSV file as an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile(output_path, ExcelVersion.Version2013)
The Conclusion
This guide showed you how to convert CSV to Excel in Python with step-by-step instructions and complete code examples. Whether you're working with a single CSV file or multiple files, Spire.XLS makes the process simple, fast, and hassle-free. Need help with more advanced scenarios or other Excel-related tasks? Feel free to contact us anytime!
FAQs about Converting CSV to Excel
Q1: How to convert CSV to Excel in Python without pandas?
A: You can use libraries like Spire.XLS, openpyxl, or xlsxwriter to convert CSV files without relying on pandas. These tools provide simple APIs to load .csv files and export them as xlsx—no Microsoft Excel installation required.
Q2: What is the easiest way to convert multiple CSV files to Excel in Python?
A: Just place all CSV files in one folder, then loop through them in Python and convert each using Workbook.SaveToFile(). This approach is ideal for batch processing. Alternatively, online converters can be a quick fix for occasional use.
Q3: How to auto-adjust column width when converting CSV to Excel in Python?
A: After loading the CSV, call worksheet.autoFitColumns() in Spire.XLS to automatically resize columns based on content before saving the Excel file.
