
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Working with large Excel workbooks can sometimes become unwieldy, especially when you need to share or distribute parts of the data independently. In these cases, it can be helpful to split your Excel file into multiple smaller files. This not only makes the individual files more manageable, but also allows you to better organize and share your data. In this article, we will demonstrate how to split an Excel file in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
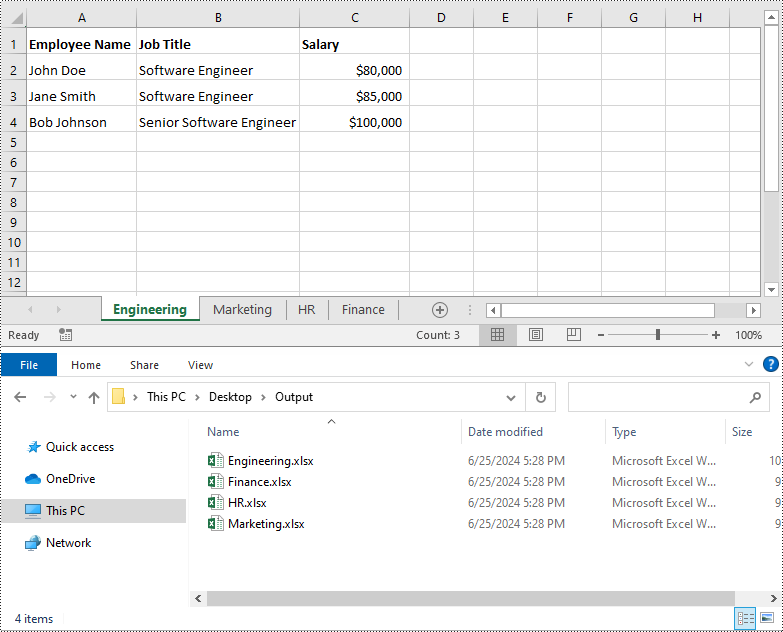
Split Excel by Worksheets in Python
If your Excel file contains multiple worksheets, you can easily split each sheet into an Excel file by using the Workbook.Worksheets.AddCopy() method provided by Spire.XLS for Python. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through the worksheets in the Excel file.
- For each worksheet, create a new Workbook object for it.
- Remove the default worksheets in the new workbook using Workbook.Worksheets.Clear() method.
- Copy the worksheet to the new workbook using Workbook.Worksheets.AddCopy() method.
- Save the new workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Specify the folder path for the generated Excel files
folderPath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Output\\"
# Iterate through all worksheets in the Excel file
for worksheet in workbook.Worksheets:
# For each worksheet, create a new Workbook object
newWorkbook = Workbook()
# Remove the worksheets from the new workbook
newWorkbook.Worksheets.Clear()
# Copy the worksheet from the Excel file to the new workbook
newWorkbook.Worksheets.AddCopy(worksheet)
# Save the new workbook to the specified folder
newWorkbook.SaveToFile(folderPath + worksheet.Name + ".xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
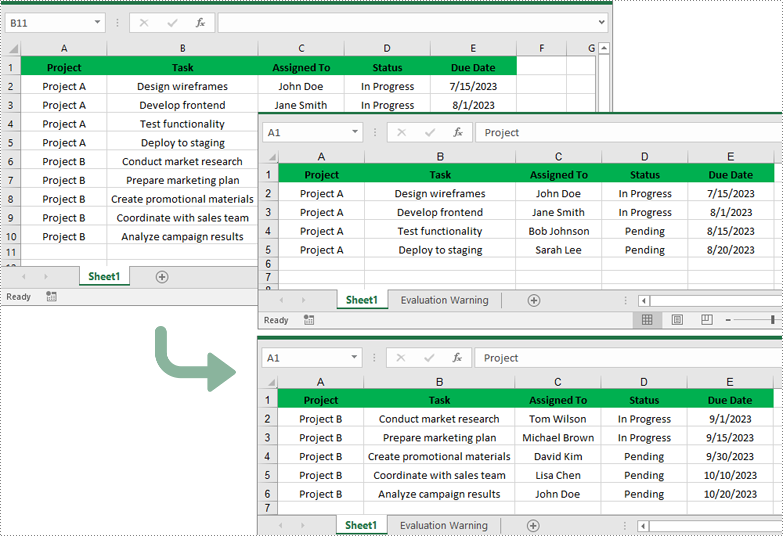
Split Excel by Rows in Python
If you have a large worksheet where a specific number of rows represent a unique record or entry, you can extract these individual rows or records into separate Excel files for focused data analysis using the Worksheet.CopyRow() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the original worksheet where you want to copy rows from using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Create a new Workbook object and remove the default worksheets from the new workbook using Workbook.Worksheets.Clear() method.
- Add a new Worksheet to the new workbook using Workbook.Worksheets.Add() method.
- Copy specific rows from the original worksheet to the new worksheet using Worksheet.CopyRow() method.
- Copy Column widths from the original worksheet to the new worksheet.
- Save the new workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object and load an Excel file
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the original (the 1st) worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the header row
header = worksheet.Rows[0]
# Specify the folder path for the generated Excel files
folderPath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Output\\"
# Create a new Workbook object
newWorkbook1 = Workbook()
# Remove the default worksheets
newWorkbook1.Worksheets.Clear()
# Add a new worksheet
newWorksheet1 = newWorkbook1.Worksheets.Add("Sheet1")
# Copy rows 1-5 from the original worksheet to the new worksheet
for i in range(1, 6):
worksheet.CopyRow(worksheet.Rows[i - 1], newWorksheet1, newWorksheet1.LastDataRow + 1, CopyRangeOptions.All)
# Copy column widths from the original worksheet to the new worksheet
for i in range(worksheet.Columns.Count):
newWorksheet1.SetColumnWidth(i + 1, worksheet.GetColumnWidth(i + 1))
# Save the new workbook to the specified folder
newWorkbook1.SaveToFile(folderPath + "Rows1-5.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
newWorkbook1.Dispose()
# Create a new Workbook object
newWorkbook2 = Workbook()
# Remove the default worksheets
newWorkbook2.Worksheets.Clear()
# Add a new worksheet
newWorksheet2 = newWorkbook2.Worksheets.Add("Sheet1")
# Copy header row from the original worksheet to the new worksheet
worksheet.CopyRow(worksheet.Rows[0], newWorksheet2, newWorksheet2.LastDataRow + 1, CopyRangeOptions.All)
# Copy rows 6-10 from the original worksheet to the new worksheet
for i in range(6, 11):
worksheet.CopyRow(worksheet.Rows[i - 1], newWorksheet2, newWorksheet2.LastDataRow + 1, CopyRangeOptions.All)
# Copy column widths from the original worksheet to the new worksheet
for i in range(worksheet.Columns.Count):
newWorksheet2.SetColumnWidth(i + 1, worksheet.GetColumnWidth(i + 1))
# Save the new workbook to the specified folder
newWorkbook2.SaveToFile(folderPath + "Rows6-10.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
newWorkbook2.Dispose()
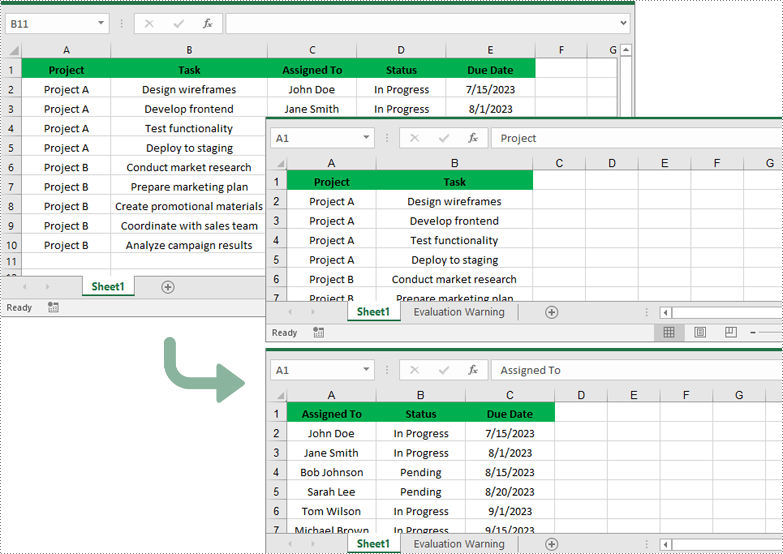
Split Excel by Columns in Python
In addition to splitting by rows, you can also split an Excel file by columns using the Worksheet.CopyColumn() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the original worksheet where you want to copy columns from using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Create a new Workbook object and remove the default worksheets from the new workbook using Workbook.Worksheets.Clear() method.
- Add a new Worksheet to the new workbook using Workbook.Worksheets.Add() method.
- Copy specific columns from the original worksheet to the new worksheet using Worksheet.CopyColumn() method.
- Copy row heights from the original worksheet to the new worksheet.
- Save the new workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object and load an Excel file
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the original (the 1st) worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Specify the folder path for the generated Excel files
folderPath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Output\\"
# Create a new Workbook object
newWorkbook1 = Workbook()
# Remove the default worksheets
newWorkbook1.Worksheets.Clear()
# Add a new worksheet
newWorksheet1 = newWorkbook1.Worksheets.Add("Sheet1")
# Copy columns 1-2 from the original worksheet to the new worksheet
for i in range(1, 3):
worksheet.CopyColumn(worksheet.Columns[i-1], newWorksheet1, newWorksheet1.LastDataColumn + 1, CopyRangeOptions.All)
# Copy row heights from the original worksheet to the new worksheet
for i in range(worksheet.Rows.Count):
newWorksheet1.SetRowHeight(i + 1, worksheet.GetRowHeight(i + 1))
# Save the new workbook to the specified folder
newWorkbook1.SaveToFile(folderPath + "Columns1-2.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
newWorkbook1.Dispose()
# Create a new Workbook object
newWorkbook2 = Workbook()
# Remove the default worksheets
newWorkbook2.Worksheets.Clear()
# Add a new worksheet
newWorksheet2 = newWorkbook2.Worksheets.Add("Sheet1")
# Copy columns 3-5 from the original worksheet to the new worksheet
for i in range(3, 6):
worksheet.CopyColumn(worksheet.Columns[i-1], newWorksheet2, newWorksheet2.LastDataColumn + 1, CopyRangeOptions.All)
# Copy row heights from the original worksheet to the new worksheet
for i in range(worksheet.Rows.Count):
newWorksheet2.SetRowHeight(i + 1, worksheet.GetRowHeight(i + 1))
# Save the new workbook to the specified folder
newWorkbook2.SaveToFile(folderPath + "Columns3-5.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
newWorkbook2.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Comparing PDF documents is a common task when collaborating on projects or tracking changes. This allows users to quickly review and understand what has been modified, added, or removed between revisions. Effective PDF comparison streamlines the review process and ensures all stakeholders are aligned on the latest document content.
In this article, you will learn how to compare two PDF documents using Python and the Spire.PDF for Python library.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Compare Two PDF Documents in Python
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfComparer.Compare() method allowing developers to compare two PDF documents and save the comparison result to another PDF document. Here are the detailed steps.
- Load the first PDF document while initializing the PdfDocument object.
- Load the second PDF document while initializing another PdfDocument object.
- Initialize an instance of PdfComparer class, passing the two PdfDocument objects are the parameter.
- Call Compare() method of the PdfComparer object to compare the two PDF documents and save the result to a different PDF document.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Load the first document
doc_one = PdfDocument("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\PDF_ONE.pdf")
# Load the section document
doc_two = PdfDocument("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\PDF_TWO.pdf")
# Create a PdfComparer object
comparer = PdfComparer(doc_two, doc_one)
# Compare two documents and save the comparison result in a pdf document
comparer.Compare("output/CompareResult.pdf")
# Dispose resources
doc_one.Dispose()
doc_two.Dispose()

Compare Selected Pages in PDF Documents in Python
Instead of comparing two entire documents, you can specify the pages to compare using the PdfComparer.PdfCompareOptions.SetPageRanges() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Load the first PDF document while initializing the PdfDocument object.
- Load the second PDF document while initializing another PdfDocument object.
- Initialize an instance of PdfComparer class, passing the two PdfDocument objects are the parameter.
- Specify the page range to compare using PdfComparer.PdfCompareOptions.SetPageRanges() method
- Call PdfComparer.Compare() method to compare the selected pages and save the result to a different PDF document.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Load the first document
doc_one = PdfDocument("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\PDF_ONE.pdf")
# Load the section document
doc_two = PdfDocument("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\PDF_TWO.pdf")
# Create a PdfComparer object
comparer = PdfComparer(doc_two, doc_one)
# Set page range for comparison
comparer.PdfCompareOptions.SetPageRanges(1, 3, 1, 3)
# Compare the selected pages and save the comparison result in a pdf document
comparer.Compare("output/CompareResult.pdf")
# Dispose resources
doc_one.Dispose()
doc_two.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
When working with large amounts of information, the ability to quickly sort data can be very beneficial at times. By arranging data in ascending, descending, or customized order, users can easily spot trends, analyze relationships, and extract valuable insights. In this article, you will learn how to sort columns or rows in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Sort By Columns in Excel in Python
- Sort By Custom List in Excel in Python
- Sort By Rows in Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Sort By Columns in Excel in Python
The Workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add(key: int, sortComparsionType: SortComparsionType, orderBy: OrderBy) method provided by Spire.XLS for Python allows users to sort data based on different criteria. For example, you can sort cell values, cell colors or font colors in ascending, descending, or other order.
The following are the steps to sort the values in a specified column:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Specify the sorting mode using Workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add() method.
- Sort data in a specified cell range using Workbook.DataSorter.Sort() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Budget.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Sort values in the specified column in ascending order
workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add(0, SortComparsionType.Values, OrderBy.Ascending)
# Sort in the specified cell range
workbook.DataSorter.Sort(worksheet["A1:E7"])
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("SortByColumns.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
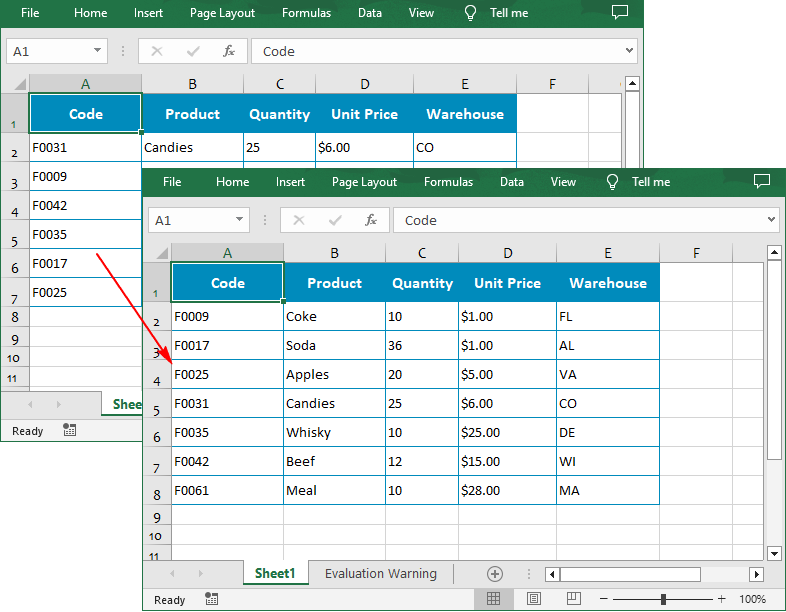
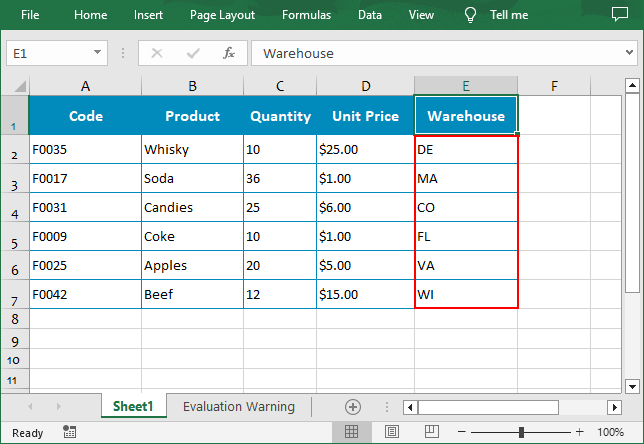
Sort By Custom List in Excel in Python
You can also create a custom list and then sort data based on it using the Workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add(key: int, customSortOrder: List[str]) method.
The following are the steps to sort data using a custom list:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Create a custom sort list, and then sort a specified column using it though Workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add() method.
- Sort data in a specified cell range using Workbook.DataSorter.Sort() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Budget.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Create a custom sort list
customList = ["DE","MA", "CO", "FL", "VA", "WI"]
# Sort a specified column using the custom list
workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add(4, customList )
# Sort in the specified cell range
workbook.DataSorter.Sort(worksheet["A1:E7"])
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("CustomSortList.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
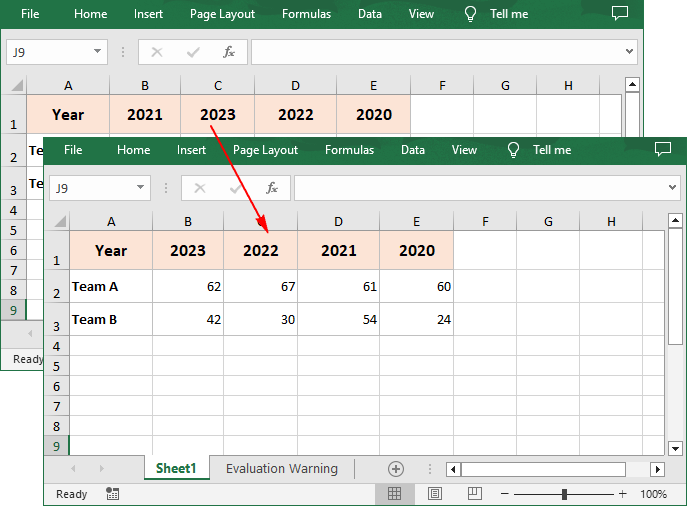
Sort By Rows in Excel in Python
To sort a specified row in Excel, you need to set the sort orientation to LeftToRight, specify the sort mode and sort row data accordingly.
The following are the steps to sort the values in a specified row:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Set whether to include titles when sorting using Workbook.DataSorter.IsIncludeTitle property.
- Set the sort orientation using Workbook.DataSorter.Orientation property.
- Specify the sorting mode, and then sort data in the first row using Workbook.DataSorter.Sort(Worksheet.Rows[0]) method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Year.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set whether to include titles when sorting
workbook.DataSorter.IsIncludeTitle = True
# Set the sort orientation
workbook.DataSorter.Orientation = SortOrientationType.LeftToRight
# Specify the sorting mode
workbook.DataSorter.SortColumns.Add(0,SortComparsionType.Values,OrderBy.Descending)
# Sort data in the first row
workbook.DataSorter.Sort(sheet.Rows[0])
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("SortByRows.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
