
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Converting PowerPoint to Html is a way to share your presentations with others online. By converting to Html, you can publish the document content on a web page, making it universally accessible and appealing to diverse audiences. In this article, you will learn how to convert PowerPoint presentations to HTML format in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Convert a PowerPoint Presentation to HTML in Python
The Presentation.SaveToFile() method offered by Spire.Presentation for Python supports converting a PowerPoint presentation to HTML format. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Presentation instance.
- Load a PowerPoint document using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the PowerPoint document to HTML format using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import * from spire.presentation import * inputFile ="Input.pptx" outputFile = "ToHTML.html" # Create a Presentation instance ppt = Presentation() # Load a PowerPoint document ppt.LoadFromFile(inputFile) #Save the document to HTML format ppt.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Html) ppt.Dispose()
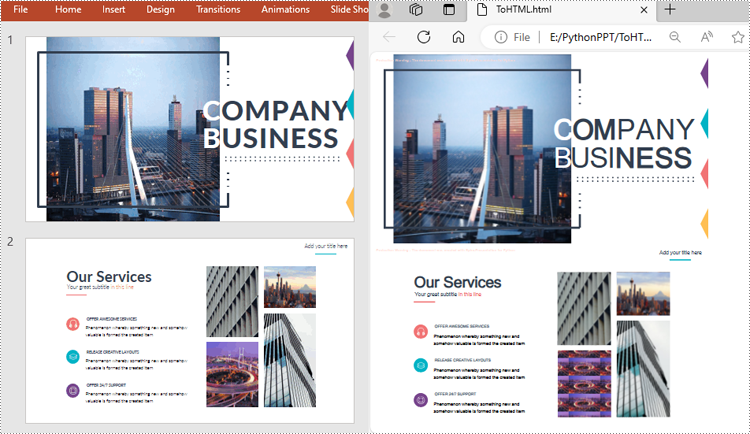
Convert a Specific PowerPoint Slide to HTML in Python
If you only need to convert a specific presentation slide to HTML, you can use the ISlide.SaveToFile(String, FileFormat) method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Presentation instance.
- Load a PowerPoint document using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific slide by its index using Presentation.Slides[] property.
- Save the presentation slide to HTML format using ISlide.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import * from spire.presentation import * inputFile ="Input.pptx" outputFile = "SlideToHTML.html" # Create a Presentation instance ppt = Presentation() # Load a PowerPoint document ppt.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get the second slide slide = ppt.Slides[1] # Save the slide to HTML format slide.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Html) ppt.Dispose()
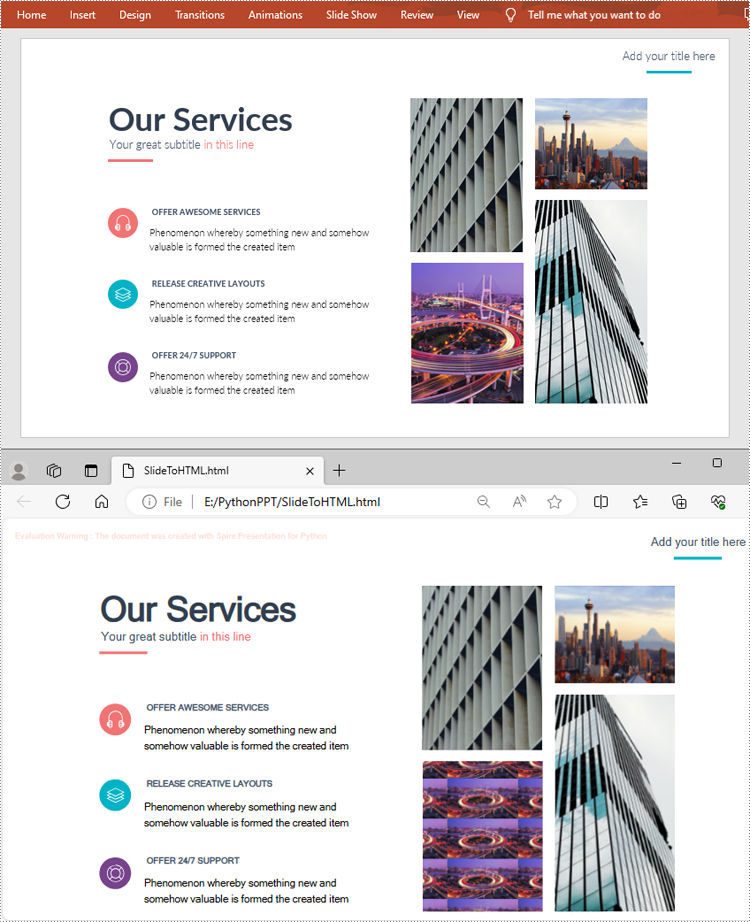
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
In PDF, you can change the page size to make the document meet different needs. For example, a smaller page size is required when creating handouts or compact versions of documents, while a larger page size could be useful for designing posters or graphics-intensive materials. In some cases, you may also need to get the page dimensions (width and height) to determine if the document is resized optimally. In this article, you will learn how to change or get PDF page size programmatically in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Change PDF Page Size to a Standard Paper Size with Python
- Change PDF Page Size to a Custom Paper Size with Python
- Get PDF Page Size with Python
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Change PDF Page Size to a Standard Paper Size with Python
The way to change the page size of a PDF file is to create a new PDF file and add pages of the desired size to it, then create templates based on the pages in the original PDF file and draw the templates onto the pages in the new PDF file. This process will preserve text, images, and other elements present in the original PDF file.
Spire.PDF for Python supports a variety of standard paper size, such as letter, legal, A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, B0, B1, B2, B3, B4 and so on. The following are the steps to change the page size of a PDF file to a standard paper size:
- Initialize a PdfDocument instance and load the original PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Initialize another PdfDocument instance to create a new PDF file.
- Loop through the pages in the original PDF.
- Add pages of the desired size to the new PDF file using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Initialize a PdfTextLayout instance and set the text layout as one page through PdfTextLayout.Layout property.
- Create templates based on the pages in the original PDF using PdfPageBase.CreateTemplate() method.
- Draw the templates onto the pages in the new PDF file with the specified text layout using PdfTemplate.Draw() method.
- Save the result file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
inputFile = "Sample1.pdf"
outputFile = "ChangePageSizeToA3.pdf"
# Create a PdfDocument instance
originalPdf = PdfDocument()
# Load the original PDF document
originalPdf.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Create a new PDF document
newPdf = PdfDocument()
# Loop through the pages in the original PDF
for i in range(originalPdf.Pages.Count):
page = originalPdf.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Add pages of size A3 to the new PDF
newPage = newPdf.Pages.Add(PdfPageSize.A3(), PdfMargins(0.0))
# Create a PdfTextLayout instance
layout = PdfTextLayout()
# Set text layout as one page (if not set the content will not scale to fit page size)
layout.Layout = PdfLayoutType.OnePage
# Create templates based on the pages in the original PDF
template = page.CreateTemplate()
# Draw the templates onto the pages in the new PDF
template.Draw(newPage, PointF.Empty(), layout)
# Save the result document
newPdf.SaveToFile(outputFile)
newPdf.Close()
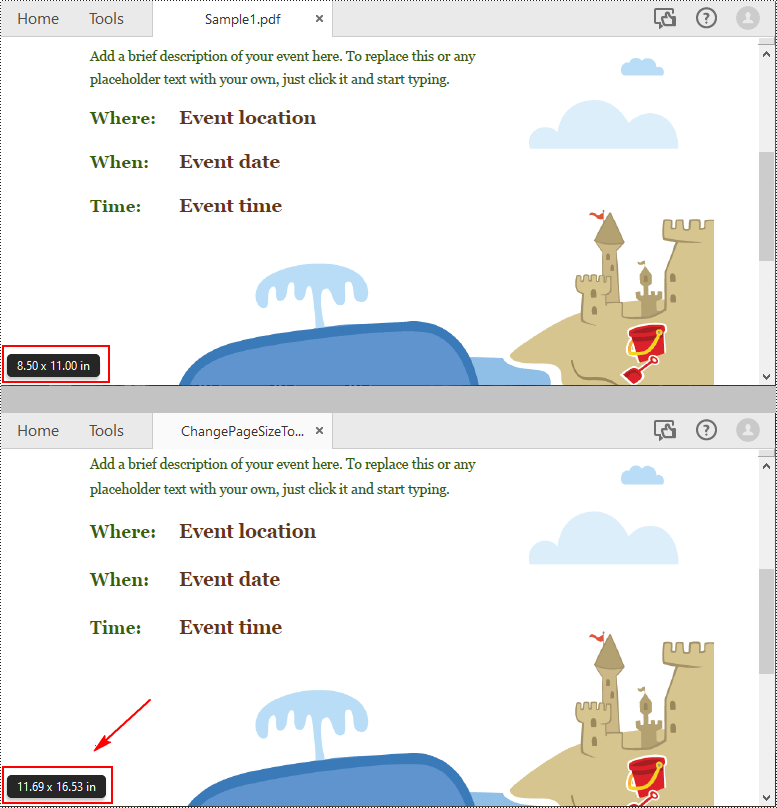
Change PDF Page Size to a Custom Paper Size with Python
Spire.PDF for Python uses point (1/72 of an inch) as the unit of measure. If you need to change the page size of a PDF to a custom paper size in other units of measure like inches or millimeters, you can use the PdfUnitConvertor class to convert them to points.
The following are steps to change the page size of a PDF file to a custom paper size in inches:
- Initialize a PdfDocument instance and load the original PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Initialize another PdfDocument instance to create a new PDF file.
- Initialize a PdfUnitConvertor instance, then convert the custom size in inches to points using PdfUnitConvertor.ConvertUnits() method.
- Initialize a SizeF instance from the custom size.
- Loop through the pages in the original PDF.
- Add pages of the custom size to the new PDF file using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Initialize a PdfTextLayout instance and set the text layout as one page through PdfTextLayout.Layout property.
- Create templates based on the pages in the original PDF using PdfPageBase.CreateTemplate() method.
- Draw the templates onto the pages in the new PDF file with the specified text layout using PdfTemplate.Draw() method.
- Save the result file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
inputFile = "Sample1.pdf"
outputFile = "CustomizePdfPageSize.pdf"
# Create a PdfDocument instance
originalPdf = PdfDocument()
# Load the original PDF document
originalPdf.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Create a new PDF document
newPdf = PdfDocument()
# Create a PdfUnitConvertor instance
unitCvtr = PdfUnitConvertor()
# Convert the custom size in inches to points
width = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(12.0, PdfGraphicsUnit.Inch, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point)
height = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(15.5, PdfGraphicsUnit.Inch, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point)
#Create a new SizeF instance from the custom size, then it will be used as the page size of the new PDF
size = SizeF(width, height)
# Loop through the pages in the original PDF
for i in range(originalPdf.Pages.Count):
page = originalPdf.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Add pages of the custom size (12.0*15.5 inches) to the new PDF
newPage = newPdf.Pages.Add(size, PdfMargins(0.0))
# Create a PdfTextLayout instance
layout = PdfTextLayout()
# Set text layout as one page (if not set the content will not scale to fit page size)
layout.Layout = PdfLayoutType.OnePage
# Create templates based on the pages in the original PDF
template = page.CreateTemplate()
# Draw the templates onto the pages in the new PDF
template.Draw(newPage, PointF.Empty(), layout)
# Save the result document
newPdf.SaveToFile(outputFile)
newPdf.Close()
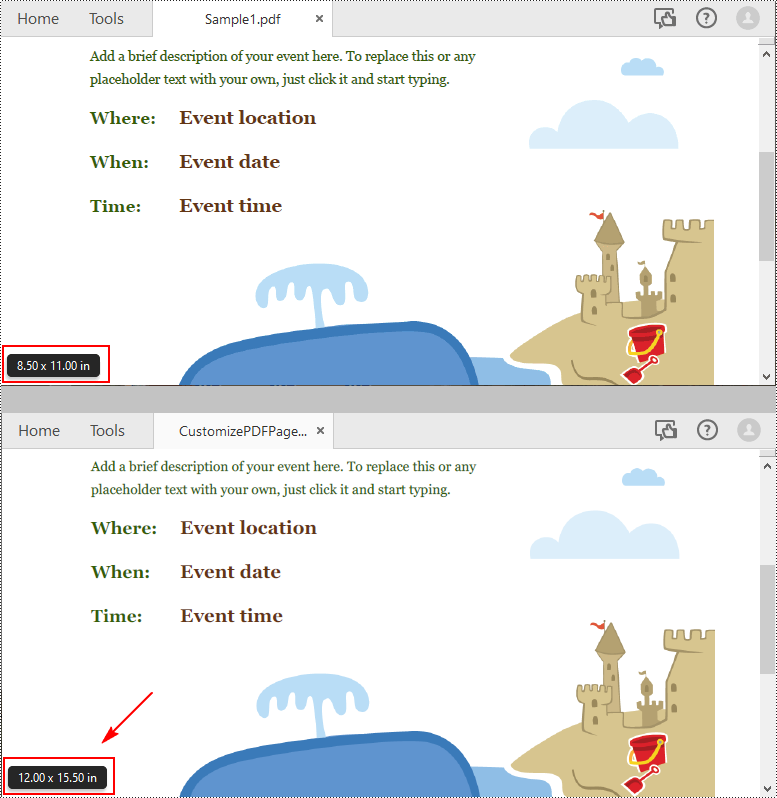
Get PDF Page Size with Python
Spire.PDF for Python offers the PdfPageBase.Size.Width and PdfPageBase.Size.Height properties to get the width and height of a PDF page in points. If you want to convert the default unit of measure to other units, you can use the PdfUnitConvertor class.
The following are the steps to get the PDF page size:
- Initialize a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified page using PdfDocument.Pages[] property.
- Get the width and height of the PDF page using PdfPageBase.Size.Width and PdfPageBase.Size.Height properties.
- Initialize a PdfUnitConvertor instance, and then convert the size units from points to other units of measure using PdfUnitConvertor.ConvertUnits() method.
- Add the size information to a StringBuilder instance, and then save the result to a TXT file.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
def AppendAllText(fname: str, text: List[str]):
fp = open(fname, "w")
for s in text:
fp.write(s + "\n")
fp.close()
inputFile = "Sample1.pdf"
outputFile = "GetPageSize.txt"
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a sample PDF from disk
pdf.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get the first page of the file
page = pdf.Pages[0]
# Get the width and height of page based on "point"
pointWidth = page.Size.Width
pointHeight = page.Size.Height
# Create PdfUnitConvertor to convert the unit
unitCvtr = PdfUnitConvertor()
# Convert size units from points to pixels
pixelWidth = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(pointWidth, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point, PdfGraphicsUnit.Pixel)
pixelHeight = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(pointHeight, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point, PdfGraphicsUnit.Pixel)
# Convert size units from points to inches
inchWidth = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(pointWidth, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point, PdfGraphicsUnit.Inch)
inchHeight = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(pointHeight, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point, PdfGraphicsUnit.Inch)
# Convert size units from points to centimeters
centimeterWidth = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(pointWidth, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point, PdfGraphicsUnit.Centimeter)
centimeterHeight = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(pointHeight, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point, PdfGraphicsUnit.Centimeter)
# Add the size information to a StringBuilder instance
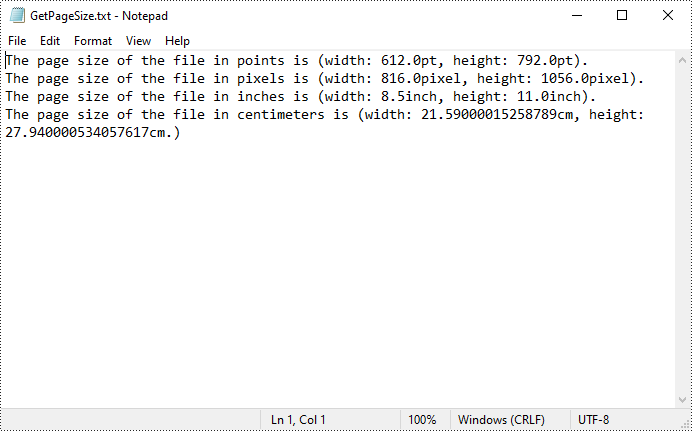
content = []
content.append("The page size of the file in points is (width: " +
str(pointWidth) + "pt, height: " + str(pointHeight) + "pt).")
content.append("The page size of the file in pixels is (width: " +
str(pixelWidth) + "pixel, height: " + str(pixelHeight) + "pixel).")
content.append("The page size of the file in inches is (width: " +
str(inchWidth) + "inch, height: " + str(inchHeight) + "inch).")
content.append("The page size of the file in centimeters is (width: " +
str(centimeterWidth) + "cm, height: " + str(centimeterHeight) + "cm.)")
# Save to a txt file
AppendAllText(outputFile, content)
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Locking cells is often used to protect the contents of specific cell ranges in a spreadsheet from accidental modification, which is useful in situations such as sharing a worksheet or protecting specific data. When you lock a cell, no one else can edit it unless they know the password or have the appropriate permissions. This feature is important for data security and integrity. In this article, we will show you how to lock specific cells, columns or rows in Excel on python platforms by using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Lock Specific Cells in Python
Spire.XLS for Python supports users to lock a specified range of cells by setting the Worksheet.Range[].Style.Locked property to "True". Below are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance and load a sample excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Unlock all cells in the used range of the worksheet by setting the Worksheet.Range.Style.Locked property to "False".
- Set text for the specific cells using Worksheet.Range[].Text property and then lock them by setting the Worksheet.Range[].Style.Locked property to "True".
- Protect the worksheet using XlsWorksheetBase.Protect() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Sample.xlsx"
outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/LockSpecificCells.xlsx"
# Create a Workbook instance and load a sample file
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Unlock all cells in the used range of the worksheet
sheet.Range.Style.Locked = False
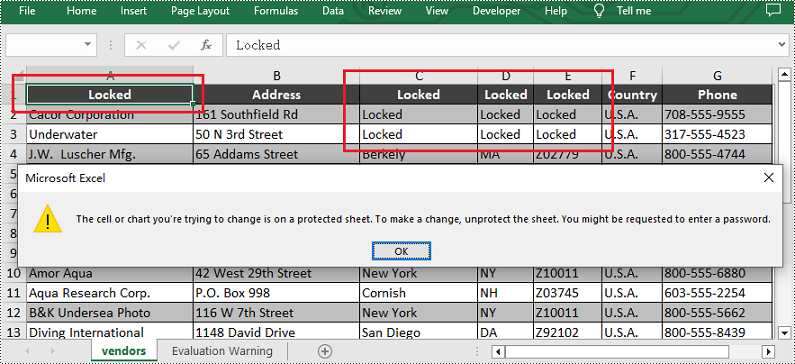
# Lock a specific cell in the sheet
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Locked"
sheet.Range["A1"].Style.Locked = True
# Lock a specific range of cells in the sheet
sheet.Range["C1:E3"].Text = "Locked"
sheet.Range["C1:E3"].Style.Locked = True
# Protect the worksheet with a password
sheet.Protect("123456", SheetProtectionType.All)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Lock a Specific Column in Python
If you want to lock a specific column in the worksheet, please set the Worksheet.Columns[].Style.Locked property to "True". Other steps are similar to the above method. Below are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance and load a sample excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Unlock all cells in the used range of the worksheet by setting the Worksheet.Range.Style.Locked property to "False".
- Set text for the fourth column using the Worksheet.Columns[].Text property and then lock it by setting the Worksheet.Columns[].Style.Locked property to "True".
- Protect the worksheet with a password by calling XlsWorksheetBase.Protect() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Sample.xlsx"
outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/LockSpecificColumn.xlsx"
# Create a Workbook instance and load a sample file
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Unlock all cells in the used range of the worksheet
sheet.Range.Style.Locked = False
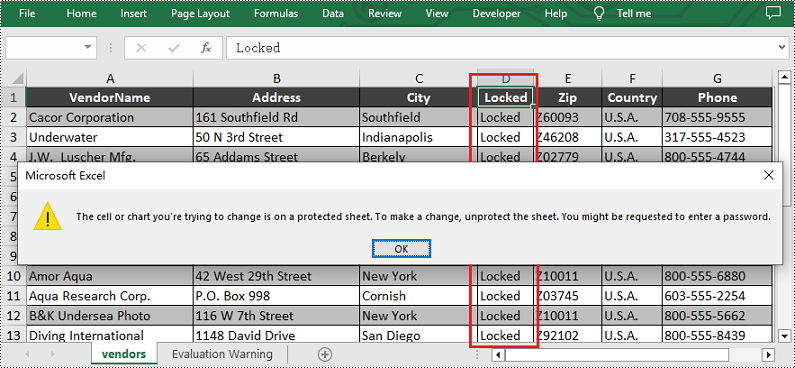
# Lock the fourth column in the sheet
sheet.Columns[3].Text = "Locked"
sheet.Columns[3].Style.Locked = True
# Protect the worksheet with a password
sheet.Protect("123456", SheetProtectionType.All)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Lock a Specific Row in Python
Similarly, if you want to lock a certain row, please set the Worksheet.Rows[].Style.Locked property to "True". Here are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance and load a sample excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Unlock all cells in the used range of the worksheet by setting the Worksheet.Range.Style.Locked property to "False".
- Set text for the third row using the Worksheet.Rows[].Text property and then lock it by setting the Worksheet.Rows[].Style.Locked property to "True".
- Protect the worksheet with a password using XlsWorksheetBase.Protect() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Sample.xlsx"
outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/LockSpecificRow.xlsx"
# Create a Workbook instance and load a sample file
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Unlock all cells in the used range of the worksheet
sheet.Range.Style.Locked = False
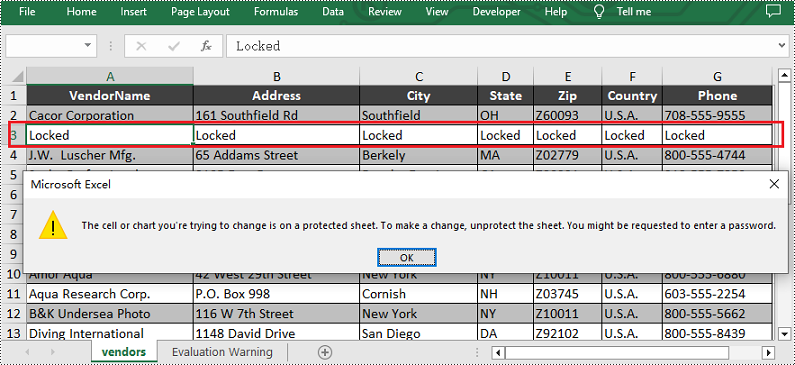
# Lock the third row in the worksheet
sheet.Rows[2].Text = "Locked"
sheet.Rows[2].Style.Locked = True
# Protect the worksheet with a password
sheet.Protect("123456", SheetProtectionType.All)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
