
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Tables in Word documents can sometimes disrupt the flow of text or the visual balance of a page. Removing these tables can help in creating a more aesthetically pleasing document, which is crucial for reports, presentations, or publications where appearance is important. In this article, you will learn how to remove tables from a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Remove a Specified Table in Word in Python
Spire.Doc for Python provides the Section.Tables.RemoveAt(int index) method to delete a specified table in a Word document by index. The following are the detailed steps.
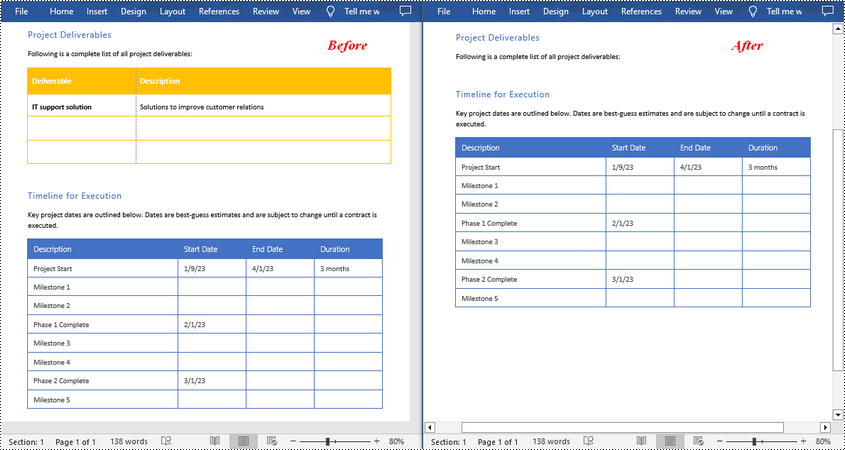
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Delete a specified table by index using Section.Tables.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import * from spire.doc.common import * inputFile = "Tables.docx" outputFile = "RemoveTable.docx" # Create a Document instance doc = Document() # Load a Word document doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get the first section in the document sec = doc.Sections[0] # Remove the first table in the section sec.Tables.RemoveAt(0) # Save the result document doc.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx) doc.Close()
Remove All Tables in Word in Python
To delete all tables from a Word document, you need to iterate through all sections in the document, then iterate through all tables in each section and remove them through the Section.Tables.Remove() method. The following are the detailed steps.
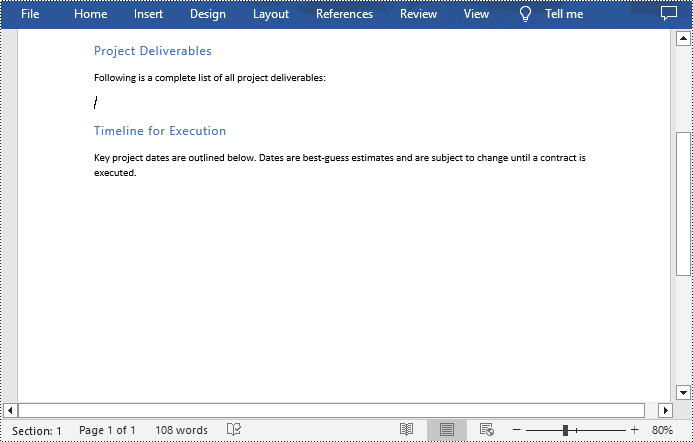
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through all sections in the document.
- Iterate through all tables in each section.
- Delete the tables using Section.Tables.Remove() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
inputFile = "Tables.docx"
outputFile = "RemoveAllTables.docx"
# Create a Document instance
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Iterate through all sections in the document
for i in range(doc.Sections.Count):
sec = doc.Sections.get_Item(i)
# Iterate through all tables in each section
for j in range(sec.Tables.Count):
table = sec.Tables.get_Item(j)
# Remove the table
sec.Tables.Remove(table)
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Markdown has become a popular choice for writing structured text due to its simplicity and readability, making it widely used for documentation, README files, and note-taking. However, sometimes there arises a need to present this content in a more universal and polished format, such as PDF, which is compatible across various devices and platforms without formatting inconsistencies. Converting Markdown files to PDF documents not only enhances portability but also adds a professional touch, enabling easier distribution for reports, manuals, or sharing content with non-technical audiences who may not be familiar with Markdown syntax.
This article will demonstrate how to convert Markdown files to PDF documents using Spire.Doc for Python to automate the conversion process.
- Convert Markdown Files to PDF Documents with Python
- Convert Markdown to PDF and Customize Page Settings
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Convert Markdown Files to PDF Documents with Python
With Spire.Doc for Python, developers can load Markdown files using Document.LoadFromFile(string: fileName, FileFormat.Markdown) method, and then save the files to PDF documents using Document.SaveToFile(string: fileName, FileFormat.PDF) method. Besides, developers can also convert Markdown files to HTML, XPS, and SVG formats by specifying enumeration items of the FileFormat enumeration class.
The detailed steps for converting a Markdown file to a PDF document are as follows:
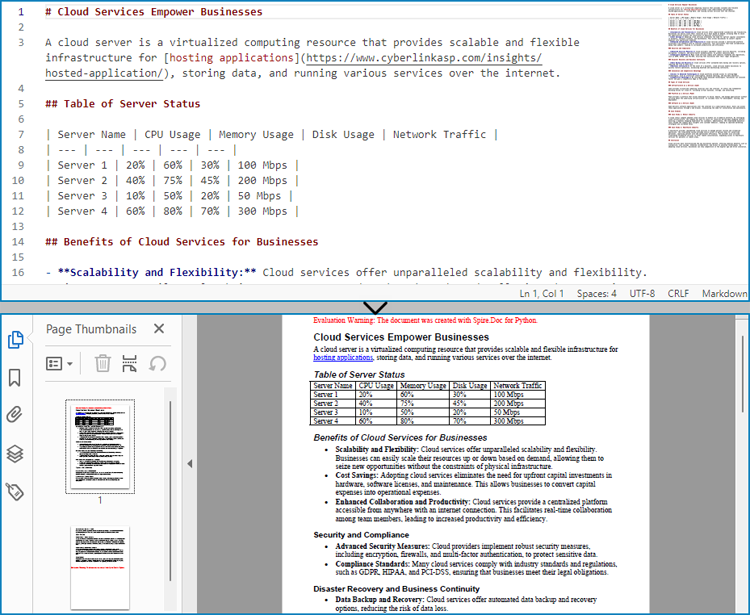
- Create an instance of Document class.
- Load a Markdown file using Document.LoadFromFile(string: fileName, FileFormat.Markdown) method.
- Convert the Markdown file to a PDF document and save it using Document.SaveToFile(string: fileName, FileFormat.PDF) method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Markdown file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.md", FileFormat.Markdown)
# Save the file to a PDF document
doc.SaveToFile("output/MarkdownToPDF.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Dispose()
Convert Markdown to PDF and Customize Page Settings
Spire.Doc for Python supports performing basic page setup before converting Markdown files to formats like PDF, allowing for control over the appearance of the converted document.
The detailed steps to convert a Markdown file to a PDF document and customize the page settings are as follows:
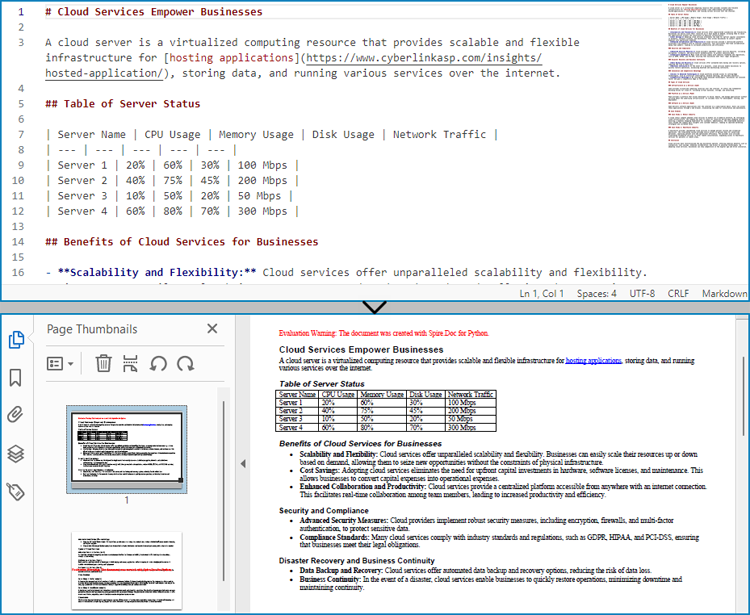
- Create an instance of Document class.
- Load a Markdown file using Document.LoadFromFile(string: fileName, FileFormat.Markdown) method.
- Get the default section using Document.Sections.get_Item() method.
- Get the page settings through Section.PageSetup property and set the page size, orientation, and margins through properties under PageSetup class.
- Convert the Markdown file to a PDF document and save it using Document.SaveToFile(string: fileName, FileFormat.PDF) method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an instance of Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.md", FileFormat.Markdown)
# Get the default section
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get the page settings
pageSetup = section.PageSetup
# Customize the page settings
pageSetup.PageSize = PageSize.A4()
pageSetup.Orientation = PageOrientation.Landscape
pageSetup.Margins.All = 50
# Save the Markdown document to a PDF file
doc.SaveToFile("output/MarkdownToPDFPageSetup.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Dispose()
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
The advantages of using an online document editor over a traditional desktop application include enhanced accessibility, seamless collaboration, automatic version control, cross-platform compatibility, and reduced hardware requirements. These features make online document editors a versatile and efficient choice for users who require the ability to access, edit, and share documents from anywhere.
This article demonstrates how to create and edit MS Word, Excel and PowerPoint documents online using the Spire.Cloud.Office document editor library.
- Spire.Cloud.Office Document Editor
- Create a New Document
- Edit an Existing Document
- Co-Edit a Document
Spire.Cloud.Office Document Editor
Spire.Cloud.Office is a feature-rich HTML-5 based document editor component that can be easily integrated into web applications. With the document editor component, your end-users can view, create, edit, and collaborate on diverse document types within a web browser.
To utilize the services offered by Spire.Cloud.Office, you will need to first install it on your system.
- Install Spire.Cloud.Office for .NET on Windows
- Install Spire.Cloud.Office for Linux on Ubuntu
- Install Spire.Cloud.Office for Linux on CentOS
After the installation is complete, you can integrate Spire.Cloud.Office editor in your own web application or visit the example application hosted on port 3000 to explore the editor’s functionality.
The example page offers options to upload existing documents or create new ones. Spire.Office.Cloud supports loading DOC/DOCX, XLS/XLSX, and PPT/PPTX files, and exporting files to DOCX, XLSX, and PPTX formats.

Create a New Document
With the "Create Document", "Create Spreadsheet", and "Create Presentation" buttons on the example page, users can create a new Word document, a new Excel spreadsheet, and a new PowerPoint presentation, respectively.
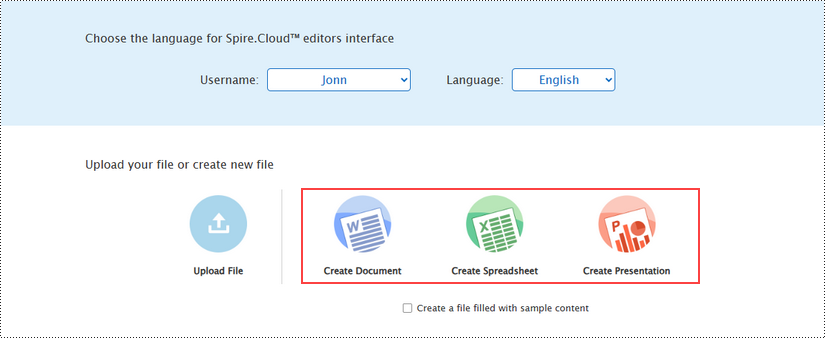
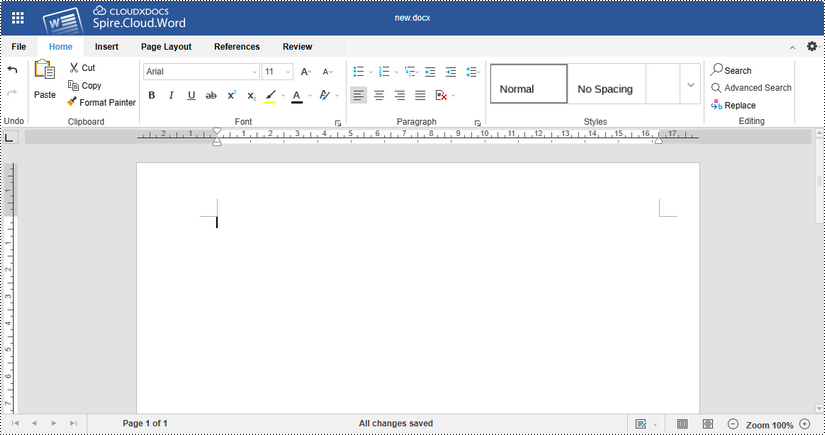
Upon clicking "Create Document", a new Word document named "new.docx" will be generated, and the editor will launch with the blank document ready for editing.
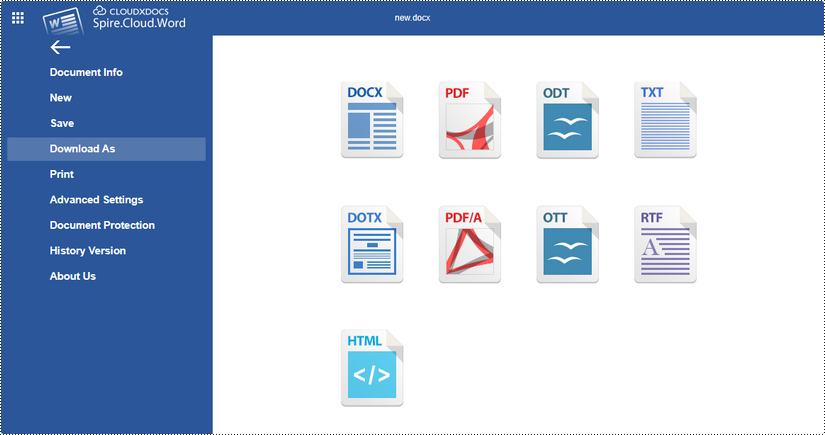
Once you've finished editing the document, click "File" on the menu and you'll get the options to download the file and save it to your local folder in the desired format.
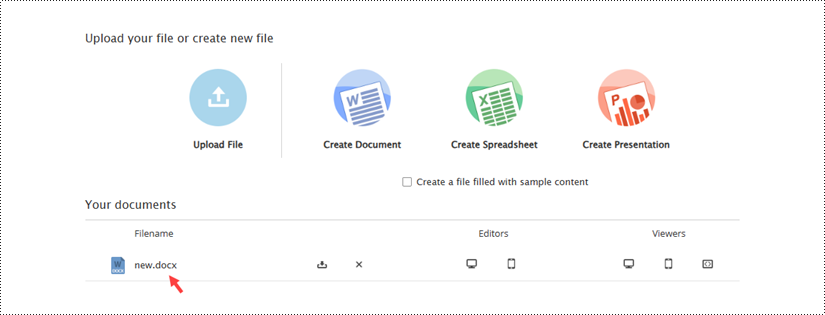
Alternatively, you can click "Save" to preserve the changes made to the "new.docx" document, which can be found on the example page.
Edit an Existing Document
On the example page, click the "Upload File" button to load an existing document for editing.
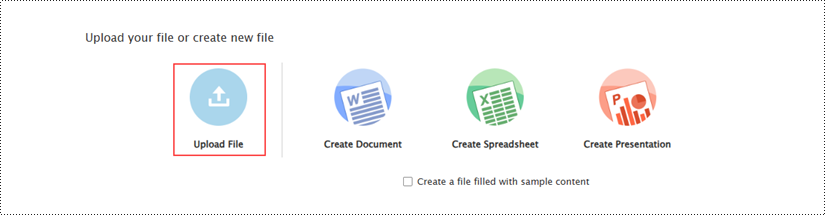
Once the file has been uploaded, it will appear on the example page. To open the document in the editor, click the computer icon in the "Editors" section.
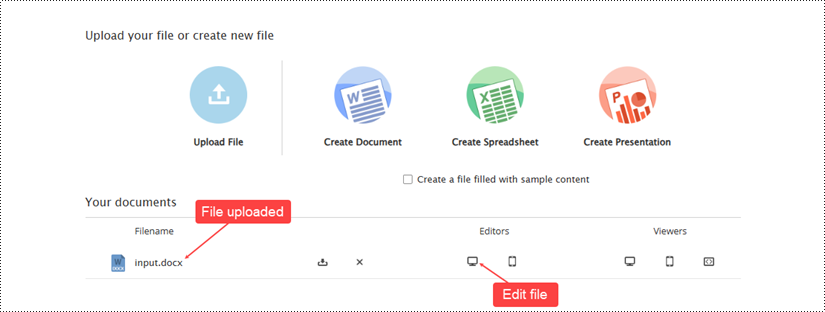
Use the editing tools provided in the document editor to make any desired modifications to the file. Once you have finished making changes, save the updated document by clicking "File" and then selecting "Save".
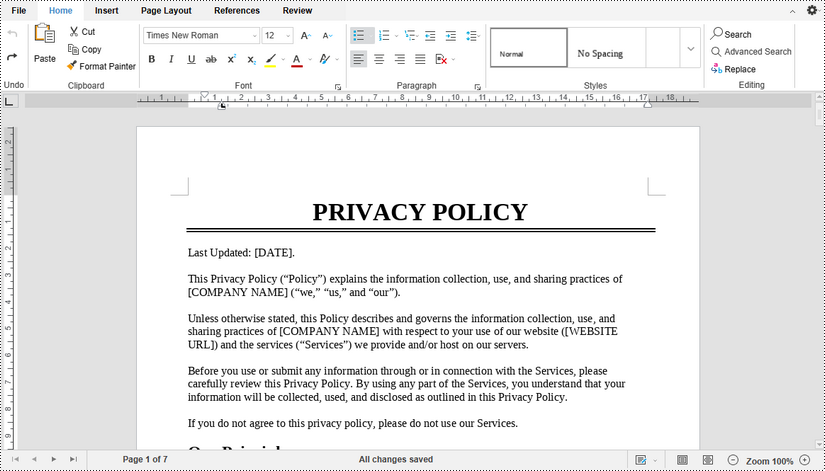
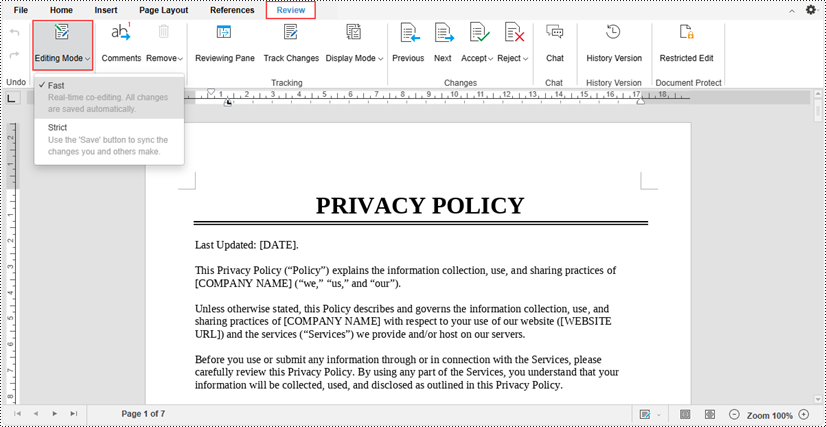
Co-Edit a Document
Spire.Cloud.Office's real-time collaboration features enable multiple users to work on the same document simultaneously. Two different collaborative editing modes are available under the "Review" tab - "Editing Mode".
- Fast Mode: All editors can see the changes made to the document in real-time as they are being typed or made.
- Strict Mode: Changes made by editors are protected and only become visible to other editors after the document has been explicitly saved.
By default, the Fast mode is enabled.
When a document is being collaboratively edited by multiple users, any changes made by one editor are instantly reflected in the document interface for all other editors in real-time.

