
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
In the modern office environment, Microsoft Word has become an indispensable part of our daily work and study. Whether it's writing reports, creating resumes, or designing promotional materials, Word provides us with a rich set of features and tools. Among them, the function of adding shapes is particularly popular among users because it allows us to easily enhance the visual appeal and expressiveness of documents. Manipulating shape elements is one of the highlights of Spire.Doc functionality, and this article will introduce you to how to add or delete shapes in Word using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Add Shapes in Word Document in Python
Spire.Doc for Python supports adding various shapes such as rectangles, trapezoids, triangles, arrows, lines, emoticons, and many other predefined shape types. By calling the Paragraph.AppendShape(width: float, height: float, shapeType: 'ShapeType') method, you can not only easily insert these shapes at any position in the document but also customize various properties of the shapes, such as fill color, border style, rotation angle, transparency, etc., to meet different typesetting needs and visual effects. Below are the detailed steps:
- Create a new Document object.
- Call Document.AddSection() and Section.AddParagraph() methods to add a section and a paragraph within the section, respectively.
- Call the Paragraph.AppendShape(width: float, height: float, shapeType: 'ShapeType') method to add a shape on the paragraph, where width and height represent the dimensions of the shape, and shapeType enum is used to specify the type of shape.
- Define the style of the shape, such as fill color, border color, border style, and width.
- Set the horizontal and vertical position of the shape relative to the page.
- Add multiple other types of shapes using the same method.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import * from spire.doc.common import * # Create a new Document object doc = Document() # Add a new section in the document sec = doc.AddSection() # Add a paragraph in the new section para = sec.AddParagraph() # Add a rectangle shape in the paragraph with width and height both 60 shape1 = para.AppendShape(60, 60, ShapeType.Rectangle) # Define the fill color of the shape shape1.FillColor = Color.get_YellowGreen() # Define the border color shape1.StrokeColor = Color.get_Gray() # Define the border style and width shape1.LineStyle = ShapeLineStyle.Single shape1.StrokeWeight = 1 # Set the horizontal and vertical position of the shape relative to the page shape1.HorizontalOrigin = HorizontalOrigin.Page shape1.HorizontalPosition = 100 shape1.VerticalOrigin = VerticalOrigin.Page shape1.VerticalPosition = 200 # Similarly, add a triangle shape in the same paragraph and set its properties shape2 = para.AppendShape(60, 60, ShapeType.Triangle) shape2.FillColor = Color.get_Green() shape2.StrokeColor = Color.get_Gray() shape2.LineStyle = ShapeLineStyle.Single shape2.StrokeWeight = 1 shape2.HorizontalOrigin = HorizontalOrigin.Page shape2.HorizontalPosition = 200 shape2.VerticalOrigin = VerticalOrigin.Page shape2.VerticalPosition = 200 # Add an arrow shape and set its properties shape3 = para.AppendShape(60, 60, ShapeType.Arrow) shape3.FillColor = Color.get_SeaGreen() shape3.StrokeColor = Color.get_Gray() shape3.LineStyle = ShapeLineStyle.Single shape3.StrokeWeight = 1 shape3.HorizontalOrigin = HorizontalOrigin.Page shape3.HorizontalPosition = 300 shape3.VerticalOrigin = VerticalOrigin.Page shape3.VerticalPosition = 200 # Add a smiley face shape and set its properties shape4 = para.AppendShape(60, 60, ShapeType.SmileyFace) shape4.FillColor = Color.get_LightGreen() shape4.StrokeColor = Color.get_Gray() shape4.LineStyle = ShapeLineStyle.Single shape4.StrokeWeight = 1 shape4.HorizontalOrigin = HorizontalOrigin.Page shape4.HorizontalPosition = 400 shape4.VerticalOrigin = VerticalOrigin.Page shape4.VerticalPosition = 200 # Save the document outputFile = "AddShapes.docx" doc.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx2016) # Release the document doc.Close()
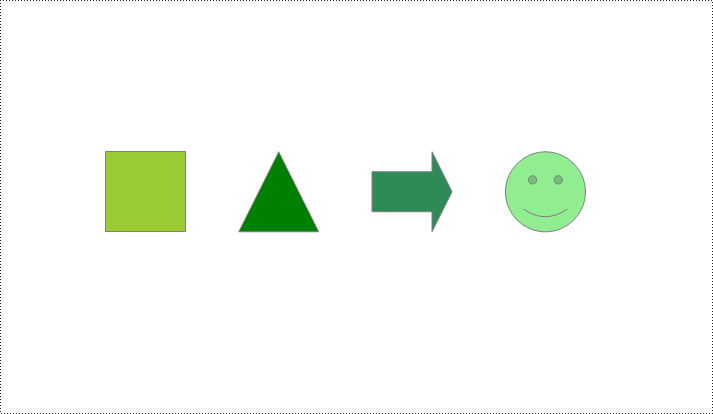
Add Shape Group in Word Document
Spire.Doc for Python not only provides the functionality to add individual shapes (such as rectangles, circles, lines, etc.) but also supports creating and managing grouped shapes. A grouped shape is a special collection of shapes that organizes multiple independent shapes together to form a whole, sharing the same transformation properties (such as position, rotation angle, etc.). Here are the specific steps to achieve this:
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Call the Document.AddSection() method to add a blank section.
- Call the Section.AddParagraph() method to add a blank paragraph in the section.
- Call Paragraph.AppendShapeGroup() to add a shape group and specify its dimensions.
- Create a Textbox and specify its shape type, dimensions, position, fill color, and other properties.
- Add paragraphs within the Textbox and insert text, setting the paragraph's horizontal alignment to center.
- Add the Textbox to the list of child objects of the shape group.
- Similar to the above steps, create shapes for symbols like arrows, diamond-shaped text boxes, octagonal text boxes, and set their properties, adding them to the list of child objects of the shape group.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section to the document
sec = doc.AddSection()
# Add a paragraph to the section
para = sec.AddParagraph()
# Add a shape group to the paragraph and specify its horizontal position
shapegroup = para.AppendShapeGroup(375, 350)
shapegroup.HorizontalPosition = 180
# Calculate the relative unit scale X and Y for the shape group for subsequent element size positioning
X = float((shapegroup.Width / 1000.0))
Y = float((shapegroup.Height / 1000.0))
# Create a rounded rectangle text box
txtBox = TextBox(doc)
# Set the shape type of the text box
txtBox.SetShapeType(ShapeType.RoundRectangle)
# Set the width and height of the text box
txtBox.Width = 125 / X
txtBox.Height = 54 / Y
# Add a paragraph inside the text box and set its horizontal alignment to center
paragraph = txtBox.Body.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
# Add the text "Step One" to the paragraph
paragraph.AppendText("Step One")
# Set the horizontal and vertical position of the text box
txtBox.HorizontalPosition = 19 / X
txtBox.VerticalPosition = 27 / Y
# Set the fill color of the text box and remove the border line
txtBox.Format.FillColor = Color.FromRgb(153, 255, 255)
txtBox.Format.NoLine = True
# Add the text box to the list of child objects of the shape group
shapegroup.ChildObjects.Add(txtBox)
# Create a downward arrow shape and specify its shape type
arrowLineShape = ShapeObject(doc, ShapeType.DownArrow)
# Set the width and height of the arrow shape
arrowLineShape.Width = 16 / X
arrowLineShape.Height = 40 / Y
# Set the horizontal and vertical position of the arrow shape
arrowLineShape.HorizontalPosition = 73 / X
arrowLineShape.VerticalPosition = 87 / Y
# Set the stroke color of the arrow shape
arrowLineShape.StrokeColor = Color.get_CadetBlue()
# Add the arrow shape to the list of child objects of the shape group
shapegroup.ChildObjects.Add(arrowLineShape)
# (Similar subsequent code, creating diamond-shaped text boxes, downward arrow shapes, and octagonal text boxes, with corresponding property settings and positioning)
txtBox = TextBox(doc)
txtBox.SetShapeType(ShapeType.Diamond)
txtBox.Width = 125 / X
txtBox.Height = 54 / Y
paragraph = txtBox.Body.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paragraph.AppendText("Step Two")
txtBox.HorizontalPosition = 19 / X
txtBox.VerticalPosition = 131 / Y
txtBox.Format.FillColor = Color.FromRgb(0, 102, 102)
txtBox.Format.NoLine = True
shapegroup.ChildObjects.Add(txtBox)
arrowLineShape = ShapeObject(doc, ShapeType.DownArrow)
arrowLineShape.Width = 16 / X
arrowLineShape.Height = 40 / Y
arrowLineShape.HorizontalPosition = 73 / X
arrowLineShape.VerticalPosition = 192 / Y
arrowLineShape.StrokeColor = Color.get_CadetBlue()
shapegroup.ChildObjects.Add(arrowLineShape)
txtBox = TextBox(doc)
txtBox.SetShapeType(ShapeType.Octagon)
txtBox.Width = 149 / X
txtBox.Height = 59 / Y
paragraph = txtBox.Body.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paragraph.AppendText("Step Three")
txtBox.HorizontalPosition = 7 / X
txtBox.VerticalPosition = 236 / Y
txtBox.Format.FillColor = Color.FromRgb(51, 204, 204)
txtBox.Format.NoLine = True
shapegroup.ChildObjects.Add(txtBox)
# Define the output file name
outputFile = "ShapeGroup.docx"
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx2016)
# Close the document object
doc.Close()
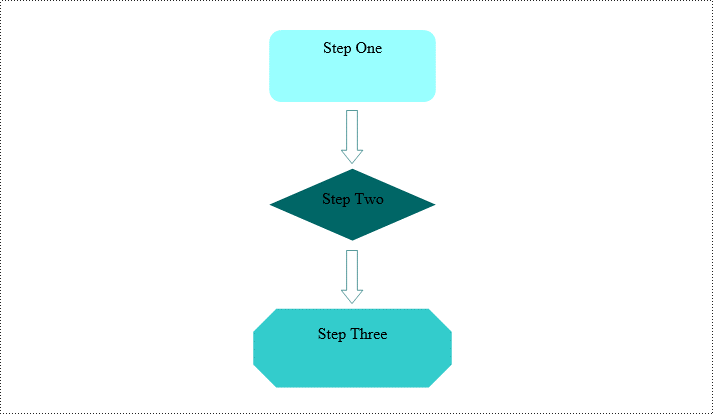
Remove Shapes from Word Document
Spire.Doc for Python supports efficiently removing individual shapes and shape groups from a Word document. Below are the detailed steps:
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Call the Document.LoadFromFile() method to load a document containing shapes.
- Traverse through all the sections of the document and the body elements within the sections to get paragraphs.
- Check if the child elements under the paragraph are shape objects or shape group objects.
- Call the Paragraph.ChildObjects.Remove() method to remove the shape object.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of the Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("ShapeGroup.docx")
# Iterate through all sections of the document
for s in range(doc.Sections.Count):
# Get the current section
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(i)
# Iterate through all child objects within the section
for i in range(section.Body.ChildObjects.Count):
# Get the current child object
document_object = section.Body.ChildObjects.get_Item(i)
# If the current child object is a paragraph
if isinstance(document_object, Paragraph):
# Convert the child object to a paragraph object
paragraph = document_object
# Initialize the inner loop index
j = 0
# Iterate through all child objects within the paragraph
while j < paragraph.ChildObjects.Count:
# Get the current child object within the paragraph
c_obj = paragraph.ChildObjects.get_Item(i)
# If the current child object is a shape group or shape object
if isinstance(c_obj, ShapeGroup) or isinstance(c_obj, ShapeObject):
# Remove the shape object from the paragraph
paragraph.ChildObjects.Remove(c_obj)
# Update the inner loop index
j -= 1
# Increment the inner loop index
j += 1
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("RemovedShapes.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
# Close the document object
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
In Microsoft Excel, text alignment and text orientation are crucial formatting options for optimizing the presentation of text within cells. Text alignment determines the horizontal or vertical positioning of text within a cell, while text orientation controls the tilt angle or display direction of the text. By flexibly utilizing these formatting options, you can customize the appearance of text within cells to create professional and visually appealing spreadsheets. In this article, we will demonstrate how to set text alignment and orientation in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Set Text Alignment and Orientation in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the CellRange.Style.HorizontalAlignment and CellRange.Style.VerticalAlignment properties that enable you to customize the horizontal and vertical alignment of text in a single cell or range of cells. Additionally, it allows you to change the orientation of text by applying rotation to cells using the CellRange.Style.Rotation property. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Set the horizontal alignment for text in specific cells to Left, Center, Right, or General using the CellRange.Style.HorizontalAlignment property.
- Set the vertical alignment for text in specific cells to Top, Center, or Bottom using the CellRange.Style.VerticalAlignment property.
- Change the orientation for text in specific cells using the CellRange.Style.Rotation property.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Example.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set the horizontal alignment for text in a specific cell to Left
sheet.Range["B1"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left
# Set the horizontal alignment for text in a specific cell to Center
sheet.Range["B2"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
# Set the horizontal alignment for text in a specific cell to Right
sheet.Range["B3"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Right
# Set the horizontal alignment for text in a specific cell to General
sheet.Range["B4"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.General
# Set the vertical alignment for text in a specific cell to Top
sheet.Range["B5"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Top
# Set the vertical alignment for text in a specific cell to Center
sheet.Range["B6"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
# Set the vertical alignment for text in a specific cell to Bottom
sheet.Range["B7"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Bottom
# Change the text orientation in specific cells by applying rotation
sheet.Range["B8"].Style.Rotation = 45
sheet.Range["B9"].Style.Rotation = 90
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("TextAlignmentAndOrientation.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
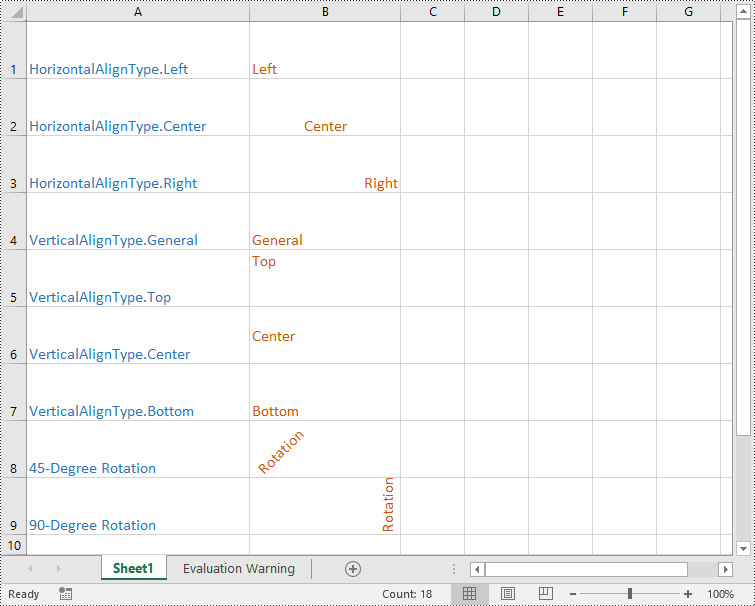
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
In a Word document, content controls allow the content of the document to be dynamically updated and modified, providing users with more flexible editing and management options. Through content controls, users can easily insert, delete, or modify content in specific sections without altering the overall structure of the document. This article will explain how to use Spire.Doc for .NET to modify content controls in a Word document within a C# project.
- Modify Content Controls in the Body using C#
- Modify Content Controls within Paragraphs using C#
- Modify Content Controls Wrapping Table Rows using C#
- Modify Content Controls Wrapping Table Cells using C#
- Modify Content Controls within Table Cells using C#
Install Spire.Doc for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Doc for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
Modify Content Controls in the Body using C#
In Spire.Doc, the object type for content controls in the body is StructureDocumentTag. You can iterate through the collection of child objects in Section.Body to find objects of type StructureDocumentTag and then modify them. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Access the body of a section in the document using Section.Body.
- Iterate through the collection of child objects in the body, Body.ChildObjects, to find objects of type StructureDocumentTag.
- Access the StructureDocumentTag.ChildObjects collection and perform the necessary modification operations based on the type of child objects.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace SpireDocDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load document content from a file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample1.docx");
// Get the body of the document
Body body = doc.Sections[0].Body;
// Create lists for paragraphs and tables
List<Paragraph> paragraphs = new List<Paragraph>();
List<Table> tables = new List<Table>();
for (int i = 0; i < body.ChildObjects.Count; i++)
{
// Get the document object
DocumentObject documentObject = body.ChildObjects[i];
// If it is a StructureDocumentTag object
if (documentObject.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.StructureDocumentTag)
{
StructureDocumentTag structureDocumentTag = (StructureDocumentTag)documentObject;
// If the tag is "c1" or the alias is "c1"
if (structureDocumentTag.SDTProperties.Tag == "c1" || structureDocumentTag.SDTProperties.Alias == "c1")
{
for (int j = 0; j < structureDocumentTag.ChildObjects.Count; j++)
{
// If it is a paragraph object
if (structureDocumentTag.ChildObjects[j].DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Paragraph)
{
Paragraph paragraph = (Paragraph)structureDocumentTag.ChildObjects[j];
paragraphs.Add(paragraph);
}
// If it is a table object
if (structureDocumentTag.ChildObjects[j].DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Table)
{
Table table = (Table)structureDocumentTag.ChildObjects[j];
tables.Add(table);
}
}
}
}
}
// Modify the text content of the first paragraph
paragraphs[0].Text = "Spire.Doc for .NET is a totally independent .NET Word class library which doesn't require Microsoft Office installed on system.";
// Reset the cells of the first table
tables[0].ResetCells(5, 4);
// Save the modified document to a file
doc.SaveToFile("ModifyBodyContentControls.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016);
// Release document resources
doc.Dispose();
}
}
}
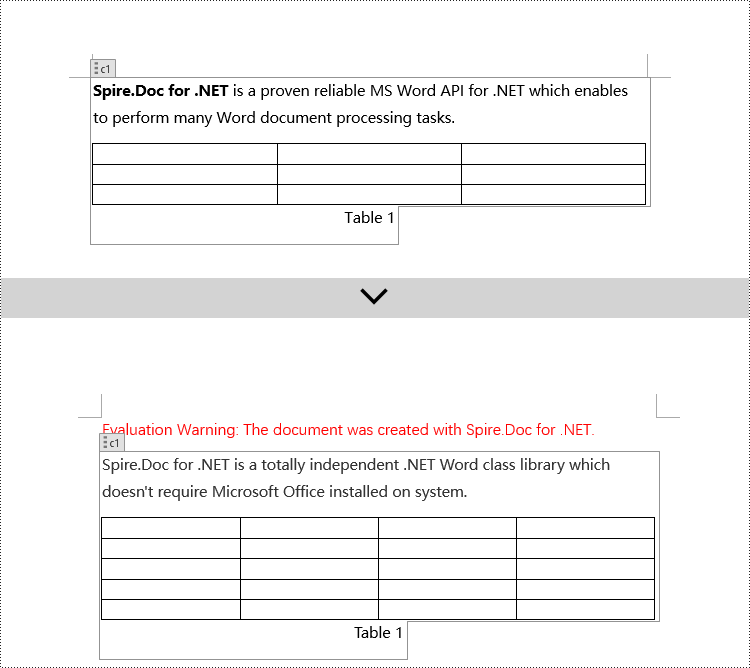
Modify Content Controls within Paragraphs using C#
In Spire.Doc, the object type for content controls within paragraphs is StructureDocumentTagInline. To modify them, you need to iterate through the collection of child objects of Paragraph.ChildObjects, find objects of type StructureDocumentTagInline, and then make the necessary modifications. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Access the body of a section in the document using Section.Body.
- Get the first paragraph of the body using Body.Paragraphs[0].
- Iterate through the collection of child objects of the paragraph, Paragraph.ChildObjects, to find objects of type StructureDocumentTagInline.
- Access the collection of child objects of StructureDocumentTagInline, StructureDocumentTagInline.ChildObjects, and perform the required modifications based on the type of the child objects.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace SpireDocDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new Document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load document content from a file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample2.docx");
// Get the body of the document
Body body = doc.Sections[0].Body;
// Get the first paragraph in the body
Paragraph paragraph = body.Paragraphs[0];
// Iterate through child objects in the paragraph
for (int i = 0; i < paragraph.ChildObjects.Count; i++)
{
// Check if the child object is StructureDocumentTagInline
if (paragraph.ChildObjects[i].DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.StructureDocumentTagInline)
{
// Convert the child object to StructureDocumentTagInline type
StructureDocumentTagInline structureDocumentTagInline = (StructureDocumentTagInline)paragraph.ChildObjects[i];
// Check if the Tag or Alias property is "text1"
if (structureDocumentTagInline.SDTProperties.Tag == "text1" || structureDocumentTagInline.SDTProperties.Alias == "text1")
{
// Iterate through child objects in the StructureDocumentTagInline object
for (int j = 0; j < structureDocumentTagInline.ChildObjects.Count; j++)
{
// Check if the child object is a TextRange object
if (structureDocumentTagInline.ChildObjects[j].DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.TextRange)
{
// Convert the child object to TextRange type
TextRange range = (TextRange)structureDocumentTagInline.ChildObjects[j];
// Set the text content to a specified content
range.Text = "97-2003/2007/2010/2013/2016/2019";
}
}
}
// Check if the Tag or Alias property is "logo1"
if (structureDocumentTagInline.SDTProperties.Tag == "logo1" || structureDocumentTagInline.SDTProperties.Alias == "logo1")
{
// Iterate through child objects in the StructureDocumentTagInline object
for (int j = 0; j < structureDocumentTagInline.ChildObjects.Count; j++)
{
// Check if the child object is an image
if (structureDocumentTagInline.ChildObjects[j].DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Picture)
{
// Convert the child object to DocPicture type
DocPicture docPicture = (DocPicture)structureDocumentTagInline.ChildObjects[j];
// Load a specified image
docPicture.LoadImage("Doc-NET.png");
// Set the width and height of the image
docPicture.Width = 100;
docPicture.Height = 100;
}
}
}
}
}
// Save the modified document to a new file
doc.SaveToFile("ModifiedContentControlsInParagraph.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016);
// Release resources of the Document object
doc.Dispose();
}
}
}

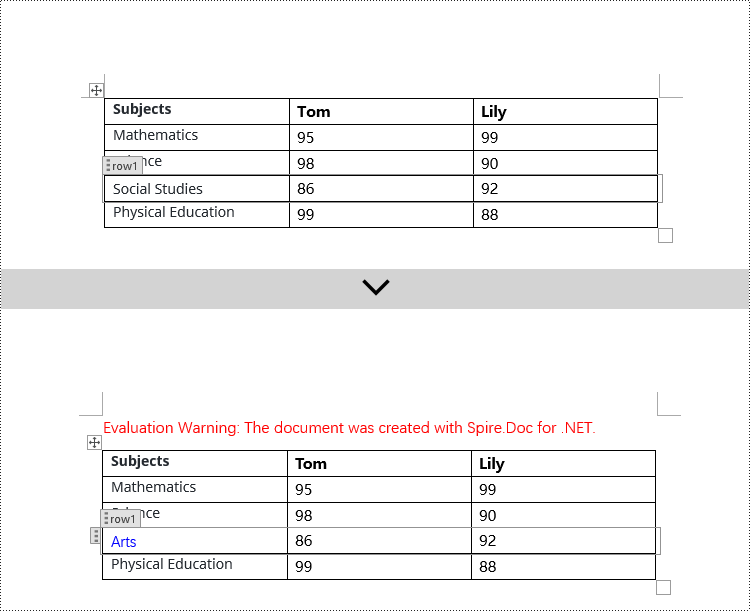
Modify Content Controls Wrapping Table Rows using C#
In Spire.Doc, the object type for a table row content control is StructureDocumentTagRow. To modify it, you need to iterate through the child objects collection of Table.ChildObjects, find objects of type StructureDocumentTagRow, and then make the necessary modifications. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Access the body of a section using Section.Body.
- Get the first table in the body using Body.Tables[0].
- Iterate through the child objects collection of the table, Table.ChildObjects, to find objects of type StructureDocumentTagRow.
- Access the collection of cells in the StructureDocumentTagRow.Cells table row content control and make the required modifications to the cell contents.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
namespace SpireDocDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load the document from a file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample3.docx");
// Get the body of the document
Body body = doc.Sections[0].Body;
// Get the first table
Table table = (Table)body.Tables[0];
// Iterate through the child objects in the table
for (int i = 0; i < table.ChildObjects.Count; i++)
{
// Check if the child object is of type StructureDocumentTagRow
if (table.ChildObjects[i].DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.StructureDocumentTagRow)
{
// Convert the child object to a StructureDocumentTagRow object
StructureDocumentTagRow structureDocumentTagRow = (StructureDocumentTagRow)table.ChildObjects[i];
// Check if the Tag or Alias property of the StructureDocumentTagRow is "row1"
if (structureDocumentTagRow.SDTProperties.Tag == "row1" || structureDocumentTagRow.SDTProperties.Alias == "row1")
{
// Clear the paragraphs in the cell
structureDocumentTagRow.Cells[0].Paragraphs.Clear();
// Add a paragraph in the cell and set the text
TextRange textRange = structureDocumentTagRow.Cells[0].AddParagraph().AppendText("Arts");
textRange.CharacterFormat.TextColor = System.Drawing.Color.Blue;
}
}
}
// Save the modified document to a file
doc.SaveToFile("ModifiedTableRowContentControl.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016);
// Release document resources
doc.Dispose();
}
}
}
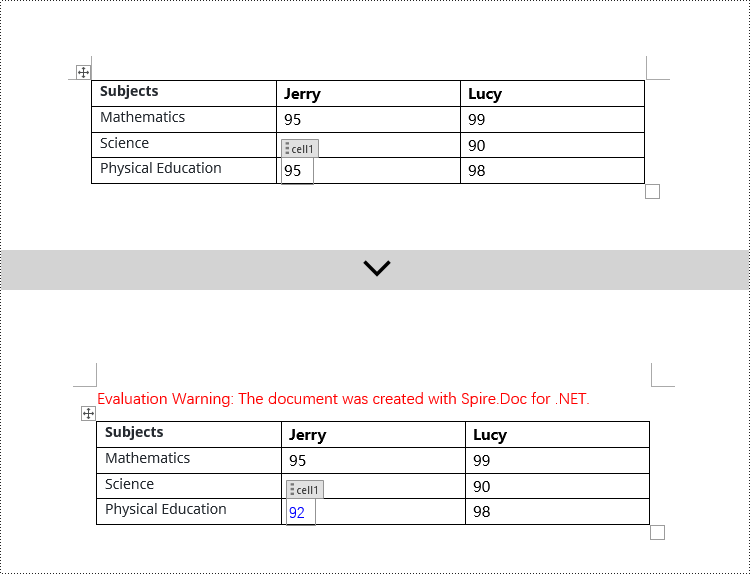
Modify Content Controls Wrapping Table Cells using C#
In Spire.Doc, the object type for the content control in a table cell is StructureDocumentTagCell. You need to iterate through the collection of child objects in TableRow.ChildObjects, find objects of type StructureDocumentTagCell, and then perform operations on them. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the body of a section using Section.Body.
- Get the first table in the body using Body.Tables[0].
- Iterate through the collection of table rows Table.Rows, accessing each TableRow object.
- Iterate through the collection of child objects in the table row TableRow.ChildObjects, finding objects of type StructureDocumentTagCell.
- Access the collection of paragraphs in the StructureDocumentTagCell content control cell, and perform the necessary modifications to the content.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
namespace SpireDocDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load the document from a file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample4.docx");
// Get the body of the document
Body body = doc.Sections[0].Body;
// Get the first table in the document
Table table = (Table)body.Tables[0];
// Iterate through the rows of the table
for (int i = 0; i < table.Rows.Count; i++)
{
// Iterate through the child objects in each row
for (int j = 0; j < table.Rows[i].ChildObjects.Count; j++)
{
// Check if the child object is a StructureDocumentTagCell
if (table.Rows[i].ChildObjects[j].DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.StructureDocumentTagCell)
{
// Convert the child object to StructureDocumentTagCell type
StructureDocumentTagCell structureDocumentTagCell = (StructureDocumentTagCell)table.Rows[i].ChildObjects[j];
// Check if the Tag or Alias property of structureDocumentTagCell is "cell1"
if (structureDocumentTagCell.SDTProperties.Tag == "cell1" || structureDocumentTagCell.SDTProperties.Alias == "cell1")
{
// Clear the paragraphs in the cell
structureDocumentTagCell.Paragraphs.Clear();
// Add a new paragraph and add text to it
TextRange textRange = structureDocumentTagCell.AddParagraph().AppendText("92");
textRange.CharacterFormat.TextColor = System.Drawing.Color.Blue;
}
}
}
}
// Save the modified document to a new file
doc.SaveToFile("ModifiedTableCellContentControl.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016);
// Dispose of the document object
doc.Dispose();
}
}
}
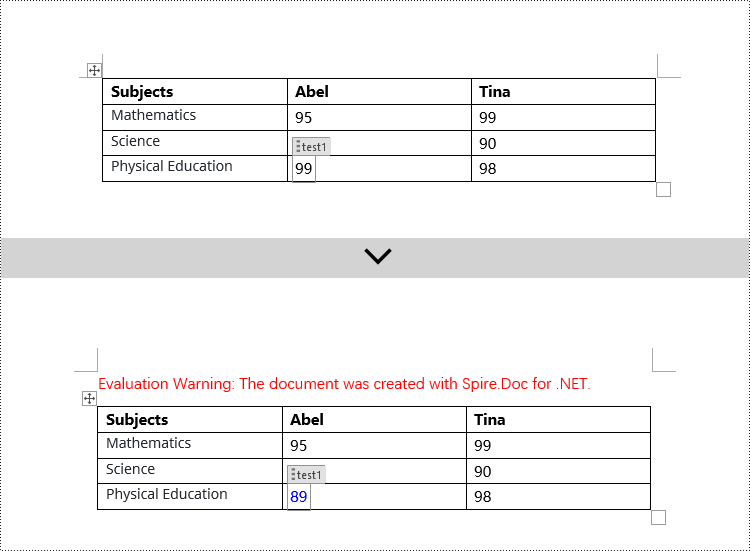
Modify Content Controls within Table Cells using C#
This case demonstrates modifying content controls within paragraphs in table cells. You need to first access the collection of paragraphs in the cell TableCell.Paragraphs, then iterate through the collection of child objects in each paragraph Paragraph.ChildObjects, find objects of type StructureDocumentTagInline, and make modifications to them. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the body of a section using Section.Body.
- Get the first table in the body using Body.Tables[0].
- Iterate through the collection of table rows Table.Rows, accessing each TableRow object.
- Iterate through the collection of cells in the table row TableRow.Cells, accessing each TableCell object.
- Iterate through the collection of paragraphs in the cell TableCell.Paragraphs, accessing each Paragraph object.
- Iterate through the collection of child objects in the paragraph Paragraph.ChildObjects, finding objects of type StructureDocumentTagInline.
- Access the ChildObjects collection of the StructureDocumentTagInline object, and perform the necessary modifications based on the type of the child objects.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
namespace SpireDocDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new Document object
Document doc = new Document();
// Load document content from file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample5.docx");
// Get the body of the document
Body body = doc.Sections[0].Body;
// Get the first table
Table table = (Table)body.Tables[0];
// Iterate through the rows of the table
for (int r = 0; r < table.Rows.Count; r++)
{
// Iterate through the cells in the table row
for (int c = 0; c < table.Rows[r].Cells.Count; c++)
{
// Iterate through the paragraphs in the cell
for (int p = 0; p < table.Rows[r].Cells[c].Paragraphs.Count; p++)
{
// Get the paragraph object
Paragraph paragraph = table.Rows[r].Cells[c].Paragraphs[p];
// Iterate through the child objects in the paragraph
for (int i = 0; i < paragraph.ChildObjects.Count; i++)
{
// Check if the child object is of type StructureDocumentTagInline
if (paragraph.ChildObjects[i].DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.StructureDocumentTagInline)
{
// Convert to StructureDocumentTagInline object
StructureDocumentTagInline structureDocumentTagInline = (StructureDocumentTagInline)paragraph.ChildObjects[i];
// Check if the Tag or Alias property of StructureDocumentTagInline is "test1"
if (structureDocumentTagInline.SDTProperties.Tag == "test1" || structureDocumentTagInline.SDTProperties.Alias == "test1")
{
// Iterate through the child objects of StructureDocumentTagInline
for (int j = 0; j < structureDocumentTagInline.ChildObjects.Count; j++)
{
// Check if the child object is of type TextRange
if (structureDocumentTagInline.ChildObjects[j].DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.TextRange)
{
// Convert to TextRange object
TextRange textRange = (TextRange)structureDocumentTagInline.ChildObjects[j];
// Set the text content
textRange.Text = "89";
// Set text color
textRange.CharacterFormat.TextColor = System.Drawing.Color.Blue;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
// Save the modified document to a new file
doc.SaveToFile("ModifiedContentControlInParagraphOfTableCell.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016);
// Dispose of the Document object resources
doc.Dispose();
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
