
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Knowing how to remove headers or footers in Word is an essential skill as there may be times you need to change the formatting of your document or collaborate with others who do not need the headers or footers. In this article, you will learn how to remove headers or footers in Word in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Remove Headers in a Word Document in Python
Spire.Doc for Python supports getting different headers in the first pages, odd pages, and even pages, and then delete all of them through the HeaderFooter.ChildObjects.Clear() method. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Iterate through all paragraphs in the section, and then all child objects in each paragraph.
- Get the headers for the first, odd, and even pages using Section.HeadersFooters[hfType: HeaderFooterType] property, and then delete them using HeaderFooter.ChildObjects.Clear() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
inputFile = "HeaderFooter.docx"
outputFile = "RemoveHeaders.docx"
# Create a Document instance
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get the first section
section = doc.Sections[0]
# Iterate through all paragraphs in the section
for i in range(section.Paragraphs.Count):
para = section.Paragraphs.get_Item(i)
# Iterate through all child objects in each paragraph
for j in range(para.ChildObjects.Count):
obj = para.ChildObjects.get_Item(j)
# Delete header in the first page
header = None
header = section.HeadersFooters[HeaderFooterType.HeaderFirstPage]
if header is not None:
header.ChildObjects.Clear()
# Delete headers in the odd pages
header = section.HeadersFooters[HeaderFooterType.HeaderOdd]
if header is not None:
header.ChildObjects.Clear()
# Delete headers in the even pages
header = section.HeadersFooters[HeaderFooterType.HeaderEven]
if header is not None:
header.ChildObjects.Clear()
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
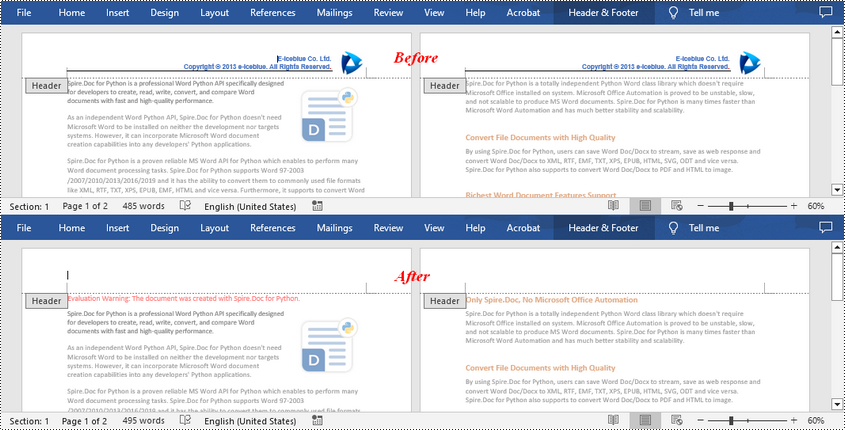
Remove Footers in a Word Document in Python
Deleting footers is similar to that of deleting headers, you can also get the footers on different pages first and then delete them at once. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Iterate through all paragraphs in the section, and then all child objects in each paragraph.
- Get the footers for the first, odd, and even pages using Section.HeadersFooters[hfType: HeaderFooterType] property, and then delete them using HeaderFooter.ChildObjects.Clear() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
inputFile = "HeaderFooter.docx"
outputFile = "RemoveFooters.docx"
# Create a Document instance
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get the first section
section = doc.Sections[0]
# Iterate through all paragraphs in the section
for i in range(section.Paragraphs.Count):
para = section.Paragraphs.get_Item(i)
# Iterate through all child objects in each paragraph
for j in range(para.ChildObjects.Count):
obj = para.ChildObjects.get_Item(j)
# Delete footer in the first page
footer = None
footer = section.HeadersFooters[HeaderFooterType.FooterFirstPage]
if footer is not None:
footer.ChildObjects.Clear()
# Delete footers in the odd pages
footer = section.HeadersFooters[HeaderFooterType.FooterOdd]
if footer is not None:
footer.ChildObjects.Clear()
# Delete footers in the even pages
footer = section.HeadersFooters[HeaderFooterType.FooterEven]
if footer is not None:
footer.ChildObjects.Clear()
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
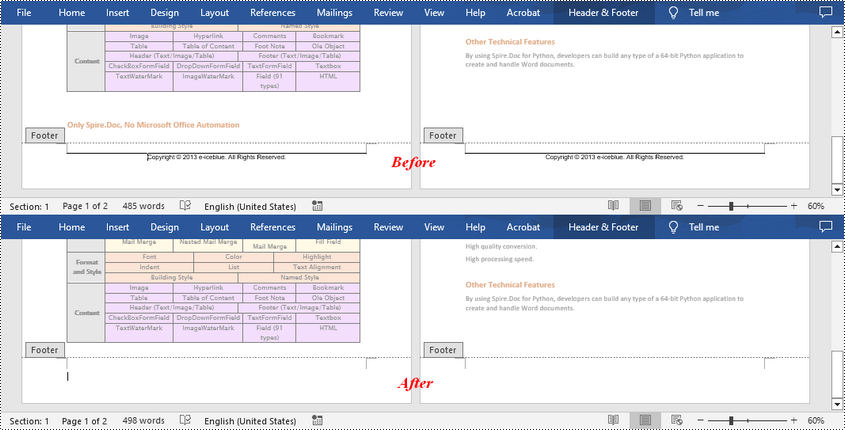
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Comments in Word documents are often used for collaborative review and feedback purposes. They may contain text and images that provide valuable information to guide document improvements. Extracting the text and images from comments allows you to analyze and evaluate the feedback provided by reviewers, helping you gain a comprehensive understanding of the strengths, weaknesses, and suggestions related to the document. In this article, we will demonstrate how to extract text and images from Word comments in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Extract Text from Word Comments in Python
You can easily retrieve the author and text of a Word comment using the Comment.Format.Author and Comment.Body.Paragraphs[index].Text properties provided by Spire.Doc for Python. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a list to store the extracted comment data.
- Iterate through the comments in the document.
- For each comment, iterate through the paragraphs of the comment body.
- For each paragraph, get the text using the Comment.Body.Paragraphs[index].Text property.
- Get the author of the comment using the Comment.Format.Author property.
- Add the text and author of the comment to the list.
- Save the content of the list to a text file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of the Document class
document = Document()
# Load a Word document containing comments
document.LoadFromFile("Comments.docx")
# Create a list to store the extracted comment data
comments = []
# Iterate through the comments in the document
for i in range(document.Comments.Count):
comment = document.Comments[i]
comment_text = ""
# Iterate through the paragraphs in the comment body
for j in range(comment.Body.Paragraphs.Count):
paragraph = comment.Body.Paragraphs[j]
comment_text += paragraph.Text + "\n"
# Get the comment author
comment_author = comment.Format.Author
# Append the comment data to the list
comments.append({
"author": comment_author,
"text": comment_text
})
# Write the comment data to a file
with open("comment_data.txt", "w", encoding="utf-8") as file:
for comment in comments:
file.write(f"Author: {comment['author']}\nText: {comment['text']}\n\n")
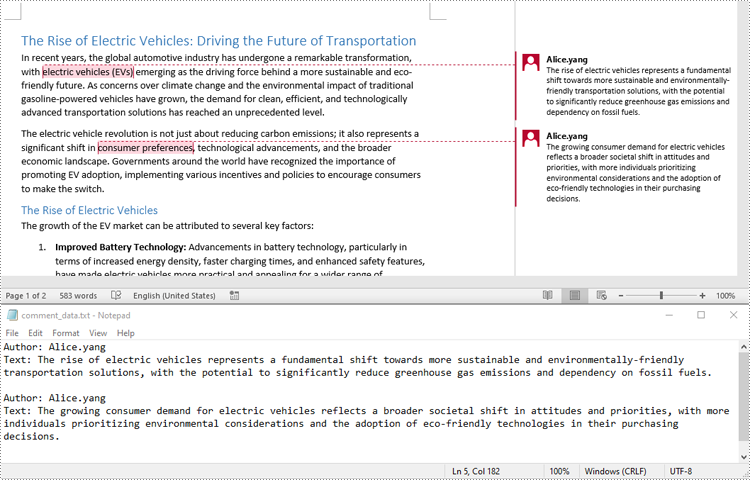
Extract Images from Word Comments in Python
To extract images from Word comments, you need to iterate through the child objects in the paragraphs of the comments to find the DocPicture objects, then get the image data using DocPicture.ImageBytes property, finally save the image data to image files.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a list to store the extracted image data.
- Iterate through the comments in the document.
- For each comment, iterate through the paragraphs of the comment body.
- For each paragraph, iterate through the child objects of the paragraph.
- Check if the object is a DocPicture object.
- If the object is a DocPicture, get the image data using the DocPicture.ImageBytes property and add it to the list.
- Save the image data in the list to individual image files.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of the Document class
document = Document()
# Load a Word document containing comments
document.LoadFromFile("Comments.docx")
# Create a list to store the extracted image data
images = []
# Iterate through the comments in the document
for i in range(document.Comments.Count):
comment = document.Comments.get_Item(i)
# Iterate through the paragraphs in the comment body
for j in range(comment.Body.Paragraphs.Count):
paragraph = comment.Body.Paragraphs.get_Item(j)
# Iterate through the child objects in the paragraph
for o in range(paragraph.ChildObjects.Count):
obj = paragraph.ChildObjects.get_Item(o)
# Find the images
if isinstance(obj, DocPicture):
picture = obj
# Get the image data and add it to the list
data_bytes = picture.ImageBytes
images.append(data_bytes)
# Save the image data to image files
for i, image_data in enumerate(images):
file_name = f"CommentImage-{i}.png"
with open(os.path.join("CommentImages/", file_name), 'wb') as image_file:
image_file.write(image_data)
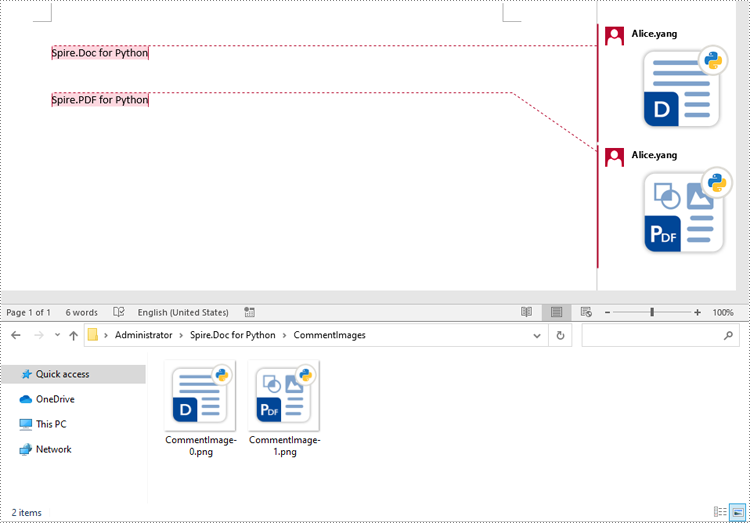
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Drop-down lists in Excel worksheets are an indispensable tool for enhancing data accuracy, efficiency, and usability in spreadsheet management. By offering pre-defined options within a cell, they not only streamline data entry processes but also enforce consistency, reducing the likelihood of input errors. This feature is particularly valuable when working with large datasets or collaborative projects where maintaining uniformity across multiple entries is crucial. This article demonstrates how to create customized drop-down lists within Excel worksheets using Spire.XLS for Python, empowering users to create organized and user-friendly worksheets.
- Create Drop-Down Lists Based on Cell Values Using Python
- Create Drop-Down Lists Based on Strings Using Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Create Drop-Down Lists Based on Cell Values Using Python
In Excel worksheets, creating drop-down lists is accomplished through the data validation feature. With Spire.XLS for Python, developers can use the CellRange.DataValidation.DataRange property to create drop-down lists within cells and use the data from the specified cell range as list options.
The detailed steps for creating a drop-down list based on cell values are as follows:
- Create an instance of Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Get a specific cell range through Worksheet.Range[] property.
- Set the data range for data validation of the cell range through CellRange.DataValidation.DataRange property to create drop-down lists with cell values.
- Save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an instance of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Get a specific cell range
cellRange = sheet.Range["C3:C7"]
# Set the data range for data validation to create drop-down lists in the cell range
cellRange.DataValidation.DataRange = sheet.Range["F4:H4"]
# Save the workbook
workbook.SaveToFile("output/DropDownListExcel.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
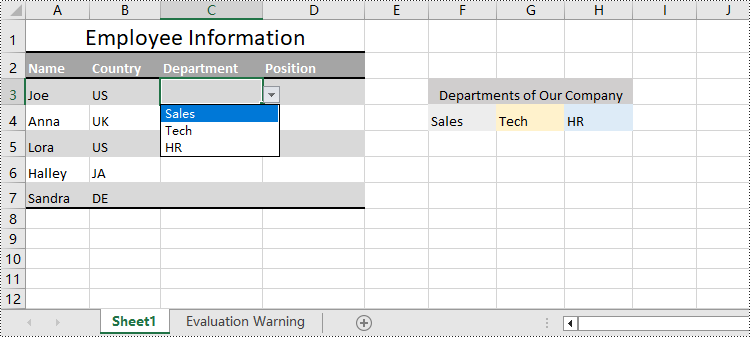
Create Drop-Down Lists Based on String Using Python
Spire.XLS for Python also provides the CellRange.DataValidation.Values property to create drop-down lists in cells directly using string lists.
The detailed steps for creating drop-down lists based on values are as follows:
- Create an instance of Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Get a specific cell range through Worksheet.Range[] property.
- Set a string list as the values of data validation in the cell range through CellRange.DataValidation.Values property to create drop-down lists based on strings.
- Save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an instance of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Get a cell range
cellRange = sheet.Range["D3:D7"]
# Set the value for data validation to create drop-down lists
cellRange.DataValidation.Values = ["Starter", "Technician", "Director", "Executive"]
# Save the workbook
workbook.SaveToFile("output/ValueDropDownListExcel.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
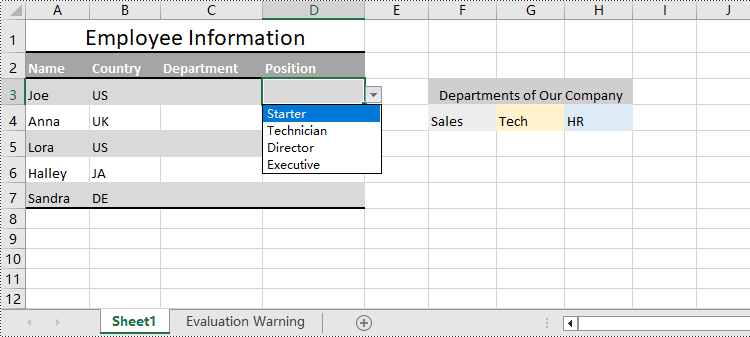
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
