Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Document properties provide additional information about an Excel file, such as author, title, subject, and other metadata associated with the file. Retrieving these properties from Excel can help users gain insight into the file content and history, enabling better organization and management of files. At times, users may also need to remove document properties to protect the privacy and confidentiality of the information contained in the file. In this article, you will learn how to read or remove document properties in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Read Standard and Custom Document Properties in Excel
- Remove Standard and Custom Document Properties in Excel
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Read Standard and Custom Document Properties in Excel in Python
Excel properties are divided into two main categories:
- Standard Properties: These are predefined properties that are built into Excel files. They typically include basic details about the file such as title, subject, author, keywords, etc.
- Custom Properties: These are user-defined attributes that can be added to Excel to track additional information about the file based on your specific needs.
Spire.XLS for Python allows to read both the standard and custom document properties of an Excel file. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a StringBuilder instance.
- Get a collection of all standard document properties using Workbook.DocumentProperties property.
- Get specific standard document properties using the properties of the BuiltInDocumentProperties class and append them to the StringBuilder instance.
- Get a collection of all custom document properties using Workbook.CustomDocumentProperties property.
- Iterate through the collection.
- Get the name, type, and value of each custom document property using ICustomDocumentProperties[].Name, ICustomDocumentProperties[].PropertyType and ICustomDocumentProperties[].Value properties.
- Determine the specific property type, and then convert the property value to the value of the corresponding data type.
- Append the property name and converted property value to the StringBuilder instance using StringBuilde.append() method.
- Write the content of the StringBuilder instance into a txt file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
def AppendAllText(fname: str, text: List[str]):
fp = open(fname, "w")
for s in text:
fp.write(s + "\n")
fp.close()
inputFile = "Budget Template.xlsx"
outputFile = "GetExcelProperties.txt"
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document from disk
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Create a StringBuilder instance
builder = []
# Get a collection of all standard document properties
standardProperties = workbook.DocumentProperties
# Get specific standard properties and append them to the StringBuilder instance
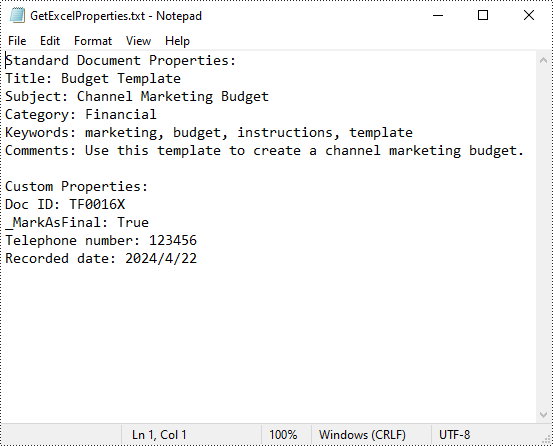
builder.append("Standard Document Properties:")
builder.append("Title: " + standardProperties.Title)
builder.append("Subject: " + standardProperties.Subject)
builder.append("Category: " + standardProperties.Category)
builder.append("Keywords: " + standardProperties.Keywords)
builder.append("Comments: " + standardProperties.Comments)
builder.append("")
# Get a collection of all custom document properties
customProperties = workbook.CustomDocumentProperties
builder.append("Custom Properties:")
# Iterate through the collection
for i in range(len(customProperties)):
# Get the name, type, and value of each custom document property
name = customProperties[i].Name
type = customProperties[i].PropertyType
obj = customProperties[i].Value
# Determine the specific property type, and then convert the property value to the value of the corresponding data type
value = None
if type == PropertyType.Double:
value = Double(obj).Value
elif type == PropertyType.DateTime:
value = DateTime(obj).ToShortDateString()
elif type == PropertyType.Bool:
value = Boolean(obj).Value
elif type == PropertyType.Int:
value = Int32(obj).Value
elif type == PropertyType.Int32:
value = Int32(obj).Value
else:
value = String(obj).Value
# Append the property name and converted property value to the StringBuilder instance
builder.append(name + ": " + str(value))
# Write the content of the StringBuilder instance into a text file
AppendAllText(outputFile, builder)
workbook.Dispose()
Remove Standard and Custom Document Properties in Excel in Python
You can easily delete standard document properties from an Excel file by setting their values as empty. For custom document properties, you can use the ICustomDocumentProperties.Remove() method to delete them. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a collection of all standard document properties using Workbook.DocumentProperties property.
- Set the values of specific standard document properties as empty through the corresponding properties of the BuiltInDocumentProperties class.
- Get a collection of all custom document properties using Workbook.CustomDocumentProperties property.
- Iterate through the collection.
- Delete each custom property from the collection by its name using ICustomDocumentProperties.Remove() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
inputFile = "Budget Template.xlsx"
outputFile = "RemoveExcelProperties.xlsx"
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document from disk
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get a collection of all standard document properties
standardProperties = workbook.DocumentProperties
# Set the value of each standard document property as empty
standardProperties.Title = ""
standardProperties.Subject = ""
standardProperties.Category = ""
standardProperties.Keywords = ""
standardProperties.Comments = ""
# Get a collection of all custom document properties
customProperties = workbook.CustomDocumentProperties
# Iterate through the collection
for i in range(len(customProperties) - 1, -1, -1):
# Delete each custom document property from the collection by its name
customProperties.Remove(customProperties[i].Name)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Proper alignment of tables and text in Microsoft Word is crucial for creating visually appealing and easy-to-read documents. By aligning table headers, numeric data, and text appropriately, you can enhance the organization and clarity of your information, making it more accessible to your readers. In this article, we will demonstrate how to align tables and the text in table cells in Microsoft Word in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Align Tables in Word in Python
A table in a Word document can be aligned to the left, center, or right side by using the Table.TableFormat.HorizontalAlignment property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an instance of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific section in the document using Document.Sections[index] property.
- Get a specific table in the section using Section.Tables[index] property.
- Set the alignment for the table using Table.TableFormat.HorizontalAlignment property.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an instance of the Document class
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Tables.docx")
# Get the first section in the document
section = document.Sections[0]
# Get the first, second, and third tables in the section
table1 = section.Tables[0]
table2 = section.Tables[1]
table3 = section.Tables[2]
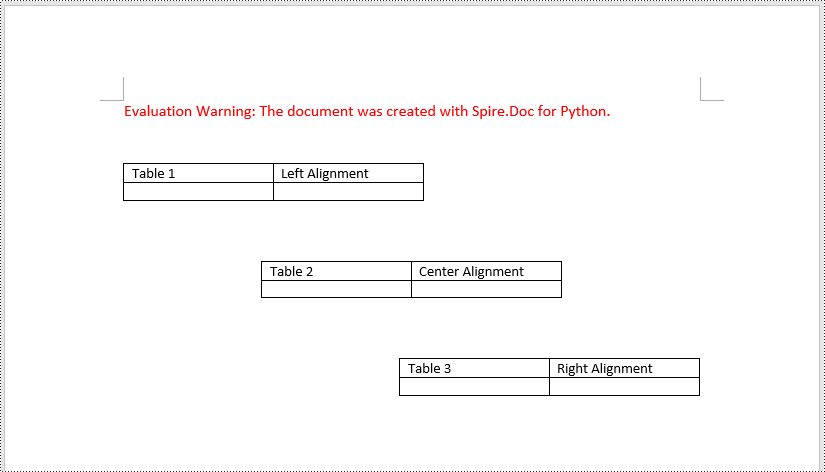
# Align the first table to the left
table1.TableFormat.HorizontalAlignment = RowAlignment.Left
# Align the second table to the center
table2.TableFormat.HorizontalAlignment = RowAlignment.Center
# Align the third table to the right
table3.TableFormat.HorizontalAlignment = RowAlignment.Right
# Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("AlignTable.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
document.Close()
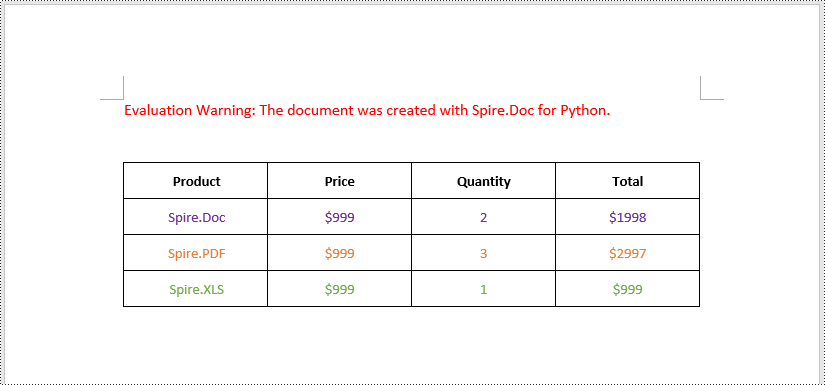
Align the Text in Table Cells in Word in Python
The text within a table cell can be horizontally aligned to the left, center, or right side using the TableCell.Paragraphs[index].Format.HorizontalAlignment property. Additionally, they can also be vertically aligned to the top, center, or bottom of the cell using the TableCell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an instance of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific section in the document using Document.Sections[index] property.
- Get a specific table in the section using Section.Tables[index] property.
- Loop through the rows in the table.
- Loop through the cells in each row.
- Set the vertical alignment for the text in each cell using TableCell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment property.
- Loop through the paragraphs in each cell.
- Set the horizontal alignment for each paragraph using TableCell.Paragraphs[index].Format.HorizontalAlignment property.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an instance of the Document class
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Table.docx")
# Get the first section in the document
section = document.Sections[0]
# Get the first tables in the section
table = section.Tables[0]
# Loop through the rows in the table
for row_index in range(table.Rows.Count):
row = table.Rows[row_index]
# Loop through the cells in the row
for cell_Index in range(row.Cells.Count):
cell = row.Cells[cell_Index]
# Vertically align the text in the cell to the center
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
# Horizontally align the text in the cell to the center
for para_index in range(cell.Paragraphs.Count):
paragraph = cell.Paragraphs[para_index]
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
# Save the result document
document.SaveToFile("AlignTableText.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
document.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
QR codes are a type of two-dimensional barcode that can store a variety of information, including URLs, contact details, and even payment information. QR codes have become increasingly popular, allowing for quick and convenient access to digital content, making them a useful tool in our modern, technology-driven world.
In this article, you will learn how to create and scan QR codes in Python using Spire.Barcode for Python.
Get a Free Trial License
The trial version of Spire.Barcode for Python does not support scanning QR code images without a valid license being applied. Additionally, it displays an evaluation message on any QR code images that are generated.
To remove these limitations, you can get a 30-day trial license for free.
Create a QR Code in Python
Spire.Barcode for Python offers the BarcodeSettings class, which enables you to configure the settings for generating a barcode. These settings encompass the barcode type, the data to be encoded, the color, the margins, and the horizontal and vertical resolution.
After you have set up the desired settings, you can create a BarcodeGenerator instance using those configurations. Subsequently, you can invoke the GenerateImage() method of the generator to produce the barcode image.
The following are the steps to create a QR code in Python.
- Create a BarcodeSettings object.
- Set the barcode type to QR code using BarcodeSettings.Type property.
- Set the data of the 2D barcode using BarcodeSettings.Data2D property.
- Set other attributes of the barcode using the properties under the BarcodeSettings object.
- Create a BarCodeGenerator object based on the settings.
- Create a QR code image using BarCodeGenerator.GenerateImage() method.
- Python
from spire.barcode import *
# Write all bytes to a file
def WriteAllBytes(fname: str, data):
with open(fname, "wb") as fp:
fp.write(data)
fp.close()
# Apply license key
License.SetLicenseKey("license key")
# Create a BarcodeSettings object
barcodeSettings = BarcodeSettings()
# Set the type of barcode to QR code
barcodeSettings.Type = BarCodeType.QRCode
# Set the data for the 2D barcode
barcodeSettings.Data2D = "Hello, World"
# Set margins
barcodeSettings.LeftMargin = 0.2
barcodeSettings.RightMargin = 0.2
barcodeSettings.TopMargin = 0.2
barcodeSettings.BottomMargin = 0.2
# Set the horizontal resolution
barcodeSettings.DpiX = 500
# Set the vertical resolution
barcodeSettings.DpiY = 500
# Set error correction level
barcodeSettings.QRCodeECL = QRCodeECL.M
# Do not display text on barcode
barcodeSettings.ShowText = False
# Add a logo at the center of the QR code
barcodeSettings.SetQRCodeLogoImage("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\logo.png")
# Create an instance of BarCodeGenerator with the specified settings
barCodeGenerator = BarCodeGenerator(barcodeSettings)
# Generate the image for the barcode
image = barCodeGenerator.GenerateImage()
# Write the PNG image to disk
WriteAllBytes("output/QRCode.png", image)

Scan a QR Code Image in Python
Spire.Barcode provides the BarcodeScanner class, which is responsible for barcode image recognition. This class offers several methods to extract data from barcodes, including:
- ScanOneFile(): Scans a single barcode image file and returns the extracted data.
- ScanFile(): Scans all barcodes present in a specified image file and returns the extracted data.
- ScanStream(): Scans barcodes from a stream of image data and returns the extracted information.
The following code demonstrates how to scan a QR code image using it.
- Python
from spire.barcode import *
# Apply license key
License.SetLicenseKey("license key")
# Scan an image file that contains one barcode
result = BarcodeScanner.ScanOneFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\QRCode.png")
# Scan an image file that contains multiple barcodes
# results = BarcodeScanner.ScanFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Image.png")
# Print the result
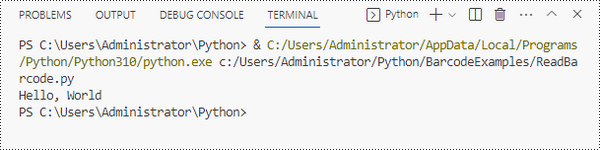
print(result)