
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Extract Tables from PDF Using Python - Easy Table Parsing Guide
2024-05-15 01:10:42 Written by Koohji
Extracting tables from PDF using Python typically involves understanding how content is visually laid out in rows and columns. Many PDF tables are defined using cell borders, making them easier to detect programmatically. In such cases, a layout-aware library that reads content positioning—rather than just raw text—is essential for accurate PDF table extraction in Python.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn a reliable method to extract tables from PDF using Python, no OCR or machine learning required. Whether your PDF contains clean grids or complex layouts, we'll show how to turn table data into structured formats like Excel or pandas DataFrames for further analysis.
Table of Contents
- Install and Set Up Spire.PDF for Python
- Extract Tables from PDF
- Tips for Better Accuracy
- Common Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
Handling Table Extraction from PDF in Python
Unlike Excel or CSV files, PDF documents don’t store tables as structured data. To extract tables from PDF files using Python, you need a library that can analyze the layout and detect tabular structures.
Spire.PDF for Python simplifies this process by providing built-in methods to extract tables page by page. It works best with clearly formatted tables and helps developers convert PDF content into usable data formats like Excel or CSV.
You can install the library with:
pip install Spire.PDF
Or install the free version for smaller PDF table extraction tasks:
pip install spire.pdf.free
Extracting Tables from PDF – Step-by-Step
To extract tables from a PDF file using Python, we start by loading the document and analyzing each page individually. With Spire.PDF for Python, you can detect tables based on their layout structure and extract them programmatically—even from multi-page documents.
Load PDF and Extract Tables
Here's a basic example that shows how to read tables from a PDF using Python. This method uses Spire.PDF to extract each table from the document page by page, making it ideal for developers who want to programmatically extract tabular data from PDFs.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTableExtractor
# Load PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Create a PdfTableExtractor object
table_extractor = PdfTableExtractor(pdf)
# Extract tables from each page
for i in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
tables = table_extractor.ExtractTable(i)
for table_index, table in enumerate(tables):
print(f"Table {table_index + 1} on page {i + 1}:")
for row in range(table.GetRowCount()):
row_data = []
for col in range(table.GetColumnCount()):
text = table.GetText(row, col).replace("\n", " ")
row_data.append(text.strip())
print("\t".join(row_data))
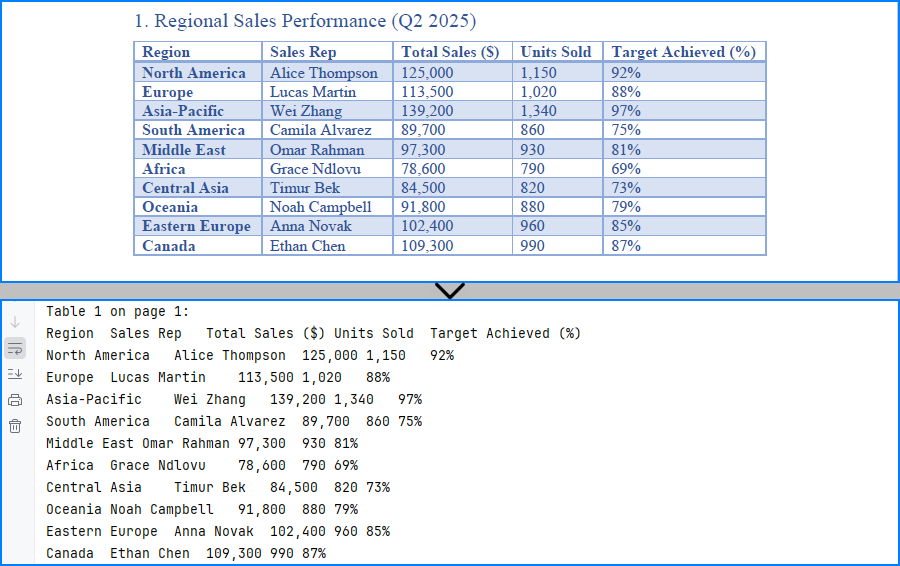
This method works reliably for bordered tables. However, for tables without visible borders—especially those with multi-line cells or unmarked headers—the extractor may fail to detect the tabular structure.
The result of extracting table data from a PDF using Python and Spire.PDF is shown below:
Export Tables to Excel and CSV
If you want to analyze or store the extracted PDF tables, you can convert them to Excel and CSV formats using Python. In this example, we use Spire.XLS for Python to create a spreadsheet for each table, allowing easy data processing or sharing. You can install the library from pip: pip install spire.xls.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTableExtractor
from spire.xls import Workbook, FileFormat
# Load PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("G:/Documents/Sample101.pdf")
# Set up extractor and Excel workbook
extractor = PdfTableExtractor(pdf)
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.Worksheets.Clear()
# Extract tables page by page
for page_index in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
tables = extractor.ExtractTable(page_index)
for t_index, table in enumerate(tables):
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add(f"Page{page_index+1}_Table{t_index+1}")
for row in range(table.GetRowCount()):
for col in range(table.GetColumnCount()):
text = table.GetText(row, col).replace("\n", " ").strip()
sheet.Range.get_Item(row + 1, col + 1).Value = text
sheet.AutoFitColumn(col + 1)
# Save all tables to one Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/Sample.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
As shown below, the extracted PDF tables are converted to Excel and CSV using Spire.XLS for Python.

You may also like: How to Insert Data into Excel Files in Python
Tips to Improve PDF Table Extraction Accuracy in Python
Extracting tables from PDFs can sometimes yield imperfect results—especially when dealing with complex layouts, page breaks, or inconsistent formatting. Below are a few practical techniques to help improve table extraction accuracy in Python and get cleaner, more structured output.
1. Merging Multi-Page Tables
Spire.PDF extracts tables on a per-page basis. If a table spans multiple pages, you can combine them manually by appending the rows:
Example:
# Extract and combine tables
combined_rows = []
for i in range(start_page, end_page + 1):
tables = table_extractor.ExtractTable(i)
if tables:
table = tables[0] # Assuming one table per page
for row in range(table.GetRowCount()):
cells = [table.GetText(row, col).strip().replace("\n", " ") for col in range(table.GetColumnCount())]
combined_rows.append(cells)
You can then convert combined_rows into Excel or CSV if you prefer analysis via these formats.
2. Filtering Out Empty or Invalid Rows
Tables may contain empty rows or columns, or the extractor may return blank rows depending on layout. You can filter them out before exporting.
Example:
# Step 1: Filter out empty rows
filtered_rows = []
for row in range(table.GetRowCount()):
row_data = [table.GetText(row, col).strip().replace("\n", " ") for col in range(table.GetColumnCount())]
if any(cell for cell in row_data): # Skip completely empty rows
filtered_rows.append(row_data)
# Step 2: Transpose and filter out empty columns
transposed = list(zip(*filtered_rows))
filtered_columns = [col for col in transposed if any(cell.strip() for cell in col)]
# Step 3: Transpose back to original row-column format
filtered_data = list(zip(*filtered_columns))
This helps improve accuracy when working with noisy or inconsistent layouts.
Common Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can I extract both text and tables from a PDF?
Yes, use PdfTextExtractor to retrieve the full page text and PdfTableExtractor to extract structured tables.
Q: Why aren't my tables detected?
Make sure the PDF is text-based (not scanned images) and that the layout follows a logical row-column format. Spire.PDF for Python detects only bordered tables; unbordered tables are often not recognized.
If you are handling an image-based PDF document, you can use Spire.OCR for Python to extract table data. Please refer to: How to Extract Text from Images Using Python.
Q: How to extract tables without borders from PDF documents?
Spire.PDF may have difficulty extracting tables without visible borders. If the tables are not extracted correctly, consider the following approaches:
- Using
PdfTextExtractorto extract raw text and then writing custom logic to identify rows and columns. - Using a large language model API (e.g., GPT) to interpret the structure from extracted plain text and return only structured table data.
- Consider adding visible borders to tables in the original document before generating the PDF, as this makes it easier to extract them using Python code.
Q: How do I convert extracted tables to a pandas DataFrame?
While Spire.PDF doesn’t provide native DataFrame output, you can collect cell values into a list of lists and then convert:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(table_data)
This lets you convert PDF tables into pandas DataFrames using Python for data analysis.
Q: Is Spire.PDF for Python free to use?
Yes, there are two options available:
- Free Spire.PDF for Python – a permanently free version with limited features (e.g., page count limits). You can install it via pip or download it from the official Free Spire.PDF for Python page.
- Temporary Free License – to unlock all features of the commercial version for evaluation or internal use, you can apply for a temporary free license here.
Conclusion
Whether you're working with structured reports, financial data, or standardized forms, extracting tables from PDFs in Python can streamline your workflow. With a layout-aware parser like Spire.PDF for Python, you can reliably detect and export tables—no OCR or manual formatting needed. By converting tables to Excel, CSV, or DataFrame, you unlock their full potential for automation and analysis.
In summary, extracting tables from PDFs in Python becomes much easier with Spire.PDF, especially when converting them into structured formats like Excel and CSV for analysis.
Adding page numbers to a Word document is a fundamental feature that enhances readability and navigation, especially in lengthy documents. It allows readers to find specific content more easily and helps authors organize their work. Word offers flexible options for adding page numbers, including choosing the location (header, footer, or body) and customizing the format and appearance to match your document's design needs.
In this article, you will learn how to add pager numbers to a Word document, as well as customizing their appearance using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Add Page Numbers to a Word Document
- Add Page Numbers to a Specific Section
- Add Discontinuous Page Numbers to Different Sections
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
Add Page Numbers to a Word Document in Python
To dynamically add page numbers to a Word document using Spire.Doc, you can leverage various fields such as FieldPage, FieldNumPages, and FieldSection. These fields serve as placeholders for the current page number, total page count, and section number, enabling you to customize and automate the pagination process.
You can embed these placeholders in the header or footer of your document by calling the Paragraph.AppendField() method.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to insert a FieldPage and FieldNumPages field in the footer, which will display the page number in the format "X / Y":
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document from a specified file path.
- Get the first section using Document.Sections[index] property
- Get the footer of the first section using Section.HeadersFooters.Footer property.
- Add a paragraph to the footer using HeaderFooter.AddParagraph() method.
- Insert a FieldPage field, and a FieldNumPages field to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendField() method.
- Save the document to a different Word file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.docx")
# Get the first section
section = document.Sections[0]
# Get the footer of the section
footer = section.HeadersFooters.Footer
# Add "page number / page count" to the footer
footerParagraph = footer.AddParagraph()
footerParagraph.AppendField("page number", FieldType.FieldPage)
footerParagraph.AppendText(" / ")
footerParagraph.AppendField("page count", FieldType.FieldNumPages)
footerParagraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
# Apply formatting to the page number
style = ParagraphStyle(document)
style.CharacterFormat.Bold = True
style.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Times New Roman"
style.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 18
style.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Red()
document.Styles.Add(style)
footerParagraph.ApplyStyle(style)
# Save the document
document.SaveToFile("Output/AddPageNumbersToDocument.docx")
# Dispose resources
document.Dispose()

Add Page Numbers to a Specific Section in Python
By default, when you add page numbers to the footer of a section, they are automatically linked to the preceding section, maintaining a continuous sequence of page numbers. This behavior is convenient for most documents but may not be ideal when you want to start numbering from a certain section without affecting the numbering in other parts of the document.
If you need to add page numbers to a specific section without them being linked to the previous section, you must unlink the subsequent sections and clear the contents of their footers. Here's how you can do it using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document from a specified file path.
- Get a specific section using Document.Sections[index] property
- Get the footer of the section using Section.HeadersFooters.Footer property.
- Restart page numbering from 1 by setting Section.PageSetup.RestartPageNumbering property to true and Section.PageSetup.PageStartingNumber property to 1.
- Insert a FieldPage field and a FieldSection field to the footer using Paragraph.AppendField() method.
- Disable "Link to previous" by setting HeadersFooters.Footer.LinkToPrevious propety to false.
- Delete the content of the footers in the subsequent sections
- Save the document to a different Word file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.docx")
# Get a specific section
sectionIndex = 1
section = document.Sections[sectionIndex]
# Restart page numbering from 1
section.PageSetup.RestartPageNumbering = True
section.PageSetup.PageStartingNumber = 1
# Get the footer of the section
footer = section.HeadersFooters.Footer
# Add "Page X, Section Y" to the footer
footerParagraph = footer.AddParagraph()
footerParagraph.AppendText("Page ")
footerParagraph.AppendField("page number", FieldType.FieldPage)
footerParagraph.AppendText(", Section ")
footerParagraph.AppendField("section number", FieldType.FieldSection)
footerParagraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
# Apply formatting to the page number
style = ParagraphStyle(document);
style.CharacterFormat.Bold = True
style.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Times New Roman"
style.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 18
style.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Red()
document.Styles.Add(style)
footerParagraph.ApplyStyle(style)
# Disable "Link to previous" in the subsequent section
document.Sections[sectionIndex + 1].HeadersFooters.Footer.LinkToPrevious = False
# Delete the content of the footers in the subsequent sections
for i in range(sectionIndex +1, document.Sections.Count, 1):
document.Sections[i].HeadersFooters.Footer.ChildObjects.Clear()
document.Sections[i].HeadersFooters.Footer.AddParagraph()
# Save the document
document.SaveToFile("Output/AddPageNumbersToSection.docx")
# Dispose resources
document.Dispose()

Add Discontinuous Page Numbers to Different Sections in Python
When working with documents that contain multiple sections, you might want to start page numbering anew for each section to clearly distinguish between them. To achieve this, you must go through each section individually, add page numbers, and then reset the page numbering for the next section.
The following are the steps to add discontinuous page numbers to different sections using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document from a specified file path.
- Iterate through the sections in the document.
- Get a specific section using Document.Sections[index] property
- Get the footer of the section using Section.HeadersFooters.Footer property.
- Restart page numbering from 1 by setting Section.PageSetup.RestartPageNumbering property to true and Section.PageSetup.PageStartingNumber property to 1.
- Insert a FieldPage field and a FieldSection field to the footer using Paragraph.AppendField() method.
- Save the document to a different Word file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.docx")
# Iterate through the sections in the document
for i in range(document.Sections.Count):
# Get a specific section
section = document.Sections[i]
# Restart page numbering from 1
section.PageSetup.RestartPageNumbering = True
section.PageSetup.PageStartingNumber = 1
# Get the footer of the section
footer = section.HeadersFooters.Footer
# Add "Page X, Section Y" to the footer
footerParagraph = footer.AddParagraph()
footerParagraph.AppendText("Page ")
footerParagraph.AppendField("page number", FieldType.FieldPage)
footerParagraph.AppendText(", Section ")
footerParagraph.AppendField("section number", FieldType.FieldSection)
footerParagraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
# Apply formatting to the page number
style = ParagraphStyle(document)
style.CharacterFormat.Bold = True
style.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Times New Roman";
style.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 18;
style.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Red()
document.Styles.Add(style)
footerParagraph.ApplyStyle(style)
# Save the document
document.SaveToFile("Output/AddDifferentPageNumbersToSections.docx")
# Dispose resources
document.Dispose()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Create, Modify, and Copy Slide Master in PowerPoint Presentations
2024-05-13 01:14:23 Written by KoohjiSlide Master in PowerPoint presentations is a powerful feature that lies at the heart of designing consistent and professional-looking slideshows. It's essentially a blueprint or a template that controls the overall design and layout of the slides, allowing users to establish uniformity across presentations without having to manually format each slide individually. In this article, we will explore how to harness the power of Spire.Presentation for Python to create, modify, and apply slide masters in PowerPoint presentations within Python programs.
- Create and Apply Slide Masters in PowerPoint Presentations
- Modify Slide Masters in PowerPoint Presentations
- Copy Slide Masters Between PowerPoint Presentations
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
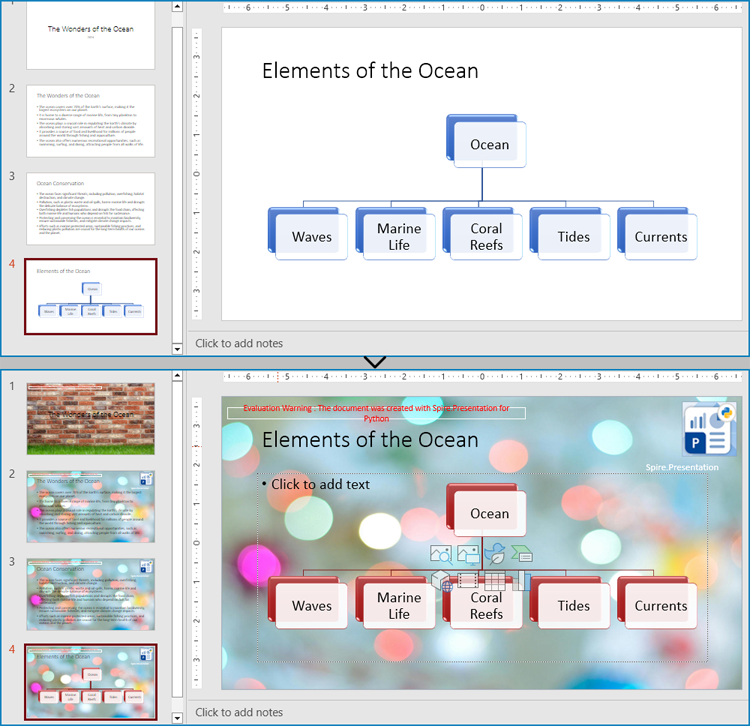
Create and Apply Slide Masters in PowerPoint Presentations
Every PowerPoint presentation in PowerPoint, regardless of whether it is newly created or not, will have at least one slide master. Developers can modify the default master or create new ones and apply them to slides with Spire.Presentation for Python to achieve a consistent style and content layout across the presentation.
The detailed steps for creating new slide masters and applying them to the slides in a presentation file are as follows:
- Create an object of Presentation class and load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create slide masters using Presentation.Masters.AppendSlide() method.
- Use the methods under IMasterSlide class to set the backgrounds, customize color schemes, insert images, shapes, and text, etc.
- Apply the slide masters to specific slides through ISlide.Layout property.
- Save the presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an instance of Presentation class
pres = Presentation()
# Load a Presentation file
pres.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Add a cover slide master and a body slide master
master1 = pres.Masters.AppendSlide(pres.Masters.get_Item(0))
coverMaster = pres.Masters.get_Item(master1)
master2 = pres.Masters.AppendSlide(pres.Masters.get_Item(0))
bodyMaster = pres.Masters.get_Item(master2)
# Set background images for the two slide masters
pic1 = "Background1.jpg"
pic2 = "Background2.jpg"
rect = RectangleF.FromLTRB (0, 0, pres.SlideSize.Size.Width, pres.SlideSize.Size.Height)
coverMaster.SlideBackground.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Picture
image1 = coverMaster.Shapes.AppendEmbedImageByPath (ShapeType.Rectangle, pic1, rect)
coverMaster.SlideBackground.Fill.PictureFill.Picture.EmbedImage = image1.PictureFill.Picture.EmbedImage
bodyMaster.SlideBackground.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Picture
image2 = bodyMaster.Shapes.AppendEmbedImageByPath (ShapeType.Rectangle, pic2, rect)
bodyMaster.SlideBackground.Fill.PictureFill.Picture.EmbedImage = image2.PictureFill.Picture.EmbedImage
# Insert a logo to the body slide master
logo = "Logo.png"
bodyMaster.Shapes.AppendEmbedImageByPath(ShapeType.Rectangle, logo, RectangleF.FromLTRB(pres.SlideSize.Size.Width - 110, 10, pres.SlideSize.Size.Width - 10, 110))
# Insert text to the body slide master
shape = bodyMaster.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, RectangleF.FromLTRB(pres.SlideSize.Size.Width - 210, 110, pres.SlideSize.Size.Width - 10, 150))
shape.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.none
shape.Line.FillType = FillFormatType.none
shape.TextFrame.Text = "Spire.Presentation"
# Set the color scheme for the two slide masters
coverMaster.Theme.ColorScheme.Accent1.Color = Color.get_Red()
coverMaster.Theme.ColorScheme.Accent2.Color = Color.get_Blue()
bodyMaster.Theme.ColorScheme.Accent1.Color = Color.get_Brown()
coverMaster.Theme.ColorScheme.Accent2.Color = Color.get_Green()
# Apply the first master with layout to the first slide
pres.Slides.get_Item(0).Layout = coverMaster.Layouts.GetByType(SlideLayoutType.Title)
# Apply the second master with layout to other slides
for i in range(1, pres.Slides.Count):
pres.Slides.get_Item(i).Layout = bodyMaster.Layouts.GetByType(SlideLayoutType.TitleAndObject)
# Save the document
pres.SaveToFile("output/CreateAndApplySlideMaster.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
pres.Dispose()
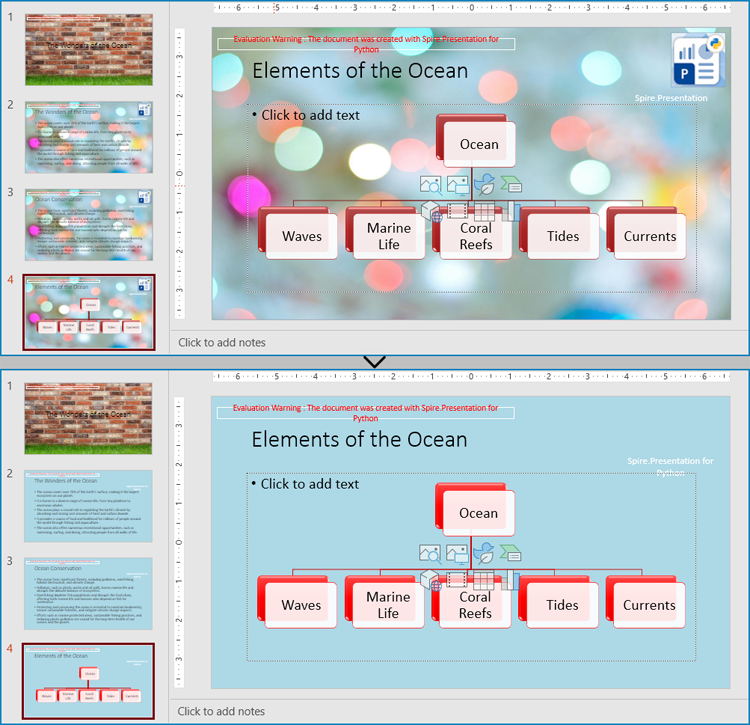
Modify Slide Masters in PowerPoint Presentations
A presentation can have multiple slide masters, which can be applied to different slides to achieve a unified style application and modification for different types of slides.
The Presentation.Masters.get_Item() method in Spire.Presentation for Python allows developers to retrieve the specified slide master in the presentation by index and modify the master. The following step-by-step example demonstrates how to retrieve a slide master and modify its background, color scheme, and embedded images:
- Create an object of Presentation class and load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a slide master through Presentation.Masters property.
- Use the methods under IMasterSlide class to change the background, set the color scheme, delete and insert text and images, etc.
- Save the presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of Presentation
pres = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
pres.LoadFromFile("output/CreateAndApplySlideMaster.pptx")
# Get the third slide master
master = pres.Masters[2]
# Change the background
master.SlideBackground.Type = BackgroundType.Custom
master.SlideBackground.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
master.SlideBackground.Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_LightBlue()
# Change the color sheme
master.Theme.ColorScheme.Accent1.Color = Color.get_Red()
master.Theme.ColorScheme.Accent2.Color = Color.get_Green()
# Remove the pictures in the slide master
pictures = [shape for shape in master.Shapes if isinstance(shape, SlidePicture)]
for picture in pictures:
master.Shapes.Remove(picture)
# Change the text in the slide master
texts = [shape for shape in master.Shapes if isinstance(shape, IAutoShape)]
for text in texts:
if len(text.TextFrame.Text) != 0:
text.TextFrame.Text = "Spire.Presentation for Python"
# Save the presentation
pres.SaveToFile("output/ModifySlideMaster.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
pres.Dispose()
Copy Slide Masters Between PowerPoint Presentations
Applying the slide style of a presentation to another presentation can be achieved by copying the slide master between presentations and applying the master style to the specified slides. The following are the steps to copy the slide master between presentations and apply it to the specified slides:
- Create two objects of Presentation class and load two presentation documents using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the slide master of the second presentation using Presentation.Masters.get_Item() method.
- Add the slide master to the first presentation using Presentation.Masters.AppendSlide() method.
- Apply the slide master to the slides in the second presentation through ISlide.Layout property.
- Save the first presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
from spire.presentation.common import *
# Create two objects of Presentation
pres1 = Presentation()
pres2 = Presentation()
# Load two PowerPoint documents
pres1.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
pres2.LoadFromFile("Template.pptx")
# Get the slide master of the second presentation
master = pres2.Masters.get_Item(0)
# Add the slide master to the first presentation
index = pres1.Masters.AppendSlide(master)
# Apply the slide master to the first presentation
pres1.Slides.get_Item(0).Layout = pres1.Masters.get_Item(index).Layouts.GetByType(SlideLayoutType.Title)
for i in range(1, pres1.Slides.Count):
pres1.Slides.get_Item(i).Layout = pres1.Masters.get_Item(index).Layouts.GetByType(SlideLayoutType.TitleAndObject)
# Save the first presentation
pres1.SaveToFile("output/CopySlideMaster.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
pres1.Dispose()
pres2.Dispose()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
