
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Python: Add, Modify, or Remove Footers from PowerPoint Documents
2024-04-18 01:08:25 Written by KoohjiIn a PowerPoint document, the footer is an area located at the bottom of each slide, typically containing textual information such as page numbers, dates, authors, and more. By adding a footer, you can give your slides a professional look and provide important information. Modifying the footer allows you to adjust the displayed content, style, and position to meet specific needs or styles. Removing the footer can clear the bottom content when extra information is not needed or to maintain a clean appearance. This article will introduce how to use Spire.Presentation for Python to add, modify, or remove footers in PowerPoint documents within a Python project.
- Python Add Footers in PowerPoint Documents
- Python Modify Footers in PowerPoint Documents
- Python Remove Footers in PowerPoint Documents
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Python Add Footers in PowerPoint Documents
Using Spire.Presentation, you can add footers, page numbers, and time information to the bottom of each page in a PowerPoint document, ensuring consistent footer content across all pages. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Presentation object.
- Load a PowerPoint document using the Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Set the footer visible using Presentation.FooterVisible = true and set the footer text.
- Set the slide number visible using Presentation.SlideNumberVisible = true, iterate through each slide, check for the lisence of a page number placeholder, and modify the text to the "Page X" format if found.
- Set the date visible using Presentation.DateTimeVisible = true.
- Set the format of the date using the Presentation.SetDateTime() method.
- Save the document using the Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load the presentation from a file
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample1.pptx")
# Set the footer visible
presentation.FooterVisible = True
# Set the footer text to "Spire.Presentation"
presentation.SetFooterText("Spire.Presentation")
# Set the slide number visible
presentation.SlideNumberVisible = True
# Iterate through each slide in the presentation
for slide in presentation.Slides:
for shape in slide.Shapes:
if shape.IsPlaceholder:
# If it is a slide number placeholder
if shape.Placeholder.Type == PlaceholderType.SlideNumber:
autoShape = shape if isinstance(shape, IAutoShape) else None
if autoShape is not None:
text = autoShape.TextFrame.TextRange.Paragraph.Text
# Modify the slide number text to "Page X"
autoShape.TextFrame.TextRange.Paragraph.Text = "Page " + text
# Set the date and time visible
presentation.DateTimeVisible = True
# Set the date and time format
presentation.SetDateTime(DateTime.get_Now(), "MM/dd/yyyy")
# Save the modified presentation to a file
presentation.SaveToFile("AddFooter.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
# Dispose of the Presentation object resources
presentation.Dispose()

Python Modify Footers in PowerPoint Documents
To modify the footer in a PowerPoint document, you first need to inspect the elements of each slide to locate footer and page number placeholders. Then, for each type of placeholder, set the desired content and format to ensure consistent and compliant footers throughout the document. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Presentation object.
- Load a PowerPoint document using the Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Use the Presentation.Slides[index] property to retrieve a slide.
- Iterate through the shapes in the slide using a for loop, check each shape to determine if it is a placeholder such as a footer or page number placeholder, and then modify its content or format accordingly.
- Save the document using the Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
def change_font(paragraph):
for textRange in paragraph.TextRanges:
# Set the text style to italic
textRange.IsItalic = TriState.TTrue
# Set the text font
textRange.EastAsianFont = TextFont("Times New Roman")
# Set the text font size to 12
textRange.FontHeight = 34
# Set the text color
textRange.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
textRange.Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_SkyBlue()
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a presentation from a file
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample2.pptx")
# Get the first slide
slide = presentation.Slides[0]
# Iterate through the shapes on the slide
for shape in slide.Shapes:
# Check if the shape is a placeholder
if shape.Placeholder is not None:
# Get the placeholder type
type = shape.Placeholder.Type
# If it is a footer placeholder
if type == PlaceholderType.Footer:
# Convert the shape to IAutoShape type
autoShape = shape if isinstance(shape, IAutoShape) else None
if autoShape is not None:
# Set the text content to "E-ICEBLUE"
autoShape.TextFrame.Text = "E-ICEBLUE"
# Modify the text font
change_font(autoShape.TextFrame.Paragraphs[0])
# If it is a slide number placeholder
if type == PlaceholderType.SlideNumber:
# Convert the shape to IAutoShape type
autoShape = shape if isinstance(shape, IAutoShape) else None
if autoShape is not None:
# Modify the text font
change_font(autoShape.TextFrame.Paragraphs[0])
# Save the modified presentation to a file
presentation.SaveToFile("ModifiedFooter.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
# Release the resources of the Presentation object
presentation.Dispose()

Python Remove Footers in PowerPoint Documents
To delete footers in a PowerPoint document, you first need to locate placeholders such as footers, page numbers, and time in the slides, and then remove them from the collection of shapes in the slide to ensure complete removal of footer content. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Presentation object.
- Load a PowerPoint document using the Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Use the Presentation.Slides[index] property to retrieve a slide.
- Iterate through the shapes in the slide using a for loop, check if they are placeholders, and if they are footer placeholders, page number placeholders, or time placeholders, remove them from the slide.
- Save the document using the Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a presentation from a file
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample2.pptx")
# Get the first slide
slide = presentation.Slides[0]
# Iterate through the shapes on the slide
for i in range(len(slide.Shapes) - 1, -1, -1):
# Check if the shape is a placeholder
if slide.Shapes[i].Placeholder is not None:
# Get the placeholder type
type = slide.Shapes[i].Placeholder.Type
# If it is a footer placeholder
if type == PlaceholderType.Footer:
# Remove it from the slide
slide.Shapes.RemoveAt(i)
# If it is a slide number placeholder
if type == PlaceholderType.SlideNumber:
# Remove it from the slide
slide.Shapes.RemoveAt(i)
# If it is a date and time placeholder
if type == PlaceholderType.DateAndTime:
# Remove it from the slide
slide.Shapes.RemoveAt(i)
# Save the modified presentation to a file
presentation.SaveToFile("RemovedFooter.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
# Release the resources of the Presentation object
presentation.Dispose()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
The AutoFit feature in Microsoft Excel is a handy tool that allows you to automatically adjust the height of rows or the width of columns in an Excel spreadsheet to fit the content within them. This feature is particularly useful when you have data that may vary in length or when you want to ensure that all the content is visible without having to manually adjust the column widths or row heights. In this article, we will explain how to AutoFit rows and columns in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
AutoFit a Specific Row and Column in Python
To AutoFit a specific row and column in an Excel worksheet, you can use the Worksheet.AutoFitRow() and Worksheet.AutoFitColumn() methods. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- AutoFit a specific row and column in the worksheet by its index (1-based) using Worksheet.AutoFitRow(rowIndex) and Worksheet.AutoFitColumn(columnIndex) methods.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Automatically adjust the height of the 3rd row in the worksheet
sheet.AutoFitRow(3)
# Automatically adjust the width of the 4th column in the worksheet
sheet.AutoFitColumn(4)
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("AutoFitSpecificRowAndColumn.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
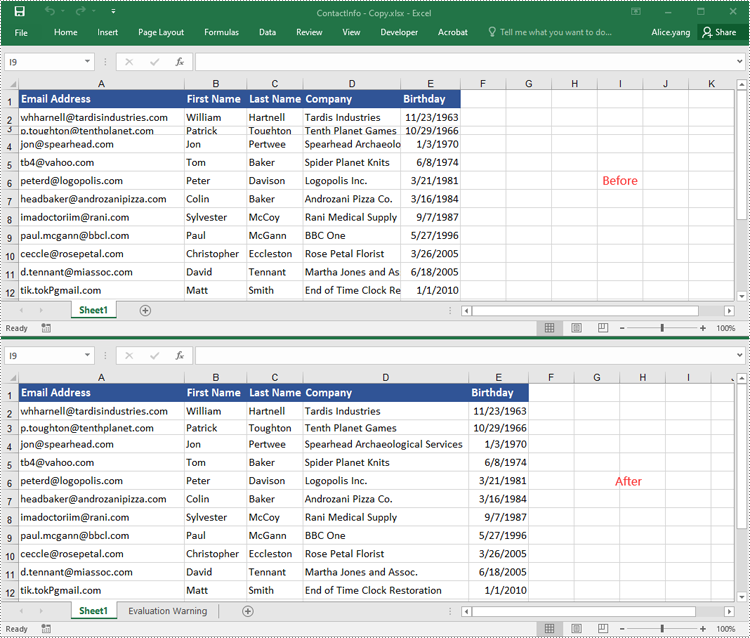
AutoFit Multiple Rows and Columns in Excel in Python
To AutoFit multiple rows and columns within a cell range, you can use the CellRange.AutoFitRows() and CellRange.AutoFitColumns() methods. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFroFmFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific cell range in the worksheet using Worksheet.Range[] property.
- AutoFit the rows and columns in the cell range using CellRange.AutoFitRows() and CellRange.AutoFitColumns() methods.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get a specific cell range in the worksheet
range = sheet.Range["A1:E14"]
# Or get the used cell range in the worksheet
# range = sheet.AllocatedRange
# Automatically adjust the heights of all rows in the cell range
range.AutoFitRows()
# Automatically adjust the widths of all columns in the cell range
range.AutoFitColumns()
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("AutoFitMultipleRowsAndColumns.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Text Alignment in Python | Left, Right, Center Align & More
2024-04-11 05:59:15 Written by hayes Liu
In the world of document automation, proper text alignment is crucial for creating professional, readable, and visually appealing documents. For developers and data professionals building reports, drafting letters, or designing invoices, mastering text alignment in Python is essential to producing polished, consistent documents without manual editing.
This guide delivers a step-by-step walkthrough on how to align text in Python using Spire.Doc for Python, a library that enables effortless control over Word document formatting.
- Why Choose Spire.Doc for Python to Align Text?
- Core Text Alignment Types in Spire.Doc
- Step-by-Step: Align Text in Word in Python
- FAQs About Python Text Alignment
- Conclusion
Why Choose Spire.Doc for Python to Align Text?
Before diving into code, let’s clarify why Spire.Doc is a top choice for text alignment tasks:
- Full Alignment Support: Natively supports all standard alignment types (Left, Right, Center, Justify) for paragraphs.
- No Microsoft Word Dependency: Runs independently - no need to install Word on your machine.
- High Compatibility: Works with .docx, .doc, and other Word formats, ensuring your aligned documents open correctly across devices.
- Fine-Grained Control: Adjust alignment for entire paragraphs or table cells.
Core Text Alignment Types in Spire.Doc
Spire.Doc uses the HorizontalAlignment enum to define text alignment. The most common values are:
- HorizontalAlignment.Left: Aligns text to the left margin (default).
- HorizontalAlignment.Right: Aligns text to the right margin.
- HorizontalAlignment.Center: Centers text horizontally between margins.
- HorizontalAlignment.Justify: Adjusts text spacing so both left and right edges align with margins.
- HorizontalAlignment.Distribute: Adjusts character spacing (adds space between letters) and word spacing to fill the line.
Below, we’ll cover how to programmatically set paragraph alignment (left, right, center, justified, and distributed) in Word using Python
Step-by-Step: Align Text in Word in Python
Here are the actionable steps to generate a Word document with 5 paragraphs, each using a different alignment style.
Step 1: Install Spire.Doc for Python
Open your terminal/command prompt, and then run the following command to install the latest version:
pip install Spire.Doc
Step 2: Import Required Modules
Import the core classes from Spire.Doc. These modules let you create documents, sections, paragraphs, and configure formatting:
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
Step 3: Create a New Word Document
Initialize a Document instance that represents your empty Word file:
# Create a Document instance
doc = Document()
Step 4: Add a Section to the Document
Word documents organize content into sections (each section can have its own margins, page size, etc.). We’ll add one section to hold our paragraphs:
# Add a section to the document
section = doc.AddSection()
Step 5: Add Paragraphs with Different Alignments
A section contains paragraphs, and each paragraph’s alignment is controlled via the HorizontalAlignment enum. We’ll create 5 paragraphs, one for each alignment type.
Left alignment is the default for most text (text aligns to the left margin).
# Left aligned text
paragraph1 = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph1.AppendText("This is left-aligned text.")
paragraph1.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Left
Right alignment is useful for dates, signatures, or page numbers (text aligns to the right margin).
# Right aligned text
paragraph2 = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph2.AppendText("This is right-aligned text.")
paragraph2.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Right
Center alignment works well for titles or headings (text centers between left and right margins). Use to center text in Python:
# Center aligned text
paragraph3 = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph3.AppendText("This is center-aligned text.")
paragraph3.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
Justified text aligns both left and right margins (spaces between words are adjusted for consistency). Ideal for formal documents like essays or reports.
# Justified
paragraph4 = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph4.AppendText("This is justified text.")
paragraph4.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Justify
Note: Justified alignment is more visible with longer text - short phrases may not show the spacing adjustment.
Distributed alignment is similar to justified, but evenly distributes single-line text (e.g., unevenly spaced words or short phrases).
# Distributed
Paragraph5 = section.AddParagraph()
Paragraph5.AppendText("This is evenly distributed text.")
Paragraph5.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Distribute
Step 6: Save and Close the Document
Finally, save the document to a specified path and close the Document instance to free resources:
# Save the document
document.SaveToFile("TextAlignment.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
# Close the document to release memory
document.Close()
Output:
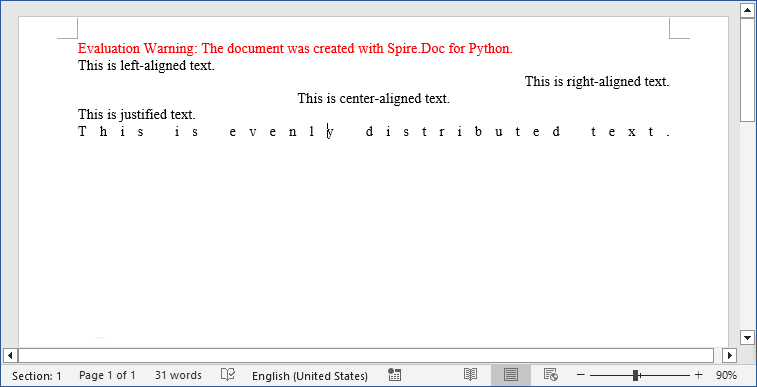
Pro Tip: Spire.Doc for Python also provides interfaces to align tables in Word or align text in table cells.
FAQs About Python Text Alignment
Q1: Is Spire.Doc for Python free?
A: Spire.Doc offers a free version with limitations. For full functionality, you can request a 30-day trial license here.
Q2: Can I set text alignment for existing Word documents
A: Yes. Spire.Doc lets you load existing documents and modify text alignment for specific paragraphs. Here’s a quick example:
from spire.doc import *
# Load an existing document
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("ExistingDocument.docx")
# Get the first section and first paragraph
section = doc.Sections[0]
paragraph = section.Paragraphs[0]
# Change alignment to center
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
# Save the modified document
doc.SaveToFile("UpdatedDocument.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
doc.Close()
Q3: Can I apply different alignments to different parts of the same paragraph?
A: No. Text alignment is a paragraph-level setting in Word, not a character-level setting. This means all text within a single paragraph must share the same alignment (left, right, center, etc.).
If you need mixed alignment in the same line, you’ll need to use a table with invisible borders.
Q4: Can Spire.Doc for Python handle other text formatting?
A: Absolutely! Spire.Doc lets you combine alignment with other formatting like fonts, line spacing, bullet points, and more.
Conclusion
Automating Word text alignment with Python and Spire.Doc saves time, reduces human error, and ensures consistency across documents. The code example provided offers a clear template for implementing left, right, center, justified, and distributed alignment, and adapting it to your needs is as simple as modifying the text or adding more formatting rules.
Try experimenting with different alignment combinations, and explore Spire.Doc’s online documentation to unlock more formatting possibilities.
