
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Layers in PDF are similar to layers in image editing software, where different elements of a document can be organized and managed separately. Each layer can contain different content, such as text, images, graphics, or annotations, and can be shown or hidden independently. PDF layers are often used to control the visibility and positioning of specific elements within a document, making it easier to manage complex layouts, create dynamic designs, or control the display of information. In this article, you will learn how to add, hide, remove layers in a PDF document in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Add a Layer to PDF in Python
- Set Visibility of a Layer in PDF in Python
- Remove a Layer from PDF in Python
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Add a Layer to PDF in Python
A layer can be added to a PDF document using the Document.Layers.AddLayer() method. After the layer object is created, you can draw text, images, fields, or other elements on it to form its appearance. The detailed steps to add a layer to PDF using Spire.PDF for Java are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a layer using Document.Layers.AddLayer() method.
- Get a specific page through PdfDocument.Pages[index] property.
- Create a canvas for the layer based on the page using PdfLayer.CreateGraphics() method.
- Draw text on the canvas using PdfCanvas.DrawString() method.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
def AddLayerWatermark(doc):
# Create a layer named "Watermark"
layer = doc.Layers.AddLayer("Watermark")
# Create a font
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Bodoni MT Black", 50.0, 1, True)
# Specify watermark text
watermarkText = "DO NOT COPY"
# Get text size
fontSize = font.MeasureString(watermarkText)
# Get page count
pageCount = doc.Pages.Count
# Loop through the pages
for i in range(0, pageCount):
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Create canvas for layer
canvas = layer.CreateGraphics(page.Canvas)
# Draw sting on the graphics
canvas.DrawString(watermarkText, font, PdfBrushes.get_Gray(), (canvas.Size.Width - fontSize.Width)/2, (canvas.Size.Height - fontSize.Height)/2 )
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.pdf")
# Invoke AddLayerWatermark method to add a layer
AddLayerWatermark(doc)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/AddLayer.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Close()
Set Visibility of a Layer in PDF in Python
To control the visibility of layers in a PDF document, you can use the PdfDocument.Layers[index].Visibility property. Set it to off to hide a layer, or set it to on to unhide a layer. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Set the visibility of a certain layer through Document.Layers[index].Visibility property.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Layer.pdf")
# Hide a layer by setting the visibility to off
doc.Layers.get_Item(0).Visibility = PdfVisibility.Off
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/HideLayer.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Close()
Remove a Layer from PDF in Python
If a layer is no more wanted, you can remove it using the PdfDocument.Layers.RmoveLayer() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific layer through PdfDocument.Layers[index] property.
- Remove the layer from the document using PdfDcument.Layers.RemoveLayer(PdfLayer.Name) method.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Layer.pdf")
# Delete the specific layer
doc.Layers.RemoveLayer(doc.Layers.get_Item(0).Name)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/RemoveLayer.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Highlighting important text with vibrant colors is a commonly employed method for navigating and emphasizing content in PDF documents. Particularly in lengthy PDFs, emphasizing key information aids readers swiftly comprehending the document content, thereby enhancing reading efficiency. Utilizing Python programs enables document creators to effortlessly and expeditiously execute the highlighting process. This article will explain how to use Spire.PDF for Python to find and highlight text in PDF documents with Python programs.
- Find and Highlight Specific Text in PDF with Python
- Find and Highlight Text in a Specified PDF Page Area with Python
- Find and Highlight Text in PDF using Regular Expression with Python
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Find and Highlight Specific Text in PDF with Python
Spire.PDF for Python enables developers to find all occurrences of specific text on a page with PdfPageBase.FindText() method and apply highlight color to an occurrence with ApplyHighLight() method. Below is an example of using Spire.PDF for Python to highlight all occurrence of specific text:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Loop through the pages in the document.
- Get a page using PdfDocument.Pages.get_Item() method.
- Find all occurrences of specific text on the page using PdfPageBase.FindText() method.
- Loop through the occurrences and apply a highlight color to each occurrence using ApplyHighLight() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import*
# Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Loop through the pages in the PDF document
for i in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
# Get a page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Find all occurrences of specific text on the page
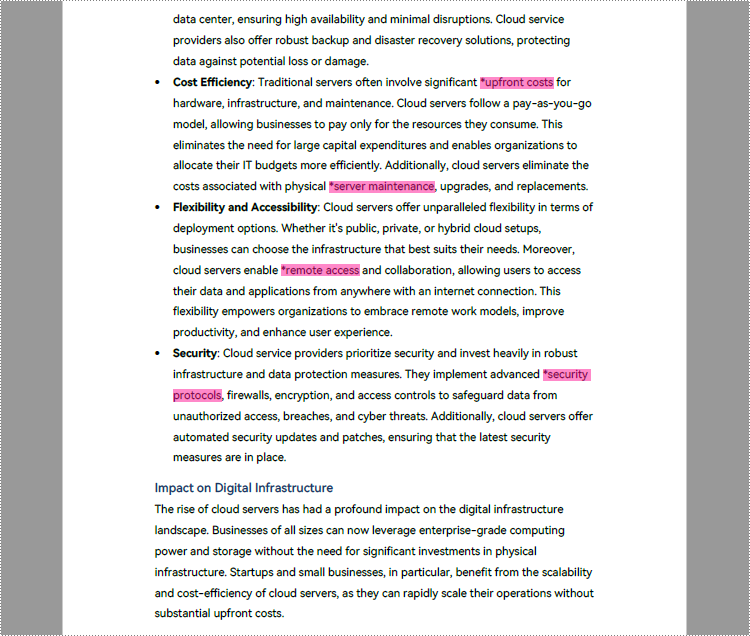
result = page.FindText("cloud server", TextFindParameter.IgnoreCase).Finds
# Highlight all the occurrences
for text in result:
text.ApplyHighLight(Color.get_Cyan())
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/FindHighlight.pdf")
pdf.Close()

Find and Highlight Text in a Specified PDF Page Area with Python
In addition to finding and highlighting specified text on the entire PDF page, Spire.PDF for Python also supports finding and highlighting specified text in specified areas on the page by passing a RectangleF instance as parameter to the PdfPageBase.FindText() method. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first page of the document using PdfDocument.Pages.get_Item() method.
- Define a rectangular area.
- Find all occurrences of specific text in the specified rectangular area on the first page using PdfPageBase.FindText() method.
- Loop through the occurrences and apply a highlight color to each occurrence using ApplyHighLight() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create an objetc of PdfDocument and load a PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get a page
pdfPageBase = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Define a rectangular area
rctg = RectangleF(0.0, 0.0, pdfPageBase.ActualSize.Width, 300.0)
# Find all the occurrences of specified text in the rectangular area
findCollection = pdfPageBase.FindText(rctg,"cloud server",TextFindParameter.IgnoreCase)
# Find text in the rectangle
for find in findCollection.Finds:
#Highlight searched text
find.ApplyHighLight(Color.get_Green())
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/FindHighlightArea.pdf")
pdf.Close()

Find and Highlight Text in PDF using Regular Expression with Python
Sometimes the text that needs to be highlighted is not exactly the same words. In this case, the use of regular expressions allows more flexibility in text search. By passing TextFindParameter.Regex as parameter to the PdfPageBase.FindText() method, we can find text using regular expression in PDF documents. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Specify the regular expression.
- Get a page using PdfDocument.Pages.get_Item() method.
- Find matched text with the regular expression on the page using PdfPageBase.FindText() method.
- Loop through the matched text and apply Highlight color to the text using ApplyHighLight() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import*
# Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Specify the regular expression that matches two words after *
regex = "\\*(\\w+\\s+\\w+)"
# Get the second page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(1)
# Find matched text on the page using regular expression
result = page.FindText(regex, TextFindParameter.Regex)
# Highlight the matched text
for text in result.Finds:
text.ApplyHighLight(Color.get_DeepPink())
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/FindHighlightRegex.pdf")
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
The use of appropriate fonts in PDF can greatly improve the overall readability and aesthetics of the document. In addition to the commonly used standard fonts, sometimes you may also need to embed private fonts. In this article, you will learn how to use different fonts in PDF in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Apply Different Fonts in a PDF Document in Python
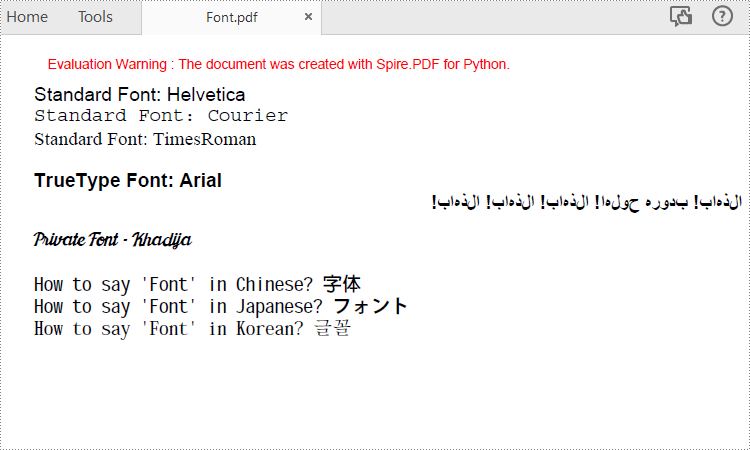
Spire.PDF for Python supports standard PDF fonts, TrueType fonts, private fonts as well as CJK font. The following are the steps to draw text in PDF using these fonts.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Add a page and then create a brush.
- Create an instance of the PdfFont class with a standard PDF font, and then use the PdfPageBase.getCanvas().drawString() method to draw text on the page with the standard font.
- Create an instance of the PdfTrueTypeFont class with a specified font, and then draw text on the page with the TrueType font.
- Load a private font and create an instance of the PdfTrueTypeFont class with it. Then draw text on the page with the private font.
- Create an instance of PdfCjkStandardFont class with a CJK font, and then draw text on the page with the CJK font.
- Save the result document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a page
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Create a brush
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
# Initialize y coordinate
y = 30.0
# Draw text using standard fonts
font = PdfFont(PdfFontFamily.Helvetica, 14.0)
page.Canvas.DrawString("Standard Font: Helvetica", font, brush, 0.0, y)
font = PdfFont(PdfFontFamily.Courier, 14.0)
page.Canvas.DrawString("Standard Font: Courier", font, brush, 0.0, (y := y + 16.0))
font = PdfFont(PdfFontFamily.TimesRoman, 14.0)
page.Canvas.DrawString("Standard Font: TimesRoman", font, brush, 0.0, (y := y + 16.0))
#Draw text using truetype font
trueTypeFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 14.0, PdfFontStyle.Bold,True)
page.Canvas.DrawString("TrueType Font: Arial", trueTypeFont, brush, 0.0, (y := y + 30.0))
# Draw Arabic text from right to left
arabicText = "\u0627\u0644\u0630\u0647\u0627\u0628\u0021\u0020" + "\u0628\u062F\u0648\u0631\u0647\u0020\u062D\u0648\u0644\u0647\u0627\u0021\u0020" + "\u0627\u0644\u0630\u0647\u0627\u0628\u0021\u0020" + "\u0627\u0644\u0630\u0647\u0627\u0628\u0021\u0020" + "\u0627\u0644\u0630\u0647\u0627\u0628\u0021"
trueTypeFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 14.0, PdfFontStyle.Bold,True)
rctg = RectangleF(PointF(0.0, (y := y + 16.0)), page.Canvas.ClientSize)
strformat = PdfStringFormat(PdfTextAlignment.Right)
strformat.RightToLeft = True
page.Canvas.DrawString(arabicText, trueTypeFont, brush, rctg, strformat)
# Draw text using private font
trueTypeFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("Khadija.ttf", 14.0)
page.Canvas.DrawString("Private Font - Khadija", trueTypeFont, brush, 0.0, (y := y + 30.0))
# Draw text using cjk fonts
cjkFont = PdfCjkStandardFont(PdfCjkFontFamily.MonotypeHeiMedium, 14.0)
page.Canvas.DrawString("How to say 'Font' in Chinese? \u5B57\u4F53", cjkFont, brush, 0.0, (y := y + 30.0))
cjkFont = PdfCjkStandardFont(PdfCjkFontFamily.HanyangSystemsGothicMedium, 14.0)
page.Canvas.DrawString("How to say 'Font' in Japanese? \u30D5\u30A9\u30F3\u30C8", cjkFont, brush, 0.0, (y := y + 16.0))
cjkFont = PdfCjkStandardFont(PdfCjkFontFamily.HanyangSystemsShinMyeongJoMedium, 14.0)
page.Canvas.DrawString("How to say 'Font' in Korean? \uAE00\uAF34", cjkFont, brush, 0.0, (y := y + 16.0))
#Save the result document
pdf.SaveToFile("Font.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
