
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
How to Adjust the Spaces between Bars in Excel Chart in C#, VB.NET
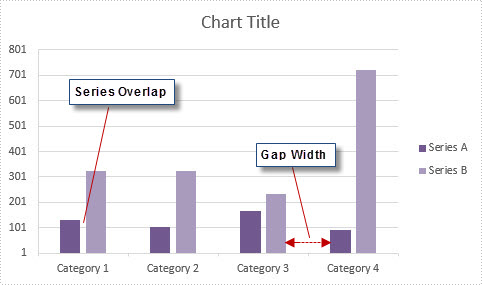
2015-12-30 07:34:49 Written by KoohjiIn MS Excel, the spaces between data bars have been defined as Series Overlap and Gap Width.
- Series Overlap: Spaces between data series within a single category.
- Gap Width: Spaces between two categories.
Check below picture, you'll have a better understanding of these two concepts. Normally the spaces are automatically calculated based on the date and chart area, the space may be very narrow or wide depending on how many date series you have in a fixed chart area. In this article, we'll introduce how to adjust the spaces between data bars using Spire.XLS.
Code Snippet:
Step 1: Initialize a new instance of Wordbook class and load the sample Excel file that contains some data in A1 to C5.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("sample.xlsx");
Step 2: Create a Column chart based on the data in cell range A1 to C5.
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]; Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered); chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:C5"]; chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false; chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MajorGridLines.LineProperties.Color = Color.LightGray;
Step 3: Set chart position.
chart.LeftColumn = 5; chart.TopRow = 7; chart.RightColumn = 13; chart.BottomRow = 21;
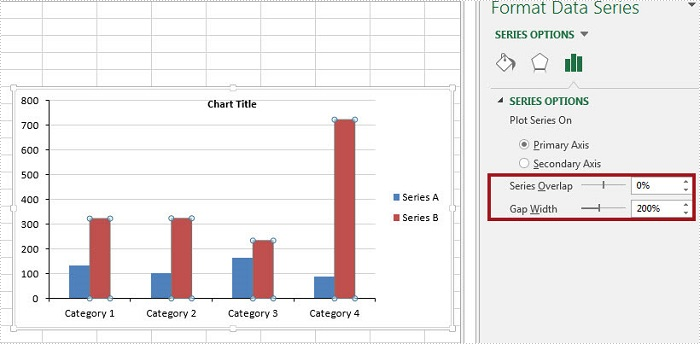
Step 4: The ChartSerieDataFormat class has two properties - GapWidth property and Overlap property to handle the Gap Width and Series Overlap respectively. The value of GapWidth varies from 0 to 500, and the value of Overlap varies from -100 to 100.
foreach (ChartSerie cs in chart.Series)
{
cs.Format.Options.GapWidth = 200;
cs.Format.Options.Overlap = 0;
}
Step 5: Save and launch the file.
workbook.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.xlsx");
Output:
Full Code:
using Spire.Xls;
using Spire.Xls.Charts;
namespace AdjustSpaces
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("data.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered);
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:C5"];
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MajorGridLines.LineProperties.Color = Color.LightGray;
chart.LeftColumn = 5;
chart.TopRow = 7;
chart.RightColumn = 13;
chart.BottomRow = 21;
foreach (ChartSerie cs in chart.Series)
{
cs.Format.Options.GapWidth = 200;
cs.Format.Options.Overlap = 0;
}
workbook.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.xlsx");
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Xls
Imports Spire.Xls.Charts
Namespace AdjustSpaces
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
Dim workbook As New Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("data.xlsx")
Dim sheet As Worksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
Dim chart As Chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered)
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range("A1:C5")
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MajorGridLines.LineProperties.Color = Color.LightGray
chart.LeftColumn = 5
chart.TopRow = 7
chart.RightColumn = 13
chart.BottomRow = 21
For Each cs As ChartSerie In chart.Series
cs.Format.Options.GapWidth = 200
cs.Format.Options.Overlap = 0
Next
workbook.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010)
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.xlsx")
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
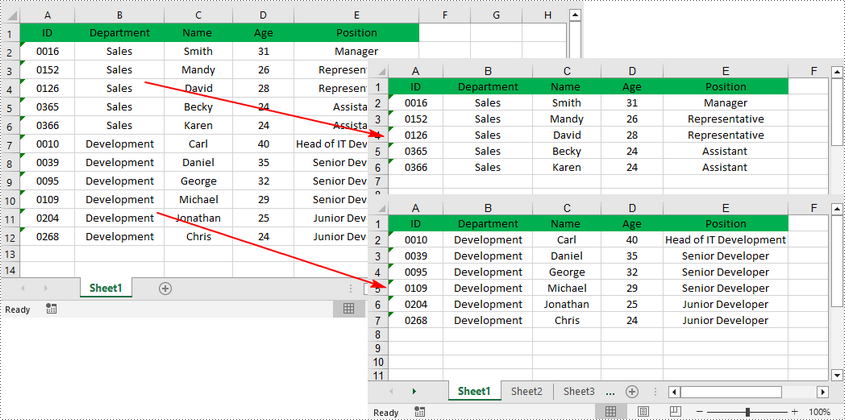
When dealing with an Excel worksheet containing a large amount of data, splitting it into several separate Excel files based on specific criteria can be beneficial. By dividing the worksheet into smaller, more manageable files, you can improve your work efficiency and make data analysis easier. This article will demonstrate how to programmatically split an Excel worksheet into multiple Excel files using Spire.XLS for .NET.
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Split an Excel Sheet into Multiple Files in C# and VB.NET
The Worksheet.Copy(CellRange sourceRange, CellRange destRange) method provided by Spire.XLS for .NET allows you to split a worksheet by copying a specified cell range from the original Excel file to a new Excel file. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Get the header row and the specified cell ranges using Worksheet.Range property.
- Create a new workbook and get its first worksheet.
- Copy the header row and specified cell range to the first worksheet of the new workbook using Worksheet.Copy(CellRange sourceRange, CellRange destRange) method.
- Copy the column width from the original workbook to the new workbook, and then save the new workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Create another new workbook, and then repeat the above steps to copy the header row and specified cell range into the new workbook.
- Save the new workbook to another Excel file.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
namespace splitworksheet
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook originalBook= new Workbook();
//Load the original Excel document from file
originalBook.LoadFromFile("Info.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = originalBook.Worksheets[0];
//Get the header row
CellRange headerRow = sheet.Range[1, 1, 1,5];
//Get two cell ranges
CellRange range1 = sheet.Range[2, 1, 6, sheet.LastColumn];
CellRange range2 = sheet.Range[7, 1, sheet.LastRow, sheet.LastColumn];
//Create a new workbook
Workbook newBook1 = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet of new workbook
Worksheet newSheet1 = newBook1.Worksheets[0];
//Copy the header row and range 1 to the first worksheet of the new workbook
sheet.Copy(headerRow, newSheet1.Range[1, 1]);
sheet.Copy(range1, newSheet1.Range[2, 1]);
//Copy the column width from the original workbook to the new workbook
for (int i = 0; (i < sheet.LastColumn); i++)
{
newBook1.Worksheets[0].SetColumnWidth(i + 1, sheet.GetColumnWidth(i + 1));
}
//Save the new workbook to an Excel file
newBook1.SaveToFile("Sales Depart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
//Create another new workbook
Workbook newBook2 = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet of new workbook
Worksheet newSheet2 = newBook2.Worksheets[0];
//Copy the header row and range 2 to the first worksheet of the new workbook
sheet.Copy(headerRow, newSheet2.Range[1, 1]);
sheet.Copy(range2, newSheet2.Range[2, 1]);
//Copy the column width from the original workbook to the new workbook
for (int i = 0; (i < sheet.LastColumn); i++)
{
newBook2.Worksheets[0].SetColumnWidth(i + 1, sheet.GetColumnWidth(i + 1));
}
//Save the new workbook to another Excel file
newBook2.SaveToFile("Development Depart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Gridlines are often added to charts to help improve the readability of the chart itself, but it is not a necessary to display the gridlines in every chart especially when we do not need to know the exact value of each data point from graphic. This article will present how to hide gridlines in Excel chart using Spire.XLS.
Code Snippet:
Step 1: Initialize a new instance of Workbook class and load a sample Excel file that contains some data in A1 to C5.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("data.xlsx");
Step 2: Create a Column chart based on the data in cell range A1 to C5.
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]; Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered); chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:C5"]; chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false;
Step 3: Set chart position.
chart.LeftColumn = 1; chart.TopRow = 6; chart.RightColumn = 8 chart.BottomRow = 19;
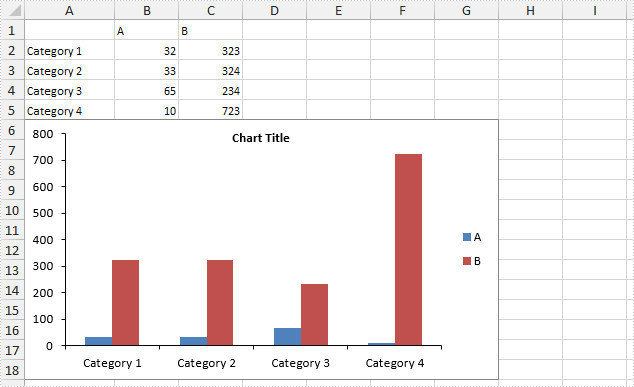
Step 4: Set the PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines property to false.
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = false;
Step 5: Save and launch the file.
workbook.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.xlsx");
Output:
Full Code:
using Spire.Xls;
namespace HideGridLine
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("data.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
Chart chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered);
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:C5"];
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = false;
chart.LeftColumn = 1;
chart.TopRow = 6;
chart.RightColumn = 8;
chart.BottomRow = 19;
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = false;
workbook.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010);
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.xlsx");
}
}
}
Imports Spire.Xls
Namespace HideGridLine
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(args As String())
Dim workbook As New Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("data.xlsx")
Dim sheet As Worksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
Dim chart As Chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered)
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range("A1:C5")
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
chart.LeftColumn = 1
chart.TopRow = 6
chart.RightColumn = 8
chart.BottomRow = 19
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = False
workbook.SaveToFile("result.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2010)
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("result.xlsx")
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
