
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Pages are the most fundamental components of a PDF document. If you want to add new information or supplemental material to an existing PDF, it is necessary to add new pages. Conversely, if there are some pages that contain incorrect or irrelevant content, you can remove them to create a more professional document. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically add or delete pages in PDF using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Add Empty Pages to a PDF Document in Python
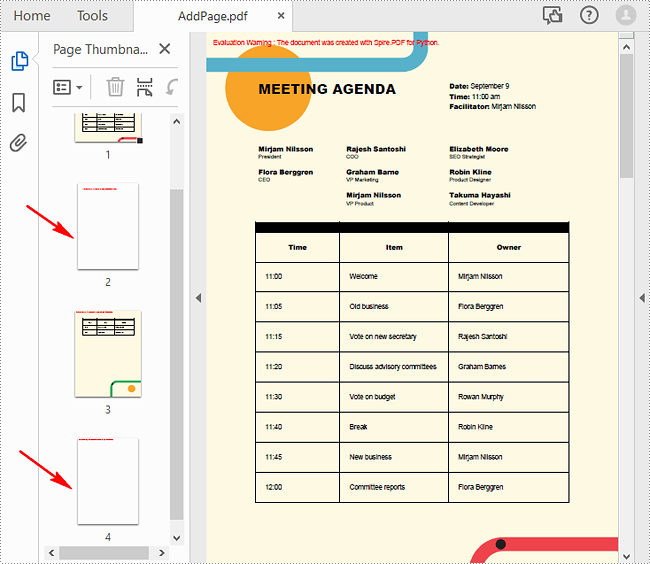
With Spire.PDF for Python, you can easily add a blank page to a specific position or to the end of the document using PdfDocument.Pages.Insert() or PdfDocument.Pages.Add(SizeF, PdfMargins) methods. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a sample PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a new blank page and insert it into a specific position of the document using PdfDocument.Pages.Insert() method.
- Create another new blank page with the specified size and margins, and then append it to the end of the document using PdfDocument.Pages.Add(SizeF, PdfMargins) method.
- Save the result document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("Test.pdf")
# Insert a blank page to the document as the second page
pdf.Pages.Insert(1)
# Add an empty page to the end of the document
pdf.Pages.Add(PdfPageSize.A4(), PdfMargins(0.0, 0.0))
# Save the result document
pdf.SaveToFile("AddPage.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Delete an Existing Page in a PDF Document in Python
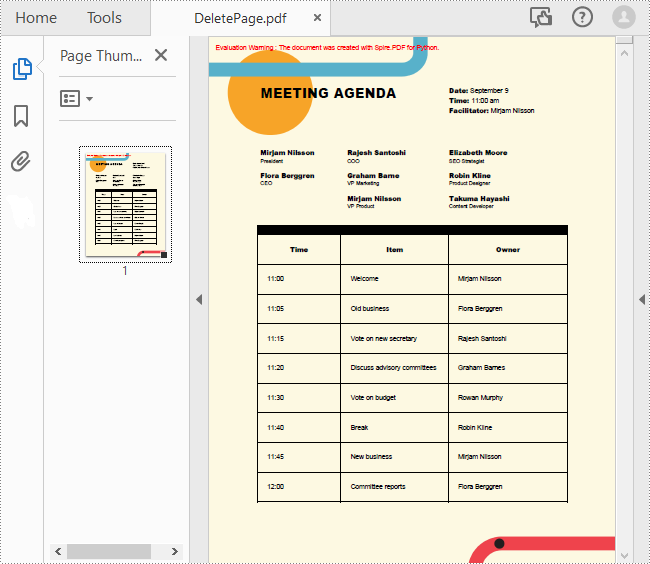
To remove a specified page from a PDF, you can use the PdfDocument.Pages.RemoveAt() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a sample PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove a specified page from the document using PdfDocument.Pages.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the result document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("Test.pdf")
# Delete the second page of the document
pdf.Pages.RemoveAt(1)
# Save the result document
pdf.SaveToFile("DeletePage.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Stamps are a powerful tool in PDF documents that allow users to mark and annotate specific areas or sections of a PDF file. Often used for approval, review, or to indicate a specific status, stamps can greatly enhance collaboration and document management. In PDF, stamps can take various forms, such as a simple checkmark, a customized graphic, a date and time stamp, or even a signature. In this article, you will learn how to add image stamps and dynamic stamps to a PDF document in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
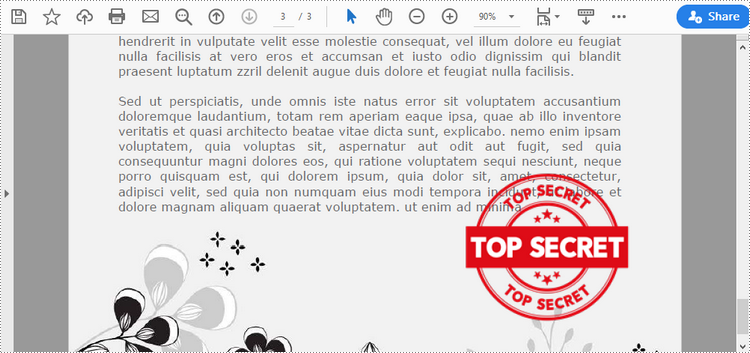
Add an Image Stamp to PDF Documents in Python
Spire.PDF for Python offers the PdfRubberStampAnnotation class to represent a rubber stamp in a PDF document. In order to create the appearance of a rubber stamp, the PdfTemplate class is used. The PdfTemplate is a piece of canvas on which you can draw whatever information you want, such as text, images, date, and time.
Image stamps can include logos, signatures, watermarks, or any other custom graphics that you want to overlay onto your PDFs. The main steps to add an image stamp to PDF using Spire.PDF for Python are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Load an image that you want to stamp on PDF using PdfImage.FromFile() method.
- Create a PdfTemplate object with the dimensions of the image.
- Draw the image on the template using PdfTemplate.Graphics.DrawImage() method.
- Create a PdfRubberStampAnnotation object, and set the template as its appearance.
- Add the stamp to a specific PDF page using PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.Add() method.
- Save the document to a different file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.pdf")
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(2)
# Load an image file
image = PdfImage.FromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\secret.png")
# Get the width and height of the image
width = (float)(image.Width)
height = (float)(image.Height)
# Create a PdfTemplate object based on the size of the image
template = PdfTemplate(width, height, True)
# Draw image on the template
template.Graphics.DrawImage(image, 0.0, 0.0, width, height)
# Create a rubber stamp annotation, specifying its location and position
rect = RectangleF((float) (page.ActualSize.Width - width - 50), (float) (page.ActualSize.Height - height - 40), width, height)
stamp = PdfRubberStampAnnotation(rect)
# Create a PdfAppearance object
pdfAppearance = PdfAppearance(stamp)
# Set the template as the normal state of the appearance
pdfAppearance.Normal = template
# Apply the appearance to the stamp
stamp.Appearance = pdfAppearance
# Add the stamp annotation to PDF
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(stamp)
# Save the file
doc.SaveToFile("output/ImageStamp.pdf")
doc.Close()
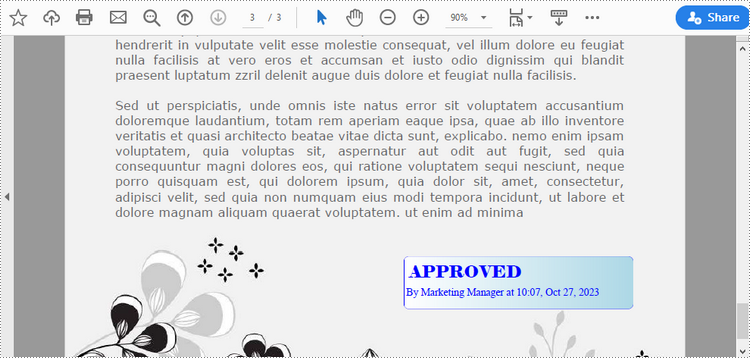
Add a Dynamic Stamp to PDF in Python
Unlike static stamps, dynamic stamps can contain variable information such as the date, time, or user input. The following are the steps to create a dynamic stamp in PDF using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a PdfTemplate object with desired size.
- Draw strings on the template using PdfTemplate.Graphics.DrawString() method.
- Create a PdfRubberStampAnnotation object, and set the template as its appearance.
- Add the stamp to a specific PDF page using PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.Add() method.
- Save the document to a different file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.pdf")
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(2)
# Create a PdfTemplate object
template = PdfTemplate(220.0, 50.0, True)
# Create two fonts
font1 = PdfTrueTypeFont("Elephant", 16.0, 0, True)
font2 = PdfTrueTypeFont("Times New Roman", 10.0, 0, True)
# Create a solid brush and a gradient brush
solidBrush = PdfSolidBrush(PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue()))
rectangle1 = RectangleF(PointF(0.0, 0.0), template.Size)
linearGradientBrush = PdfLinearGradientBrush(rectangle1, PdfRGBColor(Color.get_White()), PdfRGBColor(Color.get_LightBlue()), PdfLinearGradientMode.Horizontal)
# Create a pen
pen = PdfPen(solidBrush)
# Create a rounded rectangle path
CornerRadius = 10.0
path = PdfPath()
path.AddArc(template.GetBounds().X, template.GetBounds().Y, CornerRadius, CornerRadius, 180.0, 90.0)
path.AddArc(template.GetBounds().X + template.Width - CornerRadius, template.GetBounds().Y, CornerRadius, CornerRadius, 270.0, 90.0)
path.AddArc(template.GetBounds().X + template.Width - CornerRadius, template.GetBounds().Y + template.Height - CornerRadius, CornerRadius, CornerRadius, 0.0, 90.0)
path.AddArc(template.GetBounds().X, template.GetBounds().Y + template.Height - CornerRadius, CornerRadius, CornerRadius, 90.0, 90.0)
path.AddLine(template.GetBounds().X, template.GetBounds().Y + template.Height - CornerRadius, template.GetBounds().X, template.GetBounds().Y + CornerRadius / 2)
# Draw path on the template
template.Graphics.DrawPath(pen, path)
template.Graphics.DrawPath(linearGradientBrush, path)
# Draw text on the template
string1 = "APPROVED\n"
string2 = "By Marketing Manager at " + DateTime.get_Now().ToString("HH:mm, MMM dd, yyyy")
template.Graphics.DrawString(string1, font1, solidBrush, PointF(5.0, 5.0))
template.Graphics.DrawString(string2, font2, solidBrush, PointF(2.0, 28.0))
# Create a rubber stamp, specifying its size and location
rectangle2 = RectangleF((float) (page.ActualSize.Width - 220.0 - 50.0), (float) (page.ActualSize.Height - 50.0 - 100.0), 220.0, 50.0)
stamp = PdfRubberStampAnnotation(rectangle2)
# Create a PdfAppearance object and apply the template as its normal state
apprearance = PdfAppearance(stamp)
apprearance.Normal = template
# Apply the appearance to stamp
stamp.Appearance = apprearance
# Add the stamp annotation to annotation collection
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(stamp)
# Save the file
doc.SaveToFile("output/DynamicStamp.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Create Various Types of Lists in a Word Document
2023-10-27 00:57:31 Written by AdministratorLists are a powerful organizational tool that can be used to present information in a structured and easy-to-follow manner. Whether you want to create numbered lists, bulleted lists, or even custom lists with specific formatting, Word provides flexible options to suit your needs. By utilizing different list styles, you can improve the readability and visual appeal of your documents, making it simpler for readers to grasp key points and navigate through the content. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically create various types of lists in a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Create a Numbered List in Word in Python
- Create a Bulleted List in Word in Python
- Create a Multi-Level Numbered List in Word in Python
- Create a Multi-Level Mixed-Type List in Word in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Create a Numbered List in Word in Python
Spire.Doc for Python provides the ListStyle class, which enables you to establish either a numbered list style or a bulleted style. Subsequently, you can utilize the Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method to apply the defined list style to a paragraph. The steps to create a numbered list are as follows.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create an instance of ListStyle class, specifying the list type to Numbered.
- Get a specific level of the list through ListStyle.Levels[index] property, and set the numbering type through ListLevel.PatternType property.
- Add the list style to the document using Document.ListStyles.Add() method.
- Add several paragraphs to the document using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Apply the list style to a specific paragraph using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method.
- Specify the list level through Paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber property.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Create a numbered list style
listStyle = doc.Styles.Add(ListType.Numbered,"numberedList")
Levels = listStyle.ListRef.Levels
Levels[0].PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic
Levels[0].TextPosition = 20
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
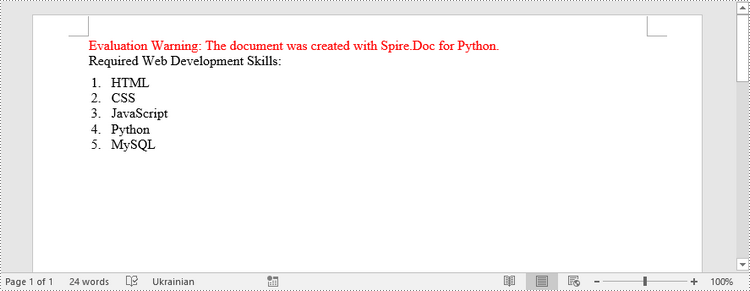
paragraph.AppendText("Required Web Development Skills:")
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 5.0
# Add a paragraph and apply the numbered list style to it
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("HTML")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Add another four paragraphs and apply the numbered list style to them
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("CSS")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("JavaScript")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Python")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("MySQL")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Save the document to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/NumberedList.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
Create a Bulleted List in Word in Python
Creating a bulleted list follows a similar process to creating a numbered list, with the main difference being that you need to specify the list type as "Bulleted" and assign a bullet symbol to it. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create an instance of ListStyle class, specifying the list type to Bulleted.
- Get a specific level of the list through ListStyle.Levels[index] property, and set the bullet symbol through ListLevel.BulletCharacter property.
- Add the list style to the document using Document.ListStyles.Add() method.
- Add several paragraphs to the document using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Apply the list style to a specific paragraph using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method.
- Specify the list level through Paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber property.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Create a bulleted list style
listStyle = doc.Styles.Add(ListType.Bulleted,"bulletedList")
Levels = listStyle.ListRef.Levels
Levels[0].BulletCharacter = "\u00B7"
Levels[0].CharacterFormat.FontName = "Symbol"
Levels[0].TextPosition = 20
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
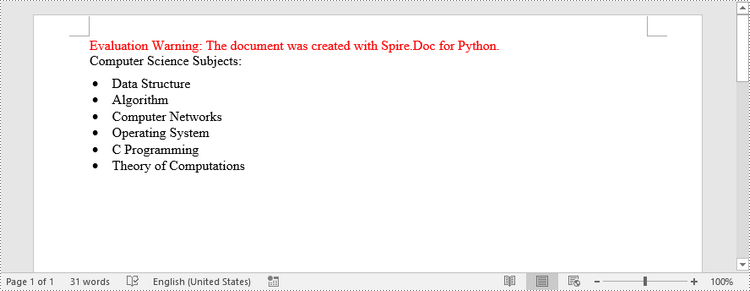
paragraph.AppendText("Computer Science Subjects:")
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 5.0
# Add a paragraph and apply the bulleted list style to it
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Data Structure")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Add another five paragraphs and apply the bulleted list style to them
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Algorithm")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Computer Networks")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Operating System")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("C Programming")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Theory of Computations")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Save the document to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/BulletedList.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
Create a Multi-Level Numbered List in Word in Python
A multi-level list consists of at least two different levels. A certain level of a nested list can be accessed by the ListStyle.Levels[index] property, through which you can set the numbering type and prefix. The following are the steps to create a multi-level numbered list in Word.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create an instance of ListStyle class, specifying the list type to Numbered.
- Get a specific level of the list through ListStyle.Levels[index] property, and set the numbering type and prefix.
- Add the list style to the document using Document.ListStyles.Add() method.
- Add several paragraphs to the document using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Apply the list style to a specific paragraph using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method.
- Specify the list level through Paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber property.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Create a numbered list style, specifying number prefix and pattern type of each level
listStyle = doc.Styles.Add(ListType.Numbered,"levelstyle")
Levels = listStyle.ListRef.Levels
Levels[0].PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic
Levels[0].TextPosition = 20.0
Levels[1].NumberPrefix = "%1."
Levels[1].PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic
Levels[2].NumberPrefix = "%1.%2."
Levels[2].PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
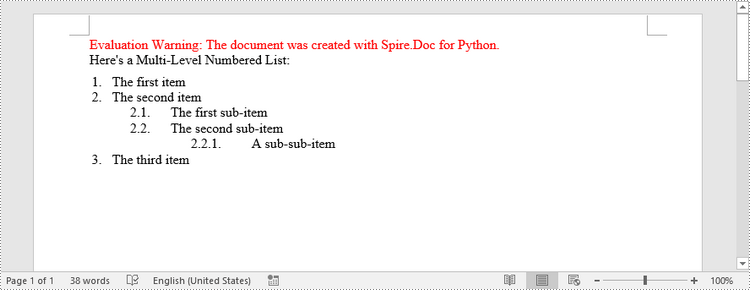
paragraph.AppendText("Here's a Multi-Level Numbered List:")
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 5.0
# Add a paragraph and apply the numbered list style to it
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The first item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Add another five paragraphs and apply the numbered list stype to them
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The second item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The first sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 1
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The second sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ContinueListNumbering()
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle")
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("A sub-sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 2
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The third item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Save the document to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/MultilevelNumberedList.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
Create a Multi-Level Mixed-Type List in Word in Python
To combine number and symbol bullet points in a multi-level list, create separate list styles (numbered and bulleted) and apply them to different paragraphs. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create a numbered list style and a bulleted list style.
- Add several paragraphs to the document using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Apply different list style to different paragraphs using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Create a numbered list style
numberList = doc.Styles.Add(ListType.Numbered, "numberedStyle")
Levels = numberList.ListRef.Levels
Levels[0].PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic
Levels[0].TextPosition = 20
Levels[1].PatternType = ListPatternType.LowLetter
# Create a bulleted list style
bulletedListStyle = doc.Styles.Add(ListType.Bulleted, "bulletedStyle")
Levels = bulletedListStyle.ListRef.Levels
Levels[2].BulletCharacter = "\u002A"
Levels[2].CharacterFormat.FontName = "Symbol"
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
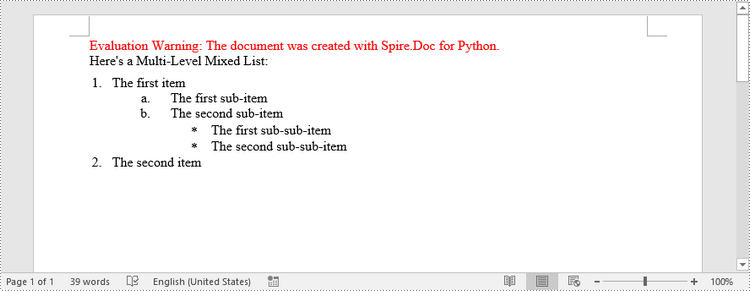
paragraph.AppendText("Here's a Multi-Level Mixed List:")
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 5.0
# Add a paragraph and apply the numbered list style to it
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The first item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedStyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Add the other five paragraphs and apply different list stype to them
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The first sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedStyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 1
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The second sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 1
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedStyle")
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The first sub-sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedStyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 2
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The second sub-sub-item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedStyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 2
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("The second item")
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedStyle")
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0
# Save the document to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/MultilevelMixedList.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
